Coronavirus-Tracking Apps Take Different Approaches in Keeping People Safe
Coronavirus-Tracking Apps Take Different Approaches in Keeping People Safe


A South African team is building a blockchain-powered COVID-19 status verification app, using a different approach to Russian, Chinese solutions.
A team of academics at the University of Cape Town in South Africa is developing a blockchain-powered application that will allow users to verify their own COVID-19 status. The platform, named Covi-ID, is still under development but aims to address a number of pressing concerns around the global coronavirus pandemic. It’s being developed by a team of academics and software developers in Cape Town and is aiming to launch on April 21.
The application intends to improve contact tracing of infected patients, while users of the platform will be able to provide a verified COVID-19 status. Additionally, the app will reward people for responsible behavior, like remaining at home during lockdown periods. Covi-ID is being built on permissioned blockchain platform Sovrin, which is a self-sovereign identity network. The primary goal is to give users ownership over their data while providing accurate information relating to COVID-19 infection hotspots to ecosystem participants.
This South African project is not the first to be exploring the use of a mobile application to improve contact tracing. Countries like China and Singapore, which were initially hit hard by the COVID-19 pandemic, rolled out their own tracing platforms while a number of European countries have also been developing interoperable applications as well. The Covi-ID app also differs from these varying projects in its privacy-centered approach that uses SSI and blockchain technology.
How will it work?
For developers, the first port of call was creating an account that verifies a user’s COVID-19 status. Potential users have two ways of creating a Covi-ID account. The first option is through a custodial wallet provided by one of the partnering commercial companies, which includes local South African banks, and government and health institutions. The second option is a completely self-sovereign identity wallet solution that is being developed by Covi-ID. Both options promise to safeguard users’ data. The latter option will store all of the users’ data on their phone, which means that personal information never physically leaves the device.
The nature of life in South Africa is also important to consider, as a large portion of the population may not have access to a smartphone. In this case, potential users can still engage with the platform by creating one of the custodial accounts with one of Covi-ID’s commercial partners.
The process entails taking a photo to prove the user’s identity, as well as providing a full name and telephone number — which can be a friend’s or relative’s in case users do not have their own number. Each user will be issued a QR code that can be printed, or potentially issued on a card similar to a bank card. This QR code can then be scanned by authorities to prove a user’s COVID-19 status.
Users’ information is stored by these commercial partners in custodial wallets, similar to how a cryptocurrency exchange stores a user’s currency holdings. Whenever their QR code is scanned, for instance, when they enter a supermarket, an event is logged in their wallet. Users can then be informed if they potentially come into contact with a COVID-19-positive user at that supermarket on that day. Users are required to provide phone numbers so that they can be easily reached in this case.
If users become symptomatic, they can go to a testing center or go see a doctor. The practitioner would scan their QR code and verify their identity with the photo that was given to the custodial wallet provider. Once the test results are confirmed, they would be logged into the users’ Covi-ID account. Once a user has recovered from COVID-19, or has received a vaccination — when they’re finally made available — they will be given a green status in the app and will pose no further health threat to the public.
All of this allows the second implementation of the Covi-ID, which is verification. This will most likely become essential as countries try to curb the spread of potential viral outbreaks in the future. If users try to enter any space that has implemented health screening, they will present their QR code, either through the app on their smartphone or a hard copy. Users then consent to give read-only access to their COVID-19 status.
A green status would indicate users have either recovered from the virus or have received a vaccination in the future. A yellow status would indicate users are COVID-19 negative but have never been infected nor been vaccinated — this would necessitate certain screening practices. A red status would indicate that a user currently has COVID-19 and would need to immediately be isolated from the public.
Blockchain technology to ensure privacy comes first
The major focus of the project is to ensure that users’ data remains protected while providing important information that will improve contact tracing and create a tool that will allow society to gradually return to some sense of normality. The developers of the application make use of users’ geolocation data, but instead of this valuable data being stored by a centralized server or institution, the users maintain possession of their actual geolocation data.
This is a fundamentally different way, in which users’ data would usually flow. The app will send out possible ‘infection hotspots’ to a user’s wallet, which will then check if the user stored location history overlaps. In this way, Covi-ID is able to carry out similar functions to a track-and-trace system that stores data in a central database. Co-Pierre Georg, an associate professor at the University of Cape Town, is a leading member of the project. Georg told Cointelegraph that the project is being developed on the open-source, decentralized SSI platform Sovrin:
“We are building using self-sovereign identity and, specifically, we are building on the Sovrin ledger at the moment. But our app will eventually be platform-agnostic, and we are complying with all standards currently being developed by the SSI community to ensure this interoperability.”
Georg said that the team wants to build an open-source system that will eventually be an enabler of “disruptive innovation,” also adding: “So, we will have an open-source version of the app and eventually also for the custodial wallets, which are currently being built as white label solutions for partner organizations like corporates, non-profits or government entities.”
Georg said that the end goal is for a large portion of the South African population to use an SSI application. However, due to the ambitious launch date, most users will initially be using a custodial wallet. He described it as a hybrid solution that will gradually move toward a completely decentralized system. Georg added that custodial wallets can be trusted:
“First, we have strict privacy regulation in place in South Africa already. And as we are working with well established corporate partners, the cost of not complying would be significant. Second, our open system incentivizes competition between the custodial wallets. As privacy is the most sensitive aspect of the system, we believe that we will see a race to the top where the best custodial wallet will eventually win the most users.”
Georg also believes that using QR codes will allow for widespread use because they can be scanned by phone cameras, which are ubiquitous in African countries. Furthermore, the project will provide an open-source application for anyone who needs to verify a user’s COVID-19 status:
“Most of the verifiers will be taxi operators or security guards, and almost all of them do have smartphones as well. What sets us apart, though, is that we do not require every user to have a smartphone as well. This makes the system more inclusive than existing and fully decentralized solutions.”
European applications to be rolled out by Mid-April
While the Covi-ID app hopes to provide a solution that is primarily suited for a South African setting, various European countries are developing track-and-trace applications that intend to share monitoring data. The initiative, dubbed Pan-European Privacy Preserving Proximity Tracing, was proposed in an effort to collate data and contract tracing through a number of applications that are being rolled out across the continent. This would enable various applications that are being developed to interact with each other to improve the efficacy of contact tracing — a crucial part in curbing the spread of COVID-19.
There are, of course, pressing privacy concerns around such projects, however, it has also been reported that the PEPP-PT program will offer both centralized and decentralized options to its users. The application will use Bluetooth technology anonymously without storing the geolocation data of users.
Many of the applications that are being developed will use Bluetooth technology to track the proximity of users to one another in relation to their COVID-19 status. Users who have come into contact with a person who is later confirmed to be infected, which is identified by the Bluetooth proximity, would then be notified by their respective applications.
Additionally, Russian authorities have announced that they will launch their own tracking application for patients who test positive for COVID-19 in Moscow at the beginning of April. The city has been in an indefinite lockdown since March 30. The monitoring application will be issued to people who have tested positive for the disease and have been ordered to self-isolate at home. It’s reported that the application will request access to users’ calls, location and camera, as well as network information — in an effort to monitor and ensure that sick patients are not leaving their homes while they’re contagious.
China also released an application in February that allows users to check whether they’ve come into contact with a person who is potentially infected with COVID-19. The New York Times reported that the application shares users’ location information to a centralized server whenever their barcodes are scanned at a checkpoint either in public transport hubs or other access-point controlled areas.
Singapore is another country that has released and made use of a contact-tracing application that uses Bluetooth technology. The TraceTogether app monitors a user’s proximity to other people using Bluetooth technology and uses timestamps to provide a history of contact. If users contract COVID-19, they can allow the app to identify people who they’ve come into contact with. Data is stored locally on users’ phones and is deleted after 21 days. The platform states that users’ locations and contacts are not tracked at any stage.
Meanwhile, another group of European researchers has been working on its very own decentralized platform for contact tracing — called Decentralized Privacy-Preserving Proximity Tracing.
The project’s white paper has been published on GitHub and is another Bluetooth-based proximity-tracing application that is primarily focused on privacy-protection. The app intends to provide warnings to users who have come into close contact with an individual suspected of being infected with COVID-19, without giving up any identity or location data.
Uncategorized
Mortgage rates fall as labor market normalizes
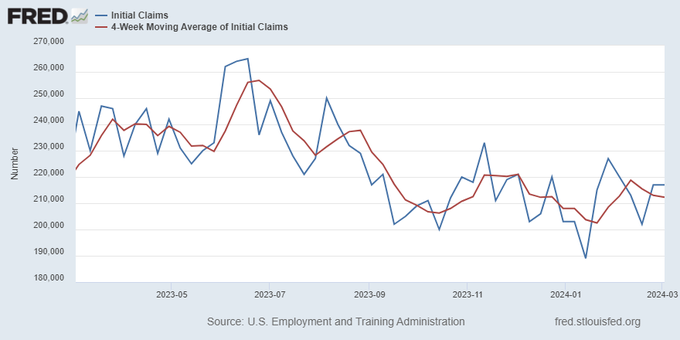
Jobless claims show an expanding economy. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
Everyone was waiting to see if this week’s jobs report would send mortgage rates higher, which is what happened last month. Instead, the 10-year yield had a muted response after the headline number beat estimates, but we have negative job revisions from previous months. The Federal Reserve’s fear of wage growth spiraling out of control hasn’t materialized for over two years now and the unemployment rate ticked up to 3.9%. For now, we can say the labor market isn’t tight anymore, but it’s also not breaking.
The key labor data line in this expansion is the weekly jobless claims report. Jobless claims show an expanding economy that has not lost jobs yet. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
From the Fed: In the week ended March 2, initial claims for unemployment insurance benefits were flat, at 217,000. The four-week moving average declined slightly by 750, to 212,250
Below is an explanation of how we got here with the labor market, which all started during COVID-19.
1. I wrote the COVID-19 recovery model on April 7, 2020, and retired it on Dec. 9, 2020. By that time, the upfront recovery phase was done, and I needed to model out when we would get the jobs lost back.
2. Early in the labor market recovery, when we saw weaker job reports, I doubled and tripled down on my assertion that job openings would get to 10 million in this recovery. Job openings rose as high as to 12 million and are currently over 9 million. Even with the massive miss on a job report in May 2021, I didn’t waver.
Currently, the jobs openings, quit percentage and hires data are below pre-COVID-19 levels, which means the labor market isn’t as tight as it once was, and this is why the employment cost index has been slowing data to move along the quits percentage.

3. I wrote that we should get back all the jobs lost to COVID-19 by September of 2022. At the time this would be a speedy labor market recovery, and it happened on schedule, too
Total employment data
4. This is the key one for right now: If COVID-19 hadn’t happened, we would have between 157 million and 159 million jobs today, which would have been in line with the job growth rate in February 2020. Today, we are at 157,808,000. This is important because job growth should be cooling down now. We are more in line with where the labor market should be when averaging 140K-165K monthly. So for now, the fact that we aren’t trending between 140K-165K means we still have a bit more recovery kick left before we get down to those levels.

From BLS: Total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 275,000 in February, and the unemployment rate increased to 3.9 percent, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Job gains occurred in health care, in government, in food services and drinking places, in social assistance, and in transportation and warehousing.
Here are the jobs that were created and lost in the previous month:

In this jobs report, the unemployment rate for education levels looks like this:
- Less than a high school diploma: 6.1%
- High school graduate and no college: 4.2%
- Some college or associate degree: 3.1%
- Bachelor’s degree or higher: 2.2%

Today’s report has continued the trend of the labor data beating my expectations, only because I am looking for the jobs data to slow down to a level of 140K-165K, which hasn’t happened yet. I wouldn’t categorize the labor market as being tight anymore because of the quits ratio and the hires data in the job openings report. This also shows itself in the employment cost index as well. These are key data lines for the Fed and the reason we are going to see three rate cuts this year.
recession unemployment covid-19 fed federal reserve mortgage rates recession recovery unemploymentUncategorized
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Last month we though that the January…
Last month we though that the January jobs report was the "most ridiculous in recent history" but, boy, were we wrong because this morning the Biden department of goalseeked propaganda (aka BLS) published the February jobs report, and holy crap was that something else. Even Goebbels would blush.
What happened? Let's take a closer look.
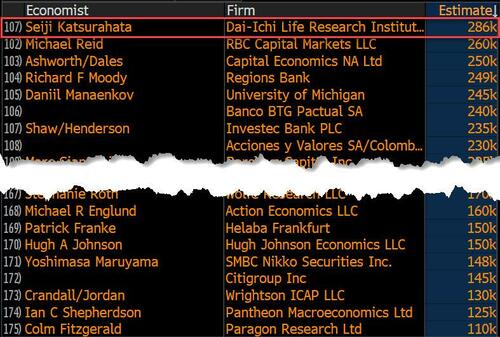
On the surface, it was (almost) another blockbuster jobs report, certainly one which nobody expected, or rather just one bank out of 76 expected. Starting at the top, the BLS reported that in February the US unexpectedly added 275K jobs, with just one research analyst (from Dai-Ichi Research) expecting a higher number.
Some context: after last month's record 4-sigma beat, today's print was "only" 3 sigma higher than estimates. Needless to say, two multiple sigma beats in a row used to only happen in the USSR... and now in the US, apparently.
Before we go any further, a quick note on what last month we said was "the most ridiculous jobs report in recent history": it appears the BLS read our comments and decided to stop beclowing itself. It did that by slashing last month's ridiculous print by over a third, and revising what was originally reported as a massive 353K beat to just 229K, a 124K revision, which was the biggest one-month negative revision in two years!
Of course, that does not mean that this month's jobs print won't be revised lower: it will be, and not just that month but every other month until the November election because that's the only tool left in the Biden admin's box: pretend the economic and jobs are strong, then revise them sharply lower the next month, something we pointed out first last summer and which has not failed to disappoint once.
In the past month the Biden department of goalseeking stuff higher before revising it lower, has revised the following data sharply lower:
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) August 30, 2023
- Jobs
- JOLTS
- New Home sales
- Housing Starts and Permits
- Industrial Production
- PCE and core PCE
To be fair, not every aspect of the jobs report was stellar (after all, the BLS had to give it some vague credibility). Take the unemployment rate, after flatlining between 3.4% and 3.8% for two years - and thus denying expectations from Sahm's Rule that a recession may have already started - in February the unemployment rate unexpectedly jumped to 3.9%, the highest since February 2022 (with Black unemployment spiking by 0.3% to 5.6%, an indicator which the Biden admin will quickly slam as widespread economic racism or something).
And then there were average hourly earnings, which after surging 0.6% MoM in January (since revised to 0.5%) and spooking markets that wage growth is so hot, the Fed will have no choice but to delay cuts, in February the number tumbled to just 0.1%, the lowest in two years...
... for one simple reason: last month's average wage surge had nothing to do with actual wages, and everything to do with the BLS estimate of hours worked (which is the denominator in the average wage calculation) which last month tumbled to just 34.1 (we were led to believe) the lowest since the covid pandemic...
... but has since been revised higher while the February print rose even more, to 34.3, hence why the latest average wage data was once again a product not of wages going up, but of how long Americans worked in any weekly period, in this case higher from 34.1 to 34.3, an increase which has a major impact on the average calculation.
While the above data points were examples of some latent weakness in the latest report, perhaps meant to give it a sheen of veracity, it was everything else in the report that was a problem starting with the BLS's latest choice of seasonal adjustments (after last month's wholesale revision), which have gone from merely laughable to full clownshow, as the following comparison between the monthly change in BLS and ADP payrolls shows. The trend is clear: the Biden admin numbers are now clearly rising even as the impartial ADP (which directly logs employment numbers at the company level and is far more accurate), shows an accelerating slowdown.
But it's more than just the Biden admin hanging its "success" on seasonal adjustments: when one digs deeper inside the jobs report, all sorts of ugly things emerge... such as the growing unprecedented divergence between the Establishment (payrolls) survey and much more accurate Household (actual employment) survey. To wit, while in January the BLS claims 275K payrolls were added, the Household survey found that the number of actually employed workers dropped for the third straight month (and 4 in the past 5), this time by 184K (from 161.152K to 160.968K).
This means that while the Payrolls series hits new all time highs every month since December 2020 (when according to the BLS the US had its last month of payrolls losses), the level of Employment has not budged in the past year. Worse, as shown in the chart below, such a gaping divergence has opened between the two series in the past 4 years, that the number of Employed workers would need to soar by 9 million (!) to catch up to what Payrolls claims is the employment situation.
There's more: shifting from a quantitative to a qualitative assessment, reveals just how ugly the composition of "new jobs" has been. Consider this: the BLS reports that in February 2024, the US had 132.9 million full-time jobs and 27.9 million part-time jobs. Well, that's great... until you look back one year and find that in February 2023 the US had 133.2 million full-time jobs, or more than it does one year later! And yes, all the job growth since then has been in part-time jobs, which have increased by 921K since February 2023 (from 27.020 million to 27.941 million).
Here is a summary of the labor composition in the past year: all the new jobs have been part-time jobs!
But wait there's even more, because now that the primary season is over and we enter the heart of election season and political talking points will be thrown around left and right, especially in the context of the immigration crisis created intentionally by the Biden administration which is hoping to import millions of new Democratic voters (maybe the US can hold the presidential election in Honduras or Guatemala, after all it is their citizens that will be illegally casting the key votes in November), what we find is that in February, the number of native-born workers tumbled again, sliding by a massive 560K to just 129.807 million. Add to this the December data, and we get a near-record 2.4 million plunge in native-born workers in just the past 3 months (only the covid crash was worse)!
The offset? A record 1.2 million foreign-born (read immigrants, both legal and illegal but mostly illegal) workers added in February!
Said otherwise, not only has all job creation in the past 6 years has been exclusively for foreign-born workers...

... but there has been zero job-creation for native born workers since June 2018!
This is a huge issue - especially at a time of an illegal alien flood at the southwest border...
... and is about to become a huge political scandal, because once the inevitable recession finally hits, there will be millions of furious unemployed Americans demanding a more accurate explanation for what happened - i.e., the illegal immigration floodgates that were opened by the Biden admin.
Which is also why Biden's handlers will do everything in their power to insure there is no official recession before November... and why after the election is over, all economic hell will finally break loose. Until then, however, expect the jobs numbers to get even more ridiculous.
International
Angry Shouting Aside, Here’s What Biden Is Running On
Angry Shouting Aside, Here’s What Biden Is Running On
Last night, Joe Biden gave an extremely dark, threatening, angry State of the Union…

Last night, Joe Biden gave an extremely dark, threatening, angry State of the Union address - in which he insisted that the American economy is doing better than ever, blamed inflation on 'corporate greed,' and warned that Donald Trump poses an existential threat to the republic.
But in between the angry rhetoric, he also laid out his 2024 election platform - for which additional details will be released on March 11, when the White House sends its proposed budget to Congress.
To that end, Goldman Sachs' Alec Phillips and Tim Krupa have summarized the key points:
Taxes
While railing against billionaires (nothing new there), Biden repeated the claim that anyone making under $400,000 per year won't see an increase in their taxes. He also proposed a 21% corporate minimum tax, up from 15% on book income outlined in the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), as well as raising the corporate tax rate from 21% to 28% (which would promptly be passed along to consumers in the form of more inflation). Goldman notes that "Congress is unlikely to consider any of these proposals this year, they would only come into play in a second Biden term, if Democrats also won House and Senate majorities."
Biden once again tells the complete lie that "nobody earning less than $400,000/year will pay additional penny in federal taxes."
— RNC Research (@RNCResearch) March 8, 2024
FACT: Biden has *already* raised the tax burden on Americans making as little as $20,000 per year. pic.twitter.com/VrZ1m0rzG3
Biden also called on Congress to restore the pandemic-era child tax credit.
Immigration
Instead of simply passing a slew of border security Executive Orders like the Trump ones he shredded on day one, Biden repeated the lie that Congress 'needs to act' before he can (translation: send money to Ukraine or the US border will continue to be a sieve).
As immigration comes into even greater focus heading into the election, we continue to expect the Administration to tighten policy (e.g., immigration has surged 20pp the last 7 months to first place with 28% in Gallup’s “most important problem” survey). As such, we estimate the foreign-born contribution to monthly labor force growth will moderate from 110k/month in 2023 to around 70-90k/month in 2024. -GS
SEE IT: Biden gets boo-ed while talking about his immigration bill. WATCH pic.twitter.com/O5FmkYx3xM
— Simon Ateba (@simonateba) March 8, 2024
Ukraine
Biden, with House Speaker Mike Johnson doing his best impression of a bobble-head, urged Congress to pass additional assistance for Ukraine based entirely on the premise that Russia 'won't stop' there (and would what, trigger article 5 and WW3 no matter what?), despite the fact that Putin explicitly told Tucker Carlson he has no further ambitions, and in fact seeks a settlement.
‼️ Breaking: Putin wants a negotiated settlement to what’s happening in Ukraine.
— Ed (@EdMagari) February 9, 2024
In a surprising turn of events, Tucker Carlson could be the key to peace, potentially playing a crucial role in ending the current conflict????️ pic.twitter.com/IKN8ajlEUX
As Goldman estimates, "While there is still a clear chance that such a deal could come together, for now there is no clear path forward for Ukraine aid in Congress."
China
Biden, forgetting about all the aggressive tariffs, suggested that Trump had been soft on China, and that he will stand up "against China's unfair economic practices" and "for peace and stability across the Taiwan Strait."
SOTU FACT CHECK:
— Wesley Hunt (@WesleyHuntTX) March 8, 2024
Biden claims we’re in a strong position to take on China.
No president in our lifetime has been WEAKER on China than Biden. pic.twitter.com/Y73JsIzmM3
Healthcare
Lastly, Biden proposed to expand drug price negotiations to 50 additional drugs each year (an increase from 20 outlined in the IRA), which Goldman said would likely require bipartisan support "even if Democrats controlled Congress and the White House," as such policies would likely be ineligible for the budget "reconciliation" process which has been used in previous years to pass the IRA and other major fiscal party when Congressional margins are just too thin.
So there you have it. With no actual accomplishments to speak of, Biden can only attack Trump, lie, and make empty promises.
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International12 hours ago
International12 hours agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges


































