Uncategorized
GOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges
GOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges
Authored by Steven Kovac via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
Massive…

Authored by Steven Kovac via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
Massive voter fraud allegations that marred the 2020 election spurred a political and grassroots movement from coast to coast to pursue an array of election reforms designed to increase election integrity.
However, with just months left ahead of the 2024 election, Republicans say little was mended, especially in contested states where they thought fixes were needed most.
Much concern is centered around five key swing states that became the focus of 2020: Georgia, Pennsylvania, Arizona, Michigan, and Wisconsin.
Election reforms tend to follow party lines. Democrats commonly castigate increased election security measures as voter suppression, while Republicans often condemn laws and directives that loosen security as aiding and abetting voter fraud.
According to a report from the Brennan Center for Justice, a left leaning, non-profit, law and research foundation, 23 states enacted 53 laws relaxing election security restrictions in 2023, while 14 states enacted 17 laws tightening them.
The statistics suggest that Democrats are still winning the nationwide battle, as they have for the past several years. The report found the states that took the most actions to tighten election security are the places that already had security measures in place.
Of the 14 states that tightened voting procedures, President Trump won all but one (New Mexico) in both 2016 and 2020. The 14 states listed by the Brennan Center include Arkansas, Florida, Idaho, Indiana, Kansas, Mississippi, North Carolina, North Dakota, Nebraska, New Mexico, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, and Wyoming.
The methods by which Americans cast their ballots have changed markedly over the last four federal election cycles, with many people embracing election procedures such as no-excuse absentee voting, early voting, and same-day voter registration.
As early as 2005, the bipartisan Carter-Baker Commission raised concerns that mail-in voting was a vehicle for potentially significant election fraud, yet the method has since steadily grown.
In 2018, a quarter of the electorate voted by mail, according to a study by the Election Assistance Commission (EAC). By 2022, it had become one-third.
Forty-six states and territories permitted no-excuse absentee voting in 2022. The number was 43 in 2020 and 40 in 2018.
Twenty-three states and territories had a permanent absentee voter list in 2022—a practice that allows a voter to request to automatically be sent a mail-in ballot in every succeeding election. No new application or update of registration information is required in most of them.
In the 2022 election, half the states and territories allowed same-day voter registration.
In the election cycles before the pandemic, the EAC study said that nearly 60 percent of Americans voted in person on election day. In 2022, the figure was 49 percent.
Before the pandemic, mail-in ballot drop boxes were rare, with most being deployed in or around an election office. By 2022, there were 13,000 drop boxes being used in 39 states, with many boxes placed in settings that lacked security and surveillance measures.
Fifteen of the 39 states and territories using drop boxes, including Georgia, Michigan, Pennsylvania, Wisconsin, New York, and Maine, couldn’t report how many ballots were collected from their receptacles in 2022, the report said.

According to the EAC study, 334,382 voting machines were used in the nation’s polling places in 2022. The utilization of electronic ballot marking devices was up 18.6 percent from 2020, while the use of electronic scanners rose 7.8 percent in the same period.
Despite the push by some election integrity activists for the hand-counting of ballots as a means to improve accuracy and security, the method was used by only 17.8 percent of jurisdictions in 2022, down from 20.7 percent in 2020.
And although chain of custody protections for ballots are being tightened in several states, dirty voter registration rolls—resulting in mail-in ballots being sent to ineligible people, undeliverable addresses, or multiple ballots being sent to the same individual—are still a widespread issue.
Georgia
The state of Georgia has been the scene of continuous controversy over the conduct of the Nov. 3, 2020, presidential election in which challenger Mr. Biden defeated incumbent President Trump by 11,779 votes (0.23 percent).
The persistent public outcry over alleged election fraud prompted the Republican-controlled Georgia General Assembly to pass the 95-page Georgia Election Integrity Act of 2021.

The declared purpose of the legislation is to apply “the lessons learned” in 2020 and “make it easy to vote and hard to cheat,” in the future.
An explanatory notation in the bill acknowledged that there was a “significant lack of confidence” in the state’s election systems stemming from persistent allegations of “rampant voter fraud” and “rampant voter suppression.”
“The changes made in this legislation in 2021 are designed to address the lack of elector confidence in the election system on all sides of the political spectrum,” the notation said.
In order to ensure that more votes are not counted than ballots cast, every precinct, by 10 p.m. on election night, must post the number of all ballots cast, including all absentee ballots received by the statutory deadline of 7 p.m.
The new law mandates that the total number of cast ballots must equal the number of ballots counted.
No pauses are allowed once the counting begins, as were seen in the early morning hours in Atlanta in 2020.
To help achieve a timely vote count, the statute allows absentee ballots to be processed days before the election, but the voter’s choices must not be tabulated until the counting begins on election day.
The act provides that ballots shall be printed with authentication marks in order to eliminate counterfeiting.
To deter duplicate voting and ballot harvesting, the statute mandates that mail-in ballot applications be sent out only at a registered elector’s request, and nobody but statutorily specified individuals may return a marked absentee ballot filled out by another person. Seeking to obtain more than one absentee ballot can now expose an individual to legal penalties.
When applying for an absentee ballot, the new law requires a person to provide the numbers from either their driver’s license or state-issued identification card or the last four digits of their social security number.
To expand opportunities to vote, early voting is now an option for three weeks before the election. The law makes early voting on Sunday available at the choice of each county.

The new legislation codifies the use of drop boxes in 2024, but mandates they be placed in secure, well-lit, locations with continuous human monitoring. To protect the chain of custody, two people are now required to deliver the contents of a drop box to an election clerk.
The act prohibits local officials from accepting non-government funds, grants, or gifts in connection with election administration.
In 2023, the Georgia legislature passed SB-222 to bolster the 2021 prohibition to make it a crime.
In protest to the new 2021 measures, Major League Baseball deemed them “restrictive,” and moved that year’s All-Star Game from Georgia to Colorado.
Georgia state Sen. Colton Moore, a Republican, said that although improvements have been made since 2020, much meaningful work is still needed.
“Nothing of substance has changed since 2020. Every mechanism to facilitate a steal is still in place,” he told The Epoch Times. “We must work to eliminate the vulnerabilities still in place today.”
Mr. Moore also highlighted the “ridiculous” number of absentee ballots still used in Georgia elections and said they ought to be restricted to military personnel and medically disabled citizens. He said he was also worried about the institutionalization of the use of absentee ballot drop boxes, which he believes should be done away with altogether.
“We need to make it a legislative priority to stop authoritarian figures like [Fulton County District Attorney] Fani Willis from prosecuting people for merely questioning our elections. Her actions have created a chilling effect among my colleagues in the legislature,” he said.
“Unless we obtain a legislative solution soon, we must resolve to overcome fraud through an overwhelming turnout in November.”

Michigan
Right after being elected in 2018, Michigan’s Democrat Gov. Gretchen Whitmer used her veto power to shoot down nearly 20 election integrity reform bills sent to her desk by the then-Republican-controlled state legislature.
In the 2020 presidential election, President Donald Trump lost Michigan to Joe Biden by 154,000 votes or 2.8 percent.
Afterwards, judges in six different court cases found that Michigan’s Democrat Secretary of State Jocelyn Benson issued inaccurate or legally unauthorized guidance to local officials in the runup to the 2020 general election.
When Ms. Whitmer was reelected in 2022 and Democrats captured control of the legislature, within a year 12 new Democrat-sponsored election laws were enacted—all of which Republicans say loosen security.
The new Democrat-authored statutes extend automatic voter registration to other state agencies and offices beyond the Secretary of State’s office, which issues driver’s licenses in Michigan.
They liberalize online registration and allow a person to apply for an absentee ballot online. They permit 16-year-olds to pre-register to vote.
During the past several election cycles, Democrat activists, backed by out-of-state, big-money donors, effectively used the ballot initiative process to repeal existing election laws, enact new laws, and amend the state constitution. Two of the largest contributors were the Sixteen Thirty Fund ($11 million) and the George Soros-founded Open Society Foundation ($1.2 million).
The ballot initiative method was employed to expand and institutionalize the use of mail-in ballot drop boxes, allow no-excuse absentee voting, permit same-day registration and voting, and shorten the length of residency required to register to vote.
The initiative process was also used to weaken photo ID requirements by mandating that election officials accept an affidavit of identity signed by the prospective voter instead. It also enabled people to request to automatically receive an absentee ballot for every election in perpetuity, and it authorized taxpayer-funded, postage-free mailing for people returning absentee ballot applications or mail-in ballots.
Left-wing activist groups also utilized the initiative process to obtain the constitutional right to nine consecutive days of early voting; and early voting sites can now be used by people from more than one community within a county.
The ballot proposals enacting these new laws were approved handily by the Michigan electorate at the polls.
Read the rest here...
Uncategorized
Stock indexes are breaking records and crossing milestones – making many investors feel wealthier
The S&P 500 topped 5,000 on Feb. 9, 2024, for the first time. The Dow Jones Industrial Average will probably hit a new big round number soon t…

The S&P 500 stock index topped 5,000 for the first time on Feb. 9, 2024, exciting some investors and garnering a flurry of media coverage. The Conversation asked Alexander Kurov, a financial markets scholar, to explain what stock indexes are and to say whether this kind of milestone is a big deal or not.
What are stock indexes?
Stock indexes measure the performance of a group of stocks. When prices rise or fall overall for the shares of those companies, so do stock indexes. The number of stocks in those baskets varies, as does the system for how this mix of shares gets updated.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, also known as the Dow, includes shares in the 30 U.S. companies with the largest market capitalization – meaning the total value of all the stock belonging to shareholders. That list currently spans companies from Apple to Walt Disney Co.
The S&P 500 tracks shares in 500 of the largest U.S. publicly traded companies.
The Nasdaq composite tracks performance of more than 2,500 stocks listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange.
The DJIA, launched on May 26, 1896, is the oldest of these three popular indexes, and it was one of the first established.
Two enterprising journalists, Charles H. Dow and Edward Jones, had created a different index tied to the railroad industry a dozen years earlier. Most of the 12 stocks the DJIA originally included wouldn’t ring many bells today, such as Chicago Gas and National Lead. But one company that only got booted in 2018 had stayed on the list for 120 years: General Electric.
The S&P 500 index was introduced in 1957 because many investors wanted an option that was more representative of the overall U.S. stock market. The Nasdaq composite was launched in 1971.
You can buy shares in an index fund that mirrors a particular index. This approach can diversify your investments and make them less prone to big losses.
Index funds, which have only existed since Vanguard Group founder John Bogle launched the first one in 1976, now hold trillions of dollars .
Why are there so many?
There are hundreds of stock indexes in the world, but only about 50 major ones.
Most of them, including the Nasdaq composite and the S&P 500, are value-weighted. That means stocks with larger market values account for a larger share of the index’s performance.
In addition to these broad-based indexes, there are many less prominent ones. Many of those emphasize a niche by tracking stocks of companies in specific industries like energy or finance.
Do these milestones matter?
Stock prices move constantly in response to corporate, economic and political news, as well as changes in investor psychology. Because company profits will typically grow gradually over time, the market usually fluctuates in the short term, while increasing in value over the long term.
The DJIA first reached 1,000 in November 1972, and it crossed the 10,000 mark on March 29, 1999. On Jan. 22, 2024, it surpassed 38,000 for the first time. Investors and the media will treat the new record set when it gets to another round number – 40,000 – as a milestone.
The S&P 500 index had never hit 5,000 before. But it had already been breaking records for several weeks.
Because there’s a lot of randomness in financial markets, the significance of round-number milestones is mostly psychological. There is no evidence they portend any further gains.
For example, the Nasdaq composite first hit 5,000 on March 10, 2000, at the end of the dot-com bubble.
The index then plunged by almost 80% by October 2002. It took 15 years – until March 3, 2015 – for it return to 5,000.
By mid-February 2024, the Nasdaq composite was nearing its prior record high of 16,057 set on Nov. 19, 2021.
Index milestones matter to the extent they pique investors’ attention and boost market sentiment.
Investors afflicted with a fear of missing out may then invest more in stocks, pushing stock prices to new highs. Chasing after stock trends may destabilize markets by moving prices away from their underlying values.
When a stock index passes a new milestone, investors become more aware of their growing portfolios. Feeling richer can lead them to spend more.
This is called the wealth effect. Many economists believe that the consumption boost that arises in response to a buoyant stock market can make the economy stronger.
Is there a best stock index to follow?
Not really. They all measure somewhat different things and have their own quirks.
For example, the S&P 500 tracks many different industries. However, because it is value-weighted, it’s heavily influenced by only seven stocks with very large market values.
Known as the “Magnificent Seven,” shares in Amazon, Apple, Alphabet, Meta, Microsoft, Nvidia and Tesla now account for over one-fourth of the S&P 500’s value. Nearly all are in the tech sector, and they played a big role in pushing the S&P across the 5,000 mark.
This makes the index more concentrated on a single sector than it appears.
But if you check out several stock indexes rather than just one, you’ll get a good sense of how the market is doing. If they’re all rising quickly or breaking records, that’s a clear sign that the market as a whole is gaining.
Sometimes the smartest thing is to not pay too much attention to any of them.
For example, after hitting record highs on Feb. 19, 2020, the S&P 500 plunged by 34% in just 23 trading days due to concerns about what COVID-19 would do to the economy. But the market rebounded, with stock indexes hitting new milestones and notching new highs by the end of that year.
Panicking in response to short-term market swings would have made investors more likely to sell off their investments in too big a hurry – a move they might have later regretted. This is why I believe advice from the immensely successful investor and fan of stock index funds Warren Buffett is worth heeding.
Buffett, whose stock-selecting prowess has made him one of the world’s 10 richest people, likes to say “Don’t watch the market closely.”
If you’re reading this because stock prices are falling and you’re wondering if you should be worried about that, consider something else Buffett has said: “The light can at any time go from green to red without pausing at yellow.”
And the opposite is true as well.
Alexander Kurov does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
dow jones sp 500 nasdaq stocks covid-19Uncategorized
Marriage is not as effective an anti-poverty strategy as you’ve been led to believe
Marriage on its own won’t do away with child poverty, and in fact it can create even more instability for low-income families.

Brides.com predicts that 2024 will be the “year of the proposal” as engagements tick back up after a pandemic-driven slowdown.
Meanwhile, support for marriage has found new grist in recent books, including sociologist Brad Wilcox’s “Get Married: Why Americans Must Defy the Elites, Forge Strong Families and Save Civilization” and economist Melissa Kearney’s “The Two-Parent Privilege.”
Kearney’s book was hailed by economist Tyler Cowen as possibly “the most important economics and policy book of this year.” This is not because it treads new ground but because, as author Kay Hymowitz writes, it breaks the supposed “taboo about an honest accounting of family decline.”
These developments are good news for the marriage promotion movement, which for decades has claimed that marriage supports children’s well-being and combats poverty. The movement dates back at least to the U.S. Department of Labor’s Moynihan Report of 1965, which argued that family structure aggravated Black poverty.
Forty years after the Moynihan Report, George W. Bush-era programs such as the Healthy Marriage Initiative sought to enlist churches and other community groups in an effort to channel childbearing back into marriage. These initiatives continue today, with the federally subsidized Healthy Marriage and Responsible Fatherhood programs.
Still, nearly 30% of U.S. children live in single-parent homes today, compared with 10% in 1965.
We are law professors who have written extensively about family structure and poverty. We, and others, have found that there is almost no evidence that federal programs that promote marriage have made a difference in encouraging two-parent households. That’s in large part because they forgo effective solutions that directly address poverty for measures that embrace the culture wars.

Marriage and social class
Today’s marriage promoters claim that marriage should not be just for elites. The emergence of marriage as a marker of class, they believe, is a sign of societal dysfunction.
According to census data released in 2021, 9.5% of children living with two parents – and 7.5% with married parents – lived below the poverty level, compared with 31.7% of children living with a single parent.
Kearney’s argument comes down to: 1 + 1 = 2. Two parents have more resources, including money and time to spend with children, than one. She marshals extensive research designed to show that children from married couple families are more likely to graduate from high school, complete college and earn higher incomes as adults than the children of single parents.
It is undoubtedly true that two parents – that is, two nonviolent parents with reliable incomes and cooperative behavior – have more resources for their children than one parent who has to work two jobs to pay the rent. However, this equation does not address causation. In other words, parents who have stable incomes and behaviors are more likely to stay together than parents who don’t.
Ethnographic studies indicate, for example, that the most common reasons unmarried women are no longer with the fathers of their children are the men’s violent behavior, infidelity and substance abuse.
Moreover, income volatility disproportionately affects parents who don’t go to college. So while they may have more money to invest in children together than apart, when one of these parents experiences a substantial drop in income, the other parent may have to decide whether to support the partner or the children on what is often a meager income.
The impact of having single parents also plays out differently by race and class. As sociologist and researcher Christina Cross explains, “Living apart from a biological parent does not carry the same cost for Black youths as for their white peers, and being raised in a two-parent family is not equally beneficial.”
For example, Cross found that living in a single-mother family is less likely to affect high school completion rates for Black children than for white children. Also, Black families tend to be more embedded in extended family than white families, and this additional support system may help protect children from negative outcomes associated with single-parent households.
Making men more ‘marriageable’
Kearney, to her credit, does note that economic insecurity largely explains what is happening to working-class families, and that no parent should have to tolerate violence or substance abuse. But she doubles down on the need to restore a norm of two-parent families.
Many of her policy prescriptions are sensible. She advocates for better opportunities for low-income men – to make them, in the words of sociologist William Julius Wilson, “marriageable.” Such policies would include wage subsidies to improve their job opportunities, investment in community colleges that provide skills training, and the removal of questions about criminal histories from job applications, so that candidates who have previously been incarcerated are not immediately disqualified.
A new marriage model
What marriage promotion efforts overlook, however, are the underlying changes in what marriage has become – both legally and practically.
The new marriage model rests on three premises.
The first is a moral command: Have sex if you want to, but don’t have children until you are ready. While the shotgun marriage once served as the primary response to unplanned pregnancy, such marriages today often derail education and careers and are more likely to result in divorce than other marriages. Research shows that lower-income women’s pregnancies are much more likely to be unplanned.
The second is the ability to pick a partner who will support you and assume joint responsibility for parenting. As women have attained more economic independence, they are less in need of men to raise children, particularly if their partners are insensitive or abusive. With healthy relationships, couples pick partners based on trust, commitment and equal respect. This is more difficult to do in communities with high rates of incarceration and few opportunities for stable employment.
And the third is economic and behavioral stability. Instability undermines even committed unions. Parents who wait until they find the right partner and have stable lives bring a lot more to parenting, whether they marry or not.
We believe that creating opportunities for low-income parents to reach this middle-class model is likely to be the most effective marriage promotion policy.
Economic support is key
In relationships that fall outside of these premises, 1 + 1 often becomes 1 + -1, which equals 0.
Being committed to a partner who can’t pay speeding tickets, runs up credit card bills, comes home drunk or can’t be relied on to pick up the children after school is not a recipe for success.
Economic principles suggest that businesses with more volatile income streams need a stronger capital base to withstand the downturns. Working-class couples who face economic insecurity see commitment as similarly misguided; without a capital base, a downturn for one partner can wipe out the other.
The Biden administration’s child tax credit expansion included in the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 helped cut the child poverty rate – after accounting for government assistance – to a record low that year. It did more to address child poverty than marriage promotion efforts have ever done.
Researchers have described such income-support policies as the “ultimate multipurpose policy instrument.” They improve the economic circumstances of single-parent families and, in doing so, may also provide greater support for two-parent relationships.
Policymakers know how to solve child poverty – and these measures are far more effective than efforts to put two married parents in every household.
The authors do not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and have disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
subsidies pandemicUncategorized
Divergences And Other Technical Warnings
While the bulls remain entirely in control of the market narrative, divergences and other technical warnings suggest becoming more cautious may be prudent….
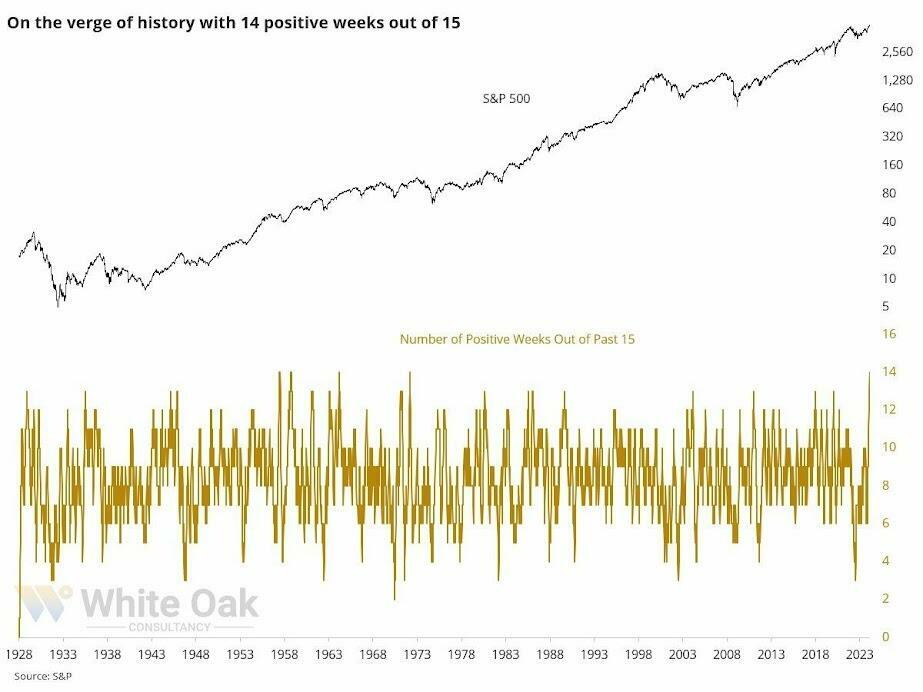
While the bulls remain entirely in control of the market narrative, divergences and other technical warnings suggest becoming more cautious may be prudent.
In January 2020, we discussed why we were taking profits and reducing risk in our portfolios. At the time, the market was surging, and there was no reason for concern. However, just over a month later, the markets fell sharply as the “pandemic” set in. While there was no evidence at the time that such an event would occur, the markets were so exuberant that only a trigger was needed to spark a correction.
“When you sit down with your portfolio management team, and the first comment made is ‘this is nuts,’ it’s probably time to think about your overall portfolio risk. On Friday, that was how the investment committee both started and ended – ‘this is nuts.'” – January 11th, 2020.
As the S&P 500 index approaches another psychological milestone of 5000, we again see numerous warning signs emerging that suggest the risk of a correction is elevated. Does that mean a correction will ensue tomorrow? Of course not. As the old saying goes, “Markets can remain irrational longer than you can remain solvent.” However, just as in 2020, it took more than a month before the warnings became reality.
While discussing the risk of a correction, it was just last October that we discussed why a rally was likely. The reasons at that time were almost precisely the opposite of what we see today. There was extremely bearish investor sentiment combined with negative divergences of technical indicators, and analysts could not cut year-end price targets fast enough.
What happened next was the longest win streak in 52 years that pushed the market to new all-time highs.
The last time we saw such a rally was between November 1971 and February 1972. Of course, the “Nifty Fifty” rally preceded the 1973-74 bear market. Then, like today, a handful of stocks were driving the markets higher as interest rates were elevated along with inflation.

While there are many differences today versus then, there are reasons for concern.
The “New Nifty 50”
My colleague Albert Edwards at Societe Generale recently discussed the rising capitalization of the technology market.
“I never thought we would get back to the point where the value of the US tech sector once again comprised an incredible one third of the US equity market. This just pips the previous all-time peak seen on 17 July 2000 at the height of the Nasdaq tech bubble.
What’s more, this high has been reached with only three of the ‘Magnificant-7’ internet stocks actually being in the tech sector (Apple, Microsoft, and Nvidia)! If you add in the market cap of Amazon, Meta, Alphabet (Google) and Tesla, then the IT and ‘internet’ stocks dominate like never before.”

Of course, there are undoubtedly important differences between today and the “Dot.com” era. The most obvious is that, unlike then, technology companies generate enormous revenues and profits. However, this was the same with the “Nifty-50” in the early 70s. The problem is always two-fold: 1) the sustainability of those earnings and growth rates and 2) the valuations paid for them. If something occurs that slows earnings growth, the valuation multiples will get revised lower.
While the economic backdrop has seemingly not caught up with technology companies yet, the divergence of corporate profits between the Technology sector and the rest of the market is likely unsustainable.

That inability to match the pace of expectations is already occurring. That divergence poses a substantial risk to investors.

Again, while the risk is somewhat evident, the “bullishness” of the market can last much longer than logic would predict. Valuations, as always, are a terrible market timing device; however, they tell you a lot about long-term returns from markets. Currently, the valuations paid for technology stocks are alarming and hard to justify.
However, despite valuations, those stocks can keep ramping higher in the short term (6-18 months) as the speculative flows continue.

However, over the next few months, some divergences and indicators suggest caution is advisable.
Technical Divergences Add To The Risk
Each weekend in the BullBearReport, investor sentiment is something that we track closely. The reason is that when investor sentiment is extremely bullish or bearish, such is the point where reversals have occurred. As Sam Stovall, the investment strategist for Standard & Poor’s, once stated:
“If everybody’s optimistic, who is left to buy? If everybody’s pessimistic, who’s left to sell?”
Currently, everyone is very optimistic about the market. Bank of America, one of the world’s largest asset custodians, monitors risk positioning across equities. Currently, “risk love” is in the 83rd percentile and at levels that have generally preceded short-term corrective actions.

At the same time, retail and professional investors are also exuberant, as noted on Tuesday.
“Another measure of bullish sentiment is comparing investor sentiment to the volatility index. Low levels of volatility exist when there is little concern about a market correction. Low volatility and bullish sentiment are often cozy roommates. The chart below compares the VIX/Sentiment ratio to the S&P Index. Once again, this measure suggests that markets are at risk of a short-term price correction.”

However, while everyone is exceedingly bullish on the market, the internal divergence of stocks sends warning signals. Andrei Sota recently showed that market breadth is weakening despite record highs. Note that prior market peaks were accompanied by peaks in the percentage of stocks above their 20, 50, and 200-day moving averages. To further hammer home this point, consider the following Tweet from Jason Goepfert of Sentimentrader:
“Man, this is weird. The S&P 500 is within .35% of a 3-year high. Fewer than 40% of its stocks are above their 10-day avg, fewer than 60% above their 50-day, and fewer than 70% above their 200-day. Since 1928, that’s only happened once before: August 8, 1929.“

That negative divergence between stocks making new highs and the underlying breadth is a good reason to be more cautious with allocations currently.
As I started this commentary, “This is nuts.”
So Why Not Go To Cash
This analysis raises an obvious question.
“Well, if this is nuts, why not go to cash and wait out the correction and then buy back in.”
The best answer to that question came from Albert Edwards this week.
“I cast my mind back to 2000 where the narrative around the then IT bubble was incredibly persuasive, just as it is now. But the problem that skeptical investors have now, as they did in 1999, is that selling, or underweighting US IT, can destroy performance if one exits too early.”
Regarding speculative bull markets, as noted above, the “this is nuts” part can remain “nuts” for much longer than you think. Therefore, given that we have to generate returns for our clients or suffer career risk, we must be careful not to exit the markets too early…or too late.
Therefore, regardless of your personal views, the bull market that started in October remains intact. The speculative frenzy is still present. As such, we are reducing equity exposure modestly and rebalancing risk by following our basic procedures.
- Trim Winning Positions back to their original portfolio weightings. (ie. Take profits)
- Sell Those Positions That Aren’t Working. If they don’t rally with the market during a bounce, they will decline when it sells off again.
- Move Trailing Stop Losses Up to new levels.
- Review Your Portfolio Allocation Relative To Your Risk Tolerance. If you have an aggressive allocation to equities at this point of the market cycle, you may want to try to recall how you felt during 2008. Raise cash levels and increase fixed income accordingly to reduce relative market exposure.
Could I be wrong? Absolutely.
But a host of indicators are sending us an early warning.
What’s worse:
- Missing out temporarily on some additional short-term gains or
- Spending time getting back to even which is not the same as making money.
“Opportunities are made up far easier than lost capital.” – Todd Harrison
The post Divergences And Other Technical Warnings appeared first on RIA.
sp 500 nasdaq equities stocks pandemic interest rates-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 month ago
International1 month agoWar Delirium
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoKey Events This Week: All Eyes On Core PCE Amid Deluge Of Fed Speakers





















