Uncategorized
Rent vs. Buy: Detailed Methodology to Simulating the Rent vs. Buy Equation
Economic question: A customer has a given lifestyle in mind. They have multiple paths they can take in gaining this lifestyle. We want to answer whether…
Economic question: A customer has a given lifestyle in mind. They have multiple paths they can take in gaining this lifestyle. We want to answer whether it is better to rent or to buy the same home to achieve that lifestyle.
Buying a home = a consumption decision for ongoing shelter and utility in the space + an investment decision on an appreciating asset (with maintenance)
So the alternative, and opportunity cost, is renting to consume shelter and utility from the space, and investing in some alternative asset unrelated to real estate that has a similar risk and return.
What we’ll do: Simulate the purely financial aspect of the decision so that the decision maker can decide if it is financially advantageous to commit to homeownership with a fixed-rate loan. Functionally, we’ll estimate the time horizon the buyer needs to maintain ownership to breakeven or if the difference in simulated costs on a short(er) horizon is at least at a price low enough to pay for the utility of full control of the property over that time.
Optimality then implies that a renter becomes a buyer if and only if:
Where SSt=T, SR t=T denote the net present value for being a buyer and a renter respectively at time T, the intended years after purchase the buyer hopes to move again. The savings accrued from renting each period are the saved/invested funds that would have been used for a down payment and transaction costs invested at the risk-free rate plus the recurring costs of owning a home net the recurring cost of renting (rent, rent insurance, application fees, etc.)
Setting the price and rent at the time of purchase, t=0
As the average of the middle third of unbiased neural Zestimates within any region studied, the Zillow Home Value Index is our most reliable estimate of a “typical” home price within an area. So we set the price at purchase,
Practical realities to knowing the price and rent on the same house:
- Set of properties ever rented is distinctly different from the set of properties ever purchased.
- Only a subset of properties are sold or listed in every period.
- Set of properties listed for rent and for sale in the same period is negligible.
Zestimation at Zillow
The Zestimate,
and Rental Zestimate
are unbiased property-level estimates of current home price and market-rate asking rent, respectively. They use advanced machine learning algorithms and neural networks trained with historical home prices or listed asking rents against property features to jointly minimize error (median absolute percent error, or MAPE) and minimize bias (median percent error) in predicting property valuation or rent.
Advantages of neural networks:
- Improved performance at higher data volumes/histories
- Radical improvement in Zestimate bias (MAPE)
- Significant improvement in accuracy (especially at price tails)
- Enough advancement to learn underlying patterns along spatial and temporal dimensions
- Ability to extrapolate, like parametric approaches, but unlike traditional ML classification methods
- Zestimate accuracy[https://www.zillow.com/z/zestimate/]
So we should be able to exploit the estimates, with some reservation discussed later, on the same individual homes to estimate a “true” or at least “truer” price-to-rent ratio than previously available. With these property-level estimates of price and asking rent, our preferred method for evaluating the breakeven simulation at scale (for many different regions and scenarios) is to set rent in the first year such that
In which K is the total number of housing units (single-family, townhouses, condos and co-ops; excludes mobile homes) in the region.
Why not just use the Zestimate and Rental Zestimate at the property level?
The computer processing load to estimate the full simulation is too great to reliably run the buy vs. rent break even simulation at the property level for public production. So we apply the typical price-to-rent ratio to the ZHVI and only have to calculate the buy vs. rent simulation for each scenario for each metro once. The MEDIANi=1,…,K(ZRi,t=0/ZFSi,t=0) also has public metrics potential for other applications by researchers beyond this one.
Alternatives used to demonstrate the importance of estimating a ZHVI-comparable rent
- Median rent of households who moved in the past year to detached, two- to four- bedroom, single-family rentals (Zillow analysis of 2021 ACS, IPUMS.org). This estimate is typically the lowest for rent, including some very long or familial tenant-landlord relationships and other ways that tenants can experience lower “off-market” rents.
- Zillow Observed Rent Index (ZORI): Rental-market propensity weighted average rental Zestimate. Propensity is conditional on property type, year built and bedroom count. ZORI is a very useful metric designed to capture the rented housing stock, not the full stock, to make it comparable to ZHVI.
Remaining concerns in this approach
- One available listing on Zillow could represent multiple units, among other data quality differences between rental Zestimation and home price Zestimation, likely driving different distributions of errors.
- A subset of all rental units is listed on Zillow in every period, and that sample is likely to be toward higher quality and larger properties. Low-end rentals are more likely to go straight to Craigslist. In contrast, we likely see a more complete sample of homes that hit the for-sale market due to our for-sale market’s maturity. However, rental stock is systematically higher quality and larger than for-sale stock. At the moment, we do not know if these dynamics balance each other out.
Setting future price growth
The user will purchase the typical home in the metro (ZHVI) with only 20% down on a 15- or 30-year fixed-rate loan. The buyer will then earn appreciation on the full purchase price. To account for the user’s level of risk and what they’re willing to accept about the future of home price growth, they can choose three different home price path scenarios that will set Pt as the consumer holds the home after purchase:
- Data-forward in the short run, optimistic in the long run
- ZHVF (Zillow’s one-year forecast for ZHVI) over the first year, after which the growth rate moves toward the long-term historical growth rate along a cubic spline over five years.
- Data-forward in the short run, more practical/conservative for the long run
- ZHVF (Zillow’s one-year forecast for ZHVI) over the first year, after which the growth rate moves toward half the long-term historical growth rate along a cubic spline over five years.
- Conservative in the short run and the long run
- Flat over the first year, after which the growth rate moves toward half the long-term historical growth rate along a cubic spline over five years.
Costs and benefit streams of buying
Transaction costs at purchase
3% x P0 at purchase and 8% x Pt=n at sale
- Assumed to include commissions, fees (title, mortgage fees and points, etc.), excise taxes, etc., and can vary greatly by individual, state and local jurisdictions.
- Ongoing work: Estimating “true” or observed transaction costs for home buyers from Zillow’s database.
Interest portion of mortgage payment
Assumes a 15- or 30-year fixed-rate loan, mortgage rate locked at t=0. Mortgage rate is set in the simulation to explore before the pandemic (3%) and now (7%). (We will use this 4 percentage point change to explore the sensitivity to many of the parameters set in the simulation.)
Property taxes
Assumed 1% x Pt annually
- This is a dramatic simplification since property taxes vary widely across different and unique sets according to county, city and school district.
- Ongoing work: Effective property taxes within these overlapping boundaries was recently estimated but are not incorporated in this simulation yet.
Property insurance
Assumed 0.5% x Pt annually
- Ongoing work:
- Insurance premiums are also available in public records within the same region cross-sections to estimate property taxes above.
- A potential collaboration with Allstate Insurance Company as well as climate risk information providers should increase the transparency in this area, especially as it relates to home purchasing decisions in locations impacted by the climate crisis.
Maintenance costs
Assumed 1% x Pt annually
- This is an oversimplification. Maintenance costs are likely highly personal as it is dependent on the human capital or professional network of the potential buyer, the costs and availability of help/skilled labor in the region, and/or the age of the house.
Capital gains taxes on profit above $375K
Assumes half of the household is married, so can deduct the average of $500K and $250K, when applying the capital gain exclusion for the primary purchase. The estimated taxes use the local median household income to set the tax rate, but this is almost always 15%.
Condo or HOA fees
Assumed 0 in our simulation
- Fair and healthy HOA costs and management are likely critical to homeowner success where an HOA is in place.
Property tax and mortgage interest deductions
These are only triggered in the simulation if property taxes and mortgage interest exceed the standard deduction (data on other itemized deductions not incorporated). Since new limits on SALT deductions and the doubling of the standard deduction, at the median, this is almost never triggered without other itemized deductions to overcome the standard, so this is more or less negligible in the simulation.
Renting and investing
Rent growth
Because of relatively short rent histories within Zillow’s database, we do not yet have a formal forecast for asking-rate rent. To explore the impact of rent growth, we allow the user to choose 2% or 6% in the first year before splining to 2% annual growth by the fifth year.
Rental broker fee
Assumed 0
Rent deposit:
You get it back, but used in opportunity cost calculations together with 1st and last months rent required at signing (and so tied up instead of invested in our simulation logic)
Renters insurance
1% of rent monthly
Opportunity cost and the renter’s investment stream
A major contribution from this work is to disentangle the investment streams of this decision from the more salient if still not totally certain upfront and monthly costs of the two options: rent or buy.
To make a comparable decision to buying, as a renter, we assume that the renter is fully investing the money that would have been used to buy a home.
Rates of return available in the simulation
- Risk free 2% over all time
- Risk free 6% over all time
The money invested by the renter includes any “savings” (the difference in monthly costs between buying and renting) each month. To keep it fair between the choices, the renter also then has to take money out of their investments to cover the difference during periods when out-of-pocket renter’s costs are larger than the homeowner’s for a similar property. The easiest way to mechanically code this is to estimate what the buyer would have earned as a return in the alternative asset with all the money they spent on housing. We then do the same thing for the renter.
The renter’s investment gains are then the buyer’s opportunity cost (what would have been earned in the stock market after capital gains taxes but can’t be earned if it’s locked up in housing as an owner) minus the renter’s opportunity cost (what they didn’t earn from stock markets because their money was tied up in renting).
Investment value of the renter
= After-tax interest earned investing everything they spent to buy and own
- After-tax interest earned investing everything they spent to rent
- Original upfront costs for the buyer
- Original upfront costs for the renter
The buyer’s comparable investment gain is their home equity (home price at sale minus the mortgage balance) minus the transaction costs and taxes they pay to liquidate the asset and get the return, and minus the down payment which they made in the first place.
Investment value of the buyer
- Home value at sale
- Mortgage balance at sale
- Seller transaction costs
- Capital gains tax of the owner after sale
The post Rent vs. Buy: Detailed Methodology to Simulating the Rent vs. Buy Equation appeared first on Zillow Research.
real estate pandemic stock marketsUncategorized
Mortgage rates fall as labor market normalizes
Jobless claims show an expanding economy. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
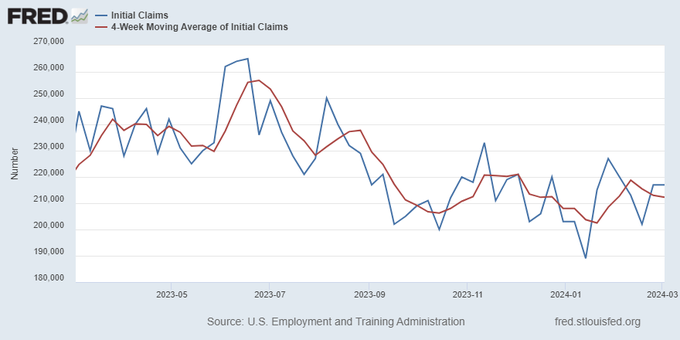
Everyone was waiting to see if this week’s jobs report would send mortgage rates higher, which is what happened last month. Instead, the 10-year yield had a muted response after the headline number beat estimates, but we have negative job revisions from previous months. The Federal Reserve’s fear of wage growth spiraling out of control hasn’t materialized for over two years now and the unemployment rate ticked up to 3.9%. For now, we can say the labor market isn’t tight anymore, but it’s also not breaking.
The key labor data line in this expansion is the weekly jobless claims report. Jobless claims show an expanding economy that has not lost jobs yet. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
From the Fed: In the week ended March 2, initial claims for unemployment insurance benefits were flat, at 217,000. The four-week moving average declined slightly by 750, to 212,250
Below is an explanation of how we got here with the labor market, which all started during COVID-19.
1. I wrote the COVID-19 recovery model on April 7, 2020, and retired it on Dec. 9, 2020. By that time, the upfront recovery phase was done, and I needed to model out when we would get the jobs lost back.
2. Early in the labor market recovery, when we saw weaker job reports, I doubled and tripled down on my assertion that job openings would get to 10 million in this recovery. Job openings rose as high as to 12 million and are currently over 9 million. Even with the massive miss on a job report in May 2021, I didn’t waver.
Currently, the jobs openings, quit percentage and hires data are below pre-COVID-19 levels, which means the labor market isn’t as tight as it once was, and this is why the employment cost index has been slowing data to move along the quits percentage.

3. I wrote that we should get back all the jobs lost to COVID-19 by September of 2022. At the time this would be a speedy labor market recovery, and it happened on schedule, too
Total employment data
4. This is the key one for right now: If COVID-19 hadn’t happened, we would have between 157 million and 159 million jobs today, which would have been in line with the job growth rate in February 2020. Today, we are at 157,808,000. This is important because job growth should be cooling down now. We are more in line with where the labor market should be when averaging 140K-165K monthly. So for now, the fact that we aren’t trending between 140K-165K means we still have a bit more recovery kick left before we get down to those levels.

From BLS: Total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 275,000 in February, and the unemployment rate increased to 3.9 percent, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Job gains occurred in health care, in government, in food services and drinking places, in social assistance, and in transportation and warehousing.
Here are the jobs that were created and lost in the previous month:

In this jobs report, the unemployment rate for education levels looks like this:
- Less than a high school diploma: 6.1%
- High school graduate and no college: 4.2%
- Some college or associate degree: 3.1%
- Bachelor’s degree or higher: 2.2%

Today’s report has continued the trend of the labor data beating my expectations, only because I am looking for the jobs data to slow down to a level of 140K-165K, which hasn’t happened yet. I wouldn’t categorize the labor market as being tight anymore because of the quits ratio and the hires data in the job openings report. This also shows itself in the employment cost index as well. These are key data lines for the Fed and the reason we are going to see three rate cuts this year.
recession unemployment covid-19 fed federal reserve mortgage rates recession recovery unemploymentUncategorized
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Last month we though that the January…
Last month we though that the January jobs report was the "most ridiculous in recent history" but, boy, were we wrong because this morning the Biden department of goalseeked propaganda (aka BLS) published the February jobs report, and holy crap was that something else. Even Goebbels would blush.
What happened? Let's take a closer look.
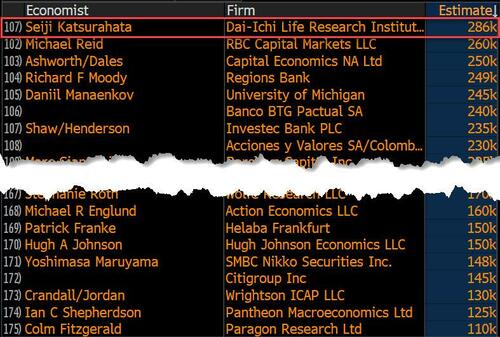
On the surface, it was (almost) another blockbuster jobs report, certainly one which nobody expected, or rather just one bank out of 76 expected. Starting at the top, the BLS reported that in February the US unexpectedly added 275K jobs, with just one research analyst (from Dai-Ichi Research) expecting a higher number.
Some context: after last month's record 4-sigma beat, today's print was "only" 3 sigma higher than estimates. Needless to say, two multiple sigma beats in a row used to only happen in the USSR... and now in the US, apparently.
Before we go any further, a quick note on what last month we said was "the most ridiculous jobs report in recent history": it appears the BLS read our comments and decided to stop beclowing itself. It did that by slashing last month's ridiculous print by over a third, and revising what was originally reported as a massive 353K beat to just 229K, a 124K revision, which was the biggest one-month negative revision in two years!
Of course, that does not mean that this month's jobs print won't be revised lower: it will be, and not just that month but every other month until the November election because that's the only tool left in the Biden admin's box: pretend the economic and jobs are strong, then revise them sharply lower the next month, something we pointed out first last summer and which has not failed to disappoint once.
In the past month the Biden department of goalseeking stuff higher before revising it lower, has revised the following data sharply lower:
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) August 30, 2023
- Jobs
- JOLTS
- New Home sales
- Housing Starts and Permits
- Industrial Production
- PCE and core PCE
To be fair, not every aspect of the jobs report was stellar (after all, the BLS had to give it some vague credibility). Take the unemployment rate, after flatlining between 3.4% and 3.8% for two years - and thus denying expectations from Sahm's Rule that a recession may have already started - in February the unemployment rate unexpectedly jumped to 3.9%, the highest since February 2022 (with Black unemployment spiking by 0.3% to 5.6%, an indicator which the Biden admin will quickly slam as widespread economic racism or something).
And then there were average hourly earnings, which after surging 0.6% MoM in January (since revised to 0.5%) and spooking markets that wage growth is so hot, the Fed will have no choice but to delay cuts, in February the number tumbled to just 0.1%, the lowest in two years...
... for one simple reason: last month's average wage surge had nothing to do with actual wages, and everything to do with the BLS estimate of hours worked (which is the denominator in the average wage calculation) which last month tumbled to just 34.1 (we were led to believe) the lowest since the covid pandemic...
... but has since been revised higher while the February print rose even more, to 34.3, hence why the latest average wage data was once again a product not of wages going up, but of how long Americans worked in any weekly period, in this case higher from 34.1 to 34.3, an increase which has a major impact on the average calculation.
While the above data points were examples of some latent weakness in the latest report, perhaps meant to give it a sheen of veracity, it was everything else in the report that was a problem starting with the BLS's latest choice of seasonal adjustments (after last month's wholesale revision), which have gone from merely laughable to full clownshow, as the following comparison between the monthly change in BLS and ADP payrolls shows. The trend is clear: the Biden admin numbers are now clearly rising even as the impartial ADP (which directly logs employment numbers at the company level and is far more accurate), shows an accelerating slowdown.
But it's more than just the Biden admin hanging its "success" on seasonal adjustments: when one digs deeper inside the jobs report, all sorts of ugly things emerge... such as the growing unprecedented divergence between the Establishment (payrolls) survey and much more accurate Household (actual employment) survey. To wit, while in January the BLS claims 275K payrolls were added, the Household survey found that the number of actually employed workers dropped for the third straight month (and 4 in the past 5), this time by 184K (from 161.152K to 160.968K).
This means that while the Payrolls series hits new all time highs every month since December 2020 (when according to the BLS the US had its last month of payrolls losses), the level of Employment has not budged in the past year. Worse, as shown in the chart below, such a gaping divergence has opened between the two series in the past 4 years, that the number of Employed workers would need to soar by 9 million (!) to catch up to what Payrolls claims is the employment situation.
There's more: shifting from a quantitative to a qualitative assessment, reveals just how ugly the composition of "new jobs" has been. Consider this: the BLS reports that in February 2024, the US had 132.9 million full-time jobs and 27.9 million part-time jobs. Well, that's great... until you look back one year and find that in February 2023 the US had 133.2 million full-time jobs, or more than it does one year later! And yes, all the job growth since then has been in part-time jobs, which have increased by 921K since February 2023 (from 27.020 million to 27.941 million).
Here is a summary of the labor composition in the past year: all the new jobs have been part-time jobs!
But wait there's even more, because now that the primary season is over and we enter the heart of election season and political talking points will be thrown around left and right, especially in the context of the immigration crisis created intentionally by the Biden administration which is hoping to import millions of new Democratic voters (maybe the US can hold the presidential election in Honduras or Guatemala, after all it is their citizens that will be illegally casting the key votes in November), what we find is that in February, the number of native-born workers tumbled again, sliding by a massive 560K to just 129.807 million. Add to this the December data, and we get a near-record 2.4 million plunge in native-born workers in just the past 3 months (only the covid crash was worse)!
The offset? A record 1.2 million foreign-born (read immigrants, both legal and illegal but mostly illegal) workers added in February!
Said otherwise, not only has all job creation in the past 6 years has been exclusively for foreign-born workers...

... but there has been zero job-creation for native born workers since June 2018!
This is a huge issue - especially at a time of an illegal alien flood at the southwest border...
... and is about to become a huge political scandal, because once the inevitable recession finally hits, there will be millions of furious unemployed Americans demanding a more accurate explanation for what happened - i.e., the illegal immigration floodgates that were opened by the Biden admin.
Which is also why Biden's handlers will do everything in their power to insure there is no official recession before November... and why after the election is over, all economic hell will finally break loose. Until then, however, expect the jobs numbers to get even more ridiculous.
Uncategorized
Economic Earthquake Ahead? The Cracks Are Spreading Fast
Economic Earthquake Ahead? The Cracks Are Spreading Fast
Authored by Brandon Smith via Alt-Market.us,
One of my favorite false narratives…

Authored by Brandon Smith via Alt-Market.us,
One of my favorite false narratives floating around corporate media platforms has been the argument that the American people “just don’t seem to understand how good the economy really is right now.” If only they would look at the stats, they would realize that we are in the middle of a financial renaissance, right? It must be that people have been brainwashed by negative press from conservative sources…
I have to laugh at this notion because it’s a very common one throughout history – it’s an assertion made by almost every single political regime right before a major collapse. These people always say the same things, and when you study economics as long as I have you can’t help but throw up your hands and marvel at their dedication to the propaganda.
One example that comes to mind immediately is the delusional optimism of the “roaring” 1920s and the lead up to the Great Depression. At the time around 60% of the U.S. population was living in poverty conditions (according to the metrics of the decade) earning less than $2000 a year. However, in the years after WWI ravaged Europe, America’s economic power was considered unrivaled.
The 1920s was an era of mass production and rampant consumerism but it was all fueled by easy access to debt, a condition which had not really existed before in America. It was this illusion of prosperity created by the unchecked application of credit that eventually led to the massive stock market bubble and the crash of 1929. This implosion, along with the Federal Reserve’s policy of raising interest rates into economic weakness, created a black hole in the U.S. financial system for over a decade.
There are two primary tools that various failing regimes will often use to distort the true conditions of the economy: Debt and inflation. In the case of America today, we are experiencing BOTH problems simultaneously and this has made certain economic indicators appear healthy when they are, in fact, highly unstable. The average American knows this is the case because they see the effects everyday. They see the damage to their wallets, to their buying power, in the jobs market and in their quality of life. This is why public faith in the economy has been stuck in the dregs since 2021.
The establishment can flash out-of-context stats in people’s faces, but they can’t force the populace to see a recovery that simply does not exist. Let’s go through a short list of the most faulty indicators and the real reasons why the fiscal picture is not a rosy as the media would like us to believe…
The “miracle” labor market recovery
In the case of the U.S. labor market, we have a clear example of distortion through inflation. The $8 trillion+ dropped on the economy in the first 18 months of the pandemic response sent the system over the edge into stagflation land. Helicopter money has a habit of doing two things very well: Blowing up a bubble in stock markets and blowing up a bubble in retail. Hence, the massive rush by Americans to go out and buy, followed by the sudden labor shortage and the race to hire (mostly for low wage part-time jobs).
The problem with this “miracle” is that inflation leads to price explosions, which we have already experienced. The average American is spending around 30% more for goods, services and housing compared to what they were spending in 2020. This is what happens when you have too much money chasing too few goods and limited production.
The jobs market looks great on paper, but the majority of jobs generated in the past few years are jobs that returned after the covid lockdowns ended. The rest are jobs created through monetary stimulus and the artificial retail rush. Part time low wage service sector jobs are not going to keep the country rolling for very long in a stagflation environment. The question is, what happens now that the stimulus punch bowl has been removed?
Just as we witnessed in the 1920s, Americans have turned to debt to make up for higher prices and stagnant wages by maxing out their credit cards. With the central bank keeping interest rates high, the credit safety net will soon falter. This condition also goes for businesses; the same businesses that will jump headlong into mass layoffs when they realize the party is over. It happened during the Great Depression and it will happen again today.
Cracks in the foundation
We saw cracks in the narrative of the financial structure in 2023 with the banking crisis, and without the Federal Reserve backstop policy many more small and medium banks would have dropped dead. The weakness of U.S. banks is offset by the relative strength of the U.S. dollar, which lures in foreign investors hoping to protect their wealth using dollar denominated assets.
But something is amiss. Gold and bitcoin have rocketed higher along with economically sensitive assets and the dollar. This is the opposite of what’s supposed to happen. Gold and BTC are supposed to be hedges against a weak dollar and a weak economy, right? If global faith in the dollar and in the U.S. economy is so high, why are investors diving into protective assets like gold?
Again, as noted above, inflation distorts everything.
Tens of trillions of extra dollars printed by the Fed are floating around and it’s no surprise that much of that cash is flooding into the economy which simply pushes higher right along with prices on the shelf. But, gold and bitcoin are telling us a more honest story about what’s really happening.
Right now, the U.S. government is adding around $600 billion per month to the national debt as the Fed holds rates higher to fight inflation. This debt is going to crush America’s financial standing for global investors who will eventually ask HOW the U.S. is going to handle that growing millstone? As I predicted years ago, the Fed has created a perfect Catch-22 scenario in which the U.S. must either return to rampant inflation, or, face a debt crisis. In either case, U.S. dollar-denominated assets will lose their appeal and their prices will plummet.
“Healthy” GDP is a complete farce
GDP is the most common out-of-context stat used by governments to convince the citizenry that all is well. It is yet another stat that is entirely manipulated by inflation. It is also manipulated by the way in which modern governments define “economic activity.”
GDP is primarily driven by spending. Meaning, the higher inflation goes, the higher prices go, and the higher GDP climbs (to a point). Eventually prices go too high, credit cards tap out and spending ceases. But, for a short time inflation makes GDP (as well as retail sales) look good.
Another factor that creates a bubble is the fact that government spending is actually included in the calculation of GDP. That’s right, every dollar of your tax money that the government wastes helps the establishment by propping up GDP numbers. This is why government spending increases will never stop – It’s too valuable for them to spend as a way to make the economy appear healthier than it is.
The REAL economy is eclipsing the fake economy
The bottom line is that Americans used to be able to ignore the warning signs because their bank accounts were not being directly affected. This is over. Now, every person in the country is dealing with a massive decline in buying power and higher prices across the board on everything – from food and fuel to housing and financial assets alike. Even the wealthy are seeing a compression to their profit and many are struggling to keep their businesses in the black.
The unfortunate truth is that the elections of 2024 will probably be the turning point at which the whole edifice comes tumbling down. Even if the public votes for change, the system is already broken and cannot be repaired without a complete overhaul.
We have consistently avoided taking our medicine and our disease has gotten worse and worse.
People have lost faith in the economy because they have not faced this kind of uncertainty since the 1930s. Even the stagflation crisis of the 1970s will likely pale in comparison to what is about to happen. On the bright side, at least a large number of Americans are aware of the threat, as opposed to the 1920s when the vast majority of people were utterly conned by the government, the banks and the media into thinking all was well. Knowing is the first step to preparing.
The second step is securing your own financial future – that’s where physical precious metals can play a role. Diversifying your savings with inflation-resistant, uninflatable assets whose intrinsic value doesn’t rely on a counterparty’s promise to pay adds resilience to your savings. That’s the main reason physical gold and silver have been the safe haven store-of-value assets of choice for centuries (among both the elite and the everyday citizen).
* * *
As the world moves away from dollars and toward Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), is your 401(k) or IRA really safe? A smart and conservative move is to diversify into a physical gold IRA. That way your savings will be in something solid and enduring. Get your FREE info kit on Gold IRAs from Birch Gold Group. No strings attached, just peace of mind. Click here to secure your future today.
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International13 hours ago
International13 hours agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges




































