New diagnoses of six major cancer types in the United States fell abruptly in early 2020, coinciding with the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to findings from part 2 of the latest Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer. The volume of pathology reports also declined sharply in early 2020, suggesting that fewer cancer screenings and other cancer-related procedures were performed during that time. Taken together, the findings suggest that many cancers were not being diagnosed in a timely manner during the early part of the COVID-19 pandemic, likely due to interruptions in medical care.
“These missed opportunities for early cancer detection are alarming, particularly for those vulnerable populations that continue to face significant barriers in accessing cancer care,” said Monica M. Bertagnolli, M.D., director of the National Cancer Institute (NCI). “This report highlights the urgency in helping all Americans get back on track with their cancer care so that we can avoid unnecessary deaths and complications from cancer. That’s exactly why expanding cancer screening access and awareness is a key priority of the Biden-Harris administration’s Cancer Moonshot.”
This study is the largest to date using population-based data from central cancer registries to assess the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer incidence (new diagnoses of cancer) in the United States. The report appeared September 27, 2023, in Cancer.
The Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer is a collaborative effort among NCI, part of the National Institutes of Health; the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); the American Cancer Society; and the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries to provide information about cancer occurrence and trends in the United States. Part 1 of the latest report, which focused on national cancer statistics, was released in October 2022.
Part 2 of the latest report focuses on changes in cancer diagnoses in the United States during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. The authors suggest that these changes were due in part to interruptions in medical care. In particular, early 2020 saw a decline in cancer screenings. In addition, diagnoses made as a result of early symptoms or in the course of routine medical visits may have been delayed when people held off on seeing their doctors.
The authors analyzed cancer incidence data for 2015 to 2020 using data from select population-based cancer registries that participate in CDC’s National Program of Cancer Registries or NCI’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program.
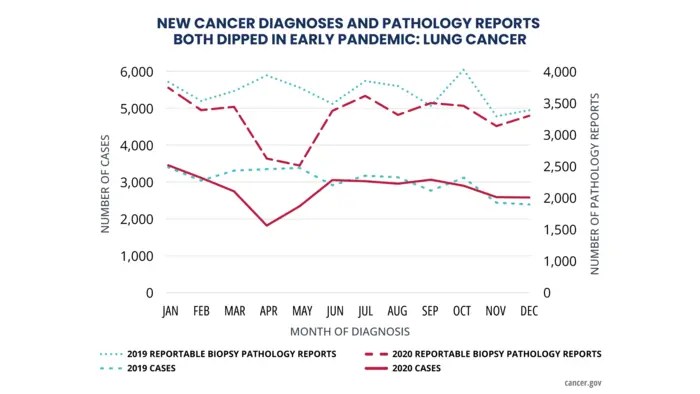
The authors compared the number of newly diagnosed cases of cancer in 2020 with what was expected based on previous years. They looked at female breast, lung, and colorectal cancers, which are often diagnosed through screening tests or other forms of early detection that may have been disrupted by the pandemic; thyroid and prostate cancers, which are often diagnosed incidentally; and pancreatic cancer, which is usually diagnosed when the patient presents with symptoms. The authors also compared the volume of electronic pathology reports sent to central cancer registries in 2020 with the volume sent in 2019.
From March to May 2020, new cases of all six cancer types fell sharply. By July 2020, however, diagnoses of all cancer types except prostate cancer had returned to pre-pandemic levels, with little difference between observed and expected numbers during the second half of the year.
Over the same period in early 2020, the volume of electronic pathology reports also declined steeply before returning to pre-pandemic levels. Because these reports are transmitted automatically to cancer registries, the findings suggest that the decline in new cancer diagnoses was not due to delays in reporting caused by pandemic disruptions but rather to missed screenings and delays in other cancer-related procedures.
The authors also looked at declines in new cancer cases by cancer stage at diagnosis, sex, age, and population group. For each cancer type in the study, new cases of early-stage cancers fell more sharply than new cases of advanced cancers. The declines were greatest for the cancers typically diagnosed through screening (female breast, lung, and colorectal cancer). For example, 7,147 cases of early-stage colorectal cancer were expected to be diagnosed in 2020, but only 5,983 cases were diagnosed—meaning that potentially more than 16% of early-stage colorectal cancer cases weren’t caught.
“We are deeply concerned about the implications of delayed diagnosis, which is typically associated with more aggressive disease and worse outcomes,” said Karen E. Knudsen, M.B.A., Ph.D., chief executive officer of the American Cancer Society. “It is imperative to ensure that we make up for lost ground on finding cancers early, and thereby maximize opportunities for effective treatment and survival.”
However, missed screenings only partly explain the observed declines in new cancer cases. Fewer in-person medical visits likely also contributed to the underdiagnoses, particularly for diseases such as thyroid cancer, which is often caught incidentally during other medical procedures.
Asian or Pacific Islander populations had greater declines in new cases of all cancer types, except for pancreatic cancer, compared with White, Black, and American Indian or Alaska Native populations. Another notable population group difference was a greater decline in prostate cancer diagnoses among White people than Black people.
The authors acknowledged that the data comprise information reported to a subset of cancer registries, which may not be representative of the entire U.S. population. Nor does it include in-depth analyses on cancer diagnoses in Hispanic populations, which will be incorporated at a later point.
Nevertheless, the findings suggest that there were missed opportunities for early cancer detection during the pandemic. Other studies have suggested that delays in cancer detection may lead to long-term consequences, such as shorter survival and greater number of deaths. The authors noted that efforts to get people back on track with screening should focus on removing barriers to preventive care visits and reducing disparities in early detection.
As part of the reignited Cancer Moonshot, the President and First Lady announced a call to action on cancer screening to jump-start progress on the nearly 10 million screenings in the United States that were missed as a result of the pandemic. To date, the Cancer Moonshot has accelerated innovations in cancer prevention, detection, and treatment and has expanded access to cancer screening across all 50 states, territories, and Tribal organizations, including through $200 million invested from CDC. The Biden-Harris administration continues to prioritize closing the screening gap so Americans can catch cancer early, when outcomes are best, and encourage Americans to get recommended screenings.
“We recommend everyone get back into routine health care, including cancer screening,” said Lisa C. Richardson, M.D., M.P.H., director of CDC’s Division of Cancer Prevention and Control. “It’s also important to make sure children, adolescents, and adults are up to date on vaccines to prevent infections with viruses—like hepatitis B virus and human papillomavirus—that can lead to cancer.”
Meanwhile, research is ongoing to gain additional insights into the impacts of the pandemic on cancer trends.
“This study is a reminder that a decline in cancer incidence may not always reflect progress in the fight against cancer,” said Betsy A. Kohler, M.P.H., North American Association of Central Cancer Registries executive director. “We are currently conducting more in-depth analysis of the full 2020 data to further understand the implications of the pandemic on cancer outcomes.”
For more about the report, see: https://seer.cancer.gov/report_to_nation/.
# # #
About the National Cancer Institute (NCI): NCI leads the National Cancer Program and NIH’s efforts to dramatically reduce the prevalence of cancer and improve the lives of cancer patients and their families, through research into prevention and cancer biology, the development of new interventions, and the training and mentoring of new researchers. For more information about cancer, please visit the NCI website at cancer.gov or call NCI’s contact center, the Cancer Information Service, at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit nih.gov.
About the American Cancer Society (ACS): The American Cancer Society is a leading cancer-fighting organization with a vision to end cancer as we know it, for everyone. For more than 100 years, we have been improving the lives of people with cancer and their families as the only organization combating cancer through advocacy, research, and patient support. We are committed to ensuring everyone has an opportunity to prevent, detect, treat, and survive cancer. To learn more, visit cancer.org or call our 24/7 helpline at 1-800-227-2345. Connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
About the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): CDC works 24/7 protecting America’s health, safety, and security. Whether diseases start at home or abroad, are curable or preventable, chronic or acute, or from human activity or deliberate attack, CDC responds to America’s most pressing health threats. CDC is headquartered in Atlanta and has experts located throughout the United States and the world.
About the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries (NAACCR): The North American Association of Central Cancer Registries, Inc., is a professional organization that develops and promotes uniform data standards for cancer registration; provides education and training; certifies population-based registries; aggregates and publishes data from central cancer registries; and promotes the use of cancer surveillance data and systems for cancer control and epidemiologic research, public health programs, and patient care to reduce the burden of cancer in North America. For more, see naaccr.org.
Journal
Cancer
DOI
10.1002/cncr.35026
Article Title
Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, Part 2: Early Assessment of the COVID-19 Pandemic’s Impact on Cancer Diagnosis
Article Publication Date
27-Sep-2023