Backbone nabs $14M for supply chain software inspired by mesh networks
Forecasting, also known as demand variability, has long been a hurdle for businesses reliant on the global supply chain. In a survey conducted long before…
Forecasting, also known as demand variability, has long been a hurdle for businesses reliant on the global supply chain. In a survey conducted long before the pandemic began (in 2015), large companies — those with revenues in the range of $500 to more than $1 billion — pegged variability as the top challenge that they faced. Predicting supply chain volatility has only grown more difficult as pandemic-related shocks, including elevated ecommerce volume, impact shipping and raw materials availability.
Vic Patil thinks the solution lies in a “mesh” — specifically what he calls a “supply mesh,” inspired by the way wireless mesh networks function. That’s the product Backbone, the startup Patil helped to cofound, is selling: a platform designed to enable companies to respond to supply chain disruptions by surfacing replacement options, including vendors.
Backbone today announced that it raised $14 million in seed funding from Nautilus Ventures, 12/12 Ventures, and individual investors to prove out its technology. The capital raised will be used to onboard new customers, expand into new markets, and develop the company’s supply mesh technology as it accelerates growth globally, Patil told TechCrunch via email.
“[We’re] looking to expand Backbone’s … group of certified vendors who can work together to ensure businesses always have reliable vendors,” Patil added. “As evidenced by the last two years of the pandemic, legacy systems aren’t very good at predicting or modeling volatility and are even worse at reacting to volatility — they overcorrect and lead to the jams we see in logistics, manufacturing and more … Backbone is a fully configurable supply chain platform that lets operators spot and address breakdowns in real time, using a mesh network approach that helps companies weather volatility and scale.”
Building a supply chain backbone
Patil cofounded Backbone, which is based in San Francisco, alongside Rajesh Chandran in 2017. Chandran is an Oracle and NetSuite veteran who’s launched several AI startups, while Patil spent time as a software engineer at Intuit before moving to Heighten, a sales tech company. Patil stayed on at Heighten after it was acquired by LinkedIn in 2017.
Patil and Chandran became investors in several supply chain-dependent brands prior to starting Backbone, which is when they realized even small hiccups, like shipping delays, could be expensive to recover from. The motivation behind Backbone was to provide greater visibility into their personal investments, but it dawned on Patil and Chandran that the product might be scalable to other industries.
“Backbone … spans the fundamentally decentralized supply chain and creates a ‘virtualized’ representation of it end-to-end … [to allow] better resilience to volatility by reducing reaction times to unexpected disruptions,” Patil said. “[U]sing its mesh model approach, [Backbone] helps companies embed resilience into their supply chain so that they’re better prepared to manage periods of volatility versus predict them. For instance, if a company received a bulk order that they don’t have enough supplies or ingredients necessary to fulfill, Backbone will quickly connect them with the appropriate suppliers so that they don’t lose out on the sale.”
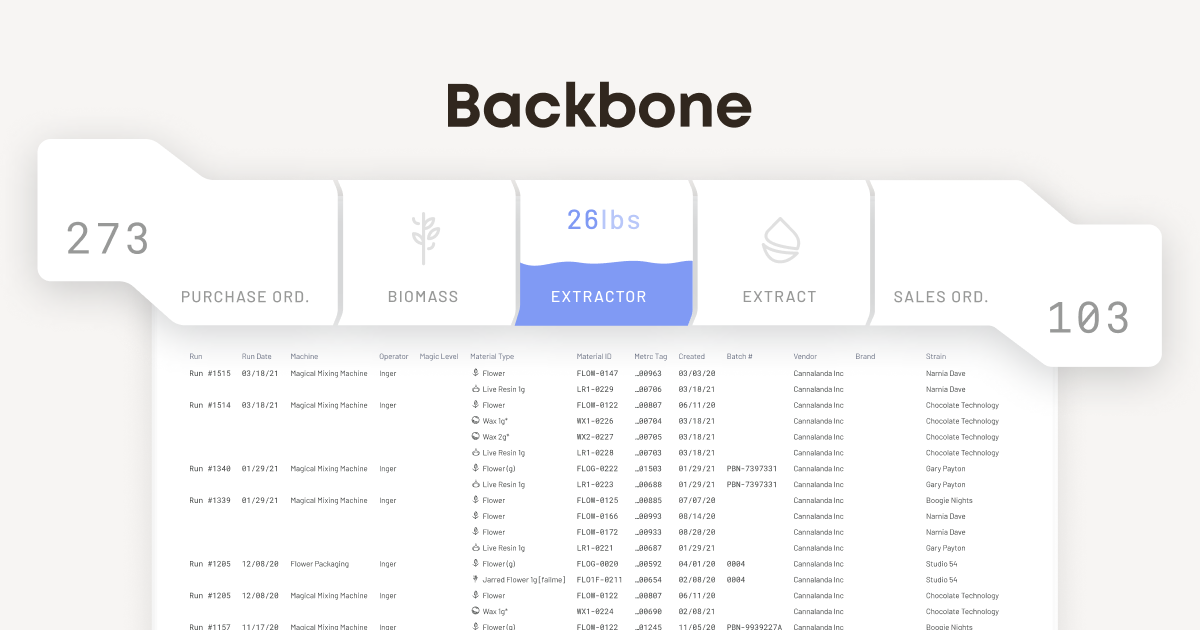
Backbone, which initially engaged with cannabis and hemp suppliers, tracks production compliance, yields, and audit reporting data in one place. The platform translates the components of a company’s supply chain to a browser-based, visual dashboard, where it tries to calculate the costs associated with items to predict how profitable they’ll be, accounting for supply chain variability.
Image Credits: Backbone
Patil emphasizes that Backbone can recommend possible solutions to route around supply chain issues, like material shortages and truck stoppages, as they’re happening. He sees this as the platform’s key differentiator, along with Backbone’s ability to customize for regulated industries like pharma and agriculture.
“The tech allows the data decision maker to act on potential supply chain breakdowns with confidence … That’s the big idea behind Backbone — a supply mesh, unlike a ‘chain,’ casts a much wider net for solutions,” Patil said. “Where traditionally if a single link in a chain breaks the whole operation is stalled until that one link is repaired, with Backbone, there is no need to wait for this repair as companies can ‘route’ around breakdown confidently … It’s essentially helping growing companies keep up with unforeseen demand so that they don’t have to scramble and miss out on significant growth opportunities that their current infrastructure might not yet support.”
Potential customers
While they might not boast about “mesh chain” technology, a number of companies compete with Backbone in the growing supply chain management software space. For example, there’s 7Bridges, which offers tools to digitize and optimize supply chains. Project44 is a behemoth rival, having recently raised $202 million in a recent funding round led by Goldman Sachs and others.
Backbone is looking to establish a foothold with agriculture, hemp, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals customers to begin with — it’s planning to facilitate cannabis transactions between the U.S. and U.K. — before expanding out from there. Patil claims that the 65-person company has over 100 customers and is on track to triple revenue for the second time in two years.
“The pandemic underlined the importance of the Backbone technology, and highlights the expected continued growth as supply chain issues continue due to [health crises], unexpected war, climate change, and more,” Patil said. “The supply chain software industry is full of legacy products that rely on traditional technology. Backbone is changing the game with new tech that includes solutions to new problems and puts companies back in control of their supply chains.”
link pandemicGovernment
Low Iron Levels In Blood Could Trigger Long COVID: Study
Low Iron Levels In Blood Could Trigger Long COVID: Study
Authored by Amie Dahnke via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
People with inadequate…

Authored by Amie Dahnke via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
People with inadequate iron levels in their blood due to a COVID-19 infection could be at greater risk of long COVID.
A new study indicates that problems with iron levels in the bloodstream likely trigger chronic inflammation and other conditions associated with the post-COVID phenomenon. The findings, published on March 1 in Nature Immunology, could offer new ways to treat or prevent the condition.
Long COVID Patients Have Low Iron Levels
Researchers at the University of Cambridge pinpointed low iron as a potential link to long-COVID symptoms thanks to a study they initiated shortly after the start of the pandemic. They recruited people who tested positive for the virus to provide blood samples for analysis over a year, which allowed the researchers to look for post-infection changes in the blood. The researchers looked at 214 samples and found that 45 percent of patients reported symptoms of long COVID that lasted between three and 10 months.
In analyzing the blood samples, the research team noticed that people experiencing long COVID had low iron levels, contributing to anemia and low red blood cell production, just two weeks after they were diagnosed with COVID-19. This was true for patients regardless of age, sex, or the initial severity of their infection.
According to one of the study co-authors, the removal of iron from the bloodstream is a natural process and defense mechanism of the body.
But it can jeopardize a person’s recovery.
“When the body has an infection, it responds by removing iron from the bloodstream. This protects us from potentially lethal bacteria that capture the iron in the bloodstream and grow rapidly. It’s an evolutionary response that redistributes iron in the body, and the blood plasma becomes an iron desert,” University of Oxford professor Hal Drakesmith said in a press release. “However, if this goes on for a long time, there is less iron for red blood cells, so oxygen is transported less efficiently affecting metabolism and energy production, and for white blood cells, which need iron to work properly. The protective mechanism ends up becoming a problem.”
The research team believes that consistently low iron levels could explain why individuals with long COVID continue to experience fatigue and difficulty exercising. As such, the researchers suggested iron supplementation to help regulate and prevent the often debilitating symptoms associated with long COVID.
“It isn’t necessarily the case that individuals don’t have enough iron in their body, it’s just that it’s trapped in the wrong place,” Aimee Hanson, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Cambridge who worked on the study, said in the press release. “What we need is a way to remobilize the iron and pull it back into the bloodstream, where it becomes more useful to the red blood cells.”
The research team pointed out that iron supplementation isn’t always straightforward. Achieving the right level of iron varies from person to person. Too much iron can cause stomach issues, ranging from constipation, nausea, and abdominal pain to gastritis and gastric lesions.
1 in 5 Still Affected by Long COVID
COVID-19 has affected nearly 40 percent of Americans, with one in five of those still suffering from symptoms of long COVID, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Long COVID is marked by health issues that continue at least four weeks after an individual was initially diagnosed with COVID-19. Symptoms can last for days, weeks, months, or years and may include fatigue, cough or chest pain, headache, brain fog, depression or anxiety, digestive issues, and joint or muscle pain.
Uncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemploymentSpread & Containment
Another beloved brewery files Chapter 11 bankruptcy
The beer industry has been devastated by covid, changing tastes, and maybe fallout from the Bud Light scandal.

Before the covid pandemic, craft beer was having a moment. Most cities had multiple breweries and taprooms with some having so many that people put together the brewery version of a pub crawl.
It was a period where beer snobbery ruled the day and it was not uncommon to hear bar patrons discuss the makeup of the beer the beer they were drinking. This boom period always seemed destined for failure, or at least a retraction as many markets seemed to have more craft breweries than they could support.
Related: Fast-food chain closes more stores after Chapter 11 bankruptcy
The pandemic, however, hastened that downfall. Many of these local and regional craft breweries counted on in-person sales to drive their business.
And while many had local and regional distribution, selling through a third party comes with much lower margins. Direct sales drove their business and the pandemic forced many breweries to shut down their taprooms during the period where social distancing rules were in effect.
During those months the breweries still had rent and employees to pay while little money was coming in. That led to a number of popular beermakers including San Francisco's nationally-known Anchor Brewing as well as many regional favorites including Chicago’s Metropolitan Brewing, New Jersey’s Flying Fish, Denver’s Joyride Brewing, Tampa’s Zydeco Brew Werks, and Cleveland’s Terrestrial Brewing filing bankruptcy.
Some of these brands hope to survive, but others, including Anchor Brewing, fell into Chapter 7 liquidation. Now, another domino has fallen as a popular regional brewery has filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection.
Image source: Shutterstock
Covid is not the only reason for brewery bankruptcies
While covid deserves some of the blame for brewery failures, it's not the only reason why so many have filed for bankruptcy protection. Overall beer sales have fallen driven by younger people embracing non-alcoholic cocktails, and the rise in popularity of non-beer alcoholic offerings,
Beer sales have fallen to their lowest levels since 1999 and some industry analysts
"Sales declined by more than 5% in the first nine months of the year, dragged down not only by the backlash and boycotts against Anheuser-Busch-owned Bud Light but the changing habits of younger drinkers," according to data from Beer Marketer’s Insights published by the New York Post.
Bud Light parent Anheuser Busch InBev (BUD) faced massive boycotts after it partnered with transgender social media influencer Dylan Mulvaney. It was a very small partnership but it led to a right-wing backlash spurred on by Kid Rock, who posted a video on social media where he chastised the company before shooting up cases of Bud Light with an automatic weapon.
Another brewery files Chapter 11 bankruptcy
Gizmo Brew Works, which does business under the name Roth Brewing Company LLC, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection on March 8. In its filing, the company checked the box that indicates that its debts are less than $7.5 million and it chooses to proceed under Subchapter V of Chapter 11.
"Both small business and subchapter V cases are treated differently than a traditional chapter 11 case primarily due to accelerated deadlines and the speed with which the plan is confirmed," USCourts.gov explained.
Roth Brewing/Gizmo Brew Works shared that it has 50-99 creditors and assets $100,000 and $500,000. The filing noted that the company does expect to have funds available for unsecured creditors.
The popular brewery operates three taprooms and sells its beer to go at those locations.
"Join us at Gizmo Brew Works Craft Brewery and Taprooms located in Raleigh, Durham, and Chapel Hill, North Carolina. Find us for entertainment, live music, food trucks, beer specials, and most importantly, great-tasting craft beer by Gizmo Brew Works," the company shared on its website.
The company estimates that it has between $1 and $10 million in liabilities (a broad range as the bankruptcy form does not provide a space to be more specific).
Gizmo Brew Works/Roth Brewing did not share a reorganization or funding plan in its bankruptcy filing. An email request for comment sent through the company's contact page was not immediately returned.
bankruptcy pandemic social distancing
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges



















