The US economy is reliant on consumer spending – can it survive a pandemic?
The US economy is reliant on consumer spending – can it survive a pandemic?


The COVID-19 pandemic has radically affected the American economy, reducing spending by American households on materials goods, air travel, leisure activities as well as the use of automobiles. As a result, greenhouse gas emissions have temporarily fallen dramatically.
While this may be a positive for the environment, the social price is high: Since the U.S. economy depends heavily on consumer spending, the country is experiencing the highest unemployment rate since the Great Depression, the threat of homelessness for tens of thousands of people and a failure of businesses large and small. How did the U.S. arrive at the point whereby mass consumption – and the greenhouse gas emissions associated with it – is necessary for economic and social well-being? Are greenhouse gas reductions and a thriving economy incompatible?
A consumer society is a 20th-century construct. The American Dream has become synonymous with buying material goods such as cars, houses, furniture or electronics, distorting its original meaning. Today, the spending habits of American households make up 70% of the U.S. gross domestic product, a measurement that describes the size of the economy. U.S. companies spend about US$230 billion on advertising each year, half of all the money spent on advertising globally.
Buy your dreams
Today’s consumer society emerged after the end of World War I, fueled by the emergence of the modern advertising industry and facilitated by widespread adoption of consumer credit. Edward Bernays, the nephew of Sigmund Freud, is generally credited with inventing the field of marketing during the 1920s. The essence of his approach was to tap into people’s desires to feel good, powerful and sexy instead of emphasizing the usefulness of a product. Bernays created the term “engineering of consent” and popularized the term “consumer” when referring to American people.
Mass consumption grew steadily until the onset of the Great Depression. But the deliberate creation of the present consumer society took off in earnest during the 1940s and 1950s. When WWII ended, so did wartime industrial production. Industry leaders shifted their enormous production capabilities from the military to the civilian sector.

At the same time, President Harry Truman was concerned with looming unemployment among returning veterans and saw mass production of consumer goods as the solution. The 1944 GI Bill helped returning veterans purchase houses with down payments and government-guaranteed loans. Mortgage interest deductions and government-financed infrastructure – local utilities and roads, a national highway system – made suburban homeownership a logical financial plan for families, while Social Security provided relief from having to save for old age.
Labor unions, too, were vested in increasing wages for their members, so working families could afford houses, cars and household appliances. At this particular historical juncture, business, government and labor came together, united in their shared goal to increase household consumption as the bedrock of economic prosperity and social harmony.
These developments took place in the context of the post-war euphoria over the uncontested power of the U.S., the post-Depression hunger for a better life, advances in cheap mass production and a demographic boom. Consumerism became a symbol of the superiority of the capitalist system over Soviet-style communism, as illustrated by the famous “Kitchen Debate” in 1959 at the American National Exhibition in Moscow. Standing among the sleek labor-saving appliances of a modern American kitchen, Vice President Richard Nixon demonstrated to Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev the higher quality of life of working people in the U.S.
The great transformation
The results of this business-government-labor alliance were astonishing. National output of goods and services doubled between 1946 and 1956, and doubled again by 1970. Mass-produced cheap and comfortable single-family homes, increasingly distant from city centers, became affordable. The iconic 1949 Levittown on Long Island, New York, was a model of the suburbs: uniform, convenient, segregated by race and dependent on the automobile. By 1960, 62% of Americans owned their homes, in contrast to 44% in 1940. Suburban shopping malls, uniform and racially segregated, became by default public gathering spaces, replacing city streets, cafes and places of commerce.
[Get the best of The Conversation, every weekend. Sign up for our weekly newsletter.]
This social transformation occurred in a span of a single generation. Consumerism and a suburban lifestyle became the organizing principles of society and synonymous with fundamental values such as family well-being, safety, democratic political freedom and the American Dream.

Basics get bigger
Since the 1950s, this version of a good life – shaped by advertising of what was necessary to live well – has been remarkably stable. But there is a twist: The notion of what represents basic comfort has been steadily moving toward larger and more – SUVs and myriad conveniences and technologies, bigger and more dispersed houses filled with furniture and stuff and additional bathrooms and bedrooms, larger kitchens, media and exercise rooms and outdoor living rooms.
Today, the best predictor of household carbon footprint is income. This correlation holds true in different countries, regardless of political views, education or environmental attitudes.
Rethinking consumption
Consumption comes at a high ecological cost. As the gross national product grows – driven largely by household consumption – so do greenhouse gas emissions. Many scientists and policy analysts believe that as technology increases energy efficiency and replaces fossil fuels with renewable energy sources, greenhouse gas emissions will be significantly reduced. But despite the rapid advances in these technologies, there is no evidence that trends in greenhouse gas emissions are separate and independent from economic growth trends. Neither is there a basis for the idea that green growth will prevent the anticipated climate catastrophe that the world is facing.
At the same time, there is little evidence that Americans have become happier in the last seven decades of growing consumerism.

This pandemic reveals to me the vulnerability of an economy heavily dependent on a single source of economic activity – consumption. From my perspective, the U.S. would be better off if the economy – our collective wealth – were more heavily weighted toward public spending on, and investment in, education, health care, public transit, housing, parks and better infrastructure, and renewable energy. Such an economy would contribute to human well-being, emit less greenhouse gas and be less vulnerable to sudden disruptions in consumer spending.
As I see it, it is time for an honest public conversation about the carbon footprint of our “basic” lifestyles and what Americans need rather than what they are told they need.
Halina Szejnwald Brown does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Uncategorized
Key shipping company files for Chapter 11 bankruptcy
The Illinois-based general freight trucking company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy to reorganize.

The U.S. trucking industry has had a difficult beginning of the year for 2024 with several logistics companies filing for bankruptcy to seek either a Chapter 7 liquidation or Chapter 11 reorganization.
The Covid-19 pandemic caused a lot of supply chain issues for logistics companies and also created a shortage of truck drivers as many left the business for other occupations. Shipping companies, in the meantime, have had extreme difficulty recruiting new drivers for thousands of unfilled jobs.
Related: Tesla rival’s filing reveals Chapter 11 bankruptcy is possible
Freight forwarder company Boateng Logistics joined a growing list of shipping companies that permanently shuttered their businesses as the firm on Feb. 22 filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy with plans to liquidate.
The Carlsbad, Calif., logistics company filed its petition in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of California listing assets up to $50,000 and and $1 million to $10 million in liabilities. Court papers said it owed millions of dollars in liabilities to trucking, logistics and factoring companies. The company filed bankruptcy before any creditors could take legal action.
Lawsuits force companies to liquidate in bankruptcy
Lawsuits, however, can force companies to file bankruptcy, which was the case for J.J. & Sons Logistics of Clint, Texas, which on Jan. 22 filed for Chapter 7 liquidation in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Western District of Texas. The company filed bankruptcy four days before the scheduled start of a trial for a wrongful death lawsuit filed by the family of a former company truck driver who had died from drowning in 2016.
California-based logistics company Wise Choice Trans Corp. shut down operations and filed for Chapter 7 liquidation on Jan. 4 in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Northern District of California, listing $1 million to $10 million in assets and liabilities.
The Hayward, Calif., third-party logistics company, founded in 2009, provided final mile, less-than-truckload and full truckload services, as well as warehouse and fulfillment services in the San Francisco Bay Area.
The Chapter 7 filing also implemented an automatic stay against all legal proceedings, as the company listed its involvement in four legal actions that were ongoing or concluded. Court papers reportedly did not list amounts for damages.
In some cases, debtors don't have to take a drastic action, such as a liquidation, and can instead file a Chapter 11 reorganization.
Shutterstock
Nationwide Cargo seeks to reorganize its business
Nationwide Cargo Inc., a general freight trucking company that also hauls fresh produce and meat, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Northern District of Illinois with plans to reorganize its business.
The East Dundee, Ill., shipping company listed $1 million to $10 million in assets and $10 million to $50 million in liabilities in its petition and said funds will not be available to pay unsecured creditors. The company operates with 183 trucks and 171 drivers, FreightWaves reported.
Nationwide Cargo's three largest secured creditors in the petition were Equify Financial LLC (owed about $3.5 million,) Commercial Credit Group (owed about $1.8 million) and Continental Bank NA (owed about $676,000.)
The shipping company reported gross revenue of about $34 million in 2022 and about $40 million in 2023. From Jan. 1 until its petition date, the company generated $9.3 million in gross revenue.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
bankruptcy pandemic covid-19 stocksUncategorized
Key shipping company files Chapter 11 bankruptcy
The Illinois-based general freight trucking company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy to reorganize.

The U.S. trucking industry has had a difficult beginning of the year for 2024 with several logistics companies filing for bankruptcy to seek either a Chapter 7 liquidation or Chapter 11 reorganization.
The Covid-19 pandemic caused a lot of supply chain issues for logistics companies and also created a shortage of truck drivers as many left the business for other occupations. Shipping companies, in the meantime, have had extreme difficulty recruiting new drivers for thousands of unfilled jobs.
Related: Tesla rival’s filing reveals Chapter 11 bankruptcy is possible
Freight forwarder company Boateng Logistics joined a growing list of shipping companies that permanently shuttered their businesses as the firm on Feb. 22 filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy with plans to liquidate.
The Carlsbad, Calif., logistics company filed its petition in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of California listing assets up to $50,000 and and $1 million to $10 million in liabilities. Court papers said it owed millions of dollars in liabilities to trucking, logistics and factoring companies. The company filed bankruptcy before any creditors could take legal action.
Lawsuits force companies to liquidate in bankruptcy
Lawsuits, however, can force companies to file bankruptcy, which was the case for J.J. & Sons Logistics of Clint, Texas, which on Jan. 22 filed for Chapter 7 liquidation in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Western District of Texas. The company filed bankruptcy four days before the scheduled start of a trial for a wrongful death lawsuit filed by the family of a former company truck driver who had died from drowning in 2016.
California-based logistics company Wise Choice Trans Corp. shut down operations and filed for Chapter 7 liquidation on Jan. 4 in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Northern District of California, listing $1 million to $10 million in assets and liabilities.
The Hayward, Calif., third-party logistics company, founded in 2009, provided final mile, less-than-truckload and full truckload services, as well as warehouse and fulfillment services in the San Francisco Bay Area.
The Chapter 7 filing also implemented an automatic stay against all legal proceedings, as the company listed its involvement in four legal actions that were ongoing or concluded. Court papers reportedly did not list amounts for damages.
In some cases, debtors don't have to take a drastic action, such as a liquidation, and can instead file a Chapter 11 reorganization.
Shutterstock
Nationwide Cargo seeks to reorganize its business
Nationwide Cargo Inc., a general freight trucking company that also hauls fresh produce and meat, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Northern District of Illinois with plans to reorganize its business.
The East Dundee, Ill., shipping company listed $1 million to $10 million in assets and $10 million to $50 million in liabilities in its petition and said funds will not be available to pay unsecured creditors. The company operates with 183 trucks and 171 drivers, FreightWaves reported.
Nationwide Cargo's three largest secured creditors in the petition were Equify Financial LLC (owed about $3.5 million,) Commercial Credit Group (owed about $1.8 million) and Continental Bank NA (owed about $676,000.)
The shipping company reported gross revenue of about $34 million in 2022 and about $40 million in 2023. From Jan. 1 until its petition date, the company generated $9.3 million in gross revenue.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
bankruptcy pandemic covid-19 stocksUncategorized
Tight inventory and frustrated buyers challenge agents in Virginia
With inventory a little more than half of what it was pre-pandemic, agents are struggling to find homes for clients in Virginia.
No matter where you are in the state, real estate agents in Virginia are facing low inventory conditions that are creating frustrating scenarios for their buyers.
“I think people are getting used to the interest rates where they are now, but there is just a huge lack of inventory,” said Chelsea Newcomb, a RE/MAX Realty Specialists agent based in Charlottesville. “I have buyers that are looking, but to find a house that you love enough to pay a high price for — and to be at over a 6.5% interest rate — it’s just a little bit harder to find something.”
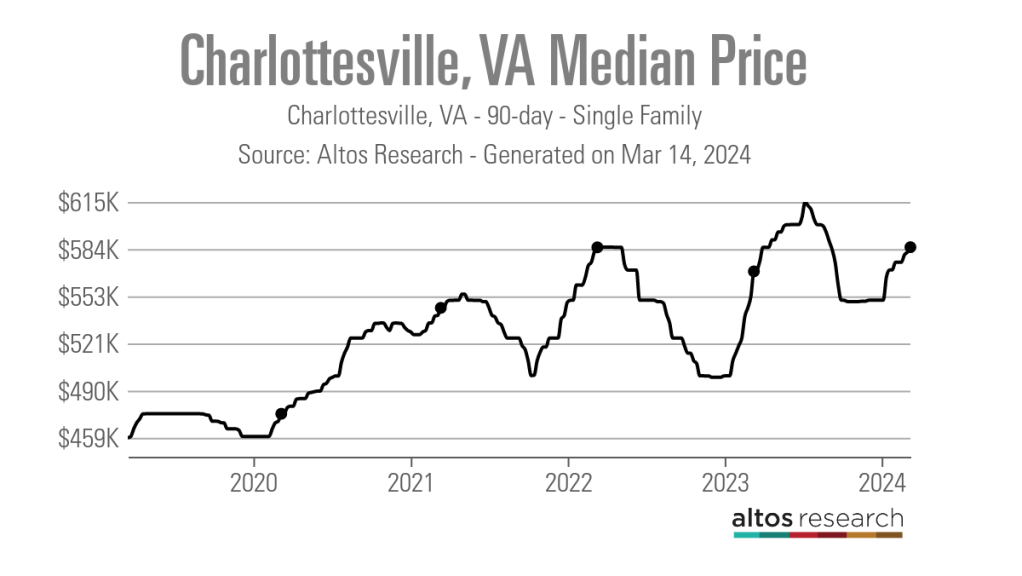
Newcomb said that interest rates and higher prices, which have risen by more than $100,000 since March 2020, according to data from Altos Research, have caused her clients to be pickier when selecting a home.
“When rates and prices were lower, people were more willing to compromise,” Newcomb said.
Out in Wise, Virginia, near the westernmost tip of the state, RE/MAX Cavaliers agent Brett Tiller and his clients are also struggling to find suitable properties.
“The thing that really stands out, especially compared to two years ago, is the lack of quality listings,” Tiller said. “The slightly more upscale single-family listings for move-up buyers with children looking for their forever home just aren’t coming on the market right now, and demand is still very high.”
Statewide, Virginia had a 90-day average of 8,068 active single-family listings as of March 8, 2024, down from 14,471 single-family listings in early March 2020 at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to Altos Research. That represents a decrease of 44%.

In Newcomb’s base metro area of Charlottesville, there were an average of only 277 active single-family listings during the same recent 90-day period, compared to 892 at the onset of the pandemic. In Wise County, there were only 56 listings.
Due to the demand from move-up buyers in Tiller’s area, the average days on market for homes with a median price of roughly $190,000 was just 17 days as of early March 2024.
“For the right home, which is rare to find right now, we are still seeing multiple offers,” Tiller said. “The demand is the same right now as it was during the heart of the pandemic.”
According to Tiller, the tight inventory has caused homebuyers to spend up to six months searching for their new property, roughly double the time it took prior to the pandemic.
For Matt Salway in the Virginia Beach metro area, the tight inventory conditions are creating a rather hot market.
“Depending on where you are in the area, your listing could have 15 offers in two days,” the agent for Iron Valley Real Estate Hampton Roads | Virginia Beach said. “It has been crazy competition for most of Virginia Beach, and Norfolk is pretty hot too, especially for anything under $400,000.”
According to Altos Research, the Virginia Beach-Norfolk-Newport News housing market had a seven-day average Market Action Index score of 52.44 as of March 14, making it the seventh hottest housing market in the country. Altos considers any Market Action Index score above 30 to be indicative of a seller’s market.

Further up the coastline on the vacation destination of Chincoteague Island, Long & Foster agent Meghan O. Clarkson is also seeing a decent amount of competition despite higher prices and interest rates.
“People are taking their time to actually come see things now instead of buying site unseen, and occasionally we see some seller concessions, but the traffic and the demand is still there; you might just work a little longer with people because we don’t have anything for sale,” Clarkson said.
“I’m busy and constantly have appointments, but the underlying frenzy from the height of the pandemic has gone away, but I think it is because we have just gotten used to it.”
While much of the demand that Clarkson’s market faces is for vacation homes and from retirees looking for a scenic spot to retire, a large portion of the demand in Salway’s market comes from military personnel and civilians working under government contracts.
“We have over a dozen military bases here, plus a bunch of shipyards, so the closer you get to all of those bases, the easier it is to sell a home and the faster the sale happens,” Salway said.
Due to this, Salway said that existing-home inventory typically does not come on the market unless an employment contract ends or the owner is reassigned to a different base, which is currently contributing to the tight inventory situation in his market.
Things are a bit different for Tiller and Newcomb, who are seeing a decent number of buyers from other, more expensive parts of the state.
“One of the crazy things about Louisa and Goochland, which are kind of like suburbs on the western side of Richmond, is that they are growing like crazy,” Newcomb said. “A lot of people are coming in from Northern Virginia because they can work remotely now.”
With a Market Action Index score of 50, it is easy to see why people are leaving the Washington-Arlington-Alexandria market for the Charlottesville market, which has an index score of 41.
In addition, the 90-day average median list price in Charlottesville is $585,000 compared to $729,900 in the D.C. area, which Newcomb said is also luring many Virginia homebuyers to move further south.

“They are very accustomed to higher prices, so they are super impressed with the prices we offer here in the central Virginia area,” Newcomb said.
For local buyers, Newcomb said this means they are frequently being outbid or outpriced.
“A couple who is local to the area and has been here their whole life, they are just now starting to get their mind wrapped around the fact that you can’t get a house for $200,000 anymore,” Newcomb said.
As the year heads closer to spring, triggering the start of the prime homebuying season, agents in Virginia feel optimistic about the market.
“We are seeing seasonal trends like we did up through 2019,” Clarkson said. “The market kind of soft launched around President’s Day and it is still building, but I expect it to pick right back up and be in full swing by Easter like it always used to.”
But while they are confident in demand, questions still remain about whether there will be enough inventory to support even more homebuyers entering the market.
“I have a lot of buyers starting to come off the sidelines, but in my office, I also have a lot of people who are going to list their house in the next two to three weeks now that the weather is starting to break,” Newcomb said. “I think we are going to have a good spring and summer.”
real estate housing market pandemic covid-19 interest rates-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges





















