International
The Extent and Implications of the China Slowdown
According to official data published by the National Bureau of Statistics, China’s growth q/q seasonally adjusted slowed considerably in Q3, to 0.2% (not annualized), below the Bloomberg consensus of 0.5%. The four quarter growth rate was 4.9%, vs consens
According to official data published by the National Bureau of Statistics, China’s growth q/q seasonally adjusted slowed considerably in Q3, to 0.2% (not annualized), below the Bloomberg consensus of 0.5%. The four quarter growth rate was 4.9%, vs consensus of 5.2%.
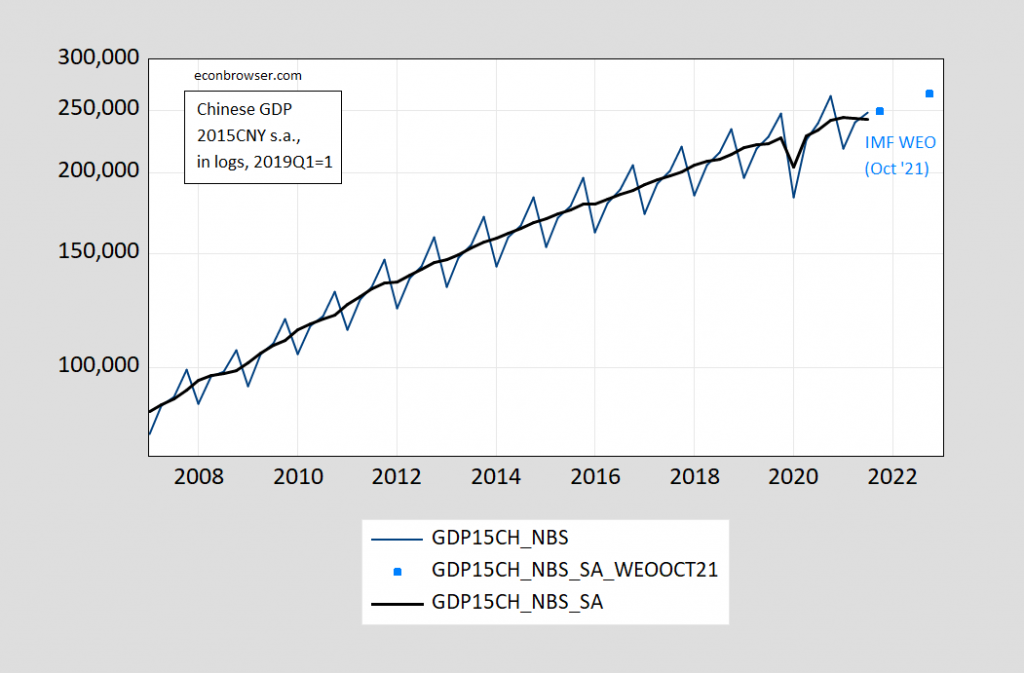
Figure 1 depicts real GDP over the period NBS reports it:
Figure 1: Chinese real GDP, in 100 mn 2015 CNY (blue), seasonally adjusted using Census X-12/X-11 seasonal filter (black), and IMF WEO forecasts applied to seasonally adjusted series (sky blue squares), on log scale. GDP in constant 2015CNY calculated by author by using IMF WEO GDP price deflator to convert implicit deflators to a common base year. Source: China National Bureau of Statistics, IMF October 2021 WEO, and author’s calculations.
Using the seasonally adjusted, and applying the IMF’s forecasts to these seasonally adjusted numbers, it’s clear how much the Q3 figure was a miss given expectations.
In my mind, it’s a bit mysterious how the NBS q/q growth numbers were obtained. On the NBS website, seasonally unadjusted nominal GDP numbers are reported, as are seasonally unadjusted real numbers in different constant yuan, and seasonally adjusted q/q real growth rates (from 2011 onward). That means it is not straightforward to replicate the implied Chinese seasonally adjusted GDP level, since they use an in-house seasonal adjustment methodology (NBS-SA, see here). I apply several seasonal adjustment procedures, including a geometric ratio to a moving average, Census X-12/seasonal filter X-11, and ARIMA Census X-12/seasonal filter X-11, and compare against the implied GDP series obtained by cumulating NBS reported q/q changes.
Figure 2: Chinese real GDP estimated using Census X-12/seasonal X-11 (black), ARIMA Census X-12/seasonal X-11 (sky blue), ratio to moving average (green), and implied by NBS reported q/q growth rates (red), all in logs, normalized to 2019Q1. Source: NBS, and author’s calculations.
Notice that the official series indicates continued growth albeit slow, while two of three standard seasonal adjustment procedures show negative growth. This can be seen in the graph of growth rates (calculated as log-differences):
Figure 3: Quarter-on-quarter growth rates of Chinese real GDP estimated using Census X-12/seasonal X-11 (black), ARIMA Census X-12/seasonal X-11 (sky blue), ratio to moving average (green), and NBS reported q/q growth rates (red), all calculated as log-differences. Source: NBS, and author’s calculations.
Over the last two quarters, cumulative growth estimated using X-12 adjusted GDP has lagged NBS reported growth, raising the question whether the numbers have been massaged. Some people would respond that it’s a foregone conclusion that they were. However, as noted in this post, Chinese measures of economic activity are not obviously over- or understating actual activity, particularly in recent years. Fernald, Hsu and Spiegel (2020) [working paper version] construct a “China Cyclical Activity Tracker” (C-CAT) [see letter], and conclude:
We choose a preferred index of eight non-GDP indicators based on their fit to Chinese imports, which we call the China Cyclical Activity Tracker (or C-CAT). We find that Chinese statistics have broadly become more reliable in measuring cyclical fluctuations over time. However, measured GDP has been excessively smooth since 2013, and adds little information relative to combinations of other indicators.
The authors have done a preliminary check on the 2021Q3 GDP, using a new, unpublished quarterly version of their C-CAT (the original published version is on a 4 quarter basis). They note that using Haver data — which does not match NBS data –, reported GDP is 31 basis points (bps) below trend in standard deviation units, while their preliminary reading indicates 119 bps below trend for a preliminary reading of q-on-q estimates of the China CAT and 170 bps below trend for q-on-q estimates of a quarterly version of their “All indicators” index (both without consumer expectations, which have yet to come in for the quarter). Those preliminary results confirm the reported results in showing a slowdown for Q3, but look even a little weaker than even what non-NBS GDP series report. (Thanks to Fernald and Spiegel for their results).
(Haver’s series indicates -2.26% q/q growth SAAR, well below NBS’s -0.8%, and closer to my X-12 series (black line) above, -2.3%).
Journalistic accounts (e.g., NYT) have attributed the Q3 slowdown to the financial fallout from the Evergrande default as well as more general real estate troubles, slowed auto production due to chip shortages, and power outages/shortages.
The deceleration is important for the obvious reason that Chinese GDP now (2021) accounts for a larger share of world GDP than it did back in 2008: 17.8% vs. 7.2%; the 2021 share for the US is 24.2% (all shares calculated using GDP in US dollars at market exchange rates as reported in the IMF’s WEO database).
What’s the spillover effect? Ahmed et al. (2019) examine implications of a China slowdown (discussed in this post).
…the VAR estimates also suggest that the hit to economic activity in different countries and regions would generally be significant (consistent with China’s strong trade links with other economies). More specifically, the output hit to EME commodity exporters would be about ¾ as large as the hit to China itself; to other EMEs would be about half; to advanced economies excluding the United States slightly more than a third; and only a relatively modest hit to the United States. The smaller U.S. effect reflects the U.S. economy being more closed, limited direct U.S. financial linkages to China, and greater capacity at the moment (than other advanced economies, say) to ease monetary policy to cushion the blow.
The impact of a 4% shock (blue), estimated using a SVAR, is shown below:

Source: Ahmed et al. (2019).
Of course, the relationships that obtained pre-pandemic are unlikely to hold fully in the current environment, but the implications are straightforward. The impact also depends on the persistence of the shock; the more long-lived the measures implemented by the Xi regime, the less likely the resumption of rapid growth (at least in the short term). In a recent op-ed, Arthur Kroeber lays out the macro challenges facing China in the context of Xi’s objectives, and hence the motivation for these regulatory measures.
default pandemic monetary policy real estate yuan gdp china
Government
CCP-Linked Virologist Fired After Transferring Ebola From Winnipeg To Wuhan Resurfaces In China – And Is Collaborating With Military Scientists
CCP-Linked Virologist Fired After Transferring Ebola From Winnipeg To Wuhan Resurfaces In China – And Is Collaborating With Military Scientists
…

A virologist who had a "clandestine relationship" with Chinese agents and was subsequently fired by the Trudeau government has popped back up in China - where she's conducting research with Chinese military scientists and other virology researchers, including at the Wuhan Institute of Virology, where she's allegedly studying antibodies for coronavirus, as well as the deadly Ebola and Niaph viruses, the Globe and Mail reports.
Xiangguo Qiu and her husband Keding Cheng were fired from the National Microbiology Laboratory in Winnipeg, Canada and stripped of their security clearances in July of 2019.
Declassified documents tabled in the House of Commons on Feb. 28 show the couple had provided confidential scientific information to China and posed a credible security threat to the country, according to the Canadian Security Intelligence Service.
The Globe found that Dr. Qiu’s name appears on four Chinese patent filings since 2020, two with the Wuhan Institute of Virology – whose work on bat coronaviruses has placed it at the centre of concerns that it played a role in the spread of COVID-19 – and two with the University of Science and Technology of China, or USTC. The patents relate to antibodies against Nipah virus and work related to nanobodies, including against coronaviruses. -Globe and Mail
Canadian authorities began questioning the pair's loyalty, as well as the potential for coercion or exploitation by a foreign entity, according to more than 600 pages of documents reported by The Counter Signal.
Highlights (via CTVNews.ca):
- Qiu and Cheng were escorted out of Winnipeg's National Microbiology Laboratory in July 2019 and subsequently fired in January 2021.
- The pair transferred deadly Ebola and Henipah viruses to China's Wuhan Institute of Virology in March 2019.
- The Canadian Security Intelligence Service assessed that Qiu repeatedly lied about the extent of her work with institutions of the Chinese government and refused to admit involvement in various Chinese programs, even when evidence was presented to her.
- [D]espite being given every opportunity in her interviews to describe her association with Chinese entities, "Ms. Qiu continued to make blanket denials, feign ignorance or tell outright lies."
- A November 2020 Public Health Agency of Canada report on Qiu says investigators "weighed the adverse information and are in agreement with the CSIS assessment."
- A Public Health Agency report on Cheng's activities says he allowed restricted visitors to work in laboratories unescorted and on at least two occasions did not prevent the unauthorized removal of laboratory materials.
- Cheng was not forthcoming about his activities and collaborations with people from government agencies "of another country, namely members of the People's Republic of China."
Following their firings, Qiu returned to China despite it being under a pandemic travel lockdown until January, 2023.
"It’s very likely that she received quite preferential treatment in China on the basis that she’s proven herself. She’s done a very good job for the government of China," said Brendan Walker-Munro, senior research fellow at Australia’s University of Queensland Law School. "She’s promoted their interests abroad. She’s returned information that is credibly useful to China and to its ongoing research."
More via the Globe and Mail;
Documents reviewed by The Globe show that Dr. Qiu is most closely aligned with the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) in Hefei. In March, 2023, a document posted by a Chinese pharmaceutical company listed Dr. Qiu as second amongst “major completion personnel” on a project awarded by the Chinese Preventive Medicine Association for study related to an anti-Ebola virus therapeutic antibody. Most of the other completion personnel were associated with the Chinese People’s Liberation Army.
USTC was founded by the Chinese Academy of Sciences and initially established to build up Chinese scientific expertise useful to the military, which at the time was pursuing technology to build satellites, intercontinental ballistic missiles and atomic bombs. The university has continued to maintain close military ties.
The document says Dr. Qiu works for USTC. Jin Tengchuan, the principal investigator at the Laboratory of Structural Immunology at USTC, lists her as a co-inventor on a patent. Mr. Jin did not respond to requests for comment.
A person who answered the phone at USTC told The Globe, “I don’t have any information about this teacher.”
In 2012, USTC signed a strategic co-operation agreement with the Army Engineering University of the People’s Liberation Army, designed to strengthen research on cutting-edge technology useful for communications, weaponry and other national-defence priorities.
Dr. Qiu is also listed as a 2019 doctoral supervisor for students studying virology at Hebei Medical University.
“Well, that makes me wonder what circumstances she was under when she emigrated to Canada. Why did she come?” asked Earl Brown, a professor emeritus of biochemistry, microbiology and immunology at the University of Ottawa’s faculty of medicine who has worked extensively in China in the past. “People leave for more freedom from China, or to make more money. But China keeps tabs on most people so I am not sure if she came over to infiltrate or whether she came and the infiltration happened later through contact with China.”
It may be impossible to answer that question. Three former colleagues at the National Microbiolgy Lab have indicated that Dr. Qiu and her husband were diligent and pleasant to deal with, but largely kept to themselves outside of work. They say Dr. Qiu was a brilliant scientist with a strong work ethic, although her English was weak. The Globe is not identifying the three who did not want to be named.
Dr. Qiu is a medical doctor from Tianjin, China, who came to Canada for graduate studies in 1996. She started at the University of Manitoba, but began working at the national lab as a research scientist in 2006, working her way up to become head of the vaccine development and antiviral therapies section in the National Microbiology Laboratory’s special pathogens program.
She was also part of the team that helped develop ZMapp, a treatment for the deadly Ebola virus, which killed more than 11,000 people in West Africa between 2014 and 2016.
“My sense is this was part of a larger strategy by China to get access to our innovation system,” said Filippa Lentzos, an associate professor of science and international security at King’s College London. “It was a way for them to to find out what was going on in Canada’s premier lab.”
Initially trained as a medical doctor, Dr. Qiu graduated in 1985 from Hebei University in the coastal city of Tianjin, which lies southeast of Beijing. Dr. Qiu went on to obtain her master of science degree in immunology at Tianjin Medical University in 1990.
Her career at Canada’s top infectious disease lab in Winnipeg began in 2003, only four years after Ottawa opened this biosafety level 4 facility at the Canadian Science Centre for Human and Animal Health.
Over time, she built up a reputation for academic collaboration, particularly with China. It was welcomed by management who felt her work was helping build a name internationally for the National Microbiology Lab.
By the time Canadian officials intervened in 2018 and began investigating, documents show, Dr. Qiu was running 44 separate projects at the Winnipeg lab, an uncommonly large workload.
Her work with former colleague and microbiologist Gary Kobinger vaulted Dr. Qiu into the international spotlight. The pair developed a treatment for Ebola, one that in its first human application led to the full recovery of 27 patients with the infection during a 2014 outbreak in Liberia.
Mr. Kobinger’s career continued to soar and he is now director of the Galveston National Laboratory, a renowned biosafety level 4 facility in Texas. In 2022, he told The Globe that it was “heartbreaking” to see what had happened to his colleague. He declined to speak for this article.
“She had lost a lot of weight with all the stress. She was so convinced that this was all a misunderstanding … and she would go back to her job,” he said in 2022. “ Her career has been destroyed with all this. She was one of the top female Canadian scientists of virology and Canada has lost that.”
Over a period of 13 months, though, the Chinese-Canadian microbiologist and her biologist husband’s lives were turned upside down.
She went from being feted at Ottawa’s Rideau Hall with a Governor-General’s Award in May, 2018, to being locked out of the Winnipeg lab in July, 2019 – the high-security facility where she had made her name as a scientist in Canada. By January, 2021, she and Mr. Cheng were fired.
Last month, after being pressed into explaining what happened, the Canadian government finally disclosed the reasons for this extraordinary dismissal: CSIS found the pair had lied about and hid their co-operation with China from Ottawa.
A big question remains following their departure: Why would Dr. Qiu risk her career, including the stature associated with developing an Ebola treatment, for China?
Read the rest here...
Spread & Containment
You can now enter this country without a passport
Singapore has been on a larger push to speed up the flow of tourists with digital immigration clearance.

In the fall of 2023, the city-state of Singapore announced that it was working on end-to-end biometrics that would allow travelers passing through its Changi Airport to check into flights, drop off bags and even leave and exit the country without a passport.
The latter is the most technologically advanced step of them all because not all countries issue passports with the same biometrics while immigration laws leave fewer room for mistakes about who enters the country.
Related: A country just went visa-free for visitors with any passport
That said, Singapore is one step closer to instituting passport-free travel by testing it at its land border with Malaysia. The two countries have two border checkpoints, Woodlands and Tuas, and as of March 20 those entering in Singapore by car are able to show a QR code that they generate through the government’s MyICA app instead of the passport.
Here is who is now able to enter Singapore passport-free
The latter will be available to citizens of Singapore, permanent residents and tourists who have already entered the country once with their current passport. The government app pulls data from one's passport and shows the border officer the conditions of one's entry clearance already recorded in the system.
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
While not truly passport-free since tourists still need to link a valid passport to an online system, the move is the first step in Singapore's larger push to get rid of physical passports.
"The QR code initiative allows travellers to enjoy a faster and more convenient experience, with estimated time savings of around 20 seconds for cars with four travellers, to approximately one minute for cars with 10 travellers," Singapore's Immigration and Checkpoints Authority wrote in a press release announcing the new feature. "Overall waiting time can be reduced by more than 30% if most car travellers use QR code for clearance."
More countries are looking at passport-free travel but it will take years to implement
The land crossings between Singapore and Malaysia can get very busy — government numbers show that a new post-pandemic record of 495,000 people crossed Woodlands and Tuas on the weekend of March 8 (the day before Singapore's holiday weekend.)
Even once Singapore implements fully digital clearance at all of its crossings, the change will in no way affect immigration rules since it's only a way of transferring the status afforded by one's nationality into a digital system (those who need a visa to enter Singapore will still need to apply for one at a consulate before the trip.) More countries are in the process of moving toward similar systems but due to the varying availability of necessary technology and the types of passports issued by different countries, the prospect of agent-free crossings is still many years away.
In the U.S., Chicago's O'Hare International Airport was chosen to take part in a pilot program in which low-risk travelers with TSA PreCheck can check into their flight and pass security on domestic flights without showing ID. The UK has also been testing similar digital crossings for British and EU citizens but no similar push for international travelers is currently being planned in the U.S.
stocks pandemic link testing singapore uk euSpread & Containment
This country became first in the world to let in tourists passport-free
Singapore has been on a larger push to speed up the flow of tourists with digital immigration clearance.

In the fall of 2023, the city-state of Singapore announced that it was working on end-to-end biometrics that would allow travelers passing through its Changi Airport to check into flights, drop off bags and even leave and exit the country without a passport.
The latter is the most technologically advanced step of them all because not all countries issue passports with the same biometrics while immigration laws leave fewer room for mistakes about who enters the country.
Related: A country just went visa-free for visitors with any passport
That said, Singapore is one step closer to instituting passport-free travel by testing it at its land border with Malaysia. The two countries have two border checkpoints, Woodlands and Tuas, and as of March 20 those entering in Singapore by car are able to show a QR code that they generate through the government’s MyICA app instead of the passport.
Here is who is now able to enter Singapore passport-free
The latter will be available to citizens of Singapore, permanent residents and tourists who have already entered the country once with their current passport. The government app pulls data from one's passport and shows the border officer the conditions of one's entry clearance already recorded in the system.
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
While not truly passport-free since tourists still need to link a valid passport to an online system, the move is the first step in Singapore's larger push to get rid of physical passports.
"The QR code initiative allows travellers to enjoy a faster and more convenient experience, with estimated time savings of around 20 seconds for cars with four travellers, to approximately one minute for cars with 10 travellers," Singapore's Immigration and Checkpoints Authority wrote in a press release announcing the new feature. "Overall waiting time can be reduced by more than 30% if most car travellers use QR code for clearance."
More countries are looking at passport-free travel but it will take years to implement
The land crossings between Singapore and Malaysia can get very busy — government numbers show that a new post-pandemic record of 495,000 people crossed Woodlands and Tuas on the weekend of March 8 (the day before Singapore's holiday weekend.)
Even once Singapore implements fully digital clearance at all of its crossings, the change will in no way affect immigration rules since it's only a way of transferring the status afforded by one's nationality into a digital system (those who need a visa to enter Singapore will still need to apply for one at a consulate before the trip.) More countries are in the process of moving toward similar systems but due to the varying availability of necessary technology and the types of passports issued by different countries, the prospect of agent-free crossings is still many years away.
In the U.S., Chicago's O'Hare International Airport was chosen to take part in a pilot program in which low-risk travelers with TSA PreCheck can check into their flight and pass security on domestic flights without showing ID. The UK has also been testing similar digital crossings for British and EU citizens but no similar push for international travelers is currently being planned in the U.S.
stocks pandemic link testing singapore uk eu-

 Spread & Containment1 week ago
Spread & Containment1 week agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges





















