‘Lab on a chip’ genetic test device can identify viruses within three minutes with top-level accuracy
Compact genetic testing device created for Covid-19 could be used to detect a range of pathogens, or conditions including cancer
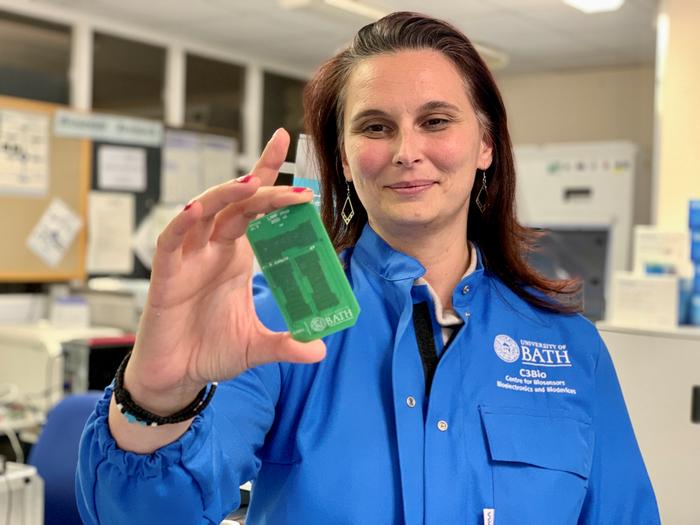
A virus diagnosis device that gives lab-quality results within just three minutes has been invented by engineers at the University of Bath, who describe it as the ‘world’s fastest Covid test’.
The prototype LoCKAmp device uses innovative ‘lab on a chip’ technology and has been proven to provide rapid and low-cost detection of Covid-19 from nasal swabs. The research team, based at the University of Bath, say the technology could easily be adapted to detect other pathogens such as bacteria – or even conditions like cancer.
The device works by rapidly releasing and amplifying genetic material from a nasal swab sample by carrying out a chemical reaction to produce a result, which can be viewed on a smartphone app.
Unlike lateral flow assay tests, commonplace during the pandemic, the LoCKAmp employs the same ‘gold standard’ genetic-based testing techniques previously reserved for lab-based PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tests, thus enabling rapid testing at laboratory-scale standard for the first time.
As well as its accuracy, the speed of the LoCKAmp sets it apart. With results shown within three minutes, the research team say that to their knowledge this makes LoCKAmp the fastest Covid-19 test reported to date.
Made with off-the-shelf components and factory-manufactured printed circuit boards, the prototype device could be made on a mass scale quickly and at low cost, presenting care providers and public health bodies around the world with an effective new tool in virus detection. The research team says a commercial partner with the relevant design and manufacturing expertise could quickly redesigned the LoCKAmp into a small, portable device – with great potential for use in remote healthcare settings.
The research team is already engaging with academic and commercial partners, and would welcome further approaches, as it seeks to bring LoCKAmp into production.
The device and how it works is detailed in the research paper LoCKAmp: lab-on-PCB technology for , published in the journal Lab on a Chip.
Dr Despina Moschou, from Bath’s Centre for Bioengineering & Biomedical Technologies (CBio), led the research. She says: “We started researching and developing LoCKAmp during the second wave of Covid in the UK. We were confident we could create a portable, low-cost device that could carry out genetic identification of the virus, like a PCR test, within 10 minutes. We have done that, but found it can actually work within just three minutes.
“This is an amazing display of the possibilities of lab-on-a-chip technology, and given the low cost and adaptability of the technology to detect a range of conditions, a potentially highly valuable and unique tool for a range of healthcare settings.”
By using readily available printed circuit board technology and the associated mass manufacturing infrastructure, the team say the device can be produced quickly and cheaply at scale. LoCKAmp comprises a portable testing unit, and disposable cartridges, which are used for each test.
The testing unit is projected to cost as little as £50 when it reaches mass production, while the test cartridges, currently made for £2.50, could cost less than 50 pence.
How LoCKAmp works
LoCKAmp harnesses a process known as RT-LAMP (reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification) to multiply specific sequences of RNA, meaning it can quickly detect the particular virus it is looking for. The team says LAMP detection is preferable to PCR testing as it has higher sensitivity, is faster and more specific.
Crucially, processing takes place at a single stable temperature of 65°, instead of needing the three thermal cycles a PCR test requires. This means the device can be made easier at a portable size, and with lower power consumption. A further benefit of the design is that no pre-processing of the nasal swab samples is required.
Once a nasal swab sample is added to the device, the LoCKAmp pumps the liquid through tiny transparent ‘microfluidic’ channels layered onto the circuit board, above copper heaters just 0.017mm thick. These heat the sample, releasing the RNA genetic material from the virus. This is then further heated and treated with RT-LAMP chemicals to encourage multiplication.
If the specific virus RNA is present in the amplified sample, it fluoresces under light – this signal is then used to denote a positive test.
LoCKAmp has been developed by a team led at the University of Bath, including staff from its departments of Chemical Engineering, Chemistry and Life Sciences, as well as colleagues from the James Watt School of Engineering at the University of Glasgow and the John Innes Centre.
The device was tested with COVID-19 patient swabs collected by Bath’s Royal United Hospital Trusts, with which the University has a longstanding research partnership, during the third wave of the pandemic.
Despite the cessation of the pandemic, particularly in the public consciousness and legislative agenda, development continued, given the adaptability and potential of the device.
Scope to track outbreaks via wastewater
As well as proving the system’s capability in analysing nasal swab samples, the LoCKAmp could also be used to carry out anonymised community-level monitoring and detection of viruses like Covid, by testing wastewater.
This alternative use, which does require some pre-processing of wastewater samples, was arrived upon as the team took advantage of expertise in wastewater-based epidemiology within Bath’s Water Innovation Research Centre.
Using LoCKAmp to carry out ongoing, real-time analysis of wastewater could allow public health bodies to quickly detect the spread of viruses like Covid, or other infectious diseases. Doing this via wastewater can give a broader community-wide view, rather than relying on individuals to regularly test for a condition.
Professor Barbara Kasprzyk-Hordern, from Bath’s Department of Chemistry, is an expert in environmental epidemiology and contributed to the research. She says: ‘With LoCKAmp technology providing both low cost and real time genetic target identification and quantification, we’re getting ever closer to real time pathogen tracking. This opens exciting opportunities enabling the establishment of early warning systems utilising wastewater for pathogen surveillance in communities.”
The research was funded by the Global Challenges Research Fund (GCRF) QR – UK Research & Innovation and the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council Impact Acceleration Account. At the John Innes Centre, the work was supported by BBSRC (Grant BB/V009087/1), the Institute Strategic Programme Grant “Molecules from Nature—Enhanced Research Capacity” (BBS/E/J/000PR9794), and the John Innes Foundation. The authors at the Department of Biology & Biochemistry, University of Bath acknowledge financial support from the Academy of Medical Sciences (SBF0061023).
ENDS
Contact:
Will McManus, Media & PR Manager, wem25@bath.ac.uk / press@bath.ac.uk, +44 (0)1225 385 798
Images are available at: https://tinyurl.com/k3f34uxy
The University of Bath
The University of Bath is one of the UK’s leading universities for high-impact research with a reputation for excellence in education, student experience and graduate prospects.
We are named ‘University of the Year’ in The Times and The Sunday Times Good University Guide 2023, and ranked among the world’s top 10% of universities, placing 148th in the QS World University Rankings 2024. We are ranked 5th in the UK in the Complete University Guide 2024, 6th in the Guardian University Guide 2024 and 8th in the The Times and Sunday Times Good University Guide 2024.
Bath is rated in the world’s top 10 universities for sport in the QS World University Ranking by Subject 2023. We produce some of the world’s most job-ready graduates and were named University of the Year for Graduate Jobs by the Daily Mail University Guide 2024, as well as ranking as one of the world’s top 90 universities for employer reputation according to the QS World University Rankings 2024.
Research from Bath is helping to change the world for the better. Across the University’s three Faculties and School of Management, our research is making an impact in society, leading to low-carbon living, positive digital futures, and improved health and wellbeing. Find out all about our Research with Impact: https://www.bath.ac.uk/campaigns/research-with-impact/
Journal
Lab on a Chip
DOI
10.1039/D3LC00441D
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
LoCKAmp: lab-on-PCB technology for
Article Publication Date
7-Sep-2023
COI Statement
There are no conflicts to declare.