Uncategorized
Apple just dropped a new Apple Pencil for the first time since 2018, and it sports a unique feature list
With now three Apple Pencils in the lineup, here’s how to pick the right one with you.

The Arena Media Brands, LLC and respective content providers to this website may receive compensation for some links to products and services on this website.
Well, surprise, Apple just unveiled a version of the quintessential iPad accessory, and it’s surprisingly affordable. The new Apple Pencil with a USB-C port is a new low-cost option at just $79 for any iPad with that port.
Specifically, this version works with the 10th Gen iPad, iPad Mini, iPad Air, and the flagship 11-inch or 12.9-inch iPad Pro. The new Apple Pencil joins the Apple Pencil first-generation ($99, discounted to $89) with a Lightning Port and the magnetically-attaching second-generation Apple Pencil ($129, discounted to $119).
The latest Apple Pencil will begin shipping in Nov., but the first-generation and second-generation are still available immediately. Not to mention, they are both discounted on Amazon as well.
Ahead, we’re breaking down everything you need to know about the new Apple Pencil and how to pick between the three models to ensure you’re getting the best one for your needs.
The new Apple Pencil: What you need to know
Just like the ever-growing iPad lineup, there are now three Apple Pencils to pick from. The new Apple Pencil looks much like the second generation, with a flat side that makes it easier to grasp and a matte finish.
It will still be a great tool for writing, drawing, and even sketching with a super low amount of latency that makes the experience of writing on paper with an actual pen or pencil. That’s been the hallmark of Apple’s stylus, and while we haven’t gone hands-on with the new model just yet, we’d be gobsmacked if that is missing here.
Like the first- and second-generation, the latest Apple Pencil also supports tilt sensitivity. If you’re drawing or need to maneuver an object on the screen, you can hold the stylus at an angle, and the iPad will still recognize it.
The one feature mussing on the new Apple Pencil is pressure sensitivity, and it’s likely how Apple got the price a little bit lower here. This means that the Pencil will not react on the screen as you press harder or opt for a lighter stroke. This will be a bummer for artists or those who want to leave a thicker impact on the digital paper. The first or second-generation Apple Pencil is still the best bet for those needing this sensitivity level.

For charging, Apple hid the USC-C port behind a cap that slides up on the top of the Pencil. It’s neat and will let you easily charge this with the iPad by simply plugging a USB-C to USB-C cable into the tablet and then into the accessory. While the new Apple Pencil magnetically attaches to any iPad with a USB-C port, it will not charge there. There is no wireless charging built-in here; however, when it is docked on the side, Apple says it goes into a sleep state to ensure your battery life doesn’t tank.
Surprisingly, the new Apple Pencil with USB-C also supports “Hover” when paired with an 11-inch or 12.9-inch iPad Pro with M2. This lets you preview a result without marking up the document, image, or whatever it might be. Essentially, the Pencil, in combination with the screen, can sense where you’re holding it and show a preview. Up until now, this was exclusive to the second-generation Apple Pencil.
Overall, it’s great to see a more affordable version of Apple’s most well-known iPad accessory, but like the 10th Gen iPad, this too sports a unique feature list. At $79, it does undercut the first and second-generation, but if you want to switch between tools with a tap, wirelessly charge it, or even use pressure, you’ll want to spend a bit more.
Plus, if you have an iPad with a Lightning port or are getting the entry-level 9th Gen iPad, your only option is still the first generation, and that’s not bad.
The new Apple Pencil with USB-C will begin shipping in Nov at $79, while the first-generation Apple Pencil at $79 and the second generation at $129 are still available and will ship immediately.
- Apple Pencil first-generation, $89 (was $99) at Amazon
- Apple Pencil second-generation, $119 (was $129) at Amazon
- Apple Pencil with USB-C, $79 at Amazon
Which Apple Pencil is right for you?

To help you decide which Apple Pencil is the best for your needs, here are a few suggestions based on our testing and analysis.
If you have a 9th Gen iPad, get the first-generation Apple Pencil. It supports all of the classic features and provides a great experience with the ability to sense pressure. Plus, when it comes time to recharge, you can simply plug it into the Lightning port.
- Apple Pencil first-generation, $89 (was $99) at Amazon
If you have an iPad Mini or 10th Gen iPad, the choice is between the second-generation and the new Apple Pencil. I’d hedge that it comes down to what you use the iPad for. If you plan on sketching and drawing or need the pressure sensitivity, it’s likely worth spending a bit more, and you’ll get it ASAP instead of waiting for it to ship. However, if you can live without pressure sensitivity or wireless charging, the new Apple Pencil checks off the right boxes and will be just $79.
- Apple Pencil second-generation, $119 (was $129) at Amazon
- Apple Pencil with USB-C, $79 at Amazon
If you have an iPad Air or iPad Pro (11-inch or 12.9-inch), I recommend opting for the second-generation Apple Pencil. It technically carries a $129 price tag but is frequently discounted by at least $10 on Amazon. It magnetically attaches to the side like the new one but also charges while there, so you’re never without it. Plus, it delivers a low-latency experience with pressure and tilt sensitivity, as well as Hover support and double-tap. This way, you can quickly hit the flat side to change the tool you’re working with.
- Apple Pencil second-generation, $119 (was $129) at Amazon
Best iPad Deals on Amazon

If you’ve been waiting to get an iPad until Apple unveiled a new Pencil or want to hop on the Apple tablet game now, many discounts are available on Amazon.
9th Gen iPad, $249 (was $329) at Amazon
Leading the pack is the entry-level 9th Gen iPad at an all-time low price of just $249. It might still feature a Home button and thicker bezels but don’t judge it just from looks. It runs iPadOS swiftly and can power through any task you want to accomplish. Plus, the 10.2-inch display delivers a vibrant viewing experience that packs in details. It’s great for light work and other productivity tasks but shines with web browsing, streaming content, gaming, and FaceTime calls.
Additionally, you can save on iPad Mini and iPad Air, among others.
- 10th Gen iPad, $399 (was $449) at Amazon
- iPad Mini 6th Gen, $469 (was $499) at Amazon
- iPad Air 5th Gen, $559 (was $599) at Amazon
- 12.9-inch iPad Pro 6th gen, $1,049 (was $1,099) at Amazon
Prices are accurate and items in stock at time of publishing.
testingUncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemploymentUncategorized
Mortgage rates fall as labor market normalizes
Jobless claims show an expanding economy. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
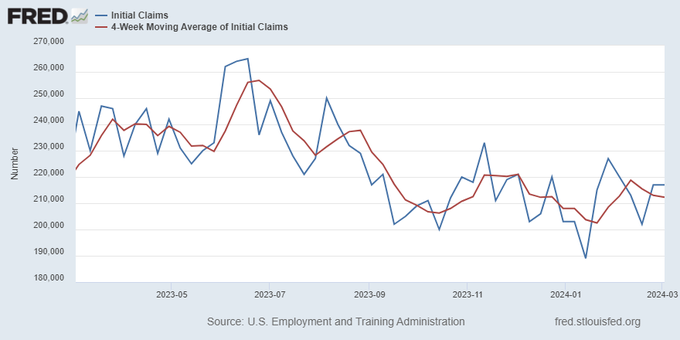
Everyone was waiting to see if this week’s jobs report would send mortgage rates higher, which is what happened last month. Instead, the 10-year yield had a muted response after the headline number beat estimates, but we have negative job revisions from previous months. The Federal Reserve’s fear of wage growth spiraling out of control hasn’t materialized for over two years now and the unemployment rate ticked up to 3.9%. For now, we can say the labor market isn’t tight anymore, but it’s also not breaking.
The key labor data line in this expansion is the weekly jobless claims report. Jobless claims show an expanding economy that has not lost jobs yet. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
From the Fed: In the week ended March 2, initial claims for unemployment insurance benefits were flat, at 217,000. The four-week moving average declined slightly by 750, to 212,250
Below is an explanation of how we got here with the labor market, which all started during COVID-19.
1. I wrote the COVID-19 recovery model on April 7, 2020, and retired it on Dec. 9, 2020. By that time, the upfront recovery phase was done, and I needed to model out when we would get the jobs lost back.
2. Early in the labor market recovery, when we saw weaker job reports, I doubled and tripled down on my assertion that job openings would get to 10 million in this recovery. Job openings rose as high as to 12 million and are currently over 9 million. Even with the massive miss on a job report in May 2021, I didn’t waver.
Currently, the jobs openings, quit percentage and hires data are below pre-COVID-19 levels, which means the labor market isn’t as tight as it once was, and this is why the employment cost index has been slowing data to move along the quits percentage.

3. I wrote that we should get back all the jobs lost to COVID-19 by September of 2022. At the time this would be a speedy labor market recovery, and it happened on schedule, too
Total employment data
4. This is the key one for right now: If COVID-19 hadn’t happened, we would have between 157 million and 159 million jobs today, which would have been in line with the job growth rate in February 2020. Today, we are at 157,808,000. This is important because job growth should be cooling down now. We are more in line with where the labor market should be when averaging 140K-165K monthly. So for now, the fact that we aren’t trending between 140K-165K means we still have a bit more recovery kick left before we get down to those levels.

From BLS: Total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 275,000 in February, and the unemployment rate increased to 3.9 percent, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Job gains occurred in health care, in government, in food services and drinking places, in social assistance, and in transportation and warehousing.
Here are the jobs that were created and lost in the previous month:

In this jobs report, the unemployment rate for education levels looks like this:
- Less than a high school diploma: 6.1%
- High school graduate and no college: 4.2%
- Some college or associate degree: 3.1%
- Bachelor’s degree or higher: 2.2%

Today’s report has continued the trend of the labor data beating my expectations, only because I am looking for the jobs data to slow down to a level of 140K-165K, which hasn’t happened yet. I wouldn’t categorize the labor market as being tight anymore because of the quits ratio and the hires data in the job openings report. This also shows itself in the employment cost index as well. These are key data lines for the Fed and the reason we are going to see three rate cuts this year.
recession unemployment covid-19 fed federal reserve mortgage rates recession recovery unemploymentUncategorized
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Last month we though that the January…
Last month we though that the January jobs report was the "most ridiculous in recent history" but, boy, were we wrong because this morning the Biden department of goalseeked propaganda (aka BLS) published the February jobs report, and holy crap was that something else. Even Goebbels would blush.
What happened? Let's take a closer look.
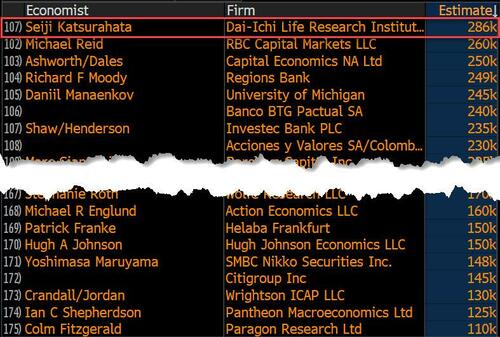
On the surface, it was (almost) another blockbuster jobs report, certainly one which nobody expected, or rather just one bank out of 76 expected. Starting at the top, the BLS reported that in February the US unexpectedly added 275K jobs, with just one research analyst (from Dai-Ichi Research) expecting a higher number.
Some context: after last month's record 4-sigma beat, today's print was "only" 3 sigma higher than estimates. Needless to say, two multiple sigma beats in a row used to only happen in the USSR... and now in the US, apparently.
Before we go any further, a quick note on what last month we said was "the most ridiculous jobs report in recent history": it appears the BLS read our comments and decided to stop beclowing itself. It did that by slashing last month's ridiculous print by over a third, and revising what was originally reported as a massive 353K beat to just 229K, a 124K revision, which was the biggest one-month negative revision in two years!
Of course, that does not mean that this month's jobs print won't be revised lower: it will be, and not just that month but every other month until the November election because that's the only tool left in the Biden admin's box: pretend the economic and jobs are strong, then revise them sharply lower the next month, something we pointed out first last summer and which has not failed to disappoint once.
In the past month the Biden department of goalseeking stuff higher before revising it lower, has revised the following data sharply lower:
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) August 30, 2023
- Jobs
- JOLTS
- New Home sales
- Housing Starts and Permits
- Industrial Production
- PCE and core PCE
To be fair, not every aspect of the jobs report was stellar (after all, the BLS had to give it some vague credibility). Take the unemployment rate, after flatlining between 3.4% and 3.8% for two years - and thus denying expectations from Sahm's Rule that a recession may have already started - in February the unemployment rate unexpectedly jumped to 3.9%, the highest since February 2022 (with Black unemployment spiking by 0.3% to 5.6%, an indicator which the Biden admin will quickly slam as widespread economic racism or something).
And then there were average hourly earnings, which after surging 0.6% MoM in January (since revised to 0.5%) and spooking markets that wage growth is so hot, the Fed will have no choice but to delay cuts, in February the number tumbled to just 0.1%, the lowest in two years...
... for one simple reason: last month's average wage surge had nothing to do with actual wages, and everything to do with the BLS estimate of hours worked (which is the denominator in the average wage calculation) which last month tumbled to just 34.1 (we were led to believe) the lowest since the covid pandemic...
... but has since been revised higher while the February print rose even more, to 34.3, hence why the latest average wage data was once again a product not of wages going up, but of how long Americans worked in any weekly period, in this case higher from 34.1 to 34.3, an increase which has a major impact on the average calculation.
While the above data points were examples of some latent weakness in the latest report, perhaps meant to give it a sheen of veracity, it was everything else in the report that was a problem starting with the BLS's latest choice of seasonal adjustments (after last month's wholesale revision), which have gone from merely laughable to full clownshow, as the following comparison between the monthly change in BLS and ADP payrolls shows. The trend is clear: the Biden admin numbers are now clearly rising even as the impartial ADP (which directly logs employment numbers at the company level and is far more accurate), shows an accelerating slowdown.
But it's more than just the Biden admin hanging its "success" on seasonal adjustments: when one digs deeper inside the jobs report, all sorts of ugly things emerge... such as the growing unprecedented divergence between the Establishment (payrolls) survey and much more accurate Household (actual employment) survey. To wit, while in January the BLS claims 275K payrolls were added, the Household survey found that the number of actually employed workers dropped for the third straight month (and 4 in the past 5), this time by 184K (from 161.152K to 160.968K).
This means that while the Payrolls series hits new all time highs every month since December 2020 (when according to the BLS the US had its last month of payrolls losses), the level of Employment has not budged in the past year. Worse, as shown in the chart below, such a gaping divergence has opened between the two series in the past 4 years, that the number of Employed workers would need to soar by 9 million (!) to catch up to what Payrolls claims is the employment situation.
There's more: shifting from a quantitative to a qualitative assessment, reveals just how ugly the composition of "new jobs" has been. Consider this: the BLS reports that in February 2024, the US had 132.9 million full-time jobs and 27.9 million part-time jobs. Well, that's great... until you look back one year and find that in February 2023 the US had 133.2 million full-time jobs, or more than it does one year later! And yes, all the job growth since then has been in part-time jobs, which have increased by 921K since February 2023 (from 27.020 million to 27.941 million).
Here is a summary of the labor composition in the past year: all the new jobs have been part-time jobs!
But wait there's even more, because now that the primary season is over and we enter the heart of election season and political talking points will be thrown around left and right, especially in the context of the immigration crisis created intentionally by the Biden administration which is hoping to import millions of new Democratic voters (maybe the US can hold the presidential election in Honduras or Guatemala, after all it is their citizens that will be illegally casting the key votes in November), what we find is that in February, the number of native-born workers tumbled again, sliding by a massive 560K to just 129.807 million. Add to this the December data, and we get a near-record 2.4 million plunge in native-born workers in just the past 3 months (only the covid crash was worse)!
The offset? A record 1.2 million foreign-born (read immigrants, both legal and illegal but mostly illegal) workers added in February!
Said otherwise, not only has all job creation in the past 6 years has been exclusively for foreign-born workers...

... but there has been zero job-creation for native born workers since June 2018!
This is a huge issue - especially at a time of an illegal alien flood at the southwest border...
... and is about to become a huge political scandal, because once the inevitable recession finally hits, there will be millions of furious unemployed Americans demanding a more accurate explanation for what happened - i.e., the illegal immigration floodgates that were opened by the Biden admin.
Which is also why Biden's handlers will do everything in their power to insure there is no official recession before November... and why after the election is over, all economic hell will finally break loose. Until then, however, expect the jobs numbers to get even more ridiculous.
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges




































