Uncategorized
5,050 Bitcoin for $5 in 2009: Helsinki’s claim to crypto fame
Helsinki played host to the first Bitcoin for fiat transaction in 2009 — 5050 Bitcoin for $5 — 6 months before Pizza Day. Crypto City Guide.
…

Helsinki played host to the first Bitcoin for fiat transaction in 2009 — 5050 Bitcoin for $5 — 6 months before Pizza Day. Crypto City Guide.
This Crypto City guide looks at Finlands crypto culture: The most notable projects and people, its financial infrastructure, which retailers accept crypto, and where you can find blockchain education courses.
City: Helsinki
Country: Finland
Population: 1.55 million
Established: 1550
Languages: Finnish and Swedish, with English widely spoken
Jump to: Crypto culture, Where to spend crypto in Helsinki, Crypto projects and companies, Local crypto controversies, Crypto education and community, Notable crypto figures from Helsinki
Situated on the Gulf of Finland, Helsinki is the capital of Finland and is arguably the worlds most northern metropolis, with 1.5 million people 30% of the countrys population calling the metro area home. Its inhabitants spend winter in a cold, still darkness but enjoy 11:00 pm sunsets in summertime.

Major population centers are nearby, with both Tampere and Turku reachable in two hours via road or rail. There are regular ferry services across the Baltic including to Estonias capital of Tallinn, which can be reached in two hours by sea, and there are also plans to link the cities via an undersea tunnel. The nearby Helsinki-Vantaa airport is the countrys main international gateway and serves as a transfer hub for Asia.
Finland has been ranked the happiest country in the world for six consecutive years by the World Happiness Report. Its income tax rate tops out at 56% one of the highest in the world and the tax data of every resident is public. Helsinki played host to the 1952 Summer Olympics. The country joined the European Union in 1995 and adopted the euro as its currency in 1999. In 2023, Finland became a member of NATO.
As the capital, Helsinkis crypto events draw participants from across the country, making it the natural meeting place for the industry. For that reason, projects and companies from nearby cities like Tampere and Turku are also included here.
The area was first settled around 5000 BC as the ice age retreated. Vikings raided the established settlements, as did Swedish crusaders in the 10th and 13th centuries. The city was formally established in 1550 as a Swedish trading post, defended by Suomenlinna (Finlands fortress), the largest sea fort in Europe. Later, under Russian control as the Grand Duchy of Finland, the emperor moved the capital from Turku to Helsinki, which was closer to St. Petersburg. Finland became independent in 1917, after which it resisted Soviet occupation in the 1940 Winter War.

Crypto culture
Helsinkis claim to crypto fame rests with Martti Malmi, a software developer who in 2009 sold 5,050 BTC for a $5.02 PayPal transfer, marking the first time that Bitcoin was exchanged for fiat currency. It occurred before the much better-known May 22, 2010, Pizza Day, when Bitcoin was first used to purchase a physical good. Eventually, Malmi used most of his Bitcoin to purchase a studio in the metro area. If hed hung on to it, itd be worth $171 million today. The Bitcoin was used to seed an exchange called New Liberty Standard, which established the first BTC price of 1,309.03 BTC for $1.
Found the first known bitcoin to USD transaction from my email backups. I sold 5,050 BTC for $5,02 on 2009-10-12. https://t.co/8XcBmzJljf
Martti Malmi (@marttimalmi) January 15, 2014
Malmi was, in some ways, a product of his environment, with Helsinki recognized as a bed of technical innovation since Nokia began to dominate the cellphone market. In 1991, Linus Torvalds began working on what became Linux at the University of Helsinki. It is also home to many video game companies, with local firm Rovios Angry Birds achieving global fame in 2009. Helsinki is also the home of Aave founder Stani Kulechov, though he has moved abroad with the company.
In 2019, a then-staunchly Bitcoin maximalist group called Konsensus organized the translation of Saifedean Ammous 2018 book The Bitcoin Standard into Finnish, and later also translated The Little Bitcoin Book by The Bitcoin Collective. According to one member, the organization has since become more accepting of other cryptocurrencies and blockchain use cases.
The crypto community in Helsinki and Finland is somewhat disorganized and divided, with many enthusiasts being interested in one facet be it Bitcoin, NFTs or Web3 without embracing the whole, and thus having few common threads. Still, a certain grassroots energy is evident.

Where can I spend crypto in Helsinki?
Paying with Bitcoin is not common in Finland, where card and app payments dominate. One notable exception is the restaurant Faro, at which a few people are likely to buy a burger and beers with sats at the monthly Bitcoin meetup.
On the bar side, Taudo Baari and Time Bar also accept crypto. There is also the Osuva shooting range.
Samuel Harjunp, CEO and co-founder of hardware startup Xellox and regular at the Faro Bitcoin meetup, tells Magazine about the state of Bitcoin acceptance:
A few restaurants and bars have already been orange-pilled the biggest obstacles are the payment infrastructure and bookkeeping.
Crypto projects and companies in Helsinki
Today, Helsinki has a vibrant tech and startup scene with many coworking spaces. The city is also host to the annual Slush startup conference, which draws 25,000 participants.
Web3 Helsinki is a student-run organization that organized its first event on April 20, 2020, with about 150 people in attendance, making it perhaps the largest single crypto event of the year.
2023s events have included the Web3 Bash in late April, followed by the Aurora Nordic Web3 Conference in June. On June 6, the BRIDG3 Blockchain summit was held at Tamperes Nokia Arena, focusing on Web3, the metaverse and decentralized autonomous organizations.

The Finnish Bitcoin Association was established on May 6, in an event attended by Magazine, with membership fees paid primarily with Bitcoin via the Lightning Network. Upon the conclusion of formalities, the saunas of the hosting coworking space were fired up.
For those interested in NFTs, Fungi is a platform advertising a no-code solution that lets organizations build NFT-based communities. One of these was a metaverse island called Cornerstone for VR studio ZOAN, where 100 plots could be purchased as NFTs.
HABBO NFT, operated by the local creators of the 23-year-old online chat room game HABBO Hotel, has dropped an 11,600-piece avatar collection on OpenSea and is currently developing an NFT-based game. A group called The Future of Art has also dedicated itself to promoting digital art and runs an NFT gallery.

An aspiring LinkedIn competitor, Kleoverse, is a proof-of-talent Web3 platform for recruiters and jobseekers that displays skills such as knowledge in programming languages through badges instead of text on a resume.
Phaver is building a Web3 social media app powered by Lens Protocol, which bills itself as the social layer of Web3. Phaver is one of many local projects that have worked with tech design studio STRGL, which specializes in protocol-level Web3 solutions. STRGLs managing director, Kasper Karimaa, sees Helsinki as a haven for developers:
Finlands role in blockchain innovation through its agile engineering community makes Helsinki the perfect place to assemble a skilled team in research, design and development.
One of the most widely known crypto companies in the country was the P2P exchange LocalBitcoins, which employed about 50 people before closing its doors in February 2023. CEO Nikolaus Kangas told Cointelegraph that this was due to a failure to turn our trade volumes and declining market share back to growth.
Bittiraha, which translates to bit money in Finnish, is another old local crypto company. It was founded circa 2012 and installed the countrys first Bitcoin ATM at the Helsinki railway station in December 2013.
The company was also a distributor of Casascius physical Bitcoin and eventually made its own line of Denarium wallets. The parent company, Coinmotion based a few hours north in Jyvskyl now operates a cryptocurrency exchange.
Another major Finnish exchange called Northcrypto can be found in Turku.
A euro stablecoin has also been developed in the city. Membrane Finances EUROe was launched in February 2023 and is designed to be an EU-regulated full-reserve stablecoin that is compliant with recent legislation. While this is notable considering the relatively few operational euro stablecoins, volume remains low at approximately $20,000 per day.
Helsinki native Anita Krypto Granny Kalergis spends most of her time in Dubai, where she organizes blockchain conferences. She feels that Finnish entrepreneurs and decision-makers lack bravery, preferring to wait for someone else to take the lead and for regulatory certainty both from the national and EU levels. Most activity is not advertised, with especially older business people afraid to rock the boat or make major moves, she observes.
Companies here will build something to 95% completion before opening their mouth, whereas projects in other countries will raise money and build partnerships based on a white paper while testing in production.

Helsinkis crypto controversies
In 2018, the Finnish customs service planned to auction 1,666 BTC that it had seized in a drug case, but decided not to proceed due to concerns that the virtual money would return to the hands of criminals, displaying a rather negative official view of cryptocurrency. In July 2022, the state eventually auctioned nearly 2,000 BTC for $47 million, with proceeds being donated to Ukraine.
In December 2021, local media reported a trend of investment scams involving the faces of prominent people, including industrialist Heikki Herlin and then-Prime Minister Sanna Marin.
Earlier in 2018, the police also made warnings regarding a trend of Bitcoin blackmail relating to bogus claims that hackers had webcam material of users visiting pornographic websites. In 2022, a Helsinki watch dealer fell victim to a common crypto scam, handing over Rolex watches worth $400,000 after mistakenly believing that he had received a Bitcoin transaction.
Cryptocurrency, often adjacent to scams in the news, has come to be viewed with a relatively high degree of suspicion across most of society. Commenting on the decision to halt the 2018 customs seizure sale, Pekka Pylkknen, head of finance at the Finnish Customs Service, highlighted concerns about money laundering, telling national broadcaster YLE that the buyers of cyber currency rarely use them for normal endeavors.
National media regularly interview outspoken cryptocurrency critic Aleksi Grym, head of fintech for the Finnish Central Bank, as an authoritative expert without seeking alternative pro-cryptocurrency views, though coverage has been improving.
As one may notice from this article, the term Web3 is preferred, presumably due to its distancing from the negative stereotypes of cryptocurrency.
Neither the countrys political establishment nor any major party or other large grouping of the population could be described outright as being pro-crypto.
One reason for this could be Finlands stable, highly functional, and high-trust society, in which most people do not see the need to disrupt or fix something with cryptocurrency. Bank transfers are free and near-instantaneous across the EU, with cash use increasingly rare. Virtually nobody is unbanked, and the most trusted institution is the police, with 95% public support. Harjunp, whose startup is working on solutions to protect private keys, explains the disconnect:
Many people dont understand Bitcoin and think its something between criminal money and a pyramid scheme.
It is also notable that the moon mentality and dreams of quick wealth found in many cryptocurrency investors are generally seen in a particularly negative light, with Malmi noting that he never set out to make money with Bitcoin, perhaps owing to Finnish culture and his idealistic mentality.
In the same vein, cryptocurrencies are seen by some as drivers of inequality in a country where large differences in wealth are often considered taboo.
Crypto education and community
The Finnish Innovation Fund, or Sitra, has stated it as a priority to accelerate the local development of Web3 services, saying that its in Finlands interest to play an active role in ensuring that the metaverse is created in line with European values.
The fund has also worked with the Finnish National Gallery to create The Finnish Metagallery, an art gallery in the Decentraland metaverse whose building is modeled from the Finnish Pavilion as it appeared at the 1900 Paris World Fair.

In the old capital of Turku, The University of Turku hosts the Critical Inquiry Into DAOs (CIDS) research group, of which the author is part.
Notable crypto figures from Helsinki
Martti Malmi, the first person to sell Bitcoin for fiat; Henri Brade, board member of Coinmotion; Aleksi Lytynoja, CEO and co-founder of Kleoverse; Niko Laamanen, founder of Konsensus.
Martin Wichmann, chairman of Konsensus; Antti Innanen, founder of Fungi; Sointu Karjalainen, founder of The Good Cartel; Juha Viitala, CEO and co-founder of Membrane Finance; Mika Timonen, founder of Habbo NFT; Olli Tianinen, CEO of Equilibrium Labs; Kasper Karimaa, managing director at STRGL; Jarmo Suoranta, CEO of TX – Tomorrow Explored.
Keir Finlow-Bates, CEO of Chainfrog; Ville Runola, CEO and founder of Northcrypto; Samuel Harjunp, CEO and co-founder of Xellox; Joonatan Lintala, CEO and co-founder of Phaver.
Cointelegraph team members often found in Helsinki: Elias Ahonen.
If you have any suggestions for additions to this guide, please contact eliasahonen@cointelegraph.com.

Uncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemploymentUncategorized
Mortgage rates fall as labor market normalizes
Jobless claims show an expanding economy. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
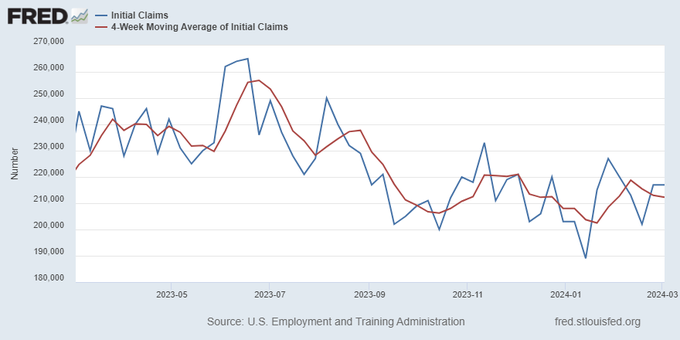
Everyone was waiting to see if this week’s jobs report would send mortgage rates higher, which is what happened last month. Instead, the 10-year yield had a muted response after the headline number beat estimates, but we have negative job revisions from previous months. The Federal Reserve’s fear of wage growth spiraling out of control hasn’t materialized for over two years now and the unemployment rate ticked up to 3.9%. For now, we can say the labor market isn’t tight anymore, but it’s also not breaking.
The key labor data line in this expansion is the weekly jobless claims report. Jobless claims show an expanding economy that has not lost jobs yet. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
From the Fed: In the week ended March 2, initial claims for unemployment insurance benefits were flat, at 217,000. The four-week moving average declined slightly by 750, to 212,250
Below is an explanation of how we got here with the labor market, which all started during COVID-19.
1. I wrote the COVID-19 recovery model on April 7, 2020, and retired it on Dec. 9, 2020. By that time, the upfront recovery phase was done, and I needed to model out when we would get the jobs lost back.
2. Early in the labor market recovery, when we saw weaker job reports, I doubled and tripled down on my assertion that job openings would get to 10 million in this recovery. Job openings rose as high as to 12 million and are currently over 9 million. Even with the massive miss on a job report in May 2021, I didn’t waver.
Currently, the jobs openings, quit percentage and hires data are below pre-COVID-19 levels, which means the labor market isn’t as tight as it once was, and this is why the employment cost index has been slowing data to move along the quits percentage.

3. I wrote that we should get back all the jobs lost to COVID-19 by September of 2022. At the time this would be a speedy labor market recovery, and it happened on schedule, too
Total employment data
4. This is the key one for right now: If COVID-19 hadn’t happened, we would have between 157 million and 159 million jobs today, which would have been in line with the job growth rate in February 2020. Today, we are at 157,808,000. This is important because job growth should be cooling down now. We are more in line with where the labor market should be when averaging 140K-165K monthly. So for now, the fact that we aren’t trending between 140K-165K means we still have a bit more recovery kick left before we get down to those levels.

From BLS: Total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 275,000 in February, and the unemployment rate increased to 3.9 percent, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Job gains occurred in health care, in government, in food services and drinking places, in social assistance, and in transportation and warehousing.
Here are the jobs that were created and lost in the previous month:

In this jobs report, the unemployment rate for education levels looks like this:
- Less than a high school diploma: 6.1%
- High school graduate and no college: 4.2%
- Some college or associate degree: 3.1%
- Bachelor’s degree or higher: 2.2%

Today’s report has continued the trend of the labor data beating my expectations, only because I am looking for the jobs data to slow down to a level of 140K-165K, which hasn’t happened yet. I wouldn’t categorize the labor market as being tight anymore because of the quits ratio and the hires data in the job openings report. This also shows itself in the employment cost index as well. These are key data lines for the Fed and the reason we are going to see three rate cuts this year.
recession unemployment covid-19 fed federal reserve mortgage rates recession recovery unemploymentUncategorized
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Last month we though that the January…
Last month we though that the January jobs report was the "most ridiculous in recent history" but, boy, were we wrong because this morning the Biden department of goalseeked propaganda (aka BLS) published the February jobs report, and holy crap was that something else. Even Goebbels would blush.
What happened? Let's take a closer look.
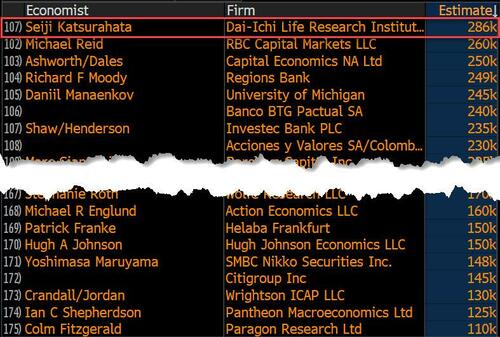
On the surface, it was (almost) another blockbuster jobs report, certainly one which nobody expected, or rather just one bank out of 76 expected. Starting at the top, the BLS reported that in February the US unexpectedly added 275K jobs, with just one research analyst (from Dai-Ichi Research) expecting a higher number.
Some context: after last month's record 4-sigma beat, today's print was "only" 3 sigma higher than estimates. Needless to say, two multiple sigma beats in a row used to only happen in the USSR... and now in the US, apparently.
Before we go any further, a quick note on what last month we said was "the most ridiculous jobs report in recent history": it appears the BLS read our comments and decided to stop beclowing itself. It did that by slashing last month's ridiculous print by over a third, and revising what was originally reported as a massive 353K beat to just 229K, a 124K revision, which was the biggest one-month negative revision in two years!
Of course, that does not mean that this month's jobs print won't be revised lower: it will be, and not just that month but every other month until the November election because that's the only tool left in the Biden admin's box: pretend the economic and jobs are strong, then revise them sharply lower the next month, something we pointed out first last summer and which has not failed to disappoint once.
In the past month the Biden department of goalseeking stuff higher before revising it lower, has revised the following data sharply lower:
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) August 30, 2023
- Jobs
- JOLTS
- New Home sales
- Housing Starts and Permits
- Industrial Production
- PCE and core PCE
To be fair, not every aspect of the jobs report was stellar (after all, the BLS had to give it some vague credibility). Take the unemployment rate, after flatlining between 3.4% and 3.8% for two years - and thus denying expectations from Sahm's Rule that a recession may have already started - in February the unemployment rate unexpectedly jumped to 3.9%, the highest since February 2022 (with Black unemployment spiking by 0.3% to 5.6%, an indicator which the Biden admin will quickly slam as widespread economic racism or something).
And then there were average hourly earnings, which after surging 0.6% MoM in January (since revised to 0.5%) and spooking markets that wage growth is so hot, the Fed will have no choice but to delay cuts, in February the number tumbled to just 0.1%, the lowest in two years...
... for one simple reason: last month's average wage surge had nothing to do with actual wages, and everything to do with the BLS estimate of hours worked (which is the denominator in the average wage calculation) which last month tumbled to just 34.1 (we were led to believe) the lowest since the covid pandemic...
... but has since been revised higher while the February print rose even more, to 34.3, hence why the latest average wage data was once again a product not of wages going up, but of how long Americans worked in any weekly period, in this case higher from 34.1 to 34.3, an increase which has a major impact on the average calculation.
While the above data points were examples of some latent weakness in the latest report, perhaps meant to give it a sheen of veracity, it was everything else in the report that was a problem starting with the BLS's latest choice of seasonal adjustments (after last month's wholesale revision), which have gone from merely laughable to full clownshow, as the following comparison between the monthly change in BLS and ADP payrolls shows. The trend is clear: the Biden admin numbers are now clearly rising even as the impartial ADP (which directly logs employment numbers at the company level and is far more accurate), shows an accelerating slowdown.
But it's more than just the Biden admin hanging its "success" on seasonal adjustments: when one digs deeper inside the jobs report, all sorts of ugly things emerge... such as the growing unprecedented divergence between the Establishment (payrolls) survey and much more accurate Household (actual employment) survey. To wit, while in January the BLS claims 275K payrolls were added, the Household survey found that the number of actually employed workers dropped for the third straight month (and 4 in the past 5), this time by 184K (from 161.152K to 160.968K).
This means that while the Payrolls series hits new all time highs every month since December 2020 (when according to the BLS the US had its last month of payrolls losses), the level of Employment has not budged in the past year. Worse, as shown in the chart below, such a gaping divergence has opened between the two series in the past 4 years, that the number of Employed workers would need to soar by 9 million (!) to catch up to what Payrolls claims is the employment situation.
There's more: shifting from a quantitative to a qualitative assessment, reveals just how ugly the composition of "new jobs" has been. Consider this: the BLS reports that in February 2024, the US had 132.9 million full-time jobs and 27.9 million part-time jobs. Well, that's great... until you look back one year and find that in February 2023 the US had 133.2 million full-time jobs, or more than it does one year later! And yes, all the job growth since then has been in part-time jobs, which have increased by 921K since February 2023 (from 27.020 million to 27.941 million).
Here is a summary of the labor composition in the past year: all the new jobs have been part-time jobs!
But wait there's even more, because now that the primary season is over and we enter the heart of election season and political talking points will be thrown around left and right, especially in the context of the immigration crisis created intentionally by the Biden administration which is hoping to import millions of new Democratic voters (maybe the US can hold the presidential election in Honduras or Guatemala, after all it is their citizens that will be illegally casting the key votes in November), what we find is that in February, the number of native-born workers tumbled again, sliding by a massive 560K to just 129.807 million. Add to this the December data, and we get a near-record 2.4 million plunge in native-born workers in just the past 3 months (only the covid crash was worse)!
The offset? A record 1.2 million foreign-born (read immigrants, both legal and illegal but mostly illegal) workers added in February!
Said otherwise, not only has all job creation in the past 6 years has been exclusively for foreign-born workers...

... but there has been zero job-creation for native born workers since June 2018!
This is a huge issue - especially at a time of an illegal alien flood at the southwest border...
... and is about to become a huge political scandal, because once the inevitable recession finally hits, there will be millions of furious unemployed Americans demanding a more accurate explanation for what happened - i.e., the illegal immigration floodgates that were opened by the Biden admin.
Which is also why Biden's handlers will do everything in their power to insure there is no official recession before November... and why after the election is over, all economic hell will finally break loose. Until then, however, expect the jobs numbers to get even more ridiculous.
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges






































