Uncategorized
When We Lose Small Businesses…
When We Lose Small Businesses…
Authored by Charles Hugh Smith via OfTwoMinds blog,
When we lose small businesses, we lose MORE than tax…

Authored by Charles Hugh Smith via OfTwoMinds blog,
When we lose small businesses, we lose MORE than tax revenues.
Small businesses receive plenty of lip service but very little appreciation--until they're gone. By then it's too late to do anything but mutter, "you don't know what you've got until it's gone."
Small businesses aren't just sources of tax revenues, they're sources of a wide range of jobs that can't be replaced by Corporate America or the government. Just as importantly, small business owners and entrepreneurs are advocates for the neighborhoods, districts and cities they depend on for customers and suppliers.
The livelihoods of the owners and their employees depend on maintaining the viability of their neighborhood / district / city, which includes public safety and services such as transportation and trash collection, and a minimum density of other private-sector services and amenities which provide residents a safe, appealing atmosphere worth visiting.
59.9 million Americans work at small businesses across the nation. An estimated 47% of Americans shop at small businesses at least twice a week, generating about 45% of the nation's economic activity. According to the most recent available numbers from the U.S. Census, approximately 47% of U.S. employees work for small businesses, compared to 54.5% in 1988.
Small business entrepreneurs are risking everything they have to open and operate a business. They have far more skin in the game than city functionaries tasked with enforcing regulations and collecting business-related fees or their employees, who have the freedom to quit and seek employment elsewhere.
Residents tend to feel powerless to stop the decay of their neighborhood safety, services and amenities. They tried contacting their elected officials or municipal functionaries and were given a meaningless feel-good reply which everyone involved knows is empty.
Small business owners are more willing to apply meaningful pressure because they know the decay follows a sobering slide in which incremental declines pile up and eventually trigger a phase change in which the character of the neighborhood / district / city goes over a cliff no one discerned: petty crime increases, paving the way for more serious crimes to proliferate; customers thin out and then become scarce, and the zeitgeist goes from friendly to wary to unpredictable or even dangerous.
The core characteristic of of neofeudal economy and society is that it's two-tier: there are two tiers of "criminal justice," one of wrist-slaps and vast white-collar crimes ignored for elites and the wealthy, and another far more brutal and Kafkaesque for the rest of us.
In terms of commerce, Big Tech is free to establish monopolies and Finance escapes all the supposed regulatory safeguards, while small business is throttled with endlessly multiplying petty regulations that have little or nothing to do with public safety or employee labor rights. Corporate America has the immense wealth and power to gut any regulations it finds onerous, but small business struggles to pay the soaring costs of compliance and the tripling of junk fees such as business license renewals.
City-provided services degrade but the costs for the privilege of doing business triple.
The majority of small businesses are sole proprietors. (see chart below) Many of these are online or at-home enterprises that are invisible to residents walking down the sidewalk. The 5.4 million small businesses with less than 20 employees are visibly consequential to the viability of bricks-and-mortar neighborhood commerce.
Demographics play a large role in the viability of small businesses. About 40% of all small businesses are owned by Boomers nearing retirement or already past the age of typical retirement. It won't take much in the way of losses or stress to nudge these owners into selling or closing the business.
But if conditions are decaying, who's going to buy a struggling business? The grim reality is "no one." Owners are already working long hours and enduring high levels of stress. This self-exploitation can only go so far before the owners' health and/or finances break down in burnout or losses.
Municipal bureaucracies tend to see small business tax donkeys as something they can count on much like a gushing spring. Should one tax donkey collapse and close a business, another tax donkey will magically appear to pick up the self-exploitation harness and start a new business in the same space.
Local-economy boosters love to cite the flood of new business applications as proof the spring is still gushing, but many of these new enterprises are sole proprietorships with no storefront presence and no employees. Many new businesses that thrived in the post-pandemic boom will soon encounter the headwinds of recession for the first time, and many will find their enterprises blown onto the unforgiving rocks of financial losses.
The phase-change shift in the character and zeitgeist of neighborhoods, districts and cities is difficult to reverse. Once people no longer feel safe, they won't come back. Once the empty storefronts and homeless encampments dominate the landscape, they won't come back. Once services deteriorate and trash accumulates, they won't come back.
Municipal bureaucracies are largely staffed by people who have never experienced what a real recession (such as 1981-2) can do to commerce, tax revenues and small businesses struggling to survive. They're confident that history demonstrates any downturn will be brief and the tax donkeys will appear as usual to fill the empty storefronts, lofts and offices.
But this time will be different. No new tax donkeys will appear to gamble their fortunes and lives on starting a stupidly expensive-to-operate business, pay prevailing wages and benefits and all the taxes, licenses and junk fees municipalities have piled on small business.
When we lose small businesses, we lose more than tax revenues. We lose the engines of employment and the commercial foundation of neighborhoods and districts. When these foundations crumble, those residents who see the slide down the slippery slope of decay sell their homes and get out while the getting's good. Those who remain will regret their inaction.
Tax donkeys don't appear by magic. There has to be an infrastructure in place that allows a real opportunity to scrape out a living despite the high costs and formidable challenges. If the infrastructure and character of a place decay, so does the opportunity, and small businesses melt into air when it's longer worth the struggle.
New Podcast: Its a Waterfall - Risk, Collateral & Productivity (48 min)
* * *
My new book is now available at a 10% discount ($8.95 ebook, $18 print): Self-Reliance in the 21st Century. Read the first chapter for free (PDF)
Uncategorized
One city held a mass passport-getting event
A New Orleans congressman organized a way for people to apply for their passports en masse.

While the number of Americans who do not have a passport has dropped steadily from more than 80% in 1990 to just over 50% now, a lack of knowledge around passport requirements still keeps a significant portion of the population away from international travel.
Over the four years that passed since the start of covid-19, passport offices have also been dealing with significant backlog due to the high numbers of people who were looking to get a passport post-pandemic.
Related: Here is why it is (still) taking forever to get a passport
To deal with these concurrent issues, the U.S. State Department recently held a mass passport-getting event in the city of New Orleans. Called the "Passport Acceptance Event," the gathering was held at a local auditorium and invited residents of Louisiana’s 2nd Congressional District to complete a passport application on-site with the help of staff and government workers.
'Come apply for your passport, no appointment is required'
"Hey #LA02," Rep. Troy A. Carter Sr. (D-LA), whose office co-hosted the event alongside the city of New Orleans, wrote to his followers on Instagram (META) . "My office is providing passport services at our #PassportAcceptance event. Come apply for your passport, no appointment is required."
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
The event was held on March 14 from 10 a.m. to 1 p.m. While it was designed for those who are already eligible for U.S. citizenship rather than as a way to help non-citizens with immigration questions, it helped those completing the application for the first time fill out forms and make sure they have the photographs and identity documents they need. The passport offices in New Orleans where one would normally have to bring already-completed forms have also been dealing with lines and would require one to book spots weeks in advance.
These are the countries with the highest-ranking passports in 2024
According to Carter Sr.'s communications team, those who submitted their passport application at the event also received expedited processing of two to three weeks (according to the State Department's website, times for regular processing are currently six to eight weeks).
While Carter Sr.'s office has not released the numbers of people who applied for a passport on March 14, photos from the event show that many took advantage of the opportunity to apply for a passport in a group setting and get expedited processing.
Every couple of months, a new ranking agency puts together a list of the most and least powerful passports in the world based on factors such as visa-free travel and opportunities for cross-border business.
In January, global citizenship and financial advisory firm Arton Capital identified United Arab Emirates as having the most powerful passport in 2024. While the United States topped the list of one such ranking in 2014, worsening relations with a number of countries as well as stricter immigration rules even as other countries have taken strides to create opportunities for investors and digital nomads caused the American passport to slip in recent years.
A UAE passport grants holders visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to 180 of the world’s 198 countries (this calculation includes disputed territories such as Kosovo and Western Sahara) while Americans currently have the same access to 151 countries.
stocks pandemic covid-19 grantsUncategorized
Fast-food chain closes restaurants after Chapter 11 bankruptcy
Several major fast-food chains recently have struggled to keep restaurants open.

Competition in the fast-food space has been brutal as operators deal with inflation, consumers who are worried about the economy and their jobs and, in recent months, the falling cost of eating at home.
Add in that many fast-food chains took on more debt during the covid pandemic and that labor costs are rising, and you have a perfect storm of problems.
It's a situation where Restaurant Brands International (QSR) has suffered as much as any company.
Related: Wendy's menu drops a fan favorite item, adds something new
Three major Burger King franchise operators filed for bankruptcy in 2023, and the chain saw hundreds of stores close. It also saw multiple Popeyes franchisees move into bankruptcy, with dozens of locations closing.
RBI also stepped in and purchased one of its key franchisees.
"Carrols is the largest Burger King franchisee in the United States today, operating 1,022 Burger King restaurants in 23 states that generated approximately $1.8 billion of system sales during the 12 months ended Sept. 30, 2023," RBI said in a news release. Carrols also owns and operates 60 Popeyes restaurants in six states."
The multichain company made the move after two of its large franchisees, Premier Kings and Meridian, saw multiple locations not purchased when they reached auction after Chapter 11 bankruptcy filings. In that case, RBI bought select locations but allowed others to close.
Image source: Chen Jianli/Xinhua via Getty
Another fast-food chain faces bankruptcy problems
Bojangles may not be as big a name as Burger King or Popeye's, but it's a popular chain with more than 800 restaurants in eight states.
"Bojangles is a Carolina-born restaurant chain specializing in craveable Southern chicken, biscuits and tea made fresh daily from real recipes, and with a friendly smile," the chain says on its website. "Founded in 1977 as a single location in Charlotte, our beloved brand continues to grow nationwide."
Like RBI, Bojangles uses a franchise model, which makes it dependent on the financial health of its operators. The company ultimately saw all its Maryland locations close due to the financial situation of one of its franchisees.
Unlike. RBI, Bojangles is not public — it was taken private by Durational Capital Management LP and Jordan Co. in 2018 — which means the company does not disclose its financial information to the public.
That makes it hard to know whether overall softness for the brand contributed to the chain seeing its five Maryland locations after a Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing.
Bojangles has a messy bankruptcy situation
Even though the locations still appear on the Bojangles website, they have been shuttered since late 2023. The locations were operated by Salim Kakakhail and Yavir Akbar Durranni. The partners operated under a variety of LLCs, including ABS Network, according to local news channel WUSA9.
The station reported that the owners face a state investigation over complaints of wage theft and fraudulent W2s. In November Durranni and ABS Network filed for bankruptcy in New Jersey, WUSA9 reported.
"Not only do former employees say these men owe them money, WUSA9 learned the former owners owe the state, too, and have over $69,000 in back property taxes."
Former employees also say that the restaurant would regularly purchase fried chicken from Popeyes and Safeway when it ran out in their stores, the station reported.
Bojangles sent the station a comment on the situation.
"The franchisee is no longer in the Bojangles system," the company said. "However, it is important to note in your coverage that franchisees are independent business owners who are licensed to operate a brand but have autonomy over many aspects of their business, including hiring employees and payroll responsibilities."
Kakakhail and Durranni did not respond to multiple requests for comment from WUSA9.
bankruptcy pandemicUncategorized
Industrial Production Increased 0.1% in February
From the Fed: Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization
Industrial production edged up 0.1 percent in February after declining 0.5 percent in January. In February, the output of manufacturing rose 0.8 percent and the index for mining climbed 2.2 p…
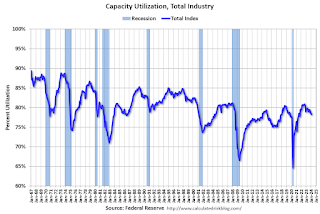
Industrial production edged up 0.1 percent in February after declining 0.5 percent in January. In February, the output of manufacturing rose 0.8 percent and the index for mining climbed 2.2 percent. Both gains partly reflected recoveries from weather-related declines in January. The index for utilities fell 7.5 percent in February because of warmer-than-typical temperatures. At 102.3 percent of its 2017 average, total industrial production in February was 0.2 percent below its year-earlier level. Capacity utilization for the industrial sector remained at 78.3 percent in February, a rate that is 1.3 percentage points below its long-run (1972–2023) average.Click on graph for larger image.
emphasis added
This graph shows Capacity Utilization. This series is up from the record low set in April 2020, and above the level in February 2020 (pre-pandemic).
Capacity utilization at 78.3% is 1.3% below the average from 1972 to 2022. This was below consensus expectations.
Note: y-axis doesn't start at zero to better show the change.
 The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.
The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.Industrial production increased to 102.3. This is above the pre-pandemic level.
Industrial production was above consensus expectations.
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Spread & Containment3 days ago
Spread & Containment3 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex






















