We Could Be Staring Down The Barrel of A Catastrophic NASDAQ Crash And Not Even Know It
We Could Be Staring Down The Barrel of A Catastrophic NASDAQ Crash And Not Even Know It
Submitted by Quoth the Raven at QTR’s Fringe Finance
It would certainly take a special confluence of factors for us to be staring down the barrel of…

Submitted by Quoth the Raven at QTR's Fringe Finance
It would certainly take a special confluence of factors for us to be staring down the barrel of a an unprecedented crash in tech stocks without noticing it’s coming. But I’m starting to entertain the idea that that is exactly where we are, we may not know how much pain we are truly in for - and we might not fathom how quickly it could come on and surprise us. While I've already talked about the folly of money printing and how it could destroy the U.S., its residual effects in markets are also worth paying close attention to.
For a little while now my friend on Twitter @rosemontseneca has been quietly pontificating that we are living 1999 all over again, we just don't notice it yet. I'm starting to seriously agree with him and I have been thinking to myself over the past week: “Why aren’t other people making this comparison yet? Stocks are extremely overvalued. What’s ‘different this time’?”
Indeed, I believe the next crash is going to come as a breakneck-style surprise. If I had a chance to publish this piece before Halloween, I was going to make the analogy of somebody sneaking in the back door of the house and waiting around the corner in the kitchen to hack us to death when we went to make our “stoned-in-our-underwear at 2AM” bologna sandwich. But instead I wound up going with the gun analogy for the title because I was too lazy to get this article out in the month of October.
But analogies aside, the point is still the same: the next big market plunge could be any day now, and will likely be led by tech. Let me explain my reasoning.
A couple of things need to happen in order for a major crash to be around the corner without us knowing it, in my opinion. The first thing that needs to happen is that the bubble needs to be more dangerous than prior crashes - nobody would panic at the nominal size of the 1999 bubble anymore and it would hardly be enough to scare today’s investors. They’d probably look at it as a “dip” to buy. The second thing that needs to happen is we need to be flying totally blind and distracted to the market’s insane valuation somehow. This is where the “surprise” factor - also known as the “oh shit” moment - comes in. The third thing that needs to happen is a catalyst that will shock and wake everybody up all at once.
So let’s talk about why this bubble could be more dangerous than previous ones. The NASDAQ is literally the 1999 tech bubble on steroids. It’s not going to come as any surprise to my readers that I want to point out that a significant amount of call buying that was done purposely back in 2020 is what sets us apart from 1999’s market.
People are weaponizing options, something that wasn’t being done in 1999. In 1999, it was just plain hysteria that drove stocks higher. Between March 2020 and now, there have been multiple documented examples - Goldman Sachs, Softbank, Bill Hwang, whatever the fuck is going on in Tesla - that the NASDAQ may not have a real bid underneath it and may be may have started its pre-hysteria run at a much higher “foundational” level thanks to planned gamma squeezes.
This was from September 2020, on the Financial Times:
SoftBank is the “Nasdaq whale” that has bought billions of dollars’ worth of US equity derivatives in a series of trades that stoked the fevered rally in big tech stocks before a sharp pullback on Thursday and Friday, according to people familiar with the matter.
The Japanese conglomerate had been snapping up options in tech stocks during the past month in huge amounts, fuelling the largest ever trading volumes in contracts linked to individual companies, these people said. One banker described it as a “dangerous” bet.
This was also from September 2020, on Zerohedge:
According to IFR Reuters, the investment bank made about $100 million trading Tesla alone over the last several months. The bank was engaged in trades that included "stock options, providing financing secured against Tesla’s shares, and buying and selling its convertible bonds," according to Bloomberg.
This means that when we start to fall, a crash could wind up running into an air pocket where bids normally would be and accelerate quicker. It also means that we may have distorted the market for hire far quicker than any other time in history.
And, of course, there were massive option bets in highly shorted names like GSX and IQ that Bill Hwang owned, before his fund, Archegos, blew up.
The weaponization of options helped the NASDAQ double in nearly 18 months. This is not normal for an individual equity, let alone an index.
But if this run higher was 1999 all over again, many would argue that we would notice it. We would learn from our mistakes, right?
Of course, that statement is great for a laugh: we never learn from our mistakes.
So how could we not notice things getting out of control? Has there been anything that has distracted us lately?
Photo: NBC
Between the 2020 election, dealing with the pandemic and then investing the time necessary to sift through the mainstream media news to try and figure out which 5% of the narrative they are telling us is actually true, it’s no surprise we literally haven’t been able to pull our collective heads out of our asses.
Put simply: we really haven’t had time to give a shit about markets.
Do you remember years ago, when markets were about 50% lower than where they are now and Janet Yellen and Carl Icahn were sounding alarm bells? Yellen said that assets appeared overvalued while Fed Chair and Icahn put a video up on his website warning about valuations. That seems like ancient history now. And hey: if they thought the markets were grossly overvalued then, what do they think now?
That silence you hear is the sound of nobody speaking up anymore. It’s a combination of groupthink buy-in, overestimating the Fed’s grip on things and people being too distraction trying to figure out how we’re gonna deal with our new lives in the age of a pandemic.
Additionally, and especially when it comes to tech stocks, bullshit begets more bullshit. What I mean by this is that when asset managers are successful thanks to the tech stock market being in an uber-bubble, they need to come up with excuses for why they’re actually outperforming markets, even if they don’t have a clue how they’re doing it. Tune into CNBC on any given day and you’ll see this: it’s why we hear asset managers like Cathie Wood alluding to things like valuations not mattering anymore. This type of toxic bilge then becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy and leads more sheep to the slaughter…I mean NASDAQ.
Finally, we need a catalyst that will set the market off lower. The easy pick for catalyst is rates and tapering. The “outside” picks are things like crypto crashing or other catalysts we may not have even fathomed yet (think Evergrande, but with another larger, unexpected company). My readers know that I have talked extensively about crypto potentially becoming a pin that picks the bubble. You can listen to more of my argument about that here.
On top of my “fringe” theses, we also have high profile asset managers like Bill Ackman coming out and begging the Fed to taper and raise rates.
Inflation is starting to get to a point where it is becoming a major political issue and the rest of the country is starting to notice how quickly prices are rising. This is doing things like pulling demand forward, as consumers anticipate continued price hikes and supply chain issues.
These types of unnatural behaviors by the consumer, coupled with Wall Street realizing that a lack of action from the Fed could be catastrophic, could wind up being a perfect storm that catalyzes a deleveraging from growth stocks. If rates do begin to rise - even slightly - it will be a tiny incentive for a few investors to get out of the market and seek yield elsewhere. Even the slightest of rate moves and the slightest of tech market selling could catalyze massive aftershocks in equity markets - especially if it catches people bit by surprise and the aforementioned bid under tech stocks rests on the air pocket that I think it does.
The point of the matter is we could be closer to a tech stock crash than we think.
Finally, many people would probably hypothesize that we would never have two crashes in such a short period of time. After all, we just “got over” a crash in March 2020; ergo, people expect the bull market to go on for decades now. The average investor has forgotten that recessions and crashes don’t care when the last bull market was and don’t care when the last bear market was. We are fooling ourselves with cognitive dissonance when we tell ourselves that another crash isn’t possible because one just happened. An easy way to accept this fact is to realize we never truly “recovered” from the post-Covid rally - we simply papered over the problem.
And while this thesis of mine is relatively simple I ask you to consider these three things when you take a step back and try to objectively examine whether a crash could take place any day now:
-
Is this tech bubble larger and more dangerous than 1999?
-
Have we been distracted to the point where we may not have noticed how deep the water is that we are treading in?
-
Is there any lack of potential catalysts on the horizon for a market crash?
My answers to these questions point me right back to my title: we really could be staring down the barrel of the next crash.
* * *
I’d love to hear your thoughts in the comments on my blog: Leave a comment
You can access this full article and all my archives by subscribing. Zerohedge readers get 10% off an annual subscription to my blog by using this special link here.
Spread & Containment
IFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
Today IFM Therapeutics announced the acquisition of IFM Due, one of its subsidiaries, by Novartis. Back in Sept 2019, IFM granted Novartis the right to…
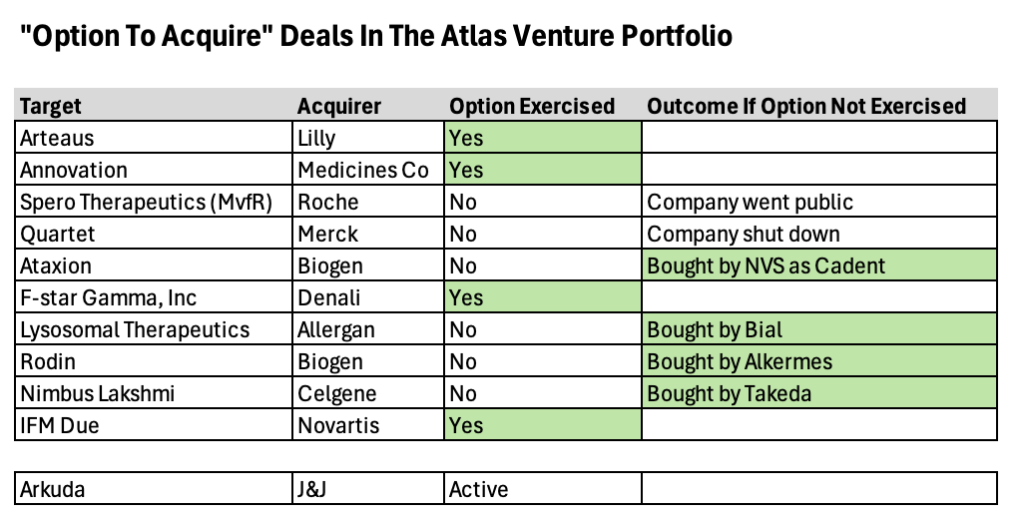
Today IFM Therapeutics announced the acquisition of IFM Due, one of its subsidiaries, by Novartis. Back in Sept 2019, IFM granted Novartis the right to acquire IFM Due as part of an “option to buy” collaboration around cGAS-STING antagonists for autoimmune disease.
This secures for IFM what is a rarity for a single biotech company: a liquidity hat trick, as this milestone represents the third successful exit of an IFM Therapeutics subsidiary since its inception in 2015.
Back in 2017, BMS purchased IFM’s NLRP3 and STING agonists for cancer. In early 2019, Novartis acquired IFM Tre for NLRP3 antagonists for autoimmune disease, which are now being studied in multiple Phase 2 studies. Then, later in 2019, Novartis secured the right to acquire IFM Due after their lead program entered clinical development. Since inception, across the three exits, IFM has secured over $700M in upfront cash payments and north of $3B in biobucks.
Kudos to the team, led by CEO Martin Seidel since 2019, for their impressive and continued R&D and BD success.
Option-to-Acquire Deals
These days option-based M&A deals aren’t in vogue: in large part because capital generally remains abundant despite the contraction, and there’s still a focus on “going big” for most startup companies. That said, lean capital efficiency around asset-centric product development with a partner can still drive great returns. In different settings or stages of the market cycle, different deal configurations can make sense.
During the pandemic boom, when the world was awash in capital chasing deals, “going long” as independent company was an easy choice for most teams. But in tighter markets, taking painful levels of equity dilution may be less compelling than securing a lucrative option-based M&A deal.
For historical context, these option-based M&A deals were largely borne out of necessity in far more challenging capital markets (2010-2012) on the venture front, when both the paucity of private financing and the tepid exit environment for early stage deals posed real risks to biotech investment theses. Pharma was willing to engage on early clinical or even preclinical assets with these risk-sharing structures as a way to secure optionality for their emerging pipelines.
As a comparison, in 2012, total venture capital funding into biotech was less than quarter of what it is now, even post bubble contraction, and back then we had witnessed only a couple dozen IPOs in the prior 3 years combined. And most of those IPOs were later stage assets in 2010-2012. Times were tough for biotech venture capital. Option-based deals and capital efficient business models were part of ecosystem’s need for experimentation and external R&D innovation.
Many flavors of these option-based deals continued to get done for the rest of the decade, and indeed some are still getting done, albeit at a much less frequent cadence. Today, the availability of capital on the supply side, and the reduced appetite for preclinical or early stage acquisitions on the demand side, have limited the role of these option to buy transactions in the current ecosystem.
But if the circumstances are right, these deals can still make some sense: a constructive combination of corporate strategy, funding needs, risk mitigation, and collaborative expertise must come together. In fact, Arkuda Therapeutics, one of our neuroscience companies, just announced a new option deal with Janssen.
Stepping back, it’ s worth asking what has been the industry’s success rate with these “option to buy” deals.
Positive anecdotes of acquisition options being exercised over the past few years are easy to find. We’ve seen Takeda exercise its right to acquire Maverick for T-cell engagers and GammaDelta for its cellular immunotherapy, among other deals. AbbVie recently did the same with Mitokinin for a Parkinson’s drug. On the negative side, in a high profile story last month, Gilead bailed on purchasing Tizona after securing that expensive $300M option a few years ago.
But these are indeed just a few anecdotes; what about data since these deal structures emerged circa 2010? Unfortunately, as these are mostly private deals with undisclosed terms, often small enough to be less material to the large Pharma buyer, there’s really no great source of comprehensive data on the subject. But a reasonable guess is that the proportion of these deals where the acquisition right is exercised is likely 30%.
This estimate comes from triangulating from a few sources. A quick and dirty dataset from DealForma, courtesy of Tim Opler at Stifel, suggests 30% or so for deals 2010-2020. Talking to lawyers from Goodwin and Cooley, they also suggest ballpark of 30-50% in their experience. The shareholder representatives at SRS Acquiom (who manage post-M&A milestones and escrows) also shared with me that about 33%+ of the option deals they tracked had converted positively to an acquisition. As you might expect, this number is not that different than milestone payouts after an outright acquisition, or future payments in licensing deals. R&D failure rates and aggregate PoS will frequently dictate that within a few years, only a third of programs will remain alive and well.
Atlas’ experience with Option-based M&A deals
Looking back, we’ve done nearly a dozen of these option-to-buy deals since 2010. These took many flavors, from strategic venture co-creation where the option was granted at inception (e.g., built-to-buy deals like Arteaus and Annovation) to other deals where the option was sold as part of BD transaction for a maturing company (e.g., Lysosomal Therapeutics for GBA-PD).
Our hit rate with the initial option holder has been about 40%; these are cases where the initial Pharma that bought the option moves ahead and exercises that right to purchase the company. Most of these initial deals were done around pre- or peri-clinical stage assets. But equally interesting, if not more so, is that in situations where the option expired without being exercised, but the asset continued forward into development, all of these were subsequently acquired by other Pharma buyers – and all eight of these investments generated positive returns for Atlas funds. For example, Rodin and Ataxion had option deals with Biogen (here, here) that weren’t exercised, and went on to be acquired by Alkermes and Novartis (here, here). And Nimbus Lakshmi for TYK2 was originally an option deal with Celgene, and went on to be purchased by Takeda.
For the two that weren’t acquired via the option or later, science was the driving factor. Spero was originally an LLC holding company model, and Roche had a right to purchase a subsidiary with a quorum-sensing antibacterial program (MvfR). And Quartet had a non-opioid pain program where Merck had acquired an option. Both of these latter programs were terminated for failing to advance in R&D.
Option deals are often criticized for “capping the upside” or creating “captive companies” – and there’s certainly some truth to that. These deals are structured, typically with pre-specified return curves, so there is a dollar value that one is locked into and the presence of the option right typically precludes a frothy IPO scenario. But in aggregate across milestones and royalties, these deals can still secure significant “Top 1%” venture upside though if negotiated properly and when the asset reaches the market: for example, based only on public disclosures, Arteaus generated north of $300M in payments across the upfront, milestones, and royalties, after spending less than $18M in equity capital. The key is to make sure the right-side of the return tail are included in the deal configuration – so if the drug progresses to the market, everyone wins.
Importantly, once in place, these deals largely protect both the founders and early stage investors from further equity dilution. While management teams that are getting reloaded with new stock with every financing may be indifferent to dilution, existing shareholders (founders and investors alike) often aren’t – so they may find these deals, when negotiated favorably, to be attractive relative to the alternative of being washed out of the cap table. This is obviously less of a risk in a world where the cost of capital is low and funding widely available.
These deal structures also have some other meaningful benefits worth considering though: they reduce financing risk in challenging equity capital markets, as the buyer often funds the entity with an option payment through the M&A trigger event, and they reduce exit risk, as they have a pre-specified path to realizing liquidity. Further, the idea that the assets are “tainted” if the buyer walks hasn’t been borne out in our experience, where all of the entities with active assets after the original option deal expired were subsequently acquired by other players, as noted above.
In addition, an outright sale often puts our prized programs in the hands of large and plodding bureaucracies before they’ve been brought to patients or later points in development. This can obviously frustrate development progress. For many capable teams, keeping the asset in their stewardship even while being “captive”, so they can move it quickly down the R&D path themselves, is an appealing alternative to an outright sale – especially if there’s greater appreciation of value with that option point.
Option-based M&A deals aren’t right for every company or every situation, and in recent years have been used only sparingly across the sector. They obviously only work in practice for private companies, often as alternative to larger dilutive financings on the road to an IPO. But for asset-centric stories with clear development paths and known capital requirements, they can still be a useful tool in the BD toolbox – and can generate attractive venture-like returns for shareholders.
Like others in the biotech ecosystem, Atlas hasn’t done many of these deals in recent funds. And it’s unlikely these deals will come back in vogue with what appears to be 2024’s more constructive fundraising environment (one that’s willing to fund early stage stories), but if things get tighter or Pharma re-engages earlier in the asset continuum, these could return to being important BD tools. It will be interesting to see what role they may play in the broader external R&D landscape over the next few years.
Most importantly, circling back to point of the blog, kudos to the team at IFM and our partners at Novartis!
The post IFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A appeared first on LifeSciVC.
preclinical pandemic mitigationGovernment
Student Loan Forgiveness Is Robbing Peter To Pay Paul
Student Loan Forgiveness Is Robbing Peter To Pay Paul
Via SchiffGold.com,
With President Biden’s Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE)…

With President Biden’s Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE) plan set to extend more student loan relief to borrowers this summer, the federal government is pretending it can wave a magic wand to make debts disappear. But the truth of student debt “relief” is that they’re simply shifting the burden to everyone else, robbing Peter to pay Paul and funneling more steam into an inflation pressure cooker that’s already set to burst.
Starting July 1st, new rules go into effect that change the discretionary income requirements for their payment plans from 10% to only 5% for undergraduates, leading to lower payments for millions. Some borrowers will even have their owed balances revert to zero.
What the plan doesn’t describe, predictably, is how that burden will be shifted to the rest of the country by stealing value out of their pockets via new taxes or increased inflation, which still simmering well above levels seen in early 2020 before the Fed printed trillions in Covid “stimulus” money. They’re rewarding students who took out loans they can’t afford and punishing those who paid their way or repaid their loans, attending school while living within their means. And they’re stealing from the entire country to finance it.
Biden actually claims that a continuing Covid “emergency” is what gives him the authority to offer student loan forgiveness to begin with. As with any “temporary” measure that gives state power a pretense to grow, or gives them an excuse to collect more revenue (I’m looking at you, federal income tax), COVID-19 continues to be the gift that keeps on giving for power and revenue-hungry politicians even as the CDC reclassifies the virus as a threat similar to the seasonal flu.
The SAVE plan takes the burden of billions of dollars in owed payments away from students and adds it to a national debt that’s already ballooning to the tune of a mind-boggling trillion dollars every 3 months. If all student loan debt were forgiven, according to the Brookings Institution, it would surpass the cumulative totals for the past 20 years for multiple existing tax credits and welfare programs:
“Forgiving all student debt would be a transfer larger than the amounts the nation has spent over the past 20 years on unemployment insurance, larger than the amount it has spent on the Earned Income Tax Credit, and larger than the amount it has spent on food stamps.”
Ironically enough, adding hundreds of billions to the national debt from Biden’s program is likely to cause the most pain to the very demographics the Biden administration claims to be helping with its plan: poor people, anyone who skipped college entirely or paid their loans back, and other already overly-indebted young adults, whose purchasing power is being rapidly eroded by out-of-control government spending and central bank monetary shenanigans. It effectively transfers even more wealth from the poor to the wealthy, a trend that Covid-era measures have taken to new extremes.
As Ron Paul pointed out in a recent op-ed for the Eurasia Review:
“…these loans will be paid off in part by taxpayers who did not go to college, paid their own way through school, or have already paid off their student loans. Since those with college degrees tend to earn more over time than those without them, this program redistributes wealth from lower to higher income Americans.”
Even some progressives are taking aim at the plan, not because it shifts the debt burden to other Americans, but because it will require cutting welfare or sacrificing other expensive social programs promised by Biden such as universal pre-K. For these critics, the issue isn’t so much that spending and debt are totally out of control, but that they’re being funneled into the wrong issues.
Progressive “solutions” always seem to take the form of slogans like “tax the wealthy,” a feel-good bromide that for lawmakers always seems to translate into increased taxes for the middle and lower-upper class. Meanwhile, the .01% continue to avoid taxes through offshore accounts, money laundering trickery dressed up as philanthropy, and general de facto ownership of the system through channels like political donations and aggressive lobbying.
If new waves of college applicants expect loan forgiveness plans to continue, it also encourages schools to continue raising tuition and motivates prospective students to continue with even more irresponsible borrowing.
This puts pressure on the Fed to keep interest rates lower to help accommodate waves of new student loan applicants from sparkly-eyed young borrowers who figure they’ll never really have to pay the money back.
With the Fed already expected to cut rates this year despite inflation not being properly under control, the loan forgiveness scheme is just one of many factors conspiring to cause inflation to start running hotter again, spiraling out of control, as the entire country is forced to pay the hidden tax of price increases for all their basic needs.
Uncategorized
Bougie Broke The Financial Reality Behind The Facade
Social media users claiming to be Bougie Broke share pictures of their fancy cars, high-fashion clothing, and selfies in exotic locations and expensive…
Social media users claiming to be Bougie Broke share pictures of their fancy cars, high-fashion clothing, and selfies in exotic locations and expensive restaurants. Yet they complain about living paycheck to paycheck and lacking the means to support their lifestyle.
Bougie broke is like “keeping up with the Joneses,” spending beyond one’s means to impress others.
Bougie Broke gives us a glimpse into the financial condition of a growing number of consumers. Since personal consumption represents about two-thirds of economic activity, it’s worth diving into the Bougie Broke fad to appreciate if a large subset of the population can continue to consume at current rates.
The Wealth Divide Disclaimer
Forecasting personal consumption is always tricky, but it has become even more challenging in the post-pandemic era. To appreciate why we share a joke told by Mike Green.
Bill Gates and I walk into the bar…
Bartender: “Wow… a couple of billionaires on average!”
Bill Gates, Jeff Bezos, Elon Musk, Mark Zuckerberg, and other billionaires make us all much richer, on average. Unfortunately, we can’t use the average to pay our bills.
According to Wikipedia, Bill Gates is one of 756 billionaires living in the United States. Many of these billionaires became much wealthier due to the pandemic as their investment fortunes proliferated.
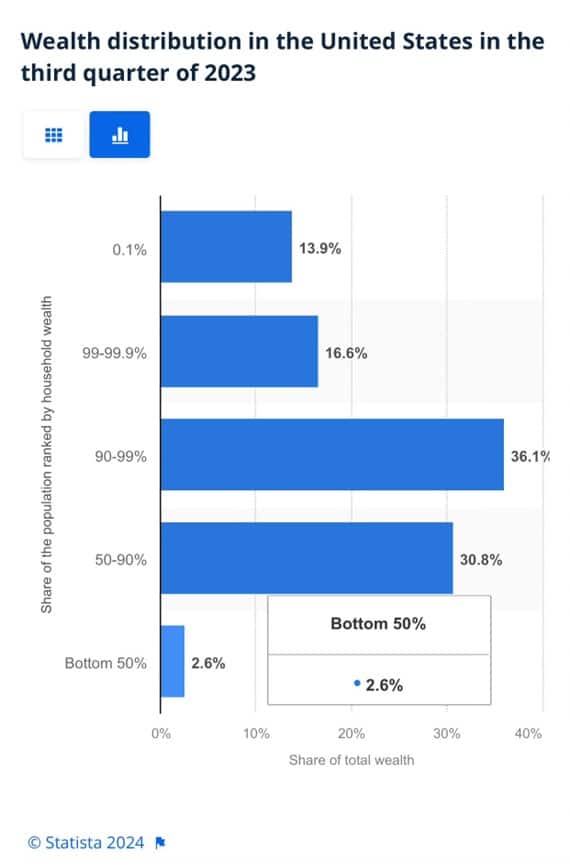
To appreciate the wealth divide, consider the graph below courtesy of Statista. 1% of the U.S. population holds 30% of the wealth. The wealthiest 10% of households have two-thirds of the wealth. The bottom half of the population accounts for less than 3% of the wealth.
The uber-wealthy grossly distorts consumption and savings data. And, with the sharp increase in their wealth over the past few years, the consumption and savings data are more distorted.
Furthermore, and critical to appreciate, the spending by the wealthy doesn’t fluctuate with the economy. Therefore, the spending of the lower wealth classes drives marginal changes in consumption. As such, the condition of the not-so-wealthy is most important for forecasting changes in consumption.
Revenge Spending
Deciphering personal data has also become more difficult because our spending habits have changed due to the pandemic.
A great example is revenge spending. Per the New York Times:
Ola Majekodunmi, the founder of All Things Money, a finance site for young adults, explained revenge spending as expenditures meant to make up for “lost time” after an event like the pandemic.
So, between the growing wealth divide and irregular spending habits, let’s quantify personal savings, debt usage, and real wages to appreciate better if Bougie Broke is a mass movement or a silly meme.
The Means To Consume
Savings, debt, and wages are the three primary sources that give consumers the ability to consume.
Savings
The graph below shows the rollercoaster on which personal savings have been since the pandemic. The savings rate is hovering at the lowest rate since those seen before the 2008 recession. The total amount of personal savings is back to 2017 levels. But, on an inflation-adjusted basis, it’s at 10-year lows. On average, most consumers are drawing down their savings or less. Given that wages are increasing and unemployment is historically low, they must be consuming more.
Now, strip out the savings of the uber-wealthy, and it’s probable that the amount of personal savings for much of the population is negligible. A survey by Payroll.org estimates that 78% of Americans live paycheck to paycheck.

More on Insufficient Savings
The Fed’s latest, albeit old, Report on the Economic Well-Being of U.S. Households from June 2023 claims that over a third of households do not have enough savings to cover an unexpected $400 expense. We venture to guess that number has grown since then. To wit, the number of households with essentially no savings rose 5% from their prior report a year earlier.
Relatively small, unexpected expenses, such as a car repair or a modest medical bill, can be a hardship for many families. When faced with a hypothetical expense of $400, 63 percent of all adults in 2022 said they would have covered it exclusively using cash, savings, or a credit card paid off at the next statement (referred to, altogether, as “cash or its equivalent”). The remainder said they would have paid by borrowing or selling something or said they would not have been able to cover the expense.
Debt
After periods where consumers drained their existing savings and/or devoted less of their paychecks to savings, they either slowed their consumption patterns or borrowed to keep them up. Currently, it seems like many are choosing the latter option. Consumer borrowing is accelerating at a quicker pace than it was before the pandemic.
The first graph below shows outstanding credit card debt fell during the pandemic as the economy cratered. However, after multiple stimulus checks and broad-based economic recovery, consumer confidence rose, and with it, credit card balances surged.
The current trend is steeper than the pre-pandemic trend. Some may be a catch-up, but the current rate is unsustainable. Consequently, borrowing will likely slow down to its pre-pandemic trend or even below it as consumers deal with higher credit card balances and 20+% interest rates on the debt.

The second graph shows that since 2022, credit card balances have grown faster than our incomes. Like the first graph, the credit usage versus income trend is unsustainable, especially with current interest rates.

With many consumers maxing out their credit cards, is it any wonder buy-now-pay-later loans (BNPL) are increasing rapidly?
Insider Intelligence believes that 79 million Americans, or a quarter of those over 18 years old, use BNPL. Lending Tree claims that “nearly 1 in 3 consumers (31%) say they’re at least considering using a buy now, pay later (BNPL) loan this month.”More telling, according to their survey, only 52% of those asked are confident they can pay off their BNPL loan without missing a payment!
Wage Growth
Wages have been growing above trend since the pandemic. Since 2022, the average annual growth in compensation has been 6.28%. Higher incomes support more consumption, but higher prices reduce the amount of goods or services one can buy. Over the same period, real compensation has grown by less than half a percent annually. The average real compensation growth was 2.30% during the three years before the pandemic.
In other words, compensation is just keeping up with inflation instead of outpacing it and providing consumers with the ability to consume, save, or pay down debt.
It’s All About Employment
The unemployment rate is 3.9%, up slightly from recent lows but still among the lowest rates in the last seventy-five years.

The uptick in credit card usage, decline in savings, and the savings rate argue that consumers are slowly running out of room to keep consuming at their current pace.
However, the most significant means by which we consume is income. If the unemployment rate stays low, consumption may moderate. But, if the recent uptick in unemployment continues, a recession is extremely likely, as we have seen every time it turned higher.
It’s not just those losing jobs that consume less. Of greater impact is a loss of confidence by those employed when they see friends or neighbors being laid off.
Accordingly, the labor market is probably the most important leading indicator of consumption and of the ability of the Bougie Broke to continue to be Bougie instead of flat-out broke!
Summary
There are always consumers living above their means. This is often harmless until their means decline or disappear. The Bougie Broke meme and the ability social media gives consumers to flaunt their “wealth” is a new medium for an age-old message.
Diving into the data, it argues that consumption will likely slow in the coming months. Such would allow some consumers to save and whittle down their debt. That situation would be healthy and unlikely to cause a recession.
The potential for the unemployment rate to continue higher is of much greater concern. The combination of a higher unemployment rate and strapped consumers could accentuate a recession.
The post Bougie Broke The Financial Reality Behind The Facade appeared first on RIA.
recession unemployment pandemic economic recovery stimulus fed recession recovery interest rates unemployment stimulus-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges























