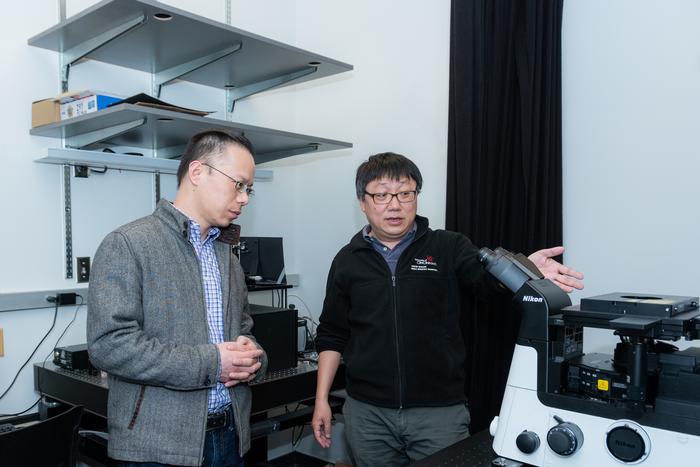
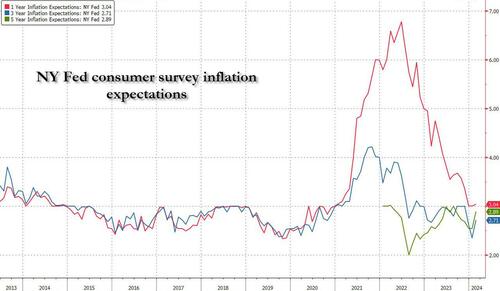
The University of Cincinnati’s Jiajie Diao and Yujie Sun have a simple approach to research: Keep an open mind, and follow the data wherever it leads.
This means even accidental findings are taken seriously, and the path toward their goals is not always straight from point A to point B. This mindset has led to a fruitful collaboration, with the researchers recently publishing articles on new probes that provide more information on how cells function in the journals Chemical Science and Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
Looking deeper into tissue
Previous probes developed by the team focused on a specialized structure called a lysosome that acts as the “recycling center” within cells, reusing broken or malfunctioning materials for different purposes. Abnormal pH levels within lysosomes are associated with cellular malfunctions that can lead to diseases like cancer and Alzheimer’s disease.
Two previous generations of probes provided increasingly more detailed information about lysosome acidity at the cellular level, but the short wavelengths of light that activated the probe were not strong enough to penetrate tissue.
“We had to use shorter wavelengths to excite the probe, and normally it’s visible wavelengths, so their penetration is really limited,” said Diao, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Cancer Biology in UC’s College of Medicine. “We could not go deep, so it’s good for cellular imaging, but it’s not good for tissue or research in living organisms (in vivo).”
The latest advancement from the researchers was to use two lower energy photons with a longer wavelength to activate the probes. Called two-photon imaging, the longer wavelengths can penetrate deeper so that research can be done on animal models and human tissue.
Sun and Diao developed three two-photon probes that locate at different areas of cells and can be used to better visualize organelles, or specialized structures within cells.
“It can be used for two-photon microscopy to show 3D images of cells, organoids and tissues,” said Sun, PhD, professor in UC’s Department of Chemistry. “We are developing new two-photon-absorbing fluorescent probes which are sensitive to various factors, such as pH, viscosity and ionic species.”
“Many times, tissue or even in vivo measurement is more important than cellular,” Diao added. “This probe will illuminate individual organelles, and it’s much better than the commercial two-photon probes currently available.”
Detailing individual cell viability
Researchers testing new treatments for diseases like cancer measure cell viability, or whether or not a cell is dying or remains active, after coming into contact with a treatment.
“When you give a treatment, the first thing you always check is the cell viability,” Diao said.
Traditionally, cell viability was measured by looking at a large population of millions of cells at a time, which Diao said is like giving an entire group of students the same exam grade based on their average score.
“As everyone can feel at some time, it’s unfair, because everyone is different,” Diao said. “And every cell is different.”
Progress in the field of cell biology has led to new interest in measuring individual cell viability, which is like grading each student based on their own performance on the exam. This provides more specific insights to researchers by showing how different types of cells react to treatments being tested.
When working on the previous probe that measured cells’ acidity levels, Diao and Sun created a control version that was not sensitive to changes in pH levels. Completely by accident, they found that even though this version of the probe was structurally similar, it behaved differently, locating itself at different organelles.
The new probe initially stains the cell’s mitochondria, which acts as the power plant providing energy to the cell. But when the cell is damaged, the probe moves itself and stains the nucleus, which contains the cell’s genetic material.
“Eventually the signal on the mitochondria will start getting dim, and the signal on the nucleus will get stronger, so by measuring the color intensity ratio between the mitochondria and the nucleus, we can quantitatively assess the viability of individual cells,” Diao said. “That’s a very new concept. Nobody has done this before.”
Long term, the team hopes the probe can be used to learn more about biological differences that affect whether a cell is immediately killed by a treatment or develops resistance and is unaffected.
“There must be something different,” Diao said. “We want to kill the bad cells and we want to make the good cells live longer. We want to assist that at an individual cell level.”
Sun said they will also work to extend what is known as the probe’s spectral window, or the maximum wavelength that can be used to activate the probe.
“Because longer wavelength photons have better tissue penetration, we will be able to see deeper,” Sun said.
Successful collaboration
Sun and Diao are the co–directors of UC’s Center for Chemical Imaging in Biomedicine, which has an aim of pushing the boundaries of imaging through developing new methods, probes and equipment.
Since joining forces, the duo has been prolific in publishing research and making advancements. Diao credits their joint mindset of not having any preconceived notions of where the research may lead for their success.
“I think the most important thing is always keeping an open mind, communicating frequently and not getting limited,” he said. “We always say data is data. Many times the biggest fight will be the fight between some preset imagination.”
With larger goals always in mind, the research team constantly adjusts expectations and goals when they see an opportunity for tangible progress.
Diao noted they originally started working together with the aim of immediately developing a two-photon probe, but they didn’t have the right experience. Rather than toiling away aimlessly, they switched gears, developed cellular probes and gained the knowledge needed to create the two-photon probes.
Sun said another key aspect of the partnership is chemistry graduate student Rui Chen, who Diao and Sun co-advise.
“Rui has been the bridge between our groups, and therefore Jiajie is fully aware of the progress we are making in my lab,” Sun said. “The complementary expertise between our two groups really makes us a great team to work synergistically together. I’m optimistic about our future achievements in bioimaging.”
Journal
Chemical Science
DOI
10.1039/D3SC01537H
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animal tissue samples
Article Title
Quantifying cell viability through organelle ratiometric probing
Article Publication Date
7-Sep-2023
COI Statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.