Uncategorized
Silence Around Surgical Errors Is Jeopardizing Patients, Experts Say
Silence Around Surgical Errors Is Jeopardizing Patients, Experts Say
Authored by Amy Denney via The Epoch Times (Emphasis ours),
Follow the…
Authored by Amy Denney via The Epoch Times (Emphasis ours),
Follow the entire "What You Need to Know About Surgery" series here.
In this series, we’ll share how to determine if your surgery is right for you, how to ask the right questions, and what you can do to prepare and recover optimally
There’s a certain logic to doctors who don’t disclose their mistakes: their reputation, discipline, and the looming threat of medical malpractice lawsuits incentivize silence. However, patients display an unexpected silence about their own suffering—even when they know mistakes have been made.
Both problems undermine a patient-focused environment and stifle error reporting that could reduce medical mistakes.
The thought of medical errors isn’t likely to be on patients' minds as they’re wheeled into an operating room, according to research by the Institute for Healthcare Improvement and National Patient Safety Foundation.
In fact, these watchdog groups discovered in their poll of 2,536 adults that nearly two-thirds of Americans don’t believe medical errors are likely to happen to them. The harsh reality is that 21 percent have experienced at least one.
Patient advocacy groups are convinced that speaking up about errors can actually make a difference in lowering systemic risks for everyone who needs surgery. However, many patients don't report mistakes even when they become aware that an error is responsible for their present suffering.
Among the most egregious surgical errors are receiving the wrong operation, having surgery on the wrong body part, having something left inside the body, or surgery for a diagnosis that wasn’t correct to begin with.
A Major Cause of Death
It’s been 24 years since the Institute of Medicine’s “To Err is Human” report was published, drawing broad attention to medical mistakes that kill up to 98,000 Americans annually. The exact number of deaths is controversial, mostly because there isn't a standardized way to collect and report this kind of data. Death certificates don't reliably code medical errors leading to death, further obscuring the problem.
A 2016 study found about 250,000 deaths annually are due to medical error, making it the third leading cause of death in the United States, where it’s more problematic than other developed countries.
Louise Aron was injured during surgery—her small intestine was nicked during a liver stent procedure—and she died shortly afterward. Though she had stage 4 colon cancer, the surgery wasn't considered high-risk. The mistake prompted the surgical team to suture her and transfer her to immediate hospice care.
Her daughter, Dr. Rosia Parrish, told The Epoch Times that she’s still overwhelmed with regret and sorrow and has yet to review the medical records to understand how the situation was handled.
“The sudden shift to hospice was heartbreaking, as the surgery was initially expected to be life-saving or at least life-extending, but it did not achieve either of these outcomes,” she said. “In hindsight, I wish we had chosen a top-tier hospital, even if it meant traveling farther.”
Not all errors result in tragedy. Most surgical errors are “near misses,” events that could have harmed a patient but by chance or mitigation did not. Surgery accounts for about a quarter of medical errors, but others might involve care received before or after an operation. For instance, medication, communication, and infection are common sources of mistakes outside a surgeon’s purview.
Regardless of who’s to blame, the lack of accountability—or even acknowledgment—breaks a learning feedback loop that protects patient safety in the future and reduces major catastrophes.
Patients Expect Errors, Not Lies
Perhaps the irony of medical errors is that honesty turns out to be the best policy for hospitals, doctors, and sometimes even patients.
A great deal of research shows that patients who are told about mistakes are more likely to follow medical advice, and continue with care while being less likely to seek malpractice lawsuits, according to “Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses.”
“Patients have the right to know; patients and the public strongly desire disclosure. Failure to disclose mistakes and unanticipated outcomes limits opportunities for evaluation of systems and processes, and for sharing knowledge gained by publishing safety alerts across organizations, conducting educational sessions, modifying practice, and offering opportunities for improved performance,” the book states.
Dr. Parrish found herself once again facing the horrors of surgical complications a year after her mother’s death when she had an emergency cesarean birth.
In this case, the staff didn’t thoroughly review her medical history. Dr. Parrish experienced cardiomegaly (enlarged heart), postpartum hypertension, and nocturnal hypoxia—a condition characterized by low nighttime oxygen levels.
She used an oxygen tank for more than a month, had a series of pulmonology and cardiology appointments for several years, and continues to have no nerve sensation above and below her c-section scar.
In stark contrast to her mother’s death after which there were no apologies, Dr. Parrish’s hospital provided exceptional postoperative care with additional visits and even provided her with internal medical records that were not part of her file. Apologies facilitated healing.
“I worked with them for approximately six months, and their support was invaluable,” she said. “In my case, there were apologies from my main surgeon, who acknowledged the shortcomings of the surgery and the birth. I also processed my birth with my team of midwives as well.”
The Problem With ‘I’m Sorry’
Many states have “apology laws,” which are designed to allow for honest communication between physicians and injured patients.
However, the American Medical Association Journal of Ethics said they don’t go far enough. For instance, few states have laws protecting expressions both of sympathy and of fault from being entered into medical malpractice lawsuit evidence. This puts an unofficial gag on doctors, it said.
On the other hand, only 10 states even require physicians to disclose an error to the patient. Some doctors hide behind the fact that the definition of “medical error” is vague.
Adverse events are a type of injury that often happens in surgical treatment that isn’t really caused by the underlying medical issue of the patient. Adverse events are preventable, but not all are the result of an error, according to medical error and prevention training for clinicians. Preventable adverse events occur when there is a “failure to follow accepted practices.”
There are 29 “serious reportable events,” dubbed “never events” for the fact that they should never happen to patients. The list was created in 2006 by the National Quality Forum.
In Search of Better Surgical Centers
Not all hospitals embrace safety enhancements, nor do they rapidly apply new findings found to lower errors. Several volunteer reporting systems have cropped up in an effort to get the stakeholders in the health care system to change their behavior.
That allows patients to get a glimpse of the safety environment before they schedule surgery. The Leapfrog Group, a nonprofit watchdog organization for health care consumers and purchasers, started publicly acknowledging in a searchable database those hospitals that respond to never events in their facilities by:
- Reporting the event to at least one reporting program: The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO), a state reporting program, or a patient safety organization.
- Performing a root cause analysis.
- Waiving all costs related to the never event and refraining from seeking reimbursement from the patient or a third-party payer.
- Apologizing to the patient and/or family affected.
Sincere apologies can bridge broken trust. Evidence shows patients are most angry when nobody takes responsibility for an adverse event, according to LeapFrog.
“Hospitals often fear that issuing a formal apology opens up a door for malpractice suits. Ironically, research indicates that malpractice suits are often the result of a failure on the hospital’s part to communicate openly with the patient and apologize for its error,” according to LeapFrog.
The Terror of Errors
In Linda Kehart’s case, errors seemed probable but the situation was full of ambiguity, which can be the case with surgery. Risks are heightened when patients are under anesthesia.
In such situations, the only witnesses to errors are the health care team. Fear of negative consequences—retribution, job security, malpractice lawsuits, and reputation damage—might mean providers only report those errors associated with harm or those that can't be “covered up,” according to “Patient Safety and Quality.”
Earlier this year, Ms. Kehart woke up in an intensive care unit unable to get answers for why she was there after a standard stent procedure.
She was told she needed a longer hospital stay. She thought she overheard someone mention that she had coded—medical language for a cardiac arrest. There was also talk amid staff of contrast dye allergy listed on her chart that she repeatedly told them was an error. Despite large teams of clinicians going in and out of her room, nobody seemed interested in anything she asked.
“This nurse gets three inches from my face and says, ‘Mrs. Kehart, I want you to listen to us, be quiet, and do what we say.’ I said, ‘Excuse me. I may be old but I’m not stupid. Let’s talk about what’s happening.’ And they wouldn’t. They said I had to stay but they wouldn’t tell me why,” Ms. Kehart recalled.
Frustrated by the lack of transparency, she demanded to be discharged. The hospital refused to let her leave in a wheelchair and made her sign paperwork, which later disappeared, on which she wrote that nobody would answer her questions about what transpired during her surgery.
“I expect the care to come from qualified professionals and caring to come from everyone associated with anyone who becomes involved in the health care system. I find both of those challenging right now,” said Ms. Kehart, whose career involved work improving access to health care.
The Power of Being Heard
She used her connections and story to challenge the local system. She had never met her surgeon prior to the procedure, and later discovered she had an arterial hematoma, an injury to a blood vessel in her neck. One hospital administrator did ask her to write about how the ordeal made her feel so he could use the example with residents that he teaches.
“I appreciated that attitude. I still have a lot of stress,” Ms. Kehart said. “I’ve had a lot of surgeries, but I’ve never had any worries before. It’s scary now.”
Most patients don’t believe filing reports will make a difference. Four in 10 of those who didn’t report medical errors in the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) poll said they didn’t know how to.
Confusion is understandable. There is no universal system that patients can use for reporting errors. Most states have few guidelines, and the burden of creating a system for reporting errors falls on each individual hospital or health system.
Errors can be reported to the state public health department and the state medical licensing board to make a complaint about a physician, as well as to the Joint Safety Commission, a nonprofit organization that accredits hospitals and is responsible for patient safety.
There are some voluntary reporting systems, too, such as the Institute for Safe Medication Practices, which takes complaints related to medication errors from patients and health care providers.
Uneducated Patients Perpetuate Harm
The burden of patient safety requires a buy-in from the entire surgical team, according to Dr. P.F. Stahel, who authored an essay on patient safety for Bone and Joint.
Patients are perhaps the less obvious stakeholder, but Dr. Stahel and patient safety groups agree that not speaking up about medical mistakes is a contributing factor to the proliferation of errors.
Research has found that patients who are involved in their care, ask questions, and speak up—having high “health literacy”—can help minimize errors.
However, recognizing when an error has occurred can be challenging. Only one-third of patients have been told that a mistake occurred to them, according to IHI data.
And nearly half of American adults have trouble understanding or using health care information, according to an Institute of Medicine report. This becomes a stumbling block to improving care quality and reducing health costs.
“At some point, most individuals will encounter health information they cannot understand,” according to a statement about the report. “Even well-educated people with strong reading and writing skills may have trouble comprehending a medical form or doctor's instructions regarding a drug or procedure.”
Empowering Patients to Reduce Surgical Errors
The Joint Commission launched its “Speak Up” program in 2002 in an effort to raise health literacy.
Among its surgical-related advice:
- Ask about safety, including requesting that the area on your body being operated on gets marked.
- Tell a health care professional if you think they are confusing you with another patient.
- Notice whether caregivers have washed their hands, and don’t be afraid to remind them.
- Make sure nurses and doctors check your wristband identification before treatment or medication.
- Write down and keep important information they’ve shared with you.
- Ask a family member or friend to be your advocate.
- Ask your surgeon if a “timeout” is performed before surgery. These help mitigate errors by pausing so the team can double-check vital information.
Read the entire "What You Need to Know About Surgery" series here.
Uncategorized
Wendy’s has a new deal for daylight savings time haters
The Daylight Savings Time promotion slashes prices on breakfast.

Daylight Savings Time, or the practice of advancing clocks an hour in the spring to maximize natural daylight, is a controversial practice because of the way it leaves many feeling off-sync and tired on the second Sunday in March when the change is made and one has one less hour to sleep in.
Despite annual "Abolish Daylight Savings Time" think pieces and online arguments that crop up with unwavering regularity, Daylight Savings in North America begins on March 10 this year.
Related: Coca-Cola has a new soda for Diet Coke fans
Tapping into some people's very vocal dislike of Daylight Savings Time, fast-food chain Wendy's (WEN) is launching a daylight savings promotion that is jokingly designed to make losing an hour of sleep less painful and encourage fans to order breakfast anyway.
Image source: Wendy's.
Promotion wants you to compensate for lost sleep with cheaper breakfast
As it is also meant to drive traffic to the Wendy's app, the promotion allows anyone who makes a purchase of $3 or more through the platform to get a free hot coffee, cold coffee or Frosty Cream Cold Brew.
More Food + Dining:
- Taco Bell menu tries new take on an American classic
- McDonald's menu goes big, brings back fan favorites (with a catch)
- The 10 best food stocks to buy now
Available during the Wendy's breakfast hours of 6 a.m. and 10:30 a.m. (which, naturally, will feel even earlier due to Daylight Savings), the deal also allows customers to buy any of its breakfast sandwiches for $3. Items like the Sausage, Egg and Cheese Biscuit, Breakfast Baconator and Maple Bacon Chicken Croissant normally range in price between $4.50 and $7.
The choice of the latter is quite wide since, in the years following the pandemic, Wendy's has made a concerted effort to expand its breakfast menu with a range of new sandwiches with egg in them and sweet items such as the French Toast Sticks. The goal was both to stand out from competitors with a wider breakfast menu and increase traffic to its stores during early-morning hours.
Wendy's deal comes after controversy over 'dynamic pricing'
But last month, the chain known for the square shape of its burger patties ignited controversy after saying that it wanted to introduce "dynamic pricing" in which the cost of many of the items on its menu will vary depending on the time of day. In an earnings call, chief executive Kirk Tanner said that electronic billboards would allow restaurants to display various deals and promotions during slower times in the early morning and late at night.
Outcry was swift and Wendy's ended up walking back its plans with words that they were "misconstrued" as an intent to surge prices during its most popular periods.
While the company issued a statement saying that any changes were meant as "discounts and value offers" during quiet periods rather than raised prices during busy ones, the reputational damage was already done since many saw the clarification as another way to obfuscate its pricing model.
"We said these menuboards would give us more flexibility to change the display of featured items," Wendy's said in its statement. "This was misconstrued in some media reports as an intent to raise prices when demand is highest at our restaurants."
The Daylight Savings Time promotion, in turn, is also a way to demonstrate the kinds of deals Wendy's wants to promote in its stores without putting up full-sized advertising or posters for what is only relevant for a few days.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
stocks pandemicUncategorized
Shipping company files surprise Chapter 7 bankruptcy, liquidation
While demand for trucking has increased, so have costs and competition, which have forced a number of players to close.

The U.S. economy is built on trucks.
As a nation we have relatively limited train assets, and while in recent years planes have played an expanded role in moving goods, trucks still represent the backbone of how everything — food, gasoline, commodities, and pretty much anything else — moves around the country.
Related: Fast-food chain closes more stores after Chapter 11 bankruptcy
"Trucks moved 61.1% of the tonnage and 64.9% of the value of these shipments. The average shipment by truck was 63 miles compared to an average of 640 miles by rail," according to the U.S. Bureau of Transportation Statistics 2023 numbers.
But running a trucking company has been tricky because the largest players have economies of scale that smaller operators don't. That puts any trucking company that's not a massive player very sensitive to increases in gas prices or drops in freight rates.
And that in turn has led a number of trucking companies, including Yellow Freight, the third-largest less-than-truckload operator; J.J. & Sons Logistics, Meadow Lark, and Boateng Logistics, to close while freight brokerage Convoy shut down in October.
Aside from Convoy, none of these brands are household names. but with the demand for trucking increasing, every company that goes out of business puts more pressure on those that remain, which contributes to increased prices.
Image source: Shutterstock
Another freight company closes and plans to liquidate
Not every bankruptcy filing explains why a company has gone out of business. In the trucking industry, multiple recent Chapter 7 bankruptcies have been tied to lawsuits that pushed otherwise successful companies into insolvency.
In the case of TBL Logistics, a Virginia-based national freight company, its Feb. 29 bankruptcy filing in U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Western District of Virginia appears to be death by too much debt.
"In its filing, TBL Logistics listed its assets and liabilities as between $1 million and $10 million. The company stated that it has up to 49 creditors and maintains that no funds will be available for unsecured creditors once it pays administrative fees," Freightwaves reported.
The company's owners, Christopher and Melinda Bradner, did not respond to the website's request for comment.
Before it closed, TBL Logistics specialized in refrigerated and oversized loads. The company described its business on its website.
"TBL Logistics is a non-asset-based third-party logistics freight broker company providing reliable and efficient transportation solutions, management, and storage for businesses of all sizes. With our extensive network of carriers and industry expertise, we streamline the shipping process, ensuring your goods reach their destination safely and on time."
The world has a truck-driver shortage
The covid pandemic forced companies to consider their supply chain in ways they never had to before. Increased demand showed the weakness in the trucking industry and drew attention to how difficult life for truck drivers can be.
That was an issue HBO's John Oliver highlighted on his "Last Week Tonight" show in October 2022. In the episode, the host suggested that the U.S. would basically start to starve if the trucking industry shut down for three days.
"Sorry, three days, every produce department in America would go from a fully stocked market to an all-you-can-eat raccoon buffet," he said. "So it’s no wonder trucking’s a huge industry, with more than 3.5 million people in America working as drivers, from port truckers who bring goods off ships to railyards and warehouses, to long-haul truckers who move them across the country, to 'last-mile' drivers, who take care of local delivery."
The show highlighted how many truck drivers face low pay, difficult working conditions and, in many cases, crushing debt.
"Hundreds of thousands of people become truck drivers every year. But hundreds of thousands also quit. Job turnover for truckers averages over 100%, and at some companies it’s as high as 300%, meaning they’re hiring three people for a single job over the course of a year. And when a field this important has a level of job satisfaction that low, it sure seems like there’s a huge problem," Oliver shared.
The truck-driver shortage is not just a U.S. problem; it's a global issue, according to IRU.org.
"IRU’s 2023 driver shortage report has found that over three million truck driver jobs are unfilled, or 7% of total positions, in 36 countries studied," the global transportation trade association reported.
"With the huge gap between young and old drivers growing, it will get much worse over the next five years without significant action."
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
bankruptcy bankruptcies pandemic stocks commoditiesUncategorized
Comments on February Employment Report
The headline jobs number in the February employment report was above expectations; however, December and January payrolls were revised down by 167,000 combined. The participation rate was unchanged, the employment population ratio decreased, and the …
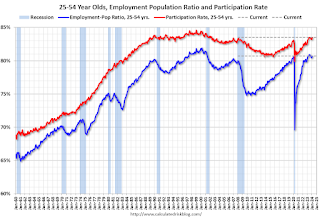
Prime (25 to 54 Years Old) Participation
Since the overall participation rate is impacted by both cyclical (recession) and demographic (aging population, younger people staying in school) reasons, here is the employment-population ratio for the key working age group: 25 to 54 years old.
The 25 to 54 years old participation rate increased in February to 83.5% from 83.3% in January, and the 25 to 54 employment population ratio increased to 80.7% from 80.6% the previous month.
Average Hourly Wages
 The graph shows the nominal year-over-year change in "Average Hourly Earnings" for all private employees from the Current Employment Statistics (CES).
The graph shows the nominal year-over-year change in "Average Hourly Earnings" for all private employees from the Current Employment Statistics (CES). Wage growth has trended down after peaking at 5.9% YoY in March 2022 and was at 4.3% YoY in February.
Part Time for Economic Reasons
 From the BLS report:
From the BLS report:"The number of people employed part time for economic reasons, at 4.4 million, changed little in February. These individuals, who would have preferred full-time employment, were working part time because their hours had been reduced or they were unable to find full-time jobs."The number of persons working part time for economic reasons decreased in February to 4.36 million from 4.42 million in February. This is slightly above pre-pandemic levels.
These workers are included in the alternate measure of labor underutilization (U-6) that increased to 7.3% from 7.2% in the previous month. This is down from the record high in April 2020 of 23.0% and up from the lowest level on record (seasonally adjusted) in December 2022 (6.5%). (This series started in 1994). This measure is above the 7.0% level in February 2020 (pre-pandemic).
Unemployed over 26 Weeks
 This graph shows the number of workers unemployed for 27 weeks or more.
This graph shows the number of workers unemployed for 27 weeks or more. According to the BLS, there are 1.203 million workers who have been unemployed for more than 26 weeks and still want a job, down from 1.277 million the previous month.
This is close to pre-pandemic levels.
Job Streak
| Headline Jobs, Top 10 Streaks | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year Ended | Streak, Months | |
| 1 | 2019 | 100 |
| 2 | 1990 | 48 |
| 3 | 2007 | 46 |
| 4 | 1979 | 45 |
| 5 | 20241 | 38 |
| 6 tie | 1943 | 33 |
| 6 tie | 1986 | 33 |
| 6 tie | 2000 | 33 |
| 9 | 1967 | 29 |
| 10 | 1995 | 25 |
| 1Currrent Streak | ||
Summary:
The headline monthly jobs number was above consensus expectations; however, December and January payrolls were revised down by 167,000 combined. The participation rate was unchanged, the employment population ratio decreased, and the unemployment rate was increased to 3.9%. Another solid report.
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International2 hours ago
International2 hours agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Government1 month ago
Government1 month agoWar Delirium
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex





















