International
Russell Napier: Central Banks Have Become Irrelevant
Russell Napier: Central Banks Have Become Irrelevant
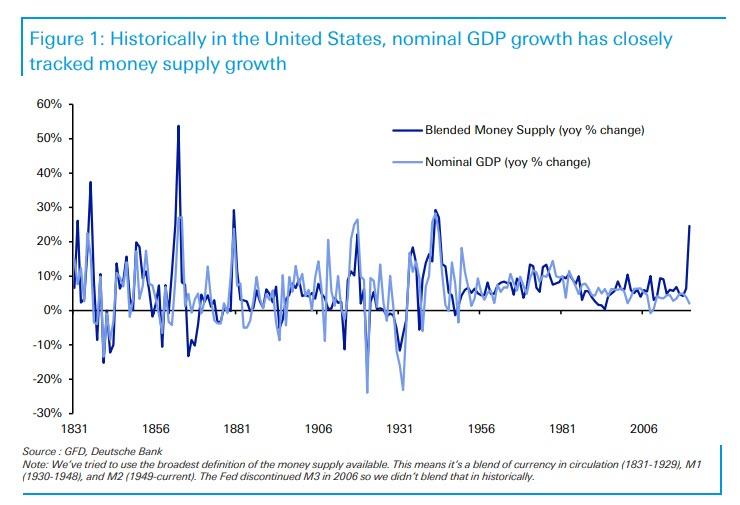
Two weeks ago, we wrote that one by one the world's legendary deflationists are taking one look at the following chart of the global money supply (as shown most recently by DB's Jim Reid) and after seeing the clear determination of central banks to spark a global inflationary conflagration, are quietly (and not so quietly) capitulating.
One month ago it was SocGen's Albert Edwards, who after calling for a deflationary Ice Age for over two decades, finally threw in the towel and conceded that "we are transitioning from The Ice Age to The Great Melt" as "massive monetary stimulus is combining with frenzied fiscal pump-priming in an attempt to paper over the current slump."
At roughly the same time, "the world's most bearish hedge fund manager", Horseman Global's Russell Clark reached a similar conclusion writing that "all the reasons that made me believe in deflation for nearly 10 years, do not really exist anymore. China looks okay to me, and potentially very good. Commodity supply is getting cut at a rate I have never seen before. The US dollar is strong but will likely weaken from here. And it is clear to me Western governments will only ever attempt fiscal austerity as a last resort, not a first. The conditions for both good and bad inflation are now in place."
Finally, it is the turn of another iconic deflationist, Russell Napier, who in the latest Solid Ground article on his Electronic Research Interchange (ERIC) writes that "we are living through another deflation shock but [he] believes that by 2021 inflation will be at or near 4%."
In the lengthy report , Napier wrote that similar to Albert Edwards' conclusion that MMT, i.e., Helicopter Money, is a gamechanger, "what has just happened is that the control of the supply of money has permanently left the hands of central bankers - the silent revolution." As a result, "the supply of money will now be set, for the foreseeable future, by democratically elected politicians seeking re-election." His conclusion: "it is time to embrace the silent revolution and the return of inflation long before such permanency is confirmed." (read our summary of his full report in the article we published on July 12 "Another Iconic Deflationist Capitulates: According To Russell Napier, "Control Of Money Supply Has Permanently Left The Hands Of Central Bankers.")
* * *
In a follow up published two days later to clarify his position, Russell sat down with Mark Dittli of the Swiss website TheMarket.ch in which he laid out his reasoning for why investors should prepare for inflation rates of 4% and more by next year. The main reason, as we expounded on previously: central banks have become irrelevant as governments have taken control of the money supply.
The full article is below, courtesy of TheMarket.ch:
Central Banks have Become Irrelevant
In the years following the financial crisis, numerous economists and market observers warned of rising inflation in the face of the unorthodox monetary p0licy by central banks. They were wrong time and again.
Russell Napier was never one of them. The Scottish market strategist has for two decades – correctly – seen disinflation as the dominant theme for financial markets. That is why investors should listen to him when he now warns of rising inflation.
"Politicians have gained control of money supply and they will not give up this instrument anymore", Napier says. In his view, we are at the beginning of a new era of financial repression, in which politicians will make sure that inflation rates remain consistently above government bond yields for years. This is the only way to reduce the crushing levels of debt, argues Napier.
In an in-depth conversation with The Market/NZZ he explains how investors can protect themselves and why central banks have lost their power.
Mr. Napier, for more than two decades, you have said that investors need to position themselves for disinflation and deflation. Now you warn that we are in a big shift towards inflation. Why, and why now?
It’s a shift in the way that money is created that has changed the game fundamentally. Most investors just look at the narrow money aggregates and central bank balance sheets. But if you look at broad money, you notice that it has been growing very slowly by historical standards for the past 30 or so years. There were many factors pushing down the rate of inflation over that time, China being the most important, but I do believe that the low level of broad money growth was one of the factors that led to low inflation.
And now this has changed?
Yes, fundamentally. We are currently in the worst recession since World War II, and yet we observe the fastest growth in broad money in at least three decades. In the US, M2, the broadest aggregate available, is growing at more than 23%. You’d have to go back to at least the Civil War to find levels like that. In the Eurozone, M3 is currently growing at 8,9%. It will only be a matter of months before the previous peak of 11.5% which was reached in 2007 will be reached. So I’m not making a forecast, I just observe the data.
Why is this relevant?
This is the big question: Does the growth of broad money matter? Investors don’t think so, as breakeven inflation rates on inflation-linked bonds are at rock bottom. So clearly the market does not believe that this broad money growth matters. The market probably thinks this is just a short-term aberration due to the Covid-19 shock. But I do believe it matters. The key point is the realization who is responsible for this money creation.
In what way?
This broad money growth is created by governments intervening in the commercial banking system. Governments tell commercial banks to grant loans to companies, and they guarantee these loans to the banks. This is money creation in a way that is completely circumventing central banks. So I make two key calls: One, with broad money growth that high, we will get inflation. And more importantly, the control of money supply has moved from central bankers to politicians. Politicians have different goals and incentives than central bankers. They need inflation to get rid of high debt levels. They now have the mechanism to create it, so they will create it.
In the aftermath of the Global Financial Crisis, central banks started their quantitative easing policies. They tried to create inflation, but did not succeed.
QE was a fiasco. All that central banks have achieved over the past ten years is creating a lot of non-bank debt. Their actions kept interest rates low, which inflated asset prices and allowed companies to borrow cheaply through the issuance of bonds. So not only did central banks fail to create money, but they created a lot of debt outside the banking system. This led to the worst of two worlds: No growth in broad money, low nominal GDP growth and high growth in debt. Most money in the world is not created by central banks, but by commercial banks. In the past ten years, central banks never succeeded in triggering commercial banks to create credit and therefore to create money.
If central banks did not succeed in pushing up nominal GDP growth, why will governments succeed?
Governments create broad money through the banking system. By exercising control over the commercial banking system, they can get money into the parts of the economy where central banks can’t get into. Banks are now under the control of the government. Politicians give credit guarantees, so of course the banks will freely give credit. They are now handing out the loans they did not give in the past ten years. This is the start.
What makes you think that this is not just a one-off extraordinary measure to fight the economic effects of the pandemic?
Politicians will realize that they have a very powerful tool in their hands. We saw a very nice example two weeks ago: The Spanish government increased their €100bn bank guarantee program to €150bn. Just like that. So there will be mission creep. There will be another one and another one, for example to finance all sorts of green projects. Also, these loans have a very long duration. The credit pulse is in the system, a pulse of money that doesn’t come back for years. And then there will be a new one, and another one. Companies won’t have any incentive to pay back these cheap loans prematurely.
So basically what you’re saying is that central banks in the past ten years never succeeded in getting commercial banks to lend. This is why governments are taking over, and they won’t let go of that tool anymore?
Exactly. Don’t forget: These are politicians. We know what mess most of the global economy is in today. Debt to GDP levels in most of the industrialized world are way too high, even before the effects of Covid-19. We know debt will have to go down. For a politician, inflation is the cheapest way out of this mess. They have found a way to gain control of the money supply and to create inflation. Remember, a credit guarantee is not fiscal spending, it’s not on the balance sheet of the state, as it’s only a contingent liability. So if you are an elected politician, you have found a cheap way of funding an economic recovery and then green projects. Politically, this is incredibly powerful.
A gift that will keep on giving?
Yes. Theresa May made a famous speech a few years ago where she said there is no magic money tree. Well, they just found it. As an economic historian and investor, I absolutely know that this is a long-term disaster. But for a politician, this is the magic money tree.
But part of that magic money tree is that governments keep control over their commercial banking system, correct?
Yes. I wrote a big report in 2016 titled «Capital management in the age of financial repression». It said the final move into financial repression will be triggered by the next crisis. So Covid-19 is just the trigger to start an aggressive financial repression.
Are you expecting a repeat of the financial repression that dominated the decades after World War Two?
Yes. Look at the tools that were used in Europe back then. They were all in place for an emergency called World War II. And most countries just didn’t lift them until the 1980s. So it’s often an emergency that gives governments these extreme powers. Total debt to GDP levels were already way too high even before Covid-19. Our governments just know these debt levels have to come down.
And the best way to do that is through financial repression, i.e. achieving a higher nominal GDP growth than the growth in debt?
That’s what we have learned in the decades after World War II: Achieve higher nominal GDP growth through higher rates of inflation. The problem is just that most active investors today have had their formative years after 1980, so they don’t know how financial repression works.
Which countries will choose that path in the coming years?
Basically the entire developed world. The US, the UK, the Eurozone, Japan. I see very few exceptions. Switzerland probably won’t have to financially repress, but only because its banking system is not in the kind of mess it was in in 2008. Government debt to GDP in Switzerland is very low. Private sector debt is high, but that is mainly because of your unique treatment of taxation for debt on residential property. So Switzerland won’t have to repress, neither will Singapore. If Germany and Austria weren’t part of the Eurozone, they wouldn’t have to repress either. Of course there is one catch: If the Swiss are not going to financially repress, you will have the same problem you had for a long time, namely far too much money trying to get into the Swiss Franc.
So we will see more upward pressure on the Franc?
Yes. But financial repression has to include capital controls at some stage. Switzerland will have to do more to avoid getting all these capital inflows. At the same time, other countries would have to introduce capital controls to stop money from getting out.
The cornerstones of the last period of financial repression after World War II were capital controls and the forcing of domestic savings institutions to buy domestic government bonds. Do you expect both of these measures to be introduced again?
Yes. Domestic savings institutions like pension funds can easily be forced to buy domestic government bonds at low interest rates.
Are capital controls really feasible in today’s open financial world?
Sure. There are two countries in the Eurozone that have had capital controls in recent history: Greece and Cyprus. They were both rather successful. Iceland had capital controls after the financial crisis, many emerging economies use them. If you can do it in Greece and Cyprus, which are members of the European Monetary Union, you can do it anywhere. Whenever a financial institution transfers money from one currency to another, it is heavily regulated.
What’s the timeline for your call on rising inflation?
I see 4% inflation in the US and most of the developed world by 2021. This is primarily based on my expectation of a normalization of the velocity of money. Velocity in the US is probably at around 0.8 right now. The lowest recorded number before that was 1.4 in December 2019, which was at the end of a multi-year downward trend. Quantitative easing was an important factor in that shrinking velocity, because central banks handed money to savings institutions in return for their Treasury securities. And all the savings institutions could do was buy financial assets. They couldn’t buy goods and services, so that money couldn’t really affect nominal GDP.
What will cause velocity to rise?
The money banks are handing out today is going straight to businesses and consumers. They are not spending it right now, but as lockdowns lift, this will have an impact. My guess is that velocity will normalize back to around 1.4 some time next year. Given the money supply we have already seen, that would give you an inflation rate of 4%. Plus, there is no reason velocity should stop at 1.4, it could easily rise above 1.7 again. There is one additional issue, and that is China: For the last three decades, China was a major source of deflation. But I think we are at the beginning of a new Cold War with China, which will mean higher prices for many things.
Most economists say there is such a huge output gap, inflation won’t be an issue for the next three years or so.
I don’t get that at all. You can point to the 1970s, where we had high unemployment and high inflation. It’s a matter of historical record that you can create inflation with high unemployment. We have done it before.
The yield on ten year US Treasury Notes is currently at around 60 basis points. What will happen to bond yields once markets realize that we are heading into an inflationary world?
Bond yields will go up sharply. They will rise because markets start to realize who is controlling the supply of money now, i.e. not central banks, but politicians. That will be the big shock.
For a successful financial repression, governments and central banks will need to stop bond yields from rising, won’t they?
Yes, and they will. But let me be precise: It will be governments who will act to stop bond yields from going up. They will force their domestic savings institutions to buy government bonds to keep yields down. The bit of your statement I disagree with is that central banks will put a cap on bond yields. They won’t be able to.
Why not? Even the Fed is toying with the idea of Yield Curve Control, an instrument they successfully used between 1942 and 1951, when they capped yields at 2.5%.
I think this is a bad parallel, because from 1942 to 1951, we also had rationing, price controls and credit controls. With that in place, it was easy for the Fed to cap Treasury yields. Yield Curve Control is easy when everyone is expecting deflation, which the current policy of the Bank of Japan shows. But once market participants start to expect inflation, they will all want to sell their bonds. The balance sheet of the central banks will just balloon to the sky. They would be spreading fuel on the fire, given that their balance sheets would expand with rising inflation expectations. Yield Curve Control in an environment of rising inflation expectations is not going to happen.
You are saying that governments now control the supply of money, and it will be governments who will make sure policies of financial repression are successfully implemented. What will be the future role of central banks?
They will be sidelined. They will become more a regulatory than a monetary organization. The next few years will be fascinating. Imagine, you and I are running a central bank and we have a 2% inflation target. And we see our own government print money with a growth rate of 12%. What are we going to do to fulfill our mandate of price stability? We would have to threaten higher interest rates. We would have to ride a full-blown attack on our democratically elected government. Would we do that?
Paul Volcker did in the early 80s.
Yes. But Paul Volcker had courage. I don’t think any of today’s central bankers will have the guts to do that. After all, governments will argue that there is still an emergency given the shocks of Covid-19. There is a good parallel to the 1960s, when the Fed did nothing about rising inflation, because the US was fighting a war in Vietnam, and the administration of Lyndon B. Johnson had launched the Great Society Project to get America more equal. Against that background of massive fiscal spending, the Fed didn’t have the guts to run a tighter monetary policy. I can see that’s exactly where we are today.
So central banks will be mostly irrelevant?
Yes. It’s ironic: Most investors believe in the seemingly unlimited power of today’s central banks. But in fact, they are the least powerful they have ever been since 1977.
As an investor, how do I protect myself?
European inflation-linked bonds are pretty attractive now, because they are pricing in such low levels of inflation. Gold is obviously a go-to asset for the long term. In the next couple of years, equities will probably do well. A bit more inflation and more nominal growth is a good environment for equities. I particularly like Japanese equities. Obviously you wouldn’t buy government bonds under any condition.
How about commodities?
In a normal inflationary cycle, I’d recommend to buy commodities. There is just one complicating factor with China. If we really enter into a new Cold War with China, that will mean big disturbances in commodities markets.
You wrote in the past that there is a sweet spot for equities up to an inflation rate of 4%, before they tip over. Is this still valid?
Yes, this playbook is still in place. But once governments truly force their savings institutions to buy more government bonds, they will obviously have to sell something. And that something will be equities. Historically, inflation above 4% hasn’t been too good for equities.
How high do you see inflation going?
If we’re taking the next 10 years, I see inflation between 4 and 8%, somewhere around that. Compounded over ten years, combined with low interest rates, this will be hugely effective in bringing down debt to GDP levels.
In which country do you see it happening first? Who will lead?
The one I worry about the most is the UK. It has a significant current account deficit, it has to sell lots of government bonds to foreigners. I never really understood why foreigners buy them. I wouldn’t. Now we have Brexit coming up, which could still go badly. I don’t think it will, but it could. So we would see a spike in bond yields in the UK.
What will it take for an investor to successfully navigate the coming years?
First, we have to realize that this is a long term phenomenon. Everyone is so caught up in the current crisis, they miss the long term shift. This will be with us for decades, not just a couple of years. The financial system is a very different place now. And it’s a very dangerous place for savers. Most of the skills we have learned in the past 40 years are probably redundant, because we have lived through a 40 year disinflationary period. It was a period where markets became more important and governments less important. Now we are reversing that. That’s why I recommend to my clients that they promote the people from their emerging markets departments to run their developed world departments. Emerging markets investors know how to deal with higher levels of inflation, government interference and capital controls. This will be our future.
Government
Looking Back At COVID’s Authoritarian Regimes
After having moved from Canada to the United States, partly to be wealthier and partly to be freer (those two are connected, by the way), I was shocked,…

After having moved from Canada to the United States, partly to be wealthier and partly to be freer (those two are connected, by the way), I was shocked, in March 2020, when President Trump and most US governors imposed heavy restrictions on people’s freedom. The purpose, said Trump and his COVID-19 advisers, was to “flatten the curve”: shut down people’s mobility for two weeks so that hospitals could catch up with the expected demand from COVID patients. In her book Silent Invasion, Dr. Deborah Birx, the coordinator of the White House Coronavirus Task Force, admitted that she was scrambling during those two weeks to come up with a reason to extend the lockdowns for much longer. As she put it, “I didn’t have the numbers in front of me yet to make the case for extending it longer, but I had two weeks to get them.” In short, she chose the goal and then tried to find the data to justify the goal. This, by the way, was from someone who, along with her task force colleague Dr. Anthony Fauci, kept talking about the importance of the scientific method. By the end of April 2020, the term “flatten the curve” had all but disappeared from public discussion.
Now that we are four years past that awful time, it makes sense to look back and see whether those heavy restrictions on the lives of people of all ages made sense. I’ll save you the suspense. They didn’t. The damage to the economy was huge. Remember that “the economy” is not a term used to describe a big machine; it’s a shorthand for the trillions of interactions among hundreds of millions of people. The lockdowns and the subsequent federal spending ballooned the budget deficit and consequent federal debt. The effect on children’s learning, not just in school but outside of school, was huge. These effects will be with us for a long time. It’s not as if there wasn’t another way to go. The people who came up with the idea of lockdowns did so on the basis of abstract models that had not been tested. They ignored a model of human behavior, which I’ll call Hayekian, that is tested every day.
These are the opening two paragraphs of my latest Defining Ideas article, “Looking Back at COVID’s Authoritarian Regimes,” Defining Ideas, March 14, 2024.
Another excerpt:
That wasn’t the only uncertainty. My daughter Karen lived in San Francisco and made her living teaching Pilates. San Francisco mayor London Breed shut down all the gyms, and so there went my daughter’s business. (The good news was that she quickly got online and shifted many of her clients to virtual Pilates. But that’s another story.) We tried to see her every six weeks or so, whether that meant our driving up to San Fran or her driving down to Monterey. But were we allowed to drive to see her? In that first month and a half, we simply didn’t know.
Read the whole thing, which is longer than usual.
(0 COMMENTS) budget deficit coronavirus covid-19 white house fauci trump canadaInternational
Problems After COVID-19 Vaccination More Prevalent Among Naturally Immune: Study
Problems After COVID-19 Vaccination More Prevalent Among Naturally Immune: Study
Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis…
Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
People who recovered from COVID-19 and received a COVID-19 shot were more likely to suffer adverse reactions, researchers in Europe are reporting.
Participants in the study were more likely to experience an adverse reaction after vaccination regardless of the type of shot, with one exception, the researchers found.
Across all vaccine brands, people with prior COVID-19 were 2.6 times as likely after dose one to suffer an adverse reaction, according to the new study. Such people are commonly known as having a type of protection known as natural immunity after recovery.
People with previous COVID-19 were also 1.25 times as likely after dose 2 to experience an adverse reaction.
The findings held true across all vaccine types following dose one.
Of the female participants who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, for instance, 82 percent who had COVID-19 previously experienced an adverse reaction after their first dose, compared to 59 percent of females who did not have prior COVID-19.
The only exception to the trend was among males who received a second AstraZeneca dose. The percentage of males who suffered an adverse reaction was higher, 33 percent to 24 percent, among those without a COVID-19 history.
“Participants who had a prior SARS-CoV-2 infection (confirmed with a positive test) experienced at least one adverse reaction more often after the 1st dose compared to participants who did not have prior COVID-19. This pattern was observed in both men and women and across vaccine brands,” Florence van Hunsel, an epidemiologist with the Netherlands Pharmacovigilance Centre Lareb, and her co-authors wrote.
There were only slightly higher odds of the naturally immune suffering an adverse reaction following receipt of a Pfizer or Moderna booster, the researchers also found.
The researchers performed what’s known as a cohort event monitoring study, following 29,387 participants as they received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine. The participants live in a European country such as Belgium, France, or Slovakia.
Overall, three-quarters of the participants reported at least one adverse reaction, although some were minor such as injection site pain.
Adverse reactions described as serious were reported by 0.24 percent of people who received a first or second dose and 0.26 percent for people who received a booster. Different examples of serious reactions were not listed in the study.
Participants were only specifically asked to record a range of minor adverse reactions (ADRs). They could provide details of other reactions in free text form.
“The unsolicited events were manually assessed and coded, and the seriousness was classified based on international criteria,” researchers said.
The free text answers were not provided by researchers in the paper.
“The authors note, ‘In this manuscript, the focus was not on serious ADRs and adverse events of special interest.’” Yet, in their highlights section they state, “The percentage of serious ADRs in the study is low for 1st and 2nd vaccination and booster.”
Dr. Joel Wallskog, co-chair of the group React19, which advocates for people who were injured by vaccines, told The Epoch Times: “It is intellectually dishonest to set out to study minor adverse events after COVID-19 vaccination then make conclusions about the frequency of serious adverse events. They also fail to provide the free text data.” He added that the paper showed “yet another study that is in my opinion, deficient by design.”
Ms. Hunsel did not respond to a request for comment.
She and other researchers listed limitations in the paper, including how they did not provide data broken down by country.
The paper was published by the journal Vaccine on March 6.
The study was funded by the European Medicines Agency and the Dutch government.
No authors declared conflicts of interest.
Some previous papers have also found that people with prior COVID-19 infection had more adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination, including a 2021 paper from French researchers. A U.S. study identified prior COVID-19 as a predictor of the severity of side effects.
Some other studies have determined COVID-19 vaccines confer little or no benefit to people with a history of infection, including those who had received a primary series.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention still recommends people who recovered from COVID-19 receive a COVID-19 vaccine, although a number of other health authorities have stopped recommending the shot for people who have prior COVID-19.
Another New Study
In another new paper, South Korean researchers outlined how they found people were more likely to report certain adverse reactions after COVID-19 vaccination than after receipt of another vaccine.
The reporting of myocarditis, a form of heart inflammation, or pericarditis, a related condition, was nearly 20 times as high among children as the reporting odds following receipt of all other vaccines, the researchers found.
The reporting odds were also much higher for multisystem inflammatory syndrome or Kawasaki disease among adolescent COVID-19 recipients.
Researchers analyzed reports made to VigiBase, which is run by the World Health Organization.
“Based on our results, close monitoring for these rare but serious inflammatory reactions after COVID-19 vaccination among adolescents until definitive causal relationship can be established,” the researchers wrote.
The study was published by the Journal of Korean Medical Science in its March edition.
Limitations include VigiBase receiving reports of problems, with some reports going unconfirmed.
Funding came from the South Korean government. One author reported receiving grants from pharmaceutical companies, including Pfizer.
International
‘Excess Mortality Skyrocketed’: Tucker Carlson and Dr. Pierre Kory Unpack ‘Criminal’ COVID Response
‘Excess Mortality Skyrocketed’: Tucker Carlson and Dr. Pierre Kory Unpack ‘Criminal’ COVID Response
As the global pandemic unfolded, government-funded…

As the global pandemic unfolded, government-funded experimental vaccines were hastily developed for a virus which primarily killed the old and fat (and those with other obvious comorbidities), and an aggressive, global campaign to coerce billions into injecting them ensued.
Then there were the lockdowns - with some countries (New Zealand, for example) building internment camps for those who tested positive for Covid-19, and others such as China welding entire apartment buildings shut to trap people inside.
It was an egregious and unnecessary response to a virus that, while highly virulent, was survivable by the vast majority of the general population.
Oh, and the vaccines, which governments are still pushing, didn't work as advertised to the point where health officials changed the definition of "vaccine" multiple times.
Tucker Carlson recently sat down with Dr. Pierre Kory, a critical care specialist and vocal critic of vaccines. The two had a wide-ranging discussion, which included vaccine safety and efficacy, excess mortality, demographic impacts of the virus, big pharma, and the professional price Kory has paid for speaking out.
Keep reading below, or if you have roughly 50 minutes, watch it in its entirety for free on X:
Ep. 81 They’re still claiming the Covid vax is safe and effective. Yet somehow Dr. Pierre Kory treats hundreds of patients who’ve been badly injured by it. Why is no one in the public health establishment paying attention? pic.twitter.com/IekW4Brhoy
— Tucker Carlson (@TuckerCarlson) March 13, 2024
"Do we have any real sense of what the cost, the physical cost to the country and world has been of those vaccines?" Carlson asked, kicking off the interview.
"I do think we have some understanding of the cost. I mean, I think, you know, you're aware of the work of of Ed Dowd, who's put together a team and looked, analytically at a lot of the epidemiologic data," Kory replied. "I mean, time with that vaccination rollout is when all of the numbers started going sideways, the excess mortality started to skyrocket."
When asked "what kind of death toll are we looking at?", Kory responded "...in 2023 alone, in the first nine months, we had what's called an excess mortality of 158,000 Americans," adding "But this is in 2023. I mean, we've had Omicron now for two years, which is a mild variant. Not that many go to the hospital."
'Safe and Effective'
Tucker also asked Kory why the people who claimed the vaccine were "safe and effective" aren't being held criminally liable for abetting the "killing of all these Americans," to which Kory replied: "It’s my kind of belief, looking back, that [safe and effective] was a predetermined conclusion. There was no data to support that, but it was agreed upon that it would be presented as safe and effective."
Tucker Carlson Asks the Forbidden Question
— The Vigilant Fox ???? (@VigilantFox) March 14, 2024
He wants to know why the people who made the claim “safe and effective” aren’t being held to criminal liability for abetting the “killing of all these Americans.”
DR. PIERRE KORY: “It’s my kind of belief, looking back, that [safe and… pic.twitter.com/Icnge18Rtz
Carlson and Kory then discussed the different segments of the population that experienced vaccine side effects, with Kory noting an "explosion in dying in the youngest and healthiest sectors of society," adding "And why did the employed fare far worse than those that weren't? And this particularly white collar, white collar, more than gray collar, more than blue collar."
Kory also said that Big Pharma is 'terrified' of Vitamin D because it "threatens the disease model." As journalist The Vigilant Fox notes on X, "Vitamin D showed about a 60% effectiveness against the incidence of COVID-19 in randomized control trials," and "showed about 40-50% effectiveness in reducing the incidence of COVID-19 in observational studies."
Dr. Pierre Kory: Big Pharma is ‘TERRIFIED’ of Vitamin D
— The Vigilant Fox ???? (@VigilantFox) March 14, 2024
Why?
Because “It threatens the DISEASE MODEL.”
A new meta-analysis out of Italy, published in the journal, Nutrients, has unearthed some shocking data about Vitamin D.
Looking at data from 16 different studies and 1.26… pic.twitter.com/q5CsMqgVju
Professional costs
Kory - while risking professional suicide by speaking out, has undoubtedly helped save countless lives by advocating for alternate treatments such as Ivermectin.
Kory shared his own experiences of job loss and censorship, highlighting the challenges of advocating for a more nuanced understanding of vaccine safety in an environment often resistant to dissenting voices.
"I wrote a book called The War on Ivermectin and the the genesis of that book," he said, adding "Not only is my expertise on Ivermectin and my vast clinical experience, but and I tell the story before, but I got an email, during this journey from a guy named William B Grant, who's a professor out in California, and he wrote to me this email just one day, my life was going totally sideways because our protocols focused on Ivermectin. I was using a lot in my practice, as were tens of thousands of doctors around the world, to really good benefits. And I was getting attacked, hit jobs in the media, and he wrote me this email on and he said, Dear Dr. Kory, what they're doing to Ivermectin, they've been doing to vitamin D for decades..."
"And it's got five tactics. And these are the five tactics that all industries employ when science emerges, that's inconvenient to their interests. And so I'm just going to give you an example. Ivermectin science was extremely inconvenient to the interests of the pharmaceutical industrial complex. I mean, it threatened the vaccine campaign. It threatened vaccine hesitancy, which was public enemy number one. We know that, that everything, all the propaganda censorship was literally going after something called vaccine hesitancy."
Money makes the world go 'round
Carlson then hit on perhaps the most devious aspect of the relationship between drug companies and the medical establishment, and how special interests completely taint science to the point where public distrust of institutions has spiked in recent years.
"I think all of it starts at the level the medical journals," said Kory. "Because once you have something established in the medical journals as a, let's say, a proven fact or a generally accepted consensus, consensus comes out of the journals."
"I have dozens of rejection letters from investigators around the world who did good trials on ivermectin, tried to publish it. No thank you, no thank you, no thank you. And then the ones that do get in all purportedly prove that ivermectin didn't work," Kory continued.
"So and then when you look at the ones that actually got in and this is where like probably my biggest estrangement and why I don't recognize science and don't trust it anymore, is the trials that flew to publication in the top journals in the world were so brazenly manipulated and corrupted in the design and conduct in, many of us wrote about it. But they flew to publication, and then every time they were published, you saw these huge PR campaigns in the media. New York Times, Boston Globe, L.A. times, ivermectin doesn't work. Latest high quality, rigorous study says. I'm sitting here in my office watching these lies just ripple throughout the media sphere based on fraudulent studies published in the top journals. And that's that's that has changed. Now that's why I say I'm estranged and I don't know what to trust anymore."
Vaccine Injuries
Carlson asked Kory about his clinical experience with vaccine injuries.
"So how this is how I divide, this is just kind of my perception of vaccine injury is that when I use the term vaccine injury, I'm usually referring to what I call a single organ problem, like pericarditis, myocarditis, stroke, something like that. An autoimmune disease," he replied.
"What I specialize in my practice, is I treat patients with what we call a long Covid long vaxx. It's the same disease, just different triggers, right? One is triggered by Covid, the other one is triggered by the spike protein from the vaccine. Much more common is long vax. The only real differences between the two conditions is that the vaccinated are, on average, sicker and more disabled than the long Covids, with some pretty prominent exceptions to that."
Watch the entire interview above, and you can support Tucker Carlson's endeavors by joining the Tucker Carlson Network here...
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Spread & Containment2 days ago
Spread & Containment2 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A

























