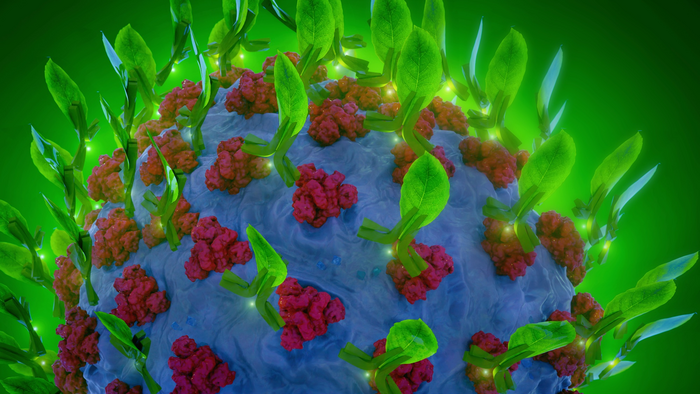
Viruses, including SARS-CoV-2, use an extensive arsenal to help them cleverly evade the immune system, proliferate and cause disease. Among their formidable weapons is the ability to ceaselessly mutate, developing new variants that the body’s natural or vaccine-induced defenses cannot fight.
In new research, Shawn Chen, a researcher with Arizona State University’s Biodesign Center for Immunotherapy, Vaccines and Virotherapy and School of Life Sciences, describes an innovative therapy for COVID-19. The method highlighted in the study uses transient expression in tobacco plants to develop and produce a monoclonal antibody, or mAb. The crucial advantage of the therapy is that it may protect against COVID-19, even as the virus attempts to evade immune detection through mutation.The novel coronavirus SARS CoV-2 is responsible for the COVID-19 global pandemic. A new form of monoclonal antibody therapeutic to treat the disease is described in a new study, which graces the cover of Plant Biology Journal. Graphic by Jason DreesDownload Full Image
The treatment could be particularly useful for elderly patients and people with compromised immune systems who are highly vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2 and its emergent variants. The new therapy could also be added to existing therapies for COVID-19, significantly enhancing their protection. Further, using plants to produce therapeutics offers several advantages over conventional methods, including reduced cost, safety and speed of development.
High-potency, multipurpose therapy
The first monoclonal antibodies were developed in the 1970s to target cancer. They have since been engineered to combat a wide range of diseases and are a powerful tool in the fight against the novel coronavirus causing COVID-19.
While there are four classes of monoclonal antibodies, nearly all successful mAb therapies for COVID-19 have relied on class 1 or 2. The new therapy, a class 4 mAb, provides some key advantages over existing treatments.
“This monoclonal antibody treatment is mostly mutation resistant, and it neutralizes several variants, including Omicrons. This provides a therapeutic candidate for fighting against new mutations of the COVID-19 virus,” Chen says. “The approach provides a universal cocktail partner to boost approved emergency use authorization therapeutics for treating COVID-19, especially current and future variants that are resistant to current monoclonal antibody treatment.”
Because the research describes a different monoclonal antibody mechanism of action, it also advances basic knowledge of how mAbs work against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The new research has been selected for the cover of the current issue of Plant Biology Journal.
Shawn Chen is a researcher with Arizona State University’s Biodesign Center for Immunotherapy, Vaccines and Virotherapy and School of Life Sciences.
Douglas Lake, a researcher in the Virginia G. Piper Biodesign Center for Personalized Diagnostics, the Biodesign Center for Immunotherapy, Vaccines and Virotherapy and associate professor with ASU’s School of Life Sciences, also collaborated on the early phase of the project.
Beyond ACE2
During COVID-19 infection, the virus’s spike protein fuses with a receptor on the cell’s surface, known as ACE2. The binding of the virus to ACE2 is a crucial step in the process of viral entry into host cells, and this interaction is targeted by many antiviral therapies, including most monoclonal antibodies.
The ACE2 binding site is highly conserved among different SARS-CoV-2 variants, although mutations in this region can occur and may affect the virus’s ability to enter cells and their success at thwarting vaccines or therapeutics designed to target them.
The ACE2 receptor is expressed in various tissues throughout the body, including the lungs, heart, kidneys and intestines, which may contribute to the diverse symptoms and complications associated with COVID-19.
Monoclonal 2.0
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-made molecules that can mimic the immune system’s ability to fight off pathogens, including SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses. They are designed to bind specifically to a target protein or antigen, which in the case of SARS-CoV-2, is usually the spike protein’s receptor-binding domain on the viral surface.
By blocking the virus’s entry into human cells, reducing viral load and triggering the immune system to fight off the infection, monoclonal antibodies can help reduce the severity of COVID-19. The class 1 and 2 mAbs, now commonly used against COVID-19, are highly potent and can neutralize a specific variant of the virus by targeting the receptor-binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Nevertheless, the virus can sometimes manage to outmaneuver such therapies.
One way SARS-CoV-2 can accomplish this is by modifying the spike protein’s ACE2 receptor-binding domain through mutation. The effect of these alterations may be to increase or decrease infectivity. They may also affect the severity of the disease caused by the virus, or the virus’s ability to evade the immune system.
This is where the monoclonal antibody described in the new study comes in. Rather than binding with the ACE2 receptor-binding domain, the novel class 4 monoclonal antibodies target a site that is distant from the ACE2 binding domain yet can effectively neutralize multiple variants of concern, including Omicron variants.
This innovation provides an important advantage. Because the binding domain targeted by the new monoclonal antibody treatment is not under strong selective pressure, it is mutation resistant, compared with ACE2, making it much harder for the virus to outwit the therapy.
Power in plants
The study highlights the potential of synergizing antibody cocktails with the addition of monoclonal antibodies that do not directly hinder ACE2 binding to the receptor-binding domain. The study also underscores the potential of plant-based monoclonal antibody expression platforms in therapeutic development against the ever-evolving SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
Plant-made COVID-19 therapies have several advantages over other production platforms. Plants can produce large quantities of therapeutic proteins in a relatively short amount of time, making them ideal for scaling up production. They are inexpensive to grow and maintain, making them a cost-effective alternative to traditional protein expression systems. Because plants are not natural hosts for human pathogens, their use reduces the risk of contamination with infectious agents.
Finally, plant-based expression systems can be rapidly reprogrammed to produce new therapeutics in response to emerging pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2, making them an attractive option for pandemic response.
Journal
Plant Biotechnology Journal
DOI
10.1111/pbi.13970
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
A novel plant-made monoclonal antibody enhances the synergetic potency of an antibody cocktail against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant
Article Publication Date
16-Dec-2022