Uncategorized
‘Massive’ crypto use cases to surface by 2030 — Coinbase exec
Cointelegraph talks with Coinbase protocols lead and Base creator Jesse Pollak about the company’s new blockchain, which is already a force to be reckoned…

Cointelegraph talks with Coinbase protocols lead and Base creator Jesse Pollak about the company’s new blockchain, which is already a force to be reckoned with.
Coinbase launched Base, its new blockchain, in late July, and it has already become a major player among Ethereum-based layer-2 chains.
On Sept. 21, for instance, the chain notched some 677,000 transactions, with 870,163 “new addresses seen,” according to Etherscan.
By comparison, Arbitrum, a prominent layer 2 that launched in June 2021, had 925,000 transactions and 54,233 new addresses on the same day.
Base is now hosting hundreds of decentralized projects, Jesse Pollak, head of protocols at Coinbase, told Cointelegraph at Messari’s Mainnet conference in New York City on Wednesday, Sept. 20, including decentralized inflation oracles, restaurant rewards projects, an insurance aggregator and everything in between.
A major force behind the Base project, Pollak sat down with Cointelegraph at Mainnet for a Q&A encompassing Coinbase’s vision for its new platform, the rising promise of decentralized applications (DApps) and the evolution of blockchain technology.
Cointelegraph: You’ve said Base was created with a “clear vision: bring the next million builders and billion users on-chain.” Those are big numbers. How long will they take to achieve?
Jesse Pollak: It’s less about Base specifically and more about a billion users coming on-chain — embracing the power of this new platform [i.e., blockchain] that’s transparent, open, global — and developing apps that can improve people’s lives. Base is obviously going to play a big role in that, but it’s much bigger than just us. We really see our role as helping grow that pie.
CT: And the timeline?
JP: I see it happening this decade, i.e., one million developer jobs by 2030. There’s already been massive change in the 2020s — not just in the industry but the entire world. It’s going to happen faster than people might expect.
CT: What still needs to be done before we see mainstream adoption?
JP: Three high-level things need to happen. First, we need to make it cheaper for people to use these apps that are being built. We’ve done the first few orders of magnitude of cost reduction with Base. The same app might have cost $5 or $10 to use now costs 5 to 10 cents.
But we don’t think that’s enough. We really want to lower it so far that the cost is almost imperceptible to users.
Second, we want to make it easier for people to use these apps. A lot of that is building better wallet experiences.
Third, we need to have better identity infrastructure on-chain. Today, most consumer borrowing in the United States and other developed countries is under-collateralized borrowing in the form of credit cards or buy-now-pay-later arrangements. And almost none of this is possible on-chain now because we don’t have reliable identity systems.
So, to enable that next wave of big use cases, we’ll need lower costs, better wallets and better identity.
CT: You’ve said that what most people have done with crypto until now is speculate on the crypto markets, and it’s time to move on. Has it been a mistake to focus so much on the market price of Bitcoin, say?
Pollak: I don’t think it’s wrong if you look at the way that technology life cycles evolve. Carlota Perez, for instance, writes that financial bubbles are almost inevitable when you have meaningful technological innovation like the internet or electricity. You have this S-curve of adoption. [See chart below.] In the beginning, a lot of innovation is fueled by speculation as people see potential in the technology. This speculation draws in capital, which basically funds the innovation and eventually leads to impacts that change the world.

CT: Where are we now?
JP: We’ve reached the point where it’s time to move out of that [speculative] phase and into the phase of really bringing utility to everyday people. The infrastructure is ready.
Even two years ago, if you wanted to use an app on Ethereum, it was going to cost you $5 or $10 or $100. That’s just not something that is supportive of building everyday use cases.
CT: Speaking of Ethereum, why did Coinbase decide to build its layer 2 on the Ethereum blockchain? Did you ever consider using another mainnet?
JP: We actually looked three times at building a chain: In 2018 and 2020, and then most recently in 2023. And the first two times, we looked at building an alternative layer 1, one which would have been competitive with Ethereum. Our takeaway was we didn’t want to put ourselves on an island disconnected from the rest of the ecosystem.
The third time, we looked at all of the options: Ethereum, alternative layer 1s, layer 2s, etc. What felt natural to us about Ethereum was it is the largest crypto ecosystem by value, by activity, by developers — by order of magnitude or two — and so by building Base as an Ethereum layer 2, we could both contribute to scaling Ethereum and be a part of this ecosystem that’s larger than us.
CT: What about Ethereum’s oft-discussed scalability shortcomings, including network congestion and sometimes ballooning fees? Have those been largely solved through extensive use of layer-2 rollups like Optimism and Arbitrum (and now Base), where transactions are “batched” and added to the mainnet in a single lot?
JP: If you look at the history of Ethereum, the original vision was: We’re going to do all this at layer 1, and we’re going to scale up through sharding. But around 2020 and 2021, as layer 2s emerged, the Ethereum community and core development groups basically said: What if we changed our strategy where instead of trying to introduce all of this complexity at layer 1, we build the infrastructure to enable innovation at layer 2?
That was something that Vitalik [Buterin, Ethereum co-founder] wrote about a lot. And over the last two years, that’s what happened. Coinbase supported an initiative over the last year-and-a-half called EIP-4844, for instance, that introduced data availability for rollups, leading to reduced fees and more transaction throughput.
But do I think we’ve solved the problem? No. These things take years to solve, and I think we are now two to three years into making those investments, and we have another two to three years or more potentially to go. But I think we’ve made a lot of progress.
You can see this at L2Beat. [See chart below]. Two years ago [Sept. 21, 2021], there were eight transactions per second [on average] on layer-2 projects and 13 TPS on the Ethereum mainnet. Today, there’s 58 TPS on layer 2s and 11 TPS on the Ethereum mainnet. So we’ve gone from less than 1x to 5.7 times faster in two years.

CT: Are you surprised that a “buzzy” social media DAPP — Friend.tech — was initially Base’s biggest performer after its summer launch? Its fees surpassed $1 million in one 24-hour period. Still, maybe this wasn’t the serious use case that some critics were hoping for.
JP: Well, when the first social apps launched on the internet, some people looked at them and said, hey, these things are toys. When are we going to go do the serious stuff like bringing newspapers online? If you look at where we are today, social apps are used by billions of people every day. They will continue to be a way that people connect, and social apps will play a critical role on-chain.
What’s powerful about this next generation of on-chain social apps is that they will enable people to have sovereign ownership. They will continue to own their creativity, and they'll continue to be in control — rather than the large corporations that are controlling them now.
CT: Can you tell us about a DApp launched on Base that excites you?
JP: Check out Blackbird, a customer engagement platform for restaurants. You walk into any participating restaurant, you tap your phone, and it instantly knows who you are. They customize the experience for you. Repeat visitors can earn rewards. It’s in 10 or 15 restaurants now in New York City but is soon expanding into California. A lot of people are talking about it on Twitter.
CT: Where will blockchain finally find its “killer app” — to do for the cryptoverse what email did for the internet? Or has it already emerged in your view?
JP: There won’t be one killer app. There will be many killer apps. We’re starting to see some of those emerge. The one with the most real-world adoption is stablecoins. If you look at the total volume of stablecoin transactions over the last year, it’s a massive number. It will be a big driver of economic freedom in the decade ahead. It gives people in places like Argentina or Turkey access to a stable currency like the U.S. dollar.
But stablecoins won’t be alone. We will see many on-chain applications that will change people’s lives for the better.
Collect this article as an NFT to preserve this moment in history and show your support for independent journalism in the crypto space.
bitcoin ethereum blockchain crypto cryptoUncategorized
Q4 Update: Delinquencies, Foreclosures and REO
Today, in the Calculated Risk Real Estate Newsletter: Q4 Update: Delinquencies, Foreclosures and REO
A brief excerpt: I’ve argued repeatedly that we would NOT see a surge in foreclosures that would significantly impact house prices (as happened followi…
A brief excerpt:
I’ve argued repeatedly that we would NOT see a surge in foreclosures that would significantly impact house prices (as happened following the housing bubble). The two key reasons are mortgage lending has been solid, and most homeowners have substantial equity in their homes..There is much more in the article. You can subscribe at https://calculatedrisk.substack.com/ mortgage rates real estate mortgages pandemic interest rates
...
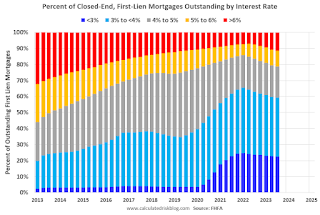
And on mortgage rates, here is some data from the FHFA’s National Mortgage Database showing the distribution of interest rates on closed-end, fixed-rate 1-4 family mortgages outstanding at the end of each quarter since Q1 2013 through Q3 2023 (Q4 2023 data will be released in a two weeks).
This shows the surge in the percent of loans under 3%, and also under 4%, starting in early 2020 as mortgage rates declined sharply during the pandemic. Currently 22.6% of loans are under 3%, 59.4% are under 4%, and 78.7% are under 5%.
With substantial equity, and low mortgage rates (mostly at a fixed rates), few homeowners will have financial difficulties.
Uncategorized
‘Bougie Broke’ – The Financial Reality Behind The Facade
‘Bougie Broke’ – The Financial Reality Behind The Facade
Authored by Michael Lebowitz via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
Social media users claiming…
Authored by Michael Lebowitz via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
Social media users claiming to be Bougie Broke share pictures of their fancy cars, high-fashion clothing, and selfies in exotic locations and expensive restaurants. Yet they complain about living paycheck to paycheck and lacking the means to support their lifestyle.
Bougie broke is like “keeping up with the Joneses,” spending beyond one’s means to impress others.
Bougie Broke gives us a glimpse into the financial condition of a growing number of consumers. Since personal consumption represents about two-thirds of economic activity, it’s worth diving into the Bougie Broke fad to appreciate if a large subset of the population can continue to consume at current rates.
The Wealth Divide Disclaimer
Forecasting personal consumption is always tricky, but it has become even more challenging in the post-pandemic era. To appreciate why we share a joke told by Mike Green.
Bill Gates and I walk into the bar…
Bartender: “Wow… a couple of billionaires on average!”
Bill Gates, Jeff Bezos, Elon Musk, Mark Zuckerberg, and other billionaires make us all much richer, on average. Unfortunately, we can’t use the average to pay our bills.
According to Wikipedia, Bill Gates is one of 756 billionaires living in the United States. Many of these billionaires became much wealthier due to the pandemic as their investment fortunes proliferated.
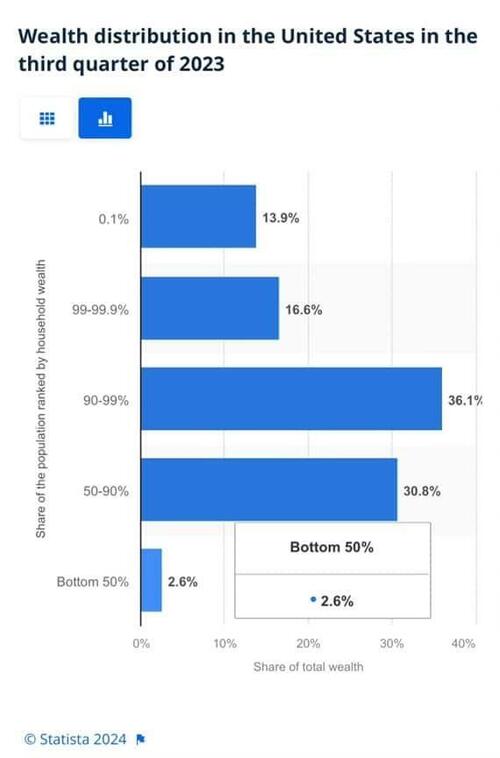
To appreciate the wealth divide, consider the graph below courtesy of Statista. 1% of the U.S. population holds 30% of the wealth. The wealthiest 10% of households have two-thirds of the wealth. The bottom half of the population accounts for less than 3% of the wealth.
The uber-wealthy grossly distorts consumption and savings data. And, with the sharp increase in their wealth over the past few years, the consumption and savings data are more distorted.
Furthermore, and critical to appreciate, the spending by the wealthy doesn’t fluctuate with the economy. Therefore, the spending of the lower wealth classes drives marginal changes in consumption. As such, the condition of the not-so-wealthy is most important for forecasting changes in consumption.
Revenge Spending
Deciphering personal data has also become more difficult because our spending habits have changed due to the pandemic.
A great example is revenge spending. Per the New York Times:
Ola Majekodunmi, the founder of All Things Money, a finance site for young adults, explained revenge spending as expenditures meant to make up for “lost time” after an event like the pandemic.
So, between the growing wealth divide and irregular spending habits, let’s quantify personal savings, debt usage, and real wages to appreciate better if Bougie Broke is a mass movement or a silly meme.
The Means To Consume
Savings, debt, and wages are the three primary sources that give consumers the ability to consume.
Savings
The graph below shows the rollercoaster on which personal savings have been since the pandemic. The savings rate is hovering at the lowest rate since those seen before the 2008 recession. The total amount of personal savings is back to 2017 levels. But, on an inflation-adjusted basis, it’s at 10-year lows. On average, most consumers are drawing down their savings or less. Given that wages are increasing and unemployment is historically low, they must be consuming more.
Now, strip out the savings of the uber-wealthy, and it’s probable that the amount of personal savings for much of the population is negligible. A survey by Payroll.org estimates that 78% of Americans live paycheck to paycheck.
More on Insufficient Savings
The Fed’s latest, albeit old, Report on the Economic Well-Being of U.S. Households from June 2023 claims that over a third of households do not have enough savings to cover an unexpected $400 expense. We venture to guess that number has grown since then. To wit, the number of households with essentially no savings rose 5% from their prior report a year earlier.
Relatively small, unexpected expenses, such as a car repair or a modest medical bill, can be a hardship for many families. When faced with a hypothetical expense of $400, 63 percent of all adults in 2022 said they would have covered it exclusively using cash, savings, or a credit card paid off at the next statement (referred to, altogether, as “cash or its equivalent”). The remainder said they would have paid by borrowing or selling something or said they would not have been able to cover the expense.
Debt
After periods where consumers drained their existing savings and/or devoted less of their paychecks to savings, they either slowed their consumption patterns or borrowed to keep them up. Currently, it seems like many are choosing the latter option. Consumer borrowing is accelerating at a quicker pace than it was before the pandemic.
The first graph below shows outstanding credit card debt fell during the pandemic as the economy cratered. However, after multiple stimulus checks and broad-based economic recovery, consumer confidence rose, and with it, credit card balances surged.
The current trend is steeper than the pre-pandemic trend. Some may be a catch-up, but the current rate is unsustainable. Consequently, borrowing will likely slow down to its pre-pandemic trend or even below it as consumers deal with higher credit card balances and 20+% interest rates on the debt.
The second graph shows that since 2022, credit card balances have grown faster than our incomes. Like the first graph, the credit usage versus income trend is unsustainable, especially with current interest rates.
With many consumers maxing out their credit cards, is it any wonder buy-now-pay-later loans (BNPL) are increasing rapidly?
Insider Intelligence believes that 79 million Americans, or a quarter of those over 18 years old, use BNPL. Lending Tree claims that “nearly 1 in 3 consumers (31%) say they’re at least considering using a buy now, pay later (BNPL) loan this month.”More telling, according to their survey, only 52% of those asked are confident they can pay off their BNPL loan without missing a payment!
Wage Growth
Wages have been growing above trend since the pandemic. Since 2022, the average annual growth in compensation has been 6.28%. Higher incomes support more consumption, but higher prices reduce the amount of goods or services one can buy. Over the same period, real compensation has grown by less than half a percent annually. The average real compensation growth was 2.30% during the three years before the pandemic.
In other words, compensation is just keeping up with inflation instead of outpacing it and providing consumers with the ability to consume, save, or pay down debt.
It’s All About Employment
The unemployment rate is 3.9%, up slightly from recent lows but still among the lowest rates in the last seventy-five years.
The uptick in credit card usage, decline in savings, and the savings rate argue that consumers are slowly running out of room to keep consuming at their current pace.
However, the most significant means by which we consume is income. If the unemployment rate stays low, consumption may moderate. But, if the recent uptick in unemployment continues, a recession is extremely likely, as we have seen every time it turned higher.
It’s not just those losing jobs that consume less. Of greater impact is a loss of confidence by those employed when they see friends or neighbors being laid off.
Accordingly, the labor market is probably the most important leading indicator of consumption and of the ability of the Bougie Broke to continue to be Bougie instead of flat-out broke!
Summary
There are always consumers living above their means. This is often harmless until their means decline or disappear. The Bougie Broke meme and the ability social media gives consumers to flaunt their “wealth” is a new medium for an age-old message.
Diving into the data, it argues that consumption will likely slow in the coming months. Such would allow some consumers to save and whittle down their debt. That situation would be healthy and unlikely to cause a recession.
The potential for the unemployment rate to continue higher is of much greater concern. The combination of a higher unemployment rate and strapped consumers could accentuate a recession.
Uncategorized
The most potent labor market indicator of all is still strongly positive
– by New Deal democratOn Monday I examined some series from last Friday’s Household survey in the jobs report, highlighting that they more frequently…
- by New Deal democrat
On Monday I examined some series from last Friday’s Household survey in the jobs report, highlighting that they more frequently than not indicated a recession was near or underway. But I concluded by noting that this survey has historically been noisy, and I thought it would be resolved away this time. Specifically, there was strong contrary data from the Establishment survey, backed up by yesterday’s inflation report, to the contrary. Today I’ll examine that, looking at two other series.
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges



























