Government
“Many Unholy Trinities” – ECB Failure Is (Almost) Guaranteed
"Many Unholy Trinities" – ECB Failure Is (Almost) Guaranteed
By Elwin de Groot, head of macro strategy at Rabobank
After last week’s recession…
By Elwin de Groot, head of macro strategy at Rabobank
After last week’s recession fear-driven bounce-back in bonds (especially those at the shorter maturity section of the curve), markets took a breather on Monday as the US were closed for Independence Day. The European 2-year swap rate (which declined by a whopping 80bp in the last two weeks of June), recovered by more than 10bp yesterday. Arguably that was also driven by hawkish comments from ECB officials, such as Bank of Slovenia Governor Vasle, who warned that there will “likely be more rate hikes […] after September”. The RBA’s second consecutive 50bp hike this morning – albeit in line with the market’s expectations – served as another reminder that short-term rates are on a (steep) upward slope, globally.
Meanwhile, the US and China are in talks over a roll-back of tariffs imposed by the former Trump administration. It is our understanding that Treasury Secretary Yellen is a proponent of such a reversal, but that there is no unity on this issue in the Biden team. US Trade Representative Katherine Tai, for example, sees the tariffs as useful leverage in broader discussions with China (although sceptics will argue that the tariffs have done little to rebalance the trade relation between the two countries). The downward impact this would have on inflation is likely to be quite modest according to many analysts. Still, if such a decision were to coincide with the start of a downward trajectory in inflation (for entirely different reasons, such as ‘peak’ commodity prices), President Biden –who has also expressed great concern over cost of living issues for US households– may spin it as a vote-winner as the November mid-term elections are drawing closer.
Overnight, we’ve seen more ‘positive’ news from China, as the Caixin composite PMI survey for June rebounded strongly (55.3 from 42.2 in May) following the relaxation of lockdown measures in big cities such as Shanghai and Beijing. However with new reports of flare-ups of Covid-19 in the eastern province of Anhui as well as the broader Yangtze Delta region, which is a key economic hub, the pick-up in activity may well prove to be short-lived.
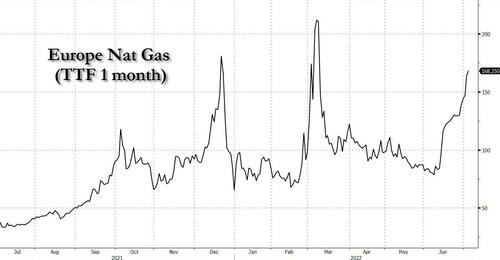
Indeed, we would argue that it is far too soon to throw recession fears out of the window. From the European side, we were also kindly reminded of that over the weekend by German Federation of Trade Unions (DGB) head Yasmin Fahini, who warned in an interview with Bild that “entire industries are in danger of permanently collapsing: aluminum, glass, the chemical industry” as a result of the current gas bottle necks. The 60% decline in Russian gas deliveries through the German Nordstream-1 pipeline system has pushed European gas prices to levels not seen since the first weeks of the Russian invasion in Ukraine. The TTF 1-month contract rose above EUR160/MWh yesterday, the highest level since 8 March. Rising import prices were also the main culprit behind Germany’s first monthly trade deficit (a EUR 1bn net loss) in May since 1991, as export activity is being hampered by Chinese lockdowns, slowing global demand and ongoing supply chain issues whilst import prices (of energy in particular) are going through the roof.
Germany has already switched to phase 2 of its national gas emergency plan, just one step shy from taking complete control over the allocation of natural gas. Its previously mothballed coal-powered electricity plants are being fired up again and the government is still in talks with Uniper, its biggest gas importer, on what support measures it will provide. According to Germany’s Spiegel magazine, the government is working on legal basis to support gas supply companies with measures that could include the acquisition of shares and/or grant loans or guarantees. The Lufthansa bailout is seen as a blueprint for such measures. Bloomberg reports this morning that the potential bailout package could be as much as EUR 9bn.
But Chancellor Scholz acknowledged yesterday that the country is facing a “historic challenge” and that the rising costs of living could have “explosive” effects on German society, as it also drives a further wedge between the rich and the poor. Arguably, the Chancellor himself is facing one of those Unholy (or Impossible) Trinities: he cannot prevent social unrest, if he wants to have lower inflation and wants to prevent a recession at the same time. One could argue that simultaneously achieving the latter two objectives are already a daunting task in itself, let alone doing so without causing tensions between those in work and those enjoying their pension, or between the providers of capital and the providers of labour.
So he’d better leave the prevention of inflation in the safe hands of the ECB, right? Oh, hang on, that other institution is actually dealing with an Unholy (or Impossible) Trinity itself. In fact, we would argue, one that is of its own making.
Before you start googling, the “Impossible trinity” concept dates back to the research by international economists Robert Mundell and John Fleming. The central tenet of their reasoning is that it is impossible to have all three of the following at the same time:
- i) independent monetary policy (i.e. full control of your money supply),
- ii) a fixed/stable exchange rate and
- iii) the free movement of capital.
The prime example often used to explain the trinity is the situation where the central bank choses its own monetary policy amidst free capital flows. Under that regime – which basically is the regime under which many developed-markets central banks are currently operating – the central bank cannot control the exchange rate. For if it wants to fix the exchange rate it would have to use its FX reserves to steer the exchange rate. Since these reserves are limited it cannot support its currency indefinitely should it want to maintain an interest rate that is below the ‘global’ interest rate. Should it want to maintain an interest rate that is above the global level, it would likely see considerable capital inflows and the only way to stabilize the exchange rate is to purchase the influx of foreign currency by printing more of its own money, thus raising the money supply and stimulating growth and inflation.
But, we hear you thinking: things are absolutely fine for the ECB, right? Because the “exchange rate is not a policy target”. So no problem there. However, we are actually thinking about yet another Impossible Trinity that is currently playing havoc with the ECB. Over the weekend, the FT reported that the ECB is in discussion over whether and how it could prevent banks from making “multibillion euro” windfall profits from the cheap loans that the ECB has provided them during the pandemic. The basic idea here is that many banks have met their TLTRO targets and therefore borrow at the average deposit facility rate over the entire life of the loan. Since this average rises much more slowly than the actual deposit facility rate when the ECB hikes rates later this month, this effectively offers banks a free lunch.
We asked ourselves: this is not a new issue and the ECB could have seen this coming when it devised the policy. So why and why now? Well, one explanation could be that the ECB has been surprised by the relative low amount of TLTRO repayments by banks so far. But a more interesting explanation – in this regard – is that, in the process of designing its Anti Fragmentation Tool, the ECB may suddenly be realising that it has to give up control of the size of its balance sheet (or better: the monetary base), if it wants to maintain control over interest rates and spreads and prevent fragmentation at the same time.
A thought experiment helps explain the issue. Let’s assume concerns over Italian spreads force the ECB to buy more Italian bonds. And let’s assume that in order to fully sterilize the impact on the monetary base, the ECB decides to sterilize by mopping up liquidity through ‘weekly deposits’ (at a slight premium over de deposit facility rate). This, however, implies that the monetary base would effectively continue to expand, posing long-term risks to inflation. Alternatively, should the ECB decide to raise its reserve requirements by the same amount as it has pumped into Italian bonds, the increase in those requirements would likely pose a problem for those banks already low on excess reserves and who would not see a commensurate increase in their reserves. As a consequence, the fragmentation issue may not be solved. And if the central bank were to issue securities with a long maturity, this would probably raise long-term interest rates (as they would compete with other core bonds). So while that may contain spreads, it would not be able to contain long-term yield levels.
So the basic conclusion here is that, with so many goals to achieve, the ECB risks becoming all tied up in its own instruments. Failure is almost guaranteed. It just has to choose where it accepts such failure.
International
Copper Soars, Iron Ore Tumbles As Goldman Says “Copper’s Time Is Now”
Copper Soars, Iron Ore Tumbles As Goldman Says "Copper’s Time Is Now"
After languishing for the past two years in a tight range despite recurring…
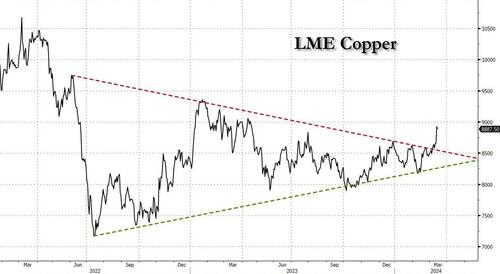
After languishing for the past two years in a tight range despite recurring speculation about declining global supply, copper has finally broken out, surging to the highest price in the past year, just shy of $9,000 a ton as supply cuts hit the market; At the same time the price of the world's "other" most important mined commodity has diverged, as iron ore has tumbled amid growing demand headwinds out of China's comatose housing sector where not even ghost cities are being built any more.
Copper surged almost 5% this week, ending a months-long spell of inertia, as investors focused on risks to supply at various global mines and smelters. As Bloomberg adds, traders also warmed to the idea that the worst of a global downturn is in the past, particularly for metals like copper that are increasingly used in electric vehicles and renewables.
Yet the commodity crash of recent years is hardly over, as signs of the headwinds in traditional industrial sectors are still all too obvious in the iron ore market, where futures fell below $100 a ton for the first time in seven months on Friday as investors bet that China’s years-long property crisis will run through 2024, keeping a lid on demand.
Indeed, while the mood surrounding copper has turned almost euphoric, sentiment on iron ore has soured since the conclusion of the latest National People’s Congress in Beijing, where the CCP set a 5% goal for economic growth, but offered few new measures that would boost infrastructure or other construction-intensive sectors.
As a result, the main steelmaking ingredient has shed more than 30% since early January as hopes of a meaningful revival in construction activity faded. Loss-making steel mills are buying less ore, and stockpiles are piling up at Chinese ports. The latest drop will embolden those who believe that the effects of President Xi Jinping’s property crackdown still have significant room to run, and that last year’s rally in iron ore may have been a false dawn.
Meanwhile, as Bloomberg notes, on Friday there were fresh signs that weakness in China’s industrial economy is hitting the copper market too, with stockpiles tracked by the Shanghai Futures Exchange surging to the highest level since the early days of the pandemic. The hope is that headwinds in traditional industrial areas will be offset by an ongoing surge in usage in electric vehicles and renewables.
And while industrial conditions in Europe and the US also look soft, there’s growing optimism about copper usage in India, where rising investment has helped fuel blowout growth rates of more than 8% — making it the fastest-growing major economy.
In any case, with the demand side of the equation still questionable, the main catalyst behind copper’s powerful rally is an unexpected tightening in global mine supplies, driven mainly by last year’s closure of a giant mine in Panama (discussed here), but there are also growing worries about output in Zambia, which is facing an El Niño-induced power crisis.
On Wednesday, copper prices jumped on huge volumes after smelters in China held a crisis meeting on how to cope with a sharp drop in processing fees following disruptions to supplies of mined ore. The group stopped short of coordinated production cuts, but pledged to re-arrange maintenance work, reduce runs and delay the startup of new projects. In the coming weeks investors will be watching Shanghai exchange inventories closely to gauge both the strength of demand and the extent of any capacity curtailments.
“The increase in SHFE stockpiles has been bigger than we’d anticipated, but we expect to see them coming down over the next few weeks,” Colin Hamilton, managing director for commodities research at BMO Capital Markets, said by phone. “If the pace of the inventory builds doesn’t start to slow, investors will start to question whether smelters are actually cutting and whether the impact of weak construction activity is starting to weigh more heavily on the market.”
* * *
Few have been as happy with the recent surge in copper prices as Goldman's commodity team, where copper has long been a preferred trade (even if it may have cost the former team head Jeff Currie his job due to his unbridled enthusiasm for copper in the past two years which saw many hedge fund clients suffer major losses).
As Goldman's Nicholas Snowdon writes in a note titled "Copper's time is now" (available to pro subscribers in the usual place)...
... there has been a "turn in the industrial cycle." Specifically according to the Goldman analyst, after a prolonged downturn, "incremental evidence now points to a bottoming out in the industrial cycle, with the global manufacturing PMI in expansion for the first time since September 2022." As a result, Goldman now expects copper to rise to $10,000/t by year-end and then $12,000/t by end of Q1-25.’
Here are the details:
Previous inflexions in global manufacturing cycles have been associated with subsequent sustained industrial metals upside, with copper and aluminium rising on average 25% and 9% over the next 12 months. Whilst seasonal surpluses have so far limited a tightening alignment at a micro level, we expect deficit inflexions to play out from quarter end, particularly for metals with severe supply binds. Supplemented by the influence of anticipated Fed easing ahead in a non-recessionary growth setting, another historically positive performance factor for metals, this should support further upside ahead with copper the headline act in this regard.
Goldman then turns to what it calls China's "green policy put":
Much of the recent focus on the “Two Sessions” event centred on the lack of significant broad stimulus, and in particular the limited property support. In our view it would be wrong – just as in 2022 and 2023 – to assume that this will result in weak onshore metals demand. Beijing’s emphasis on rapid growth in the metals intensive green economy, as an offset to property declines, continues to act as a policy put for green metals demand. After last year’s strong trends, evidence year-to-date is again supportive with aluminium and copper apparent demand rising 17% and 12% y/y respectively. Moreover, the potential for a ‘cash for clunkers’ initiative could provide meaningful right tail risk to that healthy demand base case. Yet there are also clear metal losers in this divergent policy setting, with ongoing pressure on property related steel demand generating recent sharp iron ore downside.
Meanwhile, Snowdon believes that the driver behind Goldman's long-running bullish view on copper - a global supply shock - continues:
Copper’s supply shock progresses. The metal with most significant upside potential is copper, in our view. The supply shock which began with aggressive concentrate destocking and then sharp mine supply downgrades last year, has now advanced to an increasing bind on metal production, as reflected in this week's China smelter supply rationing signal. With continued positive momentum in China's copper demand, a healthy refined import trend should generate a substantial ex-China refined deficit this year. With LME stocks having halved from Q4 peak, China’s imminent seasonal demand inflection should accelerate a path into extreme tightness by H2. Structural supply underinvestment, best reflected in peak mine supply we expect next year, implies that demand destruction will need to be the persistent solver on scarcity, an effect requiring substantially higher pricing than current, in our view. In this context, we maintain our view that the copper price will surge into next year (GSe 2025 $15,000/t average), expecting copper to rise to $10,000/t by year-end and then $12,000/t by end of Q1-25’
Another reason why Goldman is doubling down on its bullish copper outlook: gold.
The sharp rally in gold price since the beginning of March has ended the period of consolidation that had been present since late December. Whilst the initial catalyst for the break higher came from a (gold) supportive turn in US data and real rates, the move has been significantly amplified by short term systematic buying, which suggests less sticky upside. In this context, we expect gold to consolidate for now, with our economists near term view on rates and the dollar suggesting limited near-term catalysts for further upside momentum. Yet, a substantive retracement lower will also likely be limited by resilience in physical buying channels. Nonetheless, in the midterm we continue to hold a constructive view on gold underpinned by persistent strength in EM demand as well as eventual Fed easing, which should crucially reactivate the largely for now dormant ETF buying channel. In this context, we increase our average gold price forecast for 2024 from $2,090/toz to $2,180/toz, targeting a move to $2,300/toz by year-end.
Much more in the full Goldman note available to pro subs.
Government
Moderna turns the spotlight on long Covid with new initiatives
Moderna’s latest Covid effort addresses the often-overlooked chronic condition of long Covid — and encourages vaccination to reduce risks. A digital…

Moderna’s latest Covid effort addresses the often-overlooked chronic condition of long Covid — and encourages vaccination to reduce risks. A digital campaign debuted Friday along with a co-sponsored event in Detroit offering free CT scans, which will also be used in ongoing long Covid research.
In a new video, a young woman describes her three-year battle with long Covid, which includes losing her job, coping with multiple debilitating symptoms and dealing with the negative effects on her family. She ends by saying, “The only way to prevent long Covid is to not get Covid” along with an on-screen message about where to find Covid-19 vaccines through the vaccines.gov website.
“Last season we saw people would get a flu shot, but they didn’t always get a Covid shot,” said Moderna’s Chief Brand Officer Kate Cronin. “People should get their flu shot, but they should also get their Covid shot. There’s no risk of long flu, but there is the risk of long-term effects of Covid.”
It’s Moderna’s “first effort to really sound the alarm,” she said, and the debut coincides with the second annual Long Covid Awareness Day.
An estimated 17.6 million Americans are living with long Covid, according to the latest CDC data. About four million of them are out of work because of the condition, resulting in an estimated $170 billion in lost wages.
While HHS anted up $45 million in grants last year to expand long Covid support initiatives along with public health campaigns, the condition is still often ignored and underfunded.
“It’s not just about the initial infection of Covid, but also if you get it multiple times, your risks goes up significantly,” Cronin said. “It’s important that people understand that.”
grants covid-19 cdc hhsGovernment
Consequences Minus Truth
Consequences Minus Truth
Authored by James Howard Kunstler via Kunstler.com,
“People crave trust in others, because God is found there.”
-…

Authored by James Howard Kunstler via Kunstler.com,
“People crave trust in others, because God is found there.”
- Dom de Bailleul
The rewards of civilization have come to seem rather trashy in these bleak days of late empire; so, why even bother pretending to be civilized? This appears to be the ethos driving our politics and culture now. But driving us where? Why, to a spectacular sort of crack-up, and at warp speed, compared to the more leisurely breakdown of past societies that arrived at a similar inflection point where Murphy’s Law replaced the rule of law.
The US Military Academy at West point decided to “upgrade” its mission statement this week by deleting the phrase Duty, Honor, Country that summarized its essential moral orientation. They replaced it with an oblique reference to “Army Values,” without spelling out what these values are, exactly, which could range from “embrace the suck” to “charlie foxtrot” to “FUBAR” — all neatly applicable to our country’s current state of perplexity and dread.
Are you feeling more confident that the US military can competently defend our country? Probably more like the opposite, because the manipulation of language is being used deliberately to turn our country inside-out and upside-down. At this point we probably could not successfully pacify a Caribbean island if we had to, and you’ve got to wonder what might happen if we have to contend with countless hostile subversive cadres who have slipped across the border with the estimated nine-million others ushered in by the government’s welcome wagon.
Momentous events await. This Monday, the Supreme Court will entertain oral arguments on the case Missouri, et al. v. Joseph R. Biden, Jr., et al. The integrity of the First Amendment hinges on the decision. Do we have freedom of speech as set forth in the Constitution? Or is it conditional on how government officials feel about some set of circumstances? At issue specifically is the government’s conduct in coercing social media companies to censor opinion in order to suppress so-called “vaccine hesitancy” and to manipulate public debate in the 2020 election. Government lawyers have argued that they were merely “communicating” with Twitter, Facebook, Google, and others about “public health disinformation and election conspiracies.”
You can reasonably suppose that this was our government’s effort to disable the truth, especially as it conflicted with its own policy and activities — from supporting BLM riots to enabling election fraud to mandating dubious vaccines. Former employees of the FBI and the CIA were directly implanted in social media companies to oversee the carrying-out of censorship orders from their old headquarters. The former general counsel (top lawyer) for the FBI, James Baker, slid unnoticed into the general counsel seat at Twitter until Elon Musk bought the company late in 2022 and flushed him out. The so-called Twitter Files uncovered by indy reporters Matt Taibbi, Michael Shellenberger, and others, produced reams of emails from FBI officials nagging Twitter execs to de-platform people and bury their dissent. You can be sure these were threats, not mere suggestions.
One of the plaintiffs joined to Missouri v. Biden is Dr. Martin Kulldorff, a biostatistician and professor at the Harvard Medical School, who opposed Covid-19 lockdowns and vaccine mandates. He was one of the authors of the open letter called The Great Barrington Declaration (October, 2020) that articulated informed medical dissent for a bamboozled public. He was fired from his job at Harvard just this past week for continuing his refusal to take the vaccine. Harvard remains among a handful of institutions that still require it, despite massive evidence that it is ineffective and hazardous. Like West Point, maybe Harvard should ditch its motto, Veritas, Latin for “truth.”
A society hostile to truth can’t possibly remain civilized, because it will also be hostile to reality. That appears to be the disposition of the people running things in the USA these days. The problem, of course, is that this is not a reality-optional world, despite the wishes of many Americans (and other peoples of Western Civ) who wish it would be.
Next up for us will be “Joe Biden’s” attempt to complete the bankruptcy of our country with $7.3-trillion proposed budget, 20 percent over the previous years spending, based on a $5-billion tax increase. Good luck making that work. New York City alone is faced with paying $387 a day for food and shelter for each of an estimated 64,800 illegal immigrants, which amounts to $9.15-billion a year. The money doesn’t exist, of course. New York can thank “Joe Biden’s” executive agencies for sticking them with this unbearable burden. It will be the end of New York City. There will be no money left for public services or cultural institutions. That’s the reality and that’s the truth.
A financial crack-up is probably the only thing short of all-out war that will get the public’s attention at this point. I wouldn’t be at all surprised if it happened next week. Historians of the future, stir-frying crickets and fiddleheads over their campfires will marvel at America’s terminal act of gluttony: managing to eat itself alive.
* * *
Support his blog by visiting Jim’s Patreon Page or Substack
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Spread & Containment2 days ago
Spread & Containment2 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex


























