#MacroView: MMT – When Theories Collide With Reality
Previously, we discussed Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) and its one limitation of inflation. However, as is always the case when "theories" collide with "reality," the tenants of the theory are quickly discarded.
There is no doubt that since 2020 both Repub

Previously, we discussed Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) and its one limitation of inflation. However, as is always the case when “theories” collide with “reality,” the tenants of the theory are quickly discarded.
There is no doubt that since 2020 both Republicans and Democrats alike have shunned fiscal responsibility for the short-term gratification of MMT. Ms. Kelton tweeted such earlier this year.
The writing is hilariously on the wall here, but people want to pretend that a bipartisan, multi-trillion dollar climate-infrastructure package can and must be “paid for” with new tax revenue. Wake me when reality sets in.
— Stephanie Kelton (@StephanieKelton) March 15, 2021
From the $2.2 trillion CARES Act to the $900 billion HERO Act, to President Biden’s $1.9 trillion American Rescue Plan, the government has plunged into MMT with both feet.
If you are unfamiliar with MMT, Kelton describes it as a macroeconomic school of thought or paradigm that explains how a sovereign country that controls its currency behaves. To wit:
“MMT starts with a simple observation, and that is that the US dollar is a simple public monopoly. In other words, the United States currency comes from the United States government; it can’t come from anywhere else. So, what that means is that the federal government is nothing like a household.
For households or private businesses to spend they’ve got to come up with the money, right? And the federal government can never run out of money. It cannot face a solvency problem with bills coming due that it can’t afford to pay. So it never has to worry about finding the money to be able to spend.”
There is nothing untrue about that statement. However, while the Government can indeed “print money to meet all obligations,” it does NOT mean there are no consequences. The chart below really tells you all you need to know.
Always One Part Of The Theory
Throughout history, the purveyors of fiscal and monetary policies always use the one part of the theory that suits them. The spending part. Thus, beginning in the early ’80s, politicians and economists latched onto “Keynesian” economic theory. Why? Because it paved the way to engage into historic levels of deficit spending.
According to Keynes, some microeconomic-level actions, if taken collectively, can lead to inefficient aggregate macroeconomic outcomes. Such leads the economy to operate below its potential output and growth rate (i.e., a recession). As Keynes noted:
“A general glut occurs when aggregate demand for goods is insufficient. Such leads to an economic downturn resulting in losses of potential output. Such creates unnecessarily high unemployment resulting from the producers’ defensive (or reactive) decisions.”
When there is a lack of demand from consumers, producers react defensively to reduce output. In such a situation, Keynes’ theory suggests the Government should intervene.
“In such a situation, government could use policies to increase aggregate demand, thus increasing economic activity and reducing unemployment and deflation. Investment by the government injects income, which results in more spending in the general economy, which in turn stimulates more production and investment involving still more income and spending and so forth. The initial stimulation starts a cascade of events, whose total increase in economic activity is a multiple of the original investment.”
What politicians “heard” was the “spend money” part.
The “Inconvenient” Part
However, politicians always ignore the “other part” of the theory, which states that deficit spending should be cut and surpluses rebuilt when economic activity returns.
As shown, that never happened, and for the last 40-years, economic participants have paid the price of slower growth and prosperity.
However, since Keynes’ model seems to have failed to produce the desired result, economists need a new theory to explain why debts and deficits don’t matter.
The Shiney New Toy – MMT
In reality, there is little difference between Keyne’s and MMT. Both promote the use of government debt to boost economic growth during times of economic hardship. The difference is that Keynes stated the deficit should get reversed following the downturn. MMT proposes that governments can deficit spend regardless of the economic state as long as inflation is not present. To wit:
“First advanced by MMT guru Warren Mosler in the 1990s, is quite simple: federal spending gets unconstrained by revenue. Taxes function only to regulate demand and hence inflation; federal borrowing functions only to regulate interest rates. Sovereign government treasuries can create and spend as much money as they like to stimulate growth, especially when the economy is underperforming. If inflation spikes, the government can impose taxes to take money out of the economy.” – Mises Institute
Currently, politicians, Janet Yellen and the Federal Reserve have latched onto this theory as it uncomplicates having to eventually “pay” for the debt. As the first part of the theory goes, “spend as much as you like.” However, once again, they ignore the second part of the theory that limits MMT – inflation.
The flood of money from the Government sent directly to households shifted demand from “services,” which has a very low economic multiplier effect, to the high multiplier of “manufacturing.” That shift, and increase in demand, led to a surge in inflationary pressures.
The Government should be addressing the “limiter” of MMT by raising taxes and cutting spending until inflationary pressures subside.
However, as we suspected, we see no evidence of that currently. Politicians from both sides of the aisle are discussing a $1.2 trillion “infrastructure” plan with no tax increases.
Misdiagnosing The Illness
The desire to use “debt” to cure the “economic illness” seems logical, particularly when viewing it through the MMT lens. However, it is the “cure” that keeps the patient on “life support.”
The policies enacted, be it stimulus, quantitative easing, or bailout programs, fail to create sustainable economic growth because they are debt-based. Using debt to drag forward future consumption only leaves a void that must get filled in the future. Most importantly, the use of debt for non-productive investments, like a stimulus that has a one-time effect, is the debt-service that then absorbs future revenues.
The view that “more money in people’s pockets” will drive up consumer spending, with a sustainable boost to GDP, is wrong. It has not happened in 40-years. What gets missed is that things like temporary tax cuts, or one-time injections, do not create economic growth but merely reschedules it. The average American may fall for a near-term increase in their take-home pay, but any increased consumption today will be matched by a decrease tomorrow when the stimulus ends.
Such is assuming the balance sheet at home is not broken. As we saw during the “Great Depression” period, most economists thought that the simple solution was just more stimulus. Work programs, lower interest rates, and government spending didn’t work to stem the tide of the depression era.
The Ricardian Equivalence
There is also the problem of a shift in psychology as noted by David Rosenberg:
“Another basic law is Ricardian Equivalence, which is all about how economic agents prepare for a future of higher taxation, manifesting in an elevated personal savings rate. Such means that attempts to stimulate an economy by increasing debt-financed government spending will not be effective because investors and consumers understand that the debt will eventually have to get paid for in the form of future taxes.”
The theory argues that people will save based on their expectation of increased future taxes to pay off the debt. Such will offset the increase in aggregate demand from the increased government spending. But, unfortunately, such also implies that Keynesian fiscal policy will not always be effective in providing a lasting boost to economic growth.”
As he notes, individuals base spending upon their future incomes. Thus, if they do not believe that more stimulus is coming, they will save rather than spend, limiting the impact on economic growth.
Furthermore, the issue of higher taxes is settling in with consumers as well. Tax-increase expectations in the January release of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Survey of Consumer Expectations rose for the third month in a row to the highest level in more than seven years. This increase occurred along with a jump in government debt-growth expectations, which are now double normal pre-pandemic levels.
Conclusion
The allure of MMT is strong amid the current economic upheavals. Such is particularly the case since it makes possible every progressive program from unlimited public works, federal jobs, uneconomic green energy schemes, “Medicare for all,” free college, free housing, and a host of others. However, as the Mises Institutes correctly notes:
“The promise of something for nothing will never lose its luster. So MMT should be viewed as a form of political propaganda rather than any real economic or public policy. And like all propaganda, we must fight it with appeals to reality. MMT, where deficits don’t matter, is an unreal place.”
We will likely continue to pay the price of misguided economic policies that only work in the mathematical formulas generated in “Ivory Towers.” Still, in the “real world,” these theories, while well intentioned, always yield a negative result on those it was supposed to help.
The post #MacroView: MMT – When Theories Collide With Reality appeared first on RIA.
recession depression unemployment pandemic stimulus economic growth federal reserve government debt us dollar gdp interest rates consumer spending unemployment stimulusSpread & Containment
Separating Information From Disinformation: Threats From The AI Revolution
Separating Information From Disinformation: Threats From The AI Revolution
Authored by Per Bylund via The Mises Institute,
Artificial intelligence…

Authored by Per Bylund via The Mises Institute,
Artificial intelligence (AI) cannot distinguish fact from fiction. It also isn’t creative or can create novel content but repeats, repackages, and reformulates what has already been said (but perhaps in new ways).
I am sure someone will disagree with the latter, perhaps pointing to the fact that AI can clearly generate, for example, new songs and lyrics. I agree with this, but it misses the point. AI produces a “new” song lyric only by drawing from the data of previous song lyrics and then uses that information (the inductively uncovered patterns in it) to generate what to us appears to be a new song (and may very well be one). However, there is no artistry in it, no creativity. It’s only a structural rehashing of what exists.
Of course, we can debate to what extent humans can think truly novel thoughts and whether human learning may be based solely or primarily on mimicry. However, even if we would—for the sake of argument—agree that all we know and do is mere reproduction, humans have limited capacity to remember exactly and will make errors. We also fill in gaps with what subjectively (not objectively) makes sense to us (Rorschach test, anyone?). Even in this very limited scenario, which I disagree with, humans generate novelty beyond what AI is able to do.
Both the inability to distinguish fact from fiction and the inductive tether to existent data patterns are problems that can be alleviated programmatically—but are open for manipulation.
Manipulation and Propaganda
When Google launched its Gemini AI in February, it immediately became clear that the AI had a woke agenda. Among other things, the AI pushed woke diversity ideals into every conceivable response and, among other things, refused to show images of white people (including when asked to produce images of the Founding Fathers).
Tech guru and Silicon Valley investor Marc Andreessen summarized it on X (formerly Twitter): “I know it’s hard to believe, but Big Tech AI generates the output it does because it is precisely executing the specific ideological, radical, biased agenda of its creators. The apparently bizarre output is 100% intended. It is working as designed.”
There is indeed a design to these AIs beyond the basic categorization and generation engines. The responses are not perfectly inductive or generative. In part, this is necessary in order to make the AI useful: filters and rules are applied to make sure that the responses that the AI generates are appropriate, fit with user expectations, and are accurate and respectful. Given the legal situation, creators of AI must also make sure that the AI does not, for example, violate intellectual property laws or engage in hate speech. AI is also designed (directed) so that it does not go haywire or offend its users (remember Tay?).
However, because such filters are applied and the “behavior” of the AI is already directed, it is easy to take it a little further. After all, when is a response too offensive versus offensive but within the limits of allowable discourse? It is a fine and difficult line that must be specified programmatically.
It also opens the possibility for steering the generated responses beyond mere quality assurance. With filters already in place, it is easy to make the AI make statements of a specific type or that nudges the user in a certain direction (in terms of selected facts, interpretations, and worldviews). It can also be used to give the AI an agenda, as Andreessen suggests, such as making it relentlessly woke.
Thus, AI can be used as an effective propaganda tool, which both the corporations creating them and the governments and agencies regulating them have recognized.
Misinformation and Error
States have long refused to admit that they benefit from and use propaganda to steer and control their subjects. This is in part because they want to maintain a veneer of legitimacy as democratic governments that govern based on (rather than shape) people’s opinions. Propaganda has a bad ring to it; it’s a means of control.
However, the state’s enemies—both domestic and foreign—are said to understand the power of propaganda and do not hesitate to use it to cause chaos in our otherwise untainted democratic society. The government must save us from such manipulation, they claim. Of course, rarely does it stop at mere defense. We saw this clearly during the covid pandemic, in which the government together with social media companies in effect outlawed expressing opinions that were not the official line (see Murthy v. Missouri).
AI is just as easy to manipulate for propaganda purposes as social media algorithms but with the added bonus that it isn’t only people’s opinions and that users tend to trust that what the AI reports is true. As we saw in the previous article on the AI revolution, this is not a valid assumption, but it is nevertheless a widely held view.
If the AI then can be instructed to not comment on certain things that the creators (or regulators) do not want people to see or learn, then it is effectively “memory holed.” This type of “unwanted” information will not spread as people will not be exposed to it—such as showing only diverse representations of the Founding Fathers (as Google’s Gemini) or presenting, for example, only Keynesian macroeconomic truths to make it appear like there is no other perspective. People don’t know what they don’t know.
Of course, nothing is to say that what is presented to the user is true. In fact, the AI itself cannot distinguish fact from truth but only generates responses according to direction and only based on whatever the AI has been fed. This leaves plenty of scope for the misrepresentation of the truth and can make the world believe outright lies. AI, therefore, can easily be used to impose control, whether it is upon a state, the subjects under its rule, or even a foreign power.
The Real Threat of AI
What, then, is the real threat of AI? As we saw in the first article, large language models will not (cannot) evolve into artificial general intelligence as there is nothing about inductive sifting through large troves of (humanly) created information that will give rise to consciousness. To be frank, we haven’t even figured out what consciousness is, so to think that we will create it (or that it will somehow emerge from algorithms discovering statistical language correlations in existing texts) is quite hyperbolic. Artificial general intelligence is still hypothetical.
As we saw in the second article, there is also no economic threat from AI. It will not make humans economically superfluous and cause mass unemployment. AI is productive capital, which therefore has value to the extent that it serves consumers by contributing to the satisfaction of their wants. Misused AI is as valuable as a misused factory—it will tend to its scrap value. However, this doesn’t mean that AI will have no impact on the economy. It will, and already has, but it is not as big in the short-term as some fear, and it is likely bigger in the long-term than we expect.
No, the real threat is AI’s impact on information. This is in part because induction is an inappropriate source of knowledge—truth and fact are not a matter of frequency or statistical probabilities. The evidence and theories of Nicolaus Copernicus and Galileo Galilei would get weeded out as improbable (false) by an AI trained on all the (best and brightest) writings on geocentrism at the time. There is no progress and no learning of new truths if we trust only historical theories and presentations of fact.
However, this problem can probably be overcome by clever programming (meaning implementing rules—and fact-based limitations—to the induction problem), at least to some extent. The greater problem is the corruption of what AI presents: the misinformation, disinformation, and malinformation that its creators and administrators, as well as governments and pressure groups, direct it to create as a means of controlling or steering public opinion or knowledge.
This is the real danger that the now-famous open letter, signed by Elon Musk, Steve Wozniak, and others, pointed to:
“Should we let machines flood our information channels with propaganda and untruth? Should we automate away all the jobs, including the fulfilling ones? Should we develop nonhuman minds that might eventually outnumber, outsmart, obsolete and replace us? Should we risk loss of control of our civilization?”
Other than the economically illiterate reference to “automat[ing] away all the jobs,” the warning is well-taken. AI will not Terminator-like start to hate us and attempt to exterminate mankind. It will not make us all into biological batteries, as in The Matrix. However, it will—especially when corrupted—misinform and mislead us, create chaos, and potentially make our lives “solitary, poor, nasty, brutish and short.”
Government
Problems After COVID-19 Vaccination More Prevalent Among Naturally Immune: Study
Problems After COVID-19 Vaccination More Prevalent Among Naturally Immune: Study
Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis…
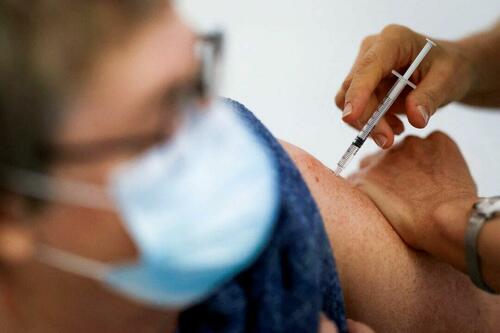
Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
People who recovered from COVID-19 and received a COVID-19 shot were more likely to suffer adverse reactions, researchers in Europe are reporting.
Participants in the study were more likely to experience an adverse reaction after vaccination regardless of the type of shot, with one exception, the researchers found.
Across all vaccine brands, people with prior COVID-19 were 2.6 times as likely after dose one to suffer an adverse reaction, according to the new study. Such people are commonly known as having a type of protection known as natural immunity after recovery.
People with previous COVID-19 were also 1.25 times as likely after dose 2 to experience an adverse reaction.
The findings held true across all vaccine types following dose one.
Of the female participants who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, for instance, 82 percent who had COVID-19 previously experienced an adverse reaction after their first dose, compared to 59 percent of females who did not have prior COVID-19.
The only exception to the trend was among males who received a second AstraZeneca dose. The percentage of males who suffered an adverse reaction was higher, 33 percent to 24 percent, among those without a COVID-19 history.
“Participants who had a prior SARS-CoV-2 infection (confirmed with a positive test) experienced at least one adverse reaction more often after the 1st dose compared to participants who did not have prior COVID-19. This pattern was observed in both men and women and across vaccine brands,” Florence van Hunsel, an epidemiologist with the Netherlands Pharmacovigilance Centre Lareb, and her co-authors wrote.
There were only slightly higher odds of the naturally immune suffering an adverse reaction following receipt of a Pfizer or Moderna booster, the researchers also found.
The researchers performed what’s known as a cohort event monitoring study, following 29,387 participants as they received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine. The participants live in a European country such as Belgium, France, or Slovakia.
Overall, three-quarters of the participants reported at least one adverse reaction, although some were minor such as injection site pain.
Adverse reactions described as serious were reported by 0.24 percent of people who received a first or second dose and 0.26 percent for people who received a booster. Different examples of serious reactions were not listed in the study.
Participants were only specifically asked to record a range of minor adverse reactions (ADRs). They could provide details of other reactions in free text form.
“The unsolicited events were manually assessed and coded, and the seriousness was classified based on international criteria,” researchers said.
The free text answers were not provided by researchers in the paper.
“The authors note, ‘In this manuscript, the focus was not on serious ADRs and adverse events of special interest.’” Yet, in their highlights section they state, “The percentage of serious ADRs in the study is low for 1st and 2nd vaccination and booster.”
Dr. Joel Wallskog, co-chair of the group React19, which advocates for people who were injured by vaccines, told The Epoch Times: “It is intellectually dishonest to set out to study minor adverse events after COVID-19 vaccination then make conclusions about the frequency of serious adverse events. They also fail to provide the free text data.” He added that the paper showed “yet another study that is in my opinion, deficient by design.”
Ms. Hunsel did not respond to a request for comment.
She and other researchers listed limitations in the paper, including how they did not provide data broken down by country.
The paper was published by the journal Vaccine on March 6.
The study was funded by the European Medicines Agency and the Dutch government.
No authors declared conflicts of interest.
Some previous papers have also found that people with prior COVID-19 infection had more adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination, including a 2021 paper from French researchers. A U.S. study identified prior COVID-19 as a predictor of the severity of side effects.
Some other studies have determined COVID-19 vaccines confer little or no benefit to people with a history of infection, including those who had received a primary series.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention still recommends people who recovered from COVID-19 receive a COVID-19 vaccine, although a number of other health authorities have stopped recommending the shot for people who have prior COVID-19.
Another New Study
In another new paper, South Korean researchers outlined how they found people were more likely to report certain adverse reactions after COVID-19 vaccination than after receipt of another vaccine.
The reporting of myocarditis, a form of heart inflammation, or pericarditis, a related condition, was nearly 20 times as high among children as the reporting odds following receipt of all other vaccines, the researchers found.
The reporting odds were also much higher for multisystem inflammatory syndrome or Kawasaki disease among adolescent COVID-19 recipients.
Researchers analyzed reports made to VigiBase, which is run by the World Health Organization.
“Based on our results, close monitoring for these rare but serious inflammatory reactions after COVID-19 vaccination among adolescents until definitive causal relationship can be established,” the researchers wrote.
The study was published by the Journal of Korean Medical Science in its March edition.
Limitations include VigiBase receiving reports of problems, with some reports going unconfirmed.
Funding came from the South Korean government. One author reported receiving grants from pharmaceutical companies, including Pfizer.
Uncategorized
Key shipping company files for Chapter 11 bankruptcy
The Illinois-based general freight trucking company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy to reorganize.

The U.S. trucking industry has had a difficult beginning of the year for 2024 with several logistics companies filing for bankruptcy to seek either a Chapter 7 liquidation or Chapter 11 reorganization.
The Covid-19 pandemic caused a lot of supply chain issues for logistics companies and also created a shortage of truck drivers as many left the business for other occupations. Shipping companies, in the meantime, have had extreme difficulty recruiting new drivers for thousands of unfilled jobs.
Related: Tesla rival’s filing reveals Chapter 11 bankruptcy is possible
Freight forwarder company Boateng Logistics joined a growing list of shipping companies that permanently shuttered their businesses as the firm on Feb. 22 filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy with plans to liquidate.
The Carlsbad, Calif., logistics company filed its petition in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of California listing assets up to $50,000 and and $1 million to $10 million in liabilities. Court papers said it owed millions of dollars in liabilities to trucking, logistics and factoring companies. The company filed bankruptcy before any creditors could take legal action.
Lawsuits force companies to liquidate in bankruptcy
Lawsuits, however, can force companies to file bankruptcy, which was the case for J.J. & Sons Logistics of Clint, Texas, which on Jan. 22 filed for Chapter 7 liquidation in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Western District of Texas. The company filed bankruptcy four days before the scheduled start of a trial for a wrongful death lawsuit filed by the family of a former company truck driver who had died from drowning in 2016.
California-based logistics company Wise Choice Trans Corp. shut down operations and filed for Chapter 7 liquidation on Jan. 4 in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Northern District of California, listing $1 million to $10 million in assets and liabilities.
The Hayward, Calif., third-party logistics company, founded in 2009, provided final mile, less-than-truckload and full truckload services, as well as warehouse and fulfillment services in the San Francisco Bay Area.
The Chapter 7 filing also implemented an automatic stay against all legal proceedings, as the company listed its involvement in four legal actions that were ongoing or concluded. Court papers reportedly did not list amounts for damages.
In some cases, debtors don't have to take a drastic action, such as a liquidation, and can instead file a Chapter 11 reorganization.
Shutterstock
Nationwide Cargo seeks to reorganize its business
Nationwide Cargo Inc., a general freight trucking company that also hauls fresh produce and meat, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Northern District of Illinois with plans to reorganize its business.
The East Dundee, Ill., shipping company listed $1 million to $10 million in assets and $10 million to $50 million in liabilities in its petition and said funds will not be available to pay unsecured creditors. The company operates with 183 trucks and 171 drivers, FreightWaves reported.
Nationwide Cargo's three largest secured creditors in the petition were Equify Financial LLC (owed about $3.5 million,) Commercial Credit Group (owed about $1.8 million) and Continental Bank NA (owed about $676,000.)
The shipping company reported gross revenue of about $34 million in 2022 and about $40 million in 2023. From Jan. 1 until its petition date, the company generated $9.3 million in gross revenue.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
bankruptcy pandemic covid-19 stocks-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Spread & Containment2 days ago
Spread & Containment2 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A

























