International
Is Hyperinflation Really A Threat?
Is Hyperinflation Really A Threat?
Authored by Lance Roberts via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
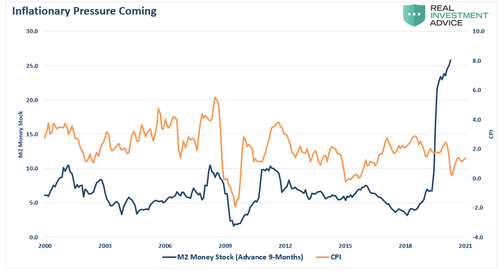
Is hyperinflation a threat? While I was on vacation this past week, I got into a discussion on the issue.
This is how capitalism will end in the…
Authored by Lance Roberts via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
Is hyperinflation a threat? While I was on vacation this past week, I got into a discussion on the issue.
This is how capitalism will end in the US
— HousePriceMania (@HousePriceMania) March 18, 2021
Same way it ended in Germany. pic.twitter.com/m3imOQJGDz
While the discussion ebbed between a broken financial system and capitalism’s failure, the gist was hyperinflation was coming. The measure of money in the system, known as M2, is skyrocketing, which certainly supports his concern. Now, with the Biden administration adding another $1.9 trillion into the economy, those concerns have risen.
In a recent Bloomberg interview, Larry Summers stated:
“There is a chance that macroeconomic stimulus on a scale closer to World War II levels will set off inflationary pressures of a kind not seen in a generation. I worry that containing an inflationary outbreak without triggering a recession could be even more difficult now than in the past.”
Are those concerns valid? Should we worry about a hyperinflationary surge like we saw in the late 70s? Or, are the deflationary pressures on the economy still present?
The Difference Between Inflation & Hyper-Inflation
Let’s start by defining the difference between an inflationary increase and hyperinflation.
Could repeated stimulus into the economy that exceeds the current output gap lead to a rise in inflationary pressures? Absolutely.
However, “hyperinflation” is not a threat. At least not yet.
“Hyper-inflation comes from a complete loss of faith in a currency from the threat of losing a war (Weimer Republic), an economic collapse, or some other catastrophic event. The U.S., even with all of our economic ills and woes, is still the safest place, in terms of liquidity, depth, and strength, to store excess reserves. The near historic low yield on government treasuries tells the story here.” – Real Investment Show
What is important is whether or not inflationary pressures, regardless of where they come from, have reached levels that could impact economic growth. While we see commodity-based inflation, primarily in food and energy, is that alone enough to offset the deflationary pressures we see economically from wages, debts, deficits, and rising dependency on social welfare?
Inflation is a function of three primary components:
-
The velocity of money,
-
Wages, and
-
Commodity prices.
The Velocity of Money
As I discussed in “2021 – A Disappointment Of Growth & Inflation,” monetary velocity is defined as:
“The velocity of money is important for measuring the rate at which money in circulation is used for purchasing goods and services. Velocity is useful in gauging the health and vitality of the economy. High money velocity is usually associated with a healthy, expanding economy. Low money velocity is usually associated with recessions and contractions.”
The chart shows what we have known for quite some time: money is not flowing through the system.
While there are many criticisms over this measure’s validity, it is a simplistic representation of demand. For prices across the entire spectrum to rise, there has to be more demand than supply. If the velocity of money is increasing, then “demand” in the system is growing. That increase in demand allows producers to raise prices and pass on costs to consumers.
Currently, companies are absorbing those costs, which eats into profit margins. To offset that increase, we have seen companies continuing to scale back employment, increase automation, and reduce CapEx. The decline in “activity” has worsened post-pandemic.
Wage Inflation
Secondly, to have “sustainable” levels of inflation, wages must be increasing.
As wages rise, individuals can consume more, increasing aggregate demand, which, as noted above, leads to higher prices. Unfortunately, wage and salary disbursements, on a year over year basis, have been on the decline since 1980. Such remains commensurate with the weaker economic growth and declining monetary velocity.
While wages have turned up post the recessionary lows, they are still sharply lower than at the turn of the century. That deterioration in wages, combined with credit constraints, has continued to put pressure on producers’ ability to raise prices. As a consequence, we continue to see more reliance on discounting to move inventories.
Commodity Prices
Finally, commodity prices are the headline event that everyone notices. Rising costs of milk, bread, gasoline, and the essentials of survival slap them in the face daily. While deflationary pressures exist in everything from apparel to iPads – these items are not consumed daily, and the psychological impact gets felt far less. Nonetheless, commodity prices are essential in consideration of inflation due to the effect on personal incomes.
Since consumption is roughly 70% of the economic calculation, higher commodity prices, particularly food and energy costs, can have a “psychological” impact on consumers. Such is especially an issue if it occurs quickly. Consumers can adjust to higher prices over time as long as wages rise at a proportional rate; however, that is not the case currently. The increase in commodity prices has been such a focal point with the average “American.”
So, what is the risk of surging inflation?
The High-Inflation Index
None of these items, individually or collectively, point to hyper-inflation. However, to measure these components’ impact on the overall economy, I created a composite index of wages, commodity prices, and velocity. The index clearly shows the inflationary pressures of the late ’70s, which gives us a confidence level in the assumptions’ validity. The dashed line is the average level of the index since 1959.
Importantly, there is a high correlation between the rise and fall of the index and overall real GDP growth. When the index has risen above its average level, the economy has begun to weaken or receded into recession. Currently, the inflation index is at 1.12, which well below the long-term average of 4.94.
The reading suggests what we already know. That since 2007, the average economic growth rate has been feeble at just 1.3%, or 1.7%, if we use estimates for 2021.
Secondly, while inflationary pressures are indeed rising short-term, we tend to agree with Jerome Powell’s assessment they could be “transient.”
There are three reasons for that statement:
-
Current inflationary pressures are a function of the stimulus flooding into the system, which is “transient.”
-
The economy is dependent on zero interest rates and $120 billion in monthly bond purchases, which suggests there is little if any, organic economic growth; and,
-
The enormous burden of debt continuing to depress economic growth, and notably, monetary velocity.

Conclusion
The threat of hyperinflation remains an outlier due to the economic detractors mounting over the last 40-years.
-
A decline in organic savings that depletes productive investments
-
An aging demographic that is top-heavy and drawing on social benefits at an advancing rate.
-
A heavily indebted economy with debt/GDP ratios above 100%.
-
The decline in exports continues due to a weak global economic environment.
-
Slowing domestic economic growth rates.
-
An underemployed younger demographic.
-
An inelastic supply-demand curve
-
Weak industrial production
-
Dependence on productivity increases to offset reduced employment
While the U.S. economy certainly has its share of problems, the U.S. is still the “cleanest shirt in a pile of filthy laundry.” With the Treasury still the safest source to store foreign currency reserves, at the moment, the likelihood of a complete economic meltdown is minimal.
Furthermore, due to the deflationary pressures that currently exist due to weak wage growth, automation, and mounting debts, it is unlikely that inflation can rise much before it triggers an economic contraction. Since interest rates adjust for inflation, a rise in inflationary pressures is a “double whammy” on consumption.
However, while the fears of a hyperinflationary event are overblown, other factors could be equally devastating to individuals and the economy.
The debt problem remains a massive risk to monetary and fiscal policy. If rates rise, the negative impact on an indebted economy quickly depresses activity. More importantly, the decline in monetary velocity clearly shows that deflation remains a persistent threat.
International
The millions of people not looking for work in the UK may be prioritising education, health and freedom
Economic inactivity is not always the worst option.

Around one in five British people of working age (16-64) are now outside the labour market. Neither in work nor looking for work, they are officially labelled as “economically inactive”.
Some of those 9.2 million people are in education, with many students not active in the labour market because they are studying full-time. Others are older workers who have chosen to take early retirement.
But that still leaves a large number who are not part of the labour market because they are unable to work. And one key driver of economic inactivity in recent years has been illness.
This increase in economic inactivity – which has grown since before the pandemic – is not just harming the economy, but also indicative of a deeper health crisis.
For those suffering ill health, there are real constraints on access to work. People with health-limiting conditions cannot just slot into jobs that are available. They need help to address the illnesses they have, and to re-engage with work through organisations offering supportive and healthy work environments.
And for other groups, such as stay-at-home parents, businesses need to offer flexible work arrangements and subsidised childcare to support the transition from economic inactivity into work.
The government has a role to play too. Most obviously, it could increase investment in the NHS. Rising levels of poor health are linked to years of under-investment in the health sector and economic inactivity will not be tackled without more funding.
Carrots and sticks
For the time being though, the UK government appears to prefer an approach which mixes carrots and sticks. In the March 2024 budget, for example, the chancellor cut national insurance by 2p as a way of “making work pay”.
But it is unclear whether small tax changes like this will have any effect on attracting the economically inactive back into work.
Jeremy Hunt also extended free childcare. But again, questions remain over whether this is sufficient to remove barriers to work for those with parental responsibilities. The high cost and lack of availability of childcare remain key weaknesses in the UK economy.
The benefit system meanwhile has been designed to push people into work. Benefits in the UK remain relatively ungenerous and hard to access compared with other rich countries. But labour shortages won’t be solved by simply forcing the economically inactive into work, because not all of them are ready or able to comply.
It is also worth noting that work itself may be a cause of bad health. The notion of “bad work” – work that does not pay enough and is unrewarding in other ways – can lead to economic inactivity.
There is also evidence that as work has become more intensive over recent decades, for some people, work itself has become a health risk.
The pandemic showed us how certain groups of workers (including so-called “essential workers”) suffered more ill health due to their greater exposure to COVID. But there are broader trends towards lower quality work that predate the pandemic, and these trends suggest improving job quality is an important step towards tackling the underlying causes of economic inactivity.
Freedom
Another big section of the economically active population who cannot be ignored are those who have retired early and deliberately left the labour market behind. These are people who want and value – and crucially, can afford – a life without work.
Here, the effects of the pandemic can be seen again. During those years of lockdowns, furlough and remote working, many of us reassessed our relationship with our jobs. Changed attitudes towards work among some (mostly older) workers can explain why they are no longer in the labour market and why they may be unresponsive to job offers of any kind.

And maybe it is from this viewpoint that we should ultimately be looking at economic inactivity – that it is actually a sign of progress. That it represents a move towards freedom from the drudgery of work and the ability of some people to live as they wish.
There are utopian visions of the future, for example, which suggest that individual and collective freedom could be dramatically increased by paying people a universal basic income.
In the meantime, for plenty of working age people, economic inactivity is a direct result of ill health and sickness. So it may be that the levels of economic inactivity right now merely show how far we are from being a society which actually supports its citizens’ wellbeing.
David Spencer has received funding from the ESRC.
uk pandemicInternational
Illegal Immigrants Leave US Hospitals With Billions In Unpaid Bills
Illegal Immigrants Leave US Hospitals With Billions In Unpaid Bills
By Autumn Spredemann of The Epoch Times
Tens of thousands of illegal…

By Autumn Spredemann of The Epoch Times
Tens of thousands of illegal immigrants are flooding into U.S. hospitals for treatment and leaving billions in uncompensated health care costs in their wake.
The House Committee on Homeland Security recently released a report illustrating that from the estimated $451 billion in annual costs stemming from the U.S. border crisis, a significant portion is going to health care for illegal immigrants.
With the majority of the illegal immigrant population lacking any kind of medical insurance, hospitals and government welfare programs such as Medicaid are feeling the weight of these unanticipated costs.
Apprehensions of illegal immigrants at the U.S. border have jumped 48 percent since the record in fiscal year 2021 and nearly tripled since fiscal year 2019, according to Customs and Border Protection data.
Last year broke a new record high for illegal border crossings, surpassing more than 3.2 million apprehensions.
And with that sea of humanity comes the need for health care and, in most cases, the inability to pay for it.
In January, CEO of Denver Health Donna Lynne told reporters that 8,000 illegal immigrants made roughly 20,000 visits to the city’s health system in 2023.
The total bill for uncompensated care costs last year to the system totaled $140 million, said Dane Roper, public information officer for Denver Health. More than $10 million of it was attributed to “care for new immigrants,” he told The Epoch Times.
Though the amount of debt assigned to illegal immigrants is a fraction of the total, uncompensated care costs in the Denver Health system have risen dramatically over the past few years.
The total uncompensated costs in 2020 came to $60 million, Mr. Roper said. In 2022, the number doubled, hitting $120 million.
He also said their city hospitals are treating issues such as “respiratory illnesses, GI [gastro-intenstinal] illnesses, dental disease, and some common chronic illnesses such as asthma and diabetes.”
“The perspective we’ve been trying to emphasize all along is that providing healthcare services for an influx of new immigrants who are unable to pay for their care is adding additional strain to an already significant uncompensated care burden,” Mr. Roper said.
He added this is why a local, state, and federal response to the needs of the new illegal immigrant population is “so important.”
Colorado is far from the only state struggling with a trail of unpaid hospital bills.

Dr. Robert Trenschel, CEO of the Yuma Regional Medical Center situated on the Arizona–Mexico border, said on average, illegal immigrants cost up to three times more in human resources to resolve their cases and provide a safe discharge.
“Some [illegal] migrants come with minor ailments, but many of them come in with significant disease,” Dr. Trenschel said during a congressional hearing last year.
“We’ve had migrant patients on dialysis, cardiac catheterization, and in need of heart surgery. Many are very sick.”
He said many illegal immigrants who enter the country and need medical assistance end up staying in the ICU ward for 60 days or more.
A large portion of the patients are pregnant women who’ve had little to no prenatal treatment. This has resulted in an increase in babies being born that require neonatal care for 30 days or longer.
Dr. Trenschel told The Epoch Times last year that illegal immigrants were overrunning healthcare services in his town, leaving the hospital with $26 million in unpaid medical bills in just 12 months.
ER Duty to Care
The Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act of 1986 requires that public hospitals participating in Medicare “must medically screen all persons seeking emergency care … regardless of payment method or insurance status.”
The numbers are difficult to gauge as the policy position of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is that it “will not require hospital staff to ask patients directly about their citizenship or immigration status.”
In southern California, again close to the border with Mexico, some hospitals are struggling with an influx of illegal immigrants.
American patients are enduring longer wait times for doctor appointments due to a nursing shortage in the state, two health care professionals told The Epoch Times in January.
A health care worker at a hospital in Southern California, who asked not to be named for fear of losing her job, told The Epoch Times that “the entire health care system is just being bombarded” by a steady stream of illegal immigrants.
“Our healthcare system is so overwhelmed, and then add on top of that tuberculosis, COVID-19, and other diseases from all over the world,” she said.

A newly-enacted law in California provides free healthcare for all illegal immigrants residing in the state. The law could cost taxpayers between $3 billion and $6 billion per year, according to recent estimates by state and federal lawmakers.
In New York, where the illegal immigration crisis has manifested most notably beyond the southern border, city and state officials have long been accommodating of illegal immigrants’ healthcare costs.
Since June 2014, when then-mayor Bill de Blasio set up The Task Force on Immigrant Health Care Access, New York City has worked to expand avenues for illegal immigrants to get free health care.
“New York City has a moral duty to ensure that all its residents have meaningful access to needed health care, regardless of their immigration status or ability to pay,” Mr. de Blasio stated in a 2015 report.
The report notes that in 2013, nearly 64 percent of illegal immigrants were uninsured. Since then, tens of thousands of illegal immigrants have settled in the city.
“The uninsured rate for undocumented immigrants is more than three times that of other noncitizens in New York City (20 percent) and more than six times greater than the uninsured rate for the rest of the city (10 percent),” the report states.
The report states that because healthcare providers don’t ask patients about documentation status, the task force lacks “data specific to undocumented patients.”
Some health care providers say a big part of the issue is that without a clear path to insurance or payment for non-emergency services, illegal immigrants are going to the hospital due to a lack of options.
“It’s insane, and it has been for years at this point,” Dana, a Texas emergency room nurse who asked to have her full name omitted, told The Epoch Times.
Working for a major hospital system in the greater Houston area, Dana has seen “a zillion” migrants pass through under her watch with “no end in sight.” She said many who are illegal immigrants arrive with treatable illnesses that require simple antibiotics. “Not a lot of GPs [general practitioners] will see you if you can’t pay and don’t have insurance.”
She said the “undocumented crowd” tends to arrive with a lot of the same conditions. Many find their way to Houston not long after crossing the southern border. Some of the common health issues Dana encounters include dehydration, unhealed fractures, respiratory illnesses, stomach ailments, and pregnancy-related concerns.
“This isn’t a new problem, it’s just worse now,” Dana said.

Medicaid Factor
One of the main government healthcare resources illegal immigrants use is Medicaid.
All those who don’t qualify for regular Medicaid are eligible for Emergency Medicaid, regardless of immigration status. By doing this, the program helps pay for the cost of uncompensated care bills at qualifying hospitals.
However, some loopholes allow access to the regular Medicaid benefits. “Qualified noncitizens” who haven’t been granted legal status within five years still qualify if they’re listed as a refugee, an asylum seeker, or a Cuban or Haitian national.
Yet the lion’s share of Medicaid usage by illegal immigrants still comes through state-level benefits and emergency medical treatment.
A Congressional report highlighted data from the CMS, which showed total Medicaid costs for “emergency services for undocumented aliens” in fiscal year 2021 surpassed $7 billion, and totaled more than $5 billion in fiscal 2022.
Both years represent a significant spike from the $3 billion in fiscal 2020.
An employee working with Medicaid who asked to be referred to only as Jennifer out of concern for her job, told The Epoch Times that at a state level, it’s easy for an illegal immigrant to access the program benefits.
Jennifer said that when exceptions are sent from states to CMS for approval, “denial is actually super rare. It’s usually always approved.”
She also said it comes as no surprise that many of the states with the highest amount of Medicaid spending are sanctuary states, which tend to have policies and laws that shield illegal immigrants from federal immigration authorities.
Moreover, Jennifer said there are ways for states to get around CMS guidelines. “It’s not easy, but it can and has been done.”
The first generation of illegal immigrants who arrive to the United States tend to be healthy enough to pass any pre-screenings, but Jennifer has observed that the subsequent generations tend to be sicker and require more access to care. If a family is illegally present, they tend to use Emergency Medicaid or nothing at all.
The Epoch Times asked Medicaid Services to provide the most recent data for the total uncompensated care that hospitals have reported. The agency didn’t respond.
Continue reading over at The Epoch Times
International
Fuel poverty in England is probably 2.5 times higher than government statistics show
The top 40% most energy efficient homes aren’t counted as being in fuel poverty, no matter what their bills or income are.

The cap set on how much UK energy suppliers can charge for domestic gas and electricity is set to fall by 15% from April 1 2024. Despite this, prices remain shockingly high. The average household energy bill in 2023 was £2,592 a year, dwarfing the pre-pandemic average of £1,308 in 2019.
The term “fuel poverty” refers to a household’s ability to afford the energy required to maintain adequate warmth and the use of other essential appliances. Quite how it is measured varies from country to country. In England, the government uses what is known as the low income low energy efficiency (Lilee) indicator.
Since energy costs started rising sharply in 2021, UK households’ spending powers have plummeted. It would be reasonable to assume that these increasingly hostile economic conditions have caused fuel poverty rates to rise.
However, according to the Lilee fuel poverty metric, in England there have only been modest changes in fuel poverty incidence year on year. In fact, government statistics show a slight decrease in the nationwide rate, from 13.2% in 2020 to 13.0% in 2023.
Our recent study suggests that these figures are incorrect. We estimate the rate of fuel poverty in England to be around 2.5 times higher than what the government’s statistics show, because the criteria underpinning the Lilee estimation process leaves out a large number of financially vulnerable households which, in reality, are unable to afford and maintain adequate warmth.

Energy security
In 2022, we undertook an in-depth analysis of Lilee fuel poverty in Greater London. First, we combined fuel poverty, housing and employment data to provide an estimate of vulnerable homes which are omitted from Lilee statistics.
We also surveyed 2,886 residents of Greater London about their experiences of fuel poverty during the winter of 2022. We wanted to gauge energy security, which refers to a type of self-reported fuel poverty. Both parts of the study aimed to demonstrate the potential flaws of the Lilee definition.
Introduced in 2019, the Lilee metric considers a household to be “fuel poor” if it meets two criteria. First, after accounting for energy expenses, its income must fall below the poverty line (which is 60% of median income).
Second, the property must have an energy performance certificate (EPC) rating of D–G (the lowest four ratings). The government’s apparent logic for the Lilee metric is to quicken the net-zero transition of the housing sector.
In Sustainable Warmth, the policy paper that defined the Lilee approach, the government says that EPC A–C-rated homes “will not significantly benefit from energy-efficiency measures”. Hence, the focus on fuel poverty in D–G-rated properties.
Generally speaking, EPC A–C-rated homes (those with the highest three ratings) are considered energy efficient, while D–G-rated homes are deemed inefficient. The problem with how Lilee fuel poverty is measured is that the process assumes that EPC A–C-rated homes are too “energy efficient” to be considered fuel poor: the main focus of the fuel poverty assessment is a characteristic of the property, not the occupant’s financial situation.
In other words, by this metric, anyone living in an energy-efficient home cannot be considered to be in fuel poverty, no matter their financial situation. There is an obvious flaw here.
Around 40% of homes in England have an EPC rating of A–C. According to the Lilee definition, none of these homes can or ever will be classed as fuel poor. Even though energy prices are going through the roof, a single-parent household with dependent children whose only income is universal credit (or some other form of benefits) will still not be considered to be living in fuel poverty if their home is rated A-C.
The lack of protection afforded to these households against an extremely volatile energy market is highly concerning.
In our study, we estimate that 4.4% of London’s homes are rated A-C and also financially vulnerable. That is around 171,091 households, which are currently omitted by the Lilee metric but remain highly likely to be unable to afford adequate energy.
In most other European nations, what is known as the 10% indicator is used to gauge fuel poverty. This metric, which was also used in England from the 1990s until the mid 2010s, considers a home to be fuel poor if more than 10% of income is spent on energy. Here, the main focus of the fuel poverty assessment is the occupant’s financial situation, not the property.
Were such alternative fuel poverty metrics to be employed, a significant portion of those 171,091 households in London would almost certainly qualify as fuel poor.
This is confirmed by the findings of our survey. Our data shows that 28.2% of the 2,886 people who responded were “energy insecure”. This includes being unable to afford energy, making involuntary spending trade-offs between food and energy, and falling behind on energy payments.
Worryingly, we found that the rate of energy insecurity in the survey sample is around 2.5 times higher than the official rate of fuel poverty in London (11.5%), as assessed according to the Lilee metric.
It is likely that this figure can be extrapolated for the rest of England. If anything, energy insecurity may be even higher in other regions, given that Londoners tend to have higher-than-average household income.
The UK government is wrongly omitting hundreds of thousands of English households from fuel poverty statistics. Without a more accurate measure, vulnerable households will continue to be overlooked and not get the assistance they desperately need to stay warm.
Torran Semple receives funding from Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) grant EP/S023305/1.
John Harvey does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
european uk pandemic-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Spread & Containment2 days ago
Spread & Containment2 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex































