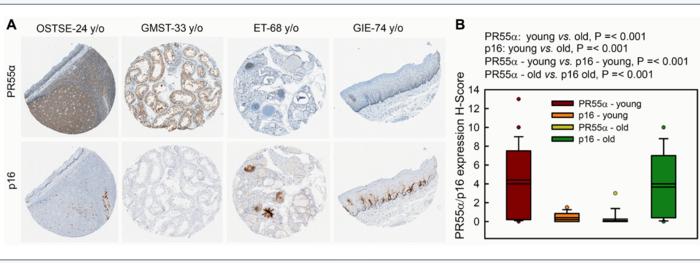
“Our results show that PR55α specifically reduces p16 expression […]”
BUFFALO, NY- March 19, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 5, entitled, “PR55α-controlled protein phosphatase 2A inhibits p16 expression and blocks cellular senescence induction by γ-irradiation.”
Cellular senescence is a permanent cell cycle arrest that can be triggered by both internal and external genotoxic stressors, such as telomere dysfunction and DNA damage. The execution of senescence is mainly by two pathways, p16/RB and p53/p21, which lead to CDK4/6 inhibition and RB activation to block cell cycle progression. While the regulation of p53/p21 signaling in response to DNA damage and other insults is well-defined, the regulation of the p16/RB pathway in response to various stressors remains poorly understood.
In this new study, researchers Chitra Palanivel, Lepakshe S. V. Madduri, Ashley L. Hein, Christopher B. Jenkins, Brendan T. Graff, Alison L. Camero, Sumin Zhou, Charles A. Enke, Michel M. Ouellette, and Ying Yan from the University of Nebraska Medical Center report a novel function of PR55α, a regulatory subunit of PP2A Ser/Thr phosphatase, as a potent inhibitor of p16 expression and senescence induction by ionizing radiation (IR), such as γ-rays.
“During natural aging, there is a gradual accumulation of p16-expressing senescent cells in tissues [76]. To investigate the significance of PR55α in this up-regulation of p16, we compared levels of the p16 and PR55α proteins in a panel of normal tissue specimens derived from young (≤43 y/o) and old (≥68 y/o) donors.”
The results show that ectopic PR55α expression in normal pancreatic cells inhibits p16 transcription, increases RB phosphorylation, and blocks IR-induced senescence. Conversely, PR55α-knockdown by shRNA in pancreatic cancer cells elevates p16 transcription, reduces RB phosphorylation, and triggers senescence induction after IR. Furthermore, this PR55α function in the regulation of p16 and senescence is p53-independent because it was unaffected by the mutational status of p53. Moreover, PR55α only affects p16 expression but not p14 (ARF) expression, which is also transcribed from the same CDKN2A locus but from an alternative promoter. In normal human tissues, levels of p16 and PR55α proteins were inversely correlated and mutually exclusive.
“Collectively, these results describe a novel function of PR55α/PP2A in blocking p16/RB signaling and IR-induced cellular senescence.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205619
Corresponding Authors: Michel M. Ouellette, Ying Yan
Corresponding Emails: mouellet@unmc.edu, yyan@unmc.edu
Keywords: p16, p14, CDKN2A locus, p53, RB, PR55α, PP2A, γ-irradiation
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
Aging publishes research papers in all fields of aging research including but not limited, aging from yeast to mammals, cellular senescence, age-related diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s diseases and their prevention and treatment, anti-aging strategies and drug development and especially the role of signal transduction pathways such as mTOR in aging and potential approaches to modulate these signaling pathways to extend lifespan. The journal aims to promote treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- X, formerly Twitter
- YouTube
- Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.205619
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
PR55α-controlled protein phosphatase 2A inhibits p16 expression and blocks cellular senescence induction by γ-irradiation
Article Publication Date
4-Mar-2024