Uncategorized
Fed Chair Powell Just Said The Quiet Part Out Loud
Fed Chair Powell Just Said The Quiet Part Out Loud
Authored by Lance Roberts via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
Regarding the surprisingly strong…
Authored by Lance Roberts via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
Regarding the surprisingly strong employment data, Fed Chair Powell said the quiet part out loud. The media hopes you didn’t hear it as we head into a contentious election in November.
Over the last several months, we have seen repeated employment reports from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) that crushed economists’ estimates and seemed to defy logic. Such is particularly the case when you read commentary about the state of the average American as follows.
“New Yorker Lohanny Santos publicly vented her frustration after her attempts to go door-to-door with her CV in hand in the hope of finally landing a job were unsuccessful.
It would appear that other young jobseekers could relate to Lohanny’s struggles. The USA and Canada rank fifth out of seven when it comes to youth unemployment and third when it comes to total unemployment, according to World Bank data based on an International Labor Organization model for 2020, as per Statista.” – Business Insider
Even M.B.A.s are finding it difficult.
“Jenna Starr stuck a blue Post-it Note to her monitor a few months after getting her M.B.A. from Yale University last May. “Get yourself the job,” it read. It wasn’t until last week—when she received a long-awaited offer—that she could finally take it down.
For months, Starr has been one of a large number of 2023 M.B.A. graduates whose job searches have collided with a slowdown in hiring for well-paid, white-collar positions. Her search for a job in sustainability began before graduation, and she applied for more than 100 openings since, including in the field she used to work in—nonprofit fundraising.” – WSJ
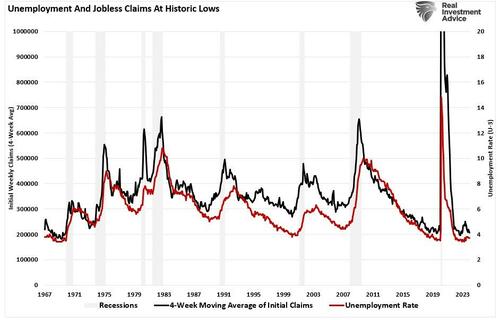
These stories are not unique. If you Google “Can’t find a job,” you will get many article links. The question, of course, is why individuals with college degrees, no less, are having such a tough time finding employment. After all, aside from record-smashing employment reports, we also continue to see near-record low jobless claims and high numbers of job openings, as shown below.
The Washington Post touched on part of the problem and why the unemployment rate for college graduates is higher than for all workers.
“Part of the problem is that the industries with the biggest worker shortages — including restaurants, hotels, daycares, and nursing homes — aren’t necessarily where recent graduates want to work. Meanwhile, the industries where they do want to work — tech, consulting, finance, media — are announcing layoffs and rethinking hiring plans.”
As the Washington Post summed up:
“The result is yet another disruption for a generation of college graduates who have already had crucial years of schooling upended by the pandemic. In interviews, many said they’d struggled to adjust to remote-learning in early 2020 and felt like they had missed out on opportunities to forge connections with professors, employers and other students that could have been crucial in lining up for postgraduate work. Now, as they enter the workforce, they say they’re feeling increasingly disillusioned about the economy, which is fueling political discontent and causing them to rethink the financial independence they thought they’d achieve after college.”
Of course, it isn’t just the shuttering of the economy and the shift to working from home causing the problem. It is also the shift in demand from consumers to more service-oriented conveniences, combined with the need by employers to maintain profitability.
Fed Chair Powell Says The Quiet Part
Since the turn of the century, the U.S. economy has shifted from a manufacturing-based economy to a service-oriented one. There are two primary reasons for this.
The first is that the “cost of labor” in the U.S. to manufacture goods is too high. Domestic workers want high wages, benefits, paid vacations, personal time off, etc. On top of that are the numerous regulations on businesses from OSHA to Sarbanes-Oxley, FDA, EPA, and many others. All those additional costs are a factor in producing goods or services. Therefore, corporations needed to offshore production to countries with lower labor costs and higher production rates to manufacture goods competitively.
During an interview with Greg Hays of Carrier Industries, the reasoning for moving a plant from Mexico to Indiana during the Trump Administration was most interesting.
“So what’s good about Mexico? We have a very talented workforce in Mexico. Wages are obviously significantly lower. About 80% lower on average. But absenteeism runs about 1%. Turnover runs about 2%. Very, very dedicated workforce.
Which is much higher versus America. And I think that’s just part of these — the jobs, again, are not jobs on an assembly line that [Amerians] really find all that attractive over the long term.“
Fed Chair Powell emphasized this point in a recent 60-Minutes Interview. To wit:
“SCOTT PELLEY: Why was immigration important?
FED CHAIR POWELL: Because, you know, immigrants come in, and they tend to work at a rate that is at or above that for non-immigrants. Immigrants who come to the country tend to be in the workforce at a slightly higher level than native Americans. But that’s primarily because of the age difference. They tend to skew younger.“
The suppression of wages, increased productivity to reduce the amount of required labor, and offshoring has been a multi-decade process to increase corporate profitability.
A Native Problem
Following the pandemic-related shutdown, corporations faced multiple threats to profitability from supply constraints, a shift to increased services, and a lack of labor. At the same time, mass immigration (both legal and illegal) provided a workforce willing to fill lower-wage paying jobs and work regardless of the shutdown. Since 2019, the cumulative employment change has favored foreign-born workers, who have gained almost 2.5 million jobs, while native-born workers have lost 1.3 million. Unsurprisingly, foreign-born workers also lost far fewer jobs during the pandemic shutdown.
Given that the bulk of employment continues to be in lower-wage paying service jobs (i.e., restaurants, retail, leisure, and hospitality) such is why part-time jobs have dominated full-time in recent reports. Relative to the working-age population, full-time employment has dropped sharply after failing to recover pre-pandemic levels.
However, as noted, full-time employment has declined since 2000 as services dominate labor-intensive processes such as manufacturing. This is because we “export” our “inflation” and import “deflation.” We do this to buy flat-screen televisions for $299 versus $3,999. Such is also why the economy continues to grow slower, requiring ever-increasing debt levels.
For recent college graduates, this all leads to a more dire outlook.
Immigration Is Needed, But It Has Consequences
To keep an economy growing, you must have population growth. In other words, “demographics are destiny.” As such, there are two ways to obtain more robust population growth rates – natural births and immigration. As shown below, the fertility rate in the United States is problematic in that we aren’t producing enough children to replace an aging workforce.
Such is particularly problematic given the rapid aging of older adults versus a declining working-age population. Such means the underfunding of entitlements will continue to grow, requiring more debt issuance to fill the gap.
However, there is a vast difference between immigration policies that import highly skilled workers, capital, and education versus those that don’t. Merit-based immigration policies bring workers who earn higher salaries, create businesses, employ labor, and create tax revenues and other economic contributions. However, current policies are creating a rush of lower-skilled, uneducated labor that will work for cheaper wages, produce less revenue, and are subsidized by tax-payers through welfare programs. As noted above, these workers tend to fill the jobs in the service areas of the economy, thereby displacing native-born workers. Such was a point made by the WSJ:
“Before the pandemic, foreign-born adults were almost as likely as the overall population to hold at least a bachelor’s degree. This was mainly because of higher educational attainment among immigrants from Asia, Africa, and Europe, which offset lower levels of schooling among people from Mexico and Central America.”
Post-pandemic, this has not been the case, which is impacting native-born employment. This is not a new issue, but one addressed by Bill Clinton in the 1995 State of the Union Address:
“The jobs they hold might otherwise be held by citizens or legal immigrants; the public services they use impose burdens on our taxpayers.”
Such is the natural consequence of a change in the economy’s demands and the need for corporations to maintain profitability in an ultimately deflationary environment.
Conclusion
While there is much debate over immigration, most of the arguments do not differentiate between legal and illegal immigration. There are certainly arguments that can be made on both sides. However, what is less debatable is the impact that immigration is having on employment. Of course, as native-born workers continue to demand higher wages, benefits, and other tax-funded support, those costs must be passed on by the companies creating those products and services. At the same time, consumers are demanding lower prices.
That imbalance between input costs and selling price drives companies to aggressively seek options to reduce the highest cost to any business – labor. Such was discussed in our article on the cost and consequences of the demand for increased minimum wages.
-
Reductions in employment would initially be concentrated at firms where higher prices quickly reduce sales.
-
Over a longer period, however, more firms would replace low-wage workers with higher-wage workers, machines, and other substitutes.
-
As employers pass some of those costs on to consumers, consumers purchase fewer goods and services.
-
Consequently, the employers produce fewer goods and services.
-
When the cost of employing low-wage workers rises, the cost of investing in machines and technology goes down.” – Congressional Budget Office.
Such is why full-time employment has declined since 2000 despite the surge in the Internet economy, robotics, and artificial intelligence. It is also why wage growth fails to grow fast enough to sustain the cost of living for the average American. These technological developments increased employee productivity, reducing the need for additional labor.
Unfortunately, these tales of college graduates expecting high-paying jobs will likely continue to find it increasingly complicated. Particularly as “Artificial Intelligence” becomes cheap enough to displace higher-paid employees.
Uncategorized
Shipping company files surprise Chapter 7 bankruptcy, liquidation
While demand for trucking has increased, so have costs and competition, which have forced a number of players to close.

The U.S. economy is built on trucks.
As a nation we have relatively limited train assets, and while in recent years planes have played an expanded role in moving goods, trucks still represent the backbone of how everything — food, gasoline, commodities, and pretty much anything else — moves around the country.
Related: Fast-food chain closes more stores after Chapter 11 bankruptcy
"Trucks moved 61.1% of the tonnage and 64.9% of the value of these shipments. The average shipment by truck was 63 miles compared to an average of 640 miles by rail," according to the U.S. Bureau of Transportation Statistics 2023 numbers.
But running a trucking company has been tricky because the largest players have economies of scale that smaller operators don't. That puts any trucking company that's not a massive player very sensitive to increases in gas prices or drops in freight rates.
And that in turn has led a number of trucking companies, including Yellow Freight, the third-largest less-than-truckload operator; J.J. & Sons Logistics, Meadow Lark, and Boateng Logistics, to close while freight brokerage Convoy shut down in October.
Aside from Convoy, none of these brands are household names. but with the demand for trucking increasing, every company that goes out of business puts more pressure on those that remain, which contributes to increased prices.
Image source: Shutterstock
Another freight company closes and plans to liquidate
Not every bankruptcy filing explains why a company has gone out of business. In the trucking industry, multiple recent Chapter 7 bankruptcies have been tied to lawsuits that pushed otherwise successful companies into insolvency.
In the case of TBL Logistics, a Virginia-based national freight company, its Feb. 29 bankruptcy filing in U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Western District of Virginia appears to be death by too much debt.
"In its filing, TBL Logistics listed its assets and liabilities as between $1 million and $10 million. The company stated that it has up to 49 creditors and maintains that no funds will be available for unsecured creditors once it pays administrative fees," Freightwaves reported.
The company's owners, Christopher and Melinda Bradner, did not respond to the website's request for comment.
Before it closed, TBL Logistics specialized in refrigerated and oversized loads. The company described its business on its website.
"TBL Logistics is a non-asset-based third-party logistics freight broker company providing reliable and efficient transportation solutions, management, and storage for businesses of all sizes. With our extensive network of carriers and industry expertise, we streamline the shipping process, ensuring your goods reach their destination safely and on time."
The world has a truck-driver shortage
The covid pandemic forced companies to consider their supply chain in ways they never had to before. Increased demand showed the weakness in the trucking industry and drew attention to how difficult life for truck drivers can be.
That was an issue HBO's John Oliver highlighted on his "Last Week Tonight" show in October 2022. In the episode, the host suggested that the U.S. would basically start to starve if the trucking industry shut down for three days.
"Sorry, three days, every produce department in America would go from a fully stocked market to an all-you-can-eat raccoon buffet," he said. "So it’s no wonder trucking’s a huge industry, with more than 3.5 million people in America working as drivers, from port truckers who bring goods off ships to railyards and warehouses, to long-haul truckers who move them across the country, to 'last-mile' drivers, who take care of local delivery."
The show highlighted how many truck drivers face low pay, difficult working conditions and, in many cases, crushing debt.
"Hundreds of thousands of people become truck drivers every year. But hundreds of thousands also quit. Job turnover for truckers averages over 100%, and at some companies it’s as high as 300%, meaning they’re hiring three people for a single job over the course of a year. And when a field this important has a level of job satisfaction that low, it sure seems like there’s a huge problem," Oliver shared.
The truck-driver shortage is not just a U.S. problem; it's a global issue, according to IRU.org.
"IRU’s 2023 driver shortage report has found that over three million truck driver jobs are unfilled, or 7% of total positions, in 36 countries studied," the global transportation trade association reported.
"With the huge gap between young and old drivers growing, it will get much worse over the next five years without significant action."
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
bankruptcy bankruptcies pandemic stocks commoditiesUncategorized
Wendy’s has a new deal for daylight savings time haters
The Daylight Savings Time promotion slashes prices on breakfast.

Daylight Savings Time, or the practice of advancing clocks an hour in the spring to maximize natural daylight, is a controversial practice because of the way it leaves many feeling off-sync and tired on the second Sunday in March when the change is made and one has one less hour to sleep in.
Despite annual "Abolish Daylight Savings Time" think pieces and online arguments that crop up with unwavering regularity, Daylight Savings in North America begins on March 10 this year.
Related: Coca-Cola has a new soda for Diet Coke fans
Tapping into some people's very vocal dislike of Daylight Savings Time, fast-food chain Wendy's (WEN) is launching a daylight savings promotion that is jokingly designed to make losing an hour of sleep less painful and encourage fans to order breakfast anyway.
Image source: Wendy's.
Promotion wants you to compensate for lost sleep with cheaper breakfast
As it is also meant to drive traffic to the Wendy's app, the promotion allows anyone who makes a purchase of $3 or more through the platform to get a free hot coffee, cold coffee or Frosty Cream Cold Brew.
More Food + Dining:
- Taco Bell menu tries new take on an American classic
- McDonald's menu goes big, brings back fan favorites (with a catch)
- The 10 best food stocks to buy now
Available during the Wendy's breakfast hours of 6 a.m. and 10:30 a.m. (which, naturally, will feel even earlier due to Daylight Savings), the deal also allows customers to buy any of its breakfast sandwiches for $3. Items like the Sausage, Egg and Cheese Biscuit, Breakfast Baconator and Maple Bacon Chicken Croissant normally range in price between $4.50 and $7.
The choice of the latter is quite wide since, in the years following the pandemic, Wendy's has made a concerted effort to expand its breakfast menu with a range of new sandwiches with egg in them and sweet items such as the French Toast Sticks. The goal was both to stand out from competitors with a wider breakfast menu and increase traffic to its stores during early-morning hours.
Wendy's deal comes after controversy over 'dynamic pricing'
But last month, the chain known for the square shape of its burger patties ignited controversy after saying that it wanted to introduce "dynamic pricing" in which the cost of many of the items on its menu will vary depending on the time of day. In an earnings call, chief executive Kirk Tanner said that electronic billboards would allow restaurants to display various deals and promotions during slower times in the early morning and late at night.
Outcry was swift and Wendy's ended up walking back its plans with words that they were "misconstrued" as an intent to surge prices during its most popular periods.
While the company issued a statement saying that any changes were meant as "discounts and value offers" during quiet periods rather than raised prices during busy ones, the reputational damage was already done since many saw the clarification as another way to obfuscate its pricing model.
"We said these menuboards would give us more flexibility to change the display of featured items," Wendy's said in its statement. "This was misconstrued in some media reports as an intent to raise prices when demand is highest at our restaurants."
The Daylight Savings Time promotion, in turn, is also a way to demonstrate the kinds of deals Wendy's wants to promote in its stores without putting up full-sized advertising or posters for what is only relevant for a few days.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
stocks pandemicUncategorized
Comments on February Employment Report
The headline jobs number in the February employment report was above expectations; however, December and January payrolls were revised down by 167,000 combined. The participation rate was unchanged, the employment population ratio decreased, and the …
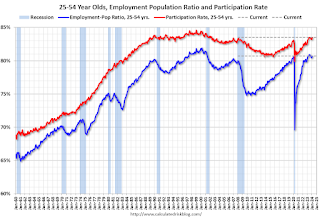
Prime (25 to 54 Years Old) Participation
Since the overall participation rate is impacted by both cyclical (recession) and demographic (aging population, younger people staying in school) reasons, here is the employment-population ratio for the key working age group: 25 to 54 years old.
The 25 to 54 years old participation rate increased in February to 83.5% from 83.3% in January, and the 25 to 54 employment population ratio increased to 80.7% from 80.6% the previous month.
Average Hourly Wages
 The graph shows the nominal year-over-year change in "Average Hourly Earnings" for all private employees from the Current Employment Statistics (CES).
The graph shows the nominal year-over-year change in "Average Hourly Earnings" for all private employees from the Current Employment Statistics (CES). Wage growth has trended down after peaking at 5.9% YoY in March 2022 and was at 4.3% YoY in February.
Part Time for Economic Reasons
 From the BLS report:
From the BLS report:"The number of people employed part time for economic reasons, at 4.4 million, changed little in February. These individuals, who would have preferred full-time employment, were working part time because their hours had been reduced or they were unable to find full-time jobs."The number of persons working part time for economic reasons decreased in February to 4.36 million from 4.42 million in February. This is slightly above pre-pandemic levels.
These workers are included in the alternate measure of labor underutilization (U-6) that increased to 7.3% from 7.2% in the previous month. This is down from the record high in April 2020 of 23.0% and up from the lowest level on record (seasonally adjusted) in December 2022 (6.5%). (This series started in 1994). This measure is above the 7.0% level in February 2020 (pre-pandemic).
Unemployed over 26 Weeks
 This graph shows the number of workers unemployed for 27 weeks or more.
This graph shows the number of workers unemployed for 27 weeks or more. According to the BLS, there are 1.203 million workers who have been unemployed for more than 26 weeks and still want a job, down from 1.277 million the previous month.
This is close to pre-pandemic levels.
Job Streak
| Headline Jobs, Top 10 Streaks | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year Ended | Streak, Months | |
| 1 | 2019 | 100 |
| 2 | 1990 | 48 |
| 3 | 2007 | 46 |
| 4 | 1979 | 45 |
| 5 | 20241 | 38 |
| 6 tie | 1943 | 33 |
| 6 tie | 1986 | 33 |
| 6 tie | 2000 | 33 |
| 9 | 1967 | 29 |
| 10 | 1995 | 25 |
| 1Currrent Streak | ||
Summary:
The headline monthly jobs number was above consensus expectations; however, December and January payrolls were revised down by 167,000 combined. The participation rate was unchanged, the employment population ratio decreased, and the unemployment rate was increased to 3.9%. Another solid report.
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International2 hours ago
International2 hours agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Government1 month ago
Government1 month agoWar Delirium
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex




























