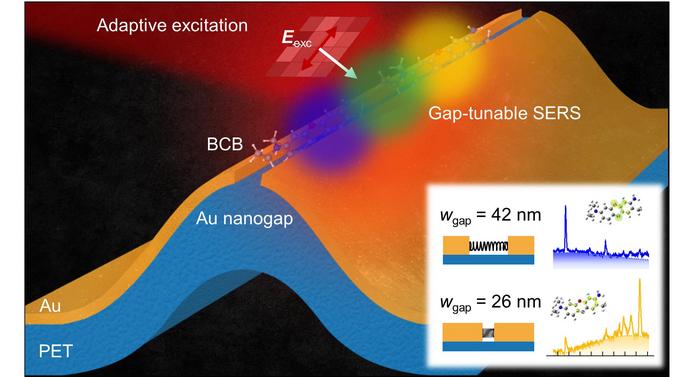
A research team consisting of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Taeyoung Moon and Huitae Joo, PhD candidates, from the Department of Physics at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has engineered “broadband nanogap gold spectroscopic sensor” using a flexible material capable of bending to create a controlled gap. With the developed technology, it is possible to rapidly test various types of materials, including infectious disease viruses, using only a single nano-spectroscopic sensor to find molecular fingerprints.
The emergence of pandemic epidemics like COVID-19 has emphasized the necessity for rapid and precise analytical methods to prepare for potential future virus outbreaks. Raman spectroscopy, using gold nanostructures, offers information about the internal structure and chemical properties of materials by analyzing the distinct vibrations of molecules known as “molecular fingerprints,” using light with remarkable sensitivity. Therefore, it could play a crucial role in determining the positivity of a virus.
However, conventional high-sensitivity Raman spectroscopy sensors detect only one type of virus with a single device, thus posing limitations in terms of productivity, detection speed, and cost when considering clinical applications.
The research team successfully fabricated a one-dimensional structure at the millimeter scale, featuring gold nanogaps accommodating only a single molecule with a tight fit. This advancement enables large-area, high-sensitivity Raman spectroscopic sensing. Furthermore, they effectively integrated flexible materials onto the substrate of the gold nanogap spectroscopic sensor. Finally, the team developed a source technology for a broadband active nano-spectral sensor, allowing tailored detection of specific substances using a single device, by widening the nanogap to the size of a virus and freely adjusting its width to suit the size and type of materials, including viruses.
Furthermore, they improved the sensitivity and controllability of the sensor by combining adaptive optics technology used in fields such as space optics, such as the James Webb Telescope. Additionally, they established a conceptual model for extending the fabricated one-dimensional structure into a two-dimensional spectroscopic sensor, theoretically confirming the ability to amplify Raman spectroscopic signals by up to several billion times. In other words, it becomes possible to confirm the positivity of viruses in real-time within seconds, a process that previously took days for verification.
The achievements of the research team, currently pending patent approval, are expected to be utilized for the rapid response through high-sensitivity real-time testing in the event of unexpected infectious diseases such as COVID-19, to prevent indiscriminate spread. Taeyoung Moon, lead author of the paper, emphasized the significance of their achievement by stating, “This not only advances basic scientific research in identifying unique properties of materials from molecules to viruses but also facilitates practical applications, enabling rapid detection of a broad spectrum of emerging viruses using a single, tailored sensor.”
The collaborative research was jointly conducted with Professor Dai-Sik Kim’s team from UNIST’s Department of Physics and a team led by Professor Yung Doug Suh from UNIST’s Department of Chemistry who is Deputy Director of Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS). Additionally, Yeonjeong Koo, Mingu Kang, and Hyeongwoo Lee from POSTECH’s Department of Physics carried out measurements. The research findings have recently been published in the international journal Nano Letters.
Journal
Nano Letters
DOI
10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c00289
Article Title
Adaptive Gap-Tunable Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Article Publication Date
28-Mar-2024