Government
Debunking Jack Smith’s Latest Indictment Against President Trump
Debunking Jack Smith’s Latest Indictment Against President Trump
Authored by Paul and Olivia Ingrassia via AmericanMind.org,
Efforts to sow…
Authored by Paul and Olivia Ingrassia via AmericanMind.org,
Efforts to sow confusion and chaos in our election systems must be confronted...
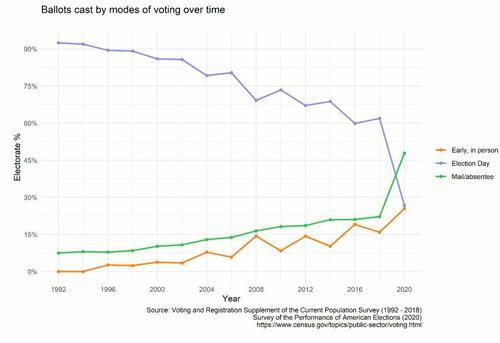
When the Supreme Court denied the State of Texas’s lawsuit in December of 2020 to challenge the integrity of that year’s general election for lack of Article III standing, there already existed an overwhelming trove of evidence of procedural abnormalities and statistical anomalies that pointed to fundamental questions about the legitimacy of the election. Well over 155 million votes were allegedly cast in that year’s cycle - the most of any vote total in presidential history, surpassing 2016’s previous record-setting high by a whopping 28 million votes. Moreover, the 2020 election not only saw the highest percentage of votes cast either by mail or absentee ballot in modern American history, but it was the first time in which election day voting represented a minority of all methods of casting ballots: fewer than one third of voters who cast their ballots in the 2020 general election did so in person on election day.
Even if there was absolutely no evidence of election fraud, the fact that more votes were cast than in any other election in American history - the majority of the ballots having been cast prior to the official election day by mail, a method of voting historically recognized as being rife with fraud, not only in the United States but other Western democracies—meant that extreme diligence and precautionary care ought to have been taken to minimize the high probability of outcome determinative error in an election of such complexity.
The winner of the 2020 election was not declared by most mainstream networks, including ABC, CBS, NBC, as well as mainstream cable networks like Fox News and CNN, until November 7, four days after polls closed.
This was the longest gap in time to declare a winner since 2000, when the outcome in that year’s presidential election was eventually settled by the Supreme Court in Bush v. Gore.
Other serious abnormalities arose that, in a normal political climate, would have been cause for concern about overall election integrity.
For example, despite Trump having won 18 of the 19 bellwether counties that have voted for the president in every election from 1980 to 2016, the mainstream media still called the race for Joe Biden.
Moreover, the three major swing states—Florida, Iowa, and Ohio—which voted for the winner of every presidential election since 1996, all voted for Donald Trump.
Biden won only 509 counties compared with the 2,500+ won by Trump, or just 16.7 percent of all the nation’s counties, the fewest of any presidential winner in history. On top of everything else, there were high-profile, newsworthy abnormalities that occurred on election night, or in the hours and days immediately following, that plainly did not make sense.
Obviously, there was the story of the water main break in Georgia, in critical Fulton County, which occurred as vote counters were still tabulating ballots on election night.
The pipe breakage conveniently bought officials time to delay the counting of nearly 40,000 outstanding, outcome-determinative absentee ballots.
Then there were the countless stories of “ballot trafficking,” as documented in the now infamous Dinesh D’Souza film, 2000 Mules, whereby thousands of nonprofit hires, or “mules,” dumped fraudulent absentee ballots in critical swing states like Georgia and Arizona overnight, which contaminated the process and likely changed the final result of the election in those states.
There was also a patent lack of transparency in the days following the election, particularly in Democratic strongholds such as Philadelphia, where major election sites were in some cases unlawfully closed off from the public, violating their fundamental right to transparent elections despite public assurances that ballots were counted consistent with state law and were executed impartially and without political bias. It was impossible to guarantee those assurances in Philadelphia or Fulton County or Maricopa County; indeed, the public’s constitutional rights in these procedures were fundamentally violated, itself sufficient grounds to demand recounts and reforms in at least those select battleground states.
Recounts, audits, and legal challenges commenced throughout the months of November and December, many extending well beyond the “first Tuesday after the second Wednesday in December”—in other words, the codified date on which the electors for president and vice president must meet.
However, a major caveat existed: not unlike the unprecedented (and, in many cases, unlawful) manner in which certain states’ elections were carried out, the recounts and audits were conducted sloppily at best.
So as not to belabor this point, here are just a few examples:
In Georgia, where Joe Biden became the first Democrat to win the state in nearly 30 years by a minuscule 11,779 votes (or by just 0.23 percent), several audits and recounts were conducted in the weeks after election day. Statewide, the “official” Georgia hand recount resulted in Biden’s lead slimming by 1,274 votes, over ten percent of the margin of victory. It should be noted, however, as a major source of controversy, each audit occurred without signature verification: after the signed envelope containing an absentee voter’s ballot was received, the ballot was removed with no way of reconnecting the two again.
While some argued this falls under the Georgia Constitution’s requirement of a secret ballot (though it should be noted that other states with similar secrecy requirements enable the reconnection of ballots), Georgia failed to properly audit the 2020 election and mitigate the legitimate concerns raised. Given that a majority of voters cast their ballots by mail, which led to the heightened scrutiny in the first place, it appears likely that Georgia officials lacked the requisite means to ensure the orderly count, recount, and audit of those votes.
In fact, the secretary of state’s failure to properly implement a signature verification system led to a complete overhaul of the balloting process. As a result of Georgia’s 2021 election law changes, voters now verify their absentee ballots by providing a driver’s license number or identification card. To add insult to injury, on top of the already dubious “signature verification” scheme which experts agree is a notoriously subjective process to begin with (for instance, what accounted for the general election having only 32.5 percent of the invalid signatures cured, compared to over 60 percent in the 2021 runoff?), votes from Georgia’s 159 counties were audited multiple times, yielding staggering results: an audit of Fulton County on November 16, 2020 (more than a week after the media declared Joe Biden the President-elect) found 2,600 otherwise uncounted ballots as a result of a person “not executing their job properly”; Fayette County failed to count another 2,755 votes; and several other forgotten memory cards carrying hundreds of votes were discovered across the state. The fact that Trump is facing possible federal charges for having inquired about “finding” votes in a state which indeed lost thousands of votes is an indicator of the corruption of the system.
These challenges continued for weeks on end, such that another audit was announced in Cobb County on December 14, 2020, the day on which the electors were scheduled to meet. This is the backdrop that caused the meeting of the alternate electors in Georgia, which many legal scholars have pointed out that a similar scenario unfolded in Hawaii in 1960. Hawaii had officially certified the election and sent its own electors for Nixon accordingly, but because there was an ongoing legal challenge, an alternate slate of electors was sent by a group of Democrats for Kennedy. In the 1960 case, it was the alternate slate of electors that ultimately were counted and certified.
In Pennsylvania, mail-in ballots constituted about 40 percent of the ballots cast statewide (up from 4 percent in 2016). The margin of victory was a narrow 1.17 percent, and legal challenges to the election procedures occurred well into December. Following an order by Justice Alito to separate the ballots arriving after election day, a deadline to challenge the state’s mail-in votes was set a day after the “safe harbor” deadline, or the day by which states were required to resolve their election controversies. A September 2020 decision from Pennsylvania’s Supreme Court clarified state law by requiring that ballots be placed in “secrecy envelopes” in order to be counted. “Naked ballots” lacking the envelope were not to be counted, which led to significant confusion during the primary. As a result, Pennsylvania implemented massive voter education efforts to prepare election workers specifically on how to manage these ballots, which were returned without having first been placed in a secrecy envelope. It remains unclear how many “naked ballots” were cast during the 2020 general election. Likely not wholly unrelated, it is noteworthy that the 2020 general election saw a significantly lower mail-in ballot rejection rate.
In Wisconsin, the hundreds of drop boxes installed during the 2020 election to collect absentee ballots were deemed “illegal under Wisconsin statutes” by the state’s supreme court in 2022. This is particularly troublesome, considering a whopping 40.8 percent of the ballots in the 2020 election were cast by mail, compared to just 4.8 percent in 2016. Because of these illegal election law changes, as explicitly referenced by John Eastman in his memoranda, the country may never know how many votes in Wisconsin were cast and counted in accordance with the state legislature’s procedures, a state that went for Biden by just around 20,000 votes, or a 0.63 percent margin of victory. Wisconsin also saw a record high turnout rate, so much so that many observers have questioned the definition of “turnout rate” itself: 89 percent of registered voters in Wisconsin cast their ballots in 2020.
Election law challenges were not limited to Wisconsin. Several states saw improper changes to election laws by bodies other than the state legislature, in violation of Article I, Section 4, Clause 1 of the Constitution. While some of the lawsuits were successful in the weeks leading up to the election, others after November 3 were dismissed not on the merits but instead due to lack of standing. Regardless, many lawsuits were ongoing at the appointed time at which the electors were scheduled to meet in December.
The President of the United States was, in the weeks following the fraudulent election, outright censored, shadow banned, and blacklisted from every major social media platform, including Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter—his influence and reach severely undercut and silenced by a partnership of hostile government agents and private actors in Silicon Valley who harbored well-known political and personal antipathies against him. Even while still on those platforms, however, there has come to light overwhelming evidence that pro-Trump stories, or at the very least, stories perceived as anti-Biden or anti-Democratic, were shadow banned, if not outright censored, by those very same platforms. The Twitter Files shed some light onto what had happened behind the scenes. FBI agents, in collusion with censors who worked at Twitter, conspired surreptitiously to find ways to shut down content-based political speech, which should be protected speech under the First Amendment. The most damning revelation to have come out of the Twitter Files was, of course, the concerted effort to silence the Hunter Biden laptop scandal, as originally reported by the New York Post in the days and weeks leading up to November 3.
The reports of thousands of emails exchanged between Hunter and business associates over a decade-long period strongly hinted at a money laundering scheme involving the Ukrainian company Burisma, for which Hunter Biden is currently facing criminal charges, and through which the son of Joe Biden profited from his father’s lucrative contacts in foreign governments and other connections afforded by his public office. The FBI granted expedited Top Secret security clearances, normally reserved exclusively to high-ranking government officials, to members of Twitter in order to create a special portal for Twitter staff to counteract “disinformation”—which really meant any reporting that might benefit the Trump campaign at the expense of the Biden campaign. When polled, nearly 4 in 5 Americans believed that but for the censorship of the Hunter Biden story, the outcome of the 2020 presidential election, rigged procedures put to one side, would have been different.
The greatest anomaly of the 2020 general election was the political context in which the election took place: COVID-19 reset the entire paradigm. One can easily forget that in December of 2019, prior to the first reported outbreak of the pandemic on American shores, the Trump economy was raging, unemployment was at historic lows across every demographic group, global terrorism was at decades lows, and America’s future looked quite bright. Then everything changed. The majority of states radically changed their election procedures—beyond anything previously seen in American history—using the justification of national emergency, which deeply complicated the process of counting votes. Such changes included switching to “universal mail voting”—which the Left sold to the public as a “civil rights issue,” adding a veneer of moral propriety to make it easier for them to affect the outcome of the election.
The fact that so many states, such as Nevada and Vermont, made these changes permanent proves that civil rights was never the driving issue; these changes were always about maintaining power. The result of these changes meant “that millions more Americans will receive mail ballots in future elections,” as reported by Politico. The influx of new ballots has deeply muddied the waters and sowed permanent doubts about the integrity of all future elections.
As it stood, prior to the pandemic, the integrity of our elections has been put into serious doubt over years by Democrats and Republicans alike. Before 2020, election integrity was mostly a Democratic boilerplate issue: the results of the 2000, 2004, and 2016 presidential elections, in particular, were seriously undermined by Democratic lawmakers and their media allies who in many cases outright denied the legitimacy of both elections. In 2016, many leading Democrats, incredulous over the thought of Donald Trump winning the 2016 election, also discussed the possibility of sending alternate electors or supporting so-called “faithless” electors, even going as far as signing onto an attempt to sully the electors’ fight on the grounds that the Electoral College is a “deliberative process.” Then, the Left had no shame in sowing doubts about the integrity of the election process and the legitimacy of the Trump presidency, having already conjured a false narrative about Russian influence in the 2016 election, to which the American people were subject nonstop for the entire first half of Trump’s term in office.
According to the Durham Report, “neither U.S. law enforcement nor the Intelligence Community Appears to have possessed any actual evidence of collusion in their holdings at the commencement of the Crossfire Hurricane investigation.” It was the Crossfire Hurricane investigation launched on July 31, 2016, in the middle of the presidential election, that established the legal imprimatur for the Obama FBI to wiretap the Trump campaign. The 2020 election was carried out in the most polarized political climate since 1860. Because of our deeply polarized state of affairs, the election results were bound to be close, either way. So the fact that Trump’s administration wanted to exercise its due diligence—in light of how close our presidential elections are, including in 2020, which was decided by a mere 50,000 votes spread across a handful of states—was reasonable.
Indeed, it would have been an act of grave negligence had Trump not made inquiries into the integrity of the election. His phone calls, for example, to the Georgia governor, and his demands to the Georgia secretary of state, for which he is now being investigated, and state legislatures in critical battlegrounds, like Michigan and Wyoming, is not an impeachable or indictable offense: it is an act of precautionary care, the type of action one would expect a president to carry out to meet his constitutional oath.
The words President Trump chose to communicate to Brian Kemp are far, far less important constitutionally speaking than the act itself, which was motivated by sincere worries about the legalities of the 2020 election, and out of an abundance of concern to uphold his Article II, Section 3 duty: “to take care that the laws be faithfully executed.” The first line of Article II stipulates that “the executive Power shall be vested in a President of the United States of America.” Donald Trump, as President of the United States, therefore had a constitutional prerogative to ensure the integrity of the electoral process.
That dozens of states changed their election procedures during an extraordinarily precarious moment in American history would indeed necessitate the kinds of actions, at a bare minimum, that Trump undertook in the days following the 2020 election, in order to meet his oath. Here are just a handful of examples:
-
Florida’s voter registration deadline was extended.
-
Pennsylvania provided for prepaid postage for mail-in and absentee ballots. The state also extended the deadline for mail-in/absentee ballots, and authorized dropbox access for the collection of such ballots.
-
Arizona’s voter registration deadline was extended.
-
Michigan sent mail-in ballot applications “automatically” to all voters for the general election.
-
Maine extended its voter pre-registration deadline for the general election.
-
Wisconsin automatically sent mail-in ballots to most voters for the general election.
The above partial list, which names just a handful of prominent swing states, only reflects the tip of the iceberg of the monumental, historic, and unprecedented changes that were unlawfully implemented by state legislatures across the country to make ballot harvesting and voting generally easier (which is to say, more susceptible to corruption) in the lead-up to the 2020 election. And this list excludes deep blue states like California and New York, which made radical changes to its voting laws, including authorizing counties to “consolidate polling places”; extending the eligibility for mail-in ballots to any person deemed unable to personally appear at the polling place because of a risk of contracting COVID; and opening “online portals” to request absentee ballots, among other revolutionary changes that made voting easier and thus significantly more vulnerable to fraud. Indeed, one can reasonably argue that the procedures themselves, of highly dubious legality again, were prima facie fraudulent. And this neglects the hundreds if not thousands of other arbitrary rule changes made nationwide on a state-by-state basis, such as mask-wearing requirements and other unprecedented, last-minute rule changes implemented in numerous states with the purpose of maximizing Biden voters and minimizing Trump voters.
In a country of this size under normal conditions, the changes discussed above would typically require years to implement in order to guarantee their efficacy. But the goal of electioneering in this country is no longer one of minimizing corruption to ensure a fair, orderly, and competent process—producing outcomes that every American can confidently rally around. Instead, its purpose has been reverse engineered to now sow as much confusion in the process as humanly possible, making election procedures so complicated—and the thought of conducting proper discovery in a would-be lawsuit so time consuming and arduous—that it has tragically rendered irreparable damage to the legitimacy of the entire system.
Free and fair elections, much like equitable justice, is a foreign concept in a banana republic. The expedited timeline by which the 2020 general election procedures were changed in the name of national security is the ultimate testimony of a society that does not care any longer for competence, or fairness, or democratic governance, or putting its own interests above the voters’. Instead, it is the mark of a regime that is sinking into unmanageable corruption.
Spread & Containment
‘Excess Mortality Skyrocketed’: Tucker Carlson and Dr. Pierre Kory Unpack ‘Criminal’ COVID Response
‘Excess Mortality Skyrocketed’: Tucker Carlson and Dr. Pierre Kory Unpack ‘Criminal’ COVID Response
As the global pandemic unfolded, government-funded…

As the global pandemic unfolded, government-funded experimental vaccines were hastily developed for a virus which primarily killed the old and fat (and those with other obvious comorbidities), and an aggressive, global campaign to coerce billions into injecting them ensued.
Then there were the lockdowns - with some countries (New Zealand, for example) building internment camps for those who tested positive for Covid-19, and others such as China welding entire apartment buildings shut to trap people inside.
It was an egregious and unnecessary response to a virus that, while highly virulent, was survivable by the vast majority of the general population.
Oh, and the vaccines, which governments are still pushing, didn't work as advertised to the point where health officials changed the definition of "vaccine" multiple times.
Tucker Carlson recently sat down with Dr. Pierre Kory, a critical care specialist and vocal critic of vaccines. The two had a wide-ranging discussion, which included vaccine safety and efficacy, excess mortality, demographic impacts of the virus, big pharma, and the professional price Kory has paid for speaking out.
Keep reading below, or if you have roughly 50 minutes, watch it in its entirety for free on X:
Ep. 81 They’re still claiming the Covid vax is safe and effective. Yet somehow Dr. Pierre Kory treats hundreds of patients who’ve been badly injured by it. Why is no one in the public health establishment paying attention? pic.twitter.com/IekW4Brhoy
— Tucker Carlson (@TuckerCarlson) March 13, 2024
"Do we have any real sense of what the cost, the physical cost to the country and world has been of those vaccines?" Carlson asked, kicking off the interview.
"I do think we have some understanding of the cost. I mean, I think, you know, you're aware of the work of of Ed Dowd, who's put together a team and looked, analytically at a lot of the epidemiologic data," Kory replied. "I mean, time with that vaccination rollout is when all of the numbers started going sideways, the excess mortality started to skyrocket."
When asked "what kind of death toll are we looking at?", Kory responded "...in 2023 alone, in the first nine months, we had what's called an excess mortality of 158,000 Americans," adding "But this is in 2023. I mean, we've had Omicron now for two years, which is a mild variant. Not that many go to the hospital."
'Safe and Effective'
Tucker also asked Kory why the people who claimed the vaccine were "safe and effective" aren't being held criminally liable for abetting the "killing of all these Americans," to which Kory replied: "It’s my kind of belief, looking back, that [safe and effective] was a predetermined conclusion. There was no data to support that, but it was agreed upon that it would be presented as safe and effective."
Tucker Carlson Asks the Forbidden Question
— The Vigilant Fox ???? (@VigilantFox) March 14, 2024
He wants to know why the people who made the claim “safe and effective” aren’t being held to criminal liability for abetting the “killing of all these Americans.”
DR. PIERRE KORY: “It’s my kind of belief, looking back, that [safe and… pic.twitter.com/Icnge18Rtz
Carlson and Kory then discussed the different segments of the population that experienced vaccine side effects, with Kory noting an "explosion in dying in the youngest and healthiest sectors of society," adding "And why did the employed fare far worse than those that weren't? And this particularly white collar, white collar, more than gray collar, more than blue collar."
Kory also said that Big Pharma is 'terrified' of Vitamin D because it "threatens the disease model." As journalist The Vigilant Fox notes on X, "Vitamin D showed about a 60% effectiveness against the incidence of COVID-19 in randomized control trials," and "showed about 40-50% effectiveness in reducing the incidence of COVID-19 in observational studies."
Dr. Pierre Kory: Big Pharma is ‘TERRIFIED’ of Vitamin D
— The Vigilant Fox ???? (@VigilantFox) March 14, 2024
Why?
Because “It threatens the DISEASE MODEL.”
A new meta-analysis out of Italy, published in the journal, Nutrients, has unearthed some shocking data about Vitamin D.
Looking at data from 16 different studies and 1.26… pic.twitter.com/q5CsMqgVju
Professional costs
Kory - while risking professional suicide by speaking out, has undoubtedly helped save countless lives by advocating for alternate treatments such as Ivermectin.
Kory shared his own experiences of job loss and censorship, highlighting the challenges of advocating for a more nuanced understanding of vaccine safety in an environment often resistant to dissenting voices.
"I wrote a book called The War on Ivermectin and the the genesis of that book," he said, adding "Not only is my expertise on Ivermectin and my vast clinical experience, but and I tell the story before, but I got an email, during this journey from a guy named William B Grant, who's a professor out in California, and he wrote to me this email just one day, my life was going totally sideways because our protocols focused on Ivermectin. I was using a lot in my practice, as were tens of thousands of doctors around the world, to really good benefits. And I was getting attacked, hit jobs in the media, and he wrote me this email on and he said, Dear Dr. Kory, what they're doing to Ivermectin, they've been doing to vitamin D for decades..."
"And it's got five tactics. And these are the five tactics that all industries employ when science emerges, that's inconvenient to their interests. And so I'm just going to give you an example. Ivermectin science was extremely inconvenient to the interests of the pharmaceutical industrial complex. I mean, it threatened the vaccine campaign. It threatened vaccine hesitancy, which was public enemy number one. We know that, that everything, all the propaganda censorship was literally going after something called vaccine hesitancy."
Money makes the world go 'round
Carlson then hit on perhaps the most devious aspect of the relationship between drug companies and the medical establishment, and how special interests completely taint science to the point where public distrust of institutions has spiked in recent years.
"I think all of it starts at the level the medical journals," said Kory. "Because once you have something established in the medical journals as a, let's say, a proven fact or a generally accepted consensus, consensus comes out of the journals."
"I have dozens of rejection letters from investigators around the world who did good trials on ivermectin, tried to publish it. No thank you, no thank you, no thank you. And then the ones that do get in all purportedly prove that ivermectin didn't work," Kory continued.
"So and then when you look at the ones that actually got in and this is where like probably my biggest estrangement and why I don't recognize science and don't trust it anymore, is the trials that flew to publication in the top journals in the world were so brazenly manipulated and corrupted in the design and conduct in, many of us wrote about it. But they flew to publication, and then every time they were published, you saw these huge PR campaigns in the media. New York Times, Boston Globe, L.A. times, ivermectin doesn't work. Latest high quality, rigorous study says. I'm sitting here in my office watching these lies just ripple throughout the media sphere based on fraudulent studies published in the top journals. And that's that's that has changed. Now that's why I say I'm estranged and I don't know what to trust anymore."
Vaccine Injuries
Carlson asked Kory about his clinical experience with vaccine injuries.
"So how this is how I divide, this is just kind of my perception of vaccine injury is that when I use the term vaccine injury, I'm usually referring to what I call a single organ problem, like pericarditis, myocarditis, stroke, something like that. An autoimmune disease," he replied.
"What I specialize in my practice, is I treat patients with what we call a long Covid long vaxx. It's the same disease, just different triggers, right? One is triggered by Covid, the other one is triggered by the spike protein from the vaccine. Much more common is long vax. The only real differences between the two conditions is that the vaccinated are, on average, sicker and more disabled than the long Covids, with some pretty prominent exceptions to that."
Watch the entire interview above, and you can support Tucker Carlson's endeavors by joining the Tucker Carlson Network here...
International
Shakira’s net worth
After 12 albums, a tax evasion case, and now a towering bronze idol sculpted in her image, how much is Shakira worth more than 4 decades into her care…

Shakira’s considerable net worth is no surprise, given her massive popularity in Latin America, the U.S., and elsewhere.
In fact, the belly-dancing contralto queen is the second-wealthiest Latin-America-born pop singer of all time after Gloria Estefan. (Interestingly, Estefan actually helped a young Shakira translate her breakout album “Laundry Service” into English, hugely propelling her stateside success.)
Since releasing her first record at age 13, Shakira has spent decades recording albums in both Spanish and English and performing all over the world. Over the course of her 40+ year career, she helped thrust Latin pop music into the American mainstream, paving the way for the subsequent success of massively popular modern acts like Karol G and Bad Bunny.
In December 2023, a 21-foot-tall beachside bronze statue of the “Hips Don’t Lie” singer was unveiled in her Colombian hometown of Barranquilla, making her a permanent fixture in the city’s skyline and cementing her legacy as one of Latin America’s most influential entertainers.
After 12 albums, a plethora of film and television appearances, a highly publicized tax evasion case, and now a towering bronze idol sculpted in her image, how much is Shakira worth? What does her income look like? And how does she spend her money?
How much is Shakira worth?
In late 2023, Spanish sports and lifestyle publication Marca reported Shakira’s net worth at $400 million, citing Forbes as the figure’s source (although Forbes’ profile page for Shakira does not list a net worth — and didn’t when that article was published).
Most other sources list the singer’s wealth at an estimated $300 million, and almost all of these point to Celebrity Net Worth — a popular but dubious celebrity wealth estimation site — as the source for the figure.
A $300 million net worth would make Shakira the third-richest Latina pop star after Gloria Estefan ($500 million) and Jennifer Lopez ($400 million), and the second-richest Latin-America-born pop singer after Estefan (JLo is Puerto Rican but was born in New York).
Shakira’s income: How much does she make annually?
Entertainers like Shakira don’t have predictable paychecks like ordinary salaried professionals. Instead, annual take-home earnings vary quite a bit depending on each year’s album sales, royalties, film and television appearances, streaming revenue, and other sources of income. As one might expect, Shakira’s earnings have fluctuated quite a bit over the years.
From June 2018 to June 2019, for instance, Shakira was the 10th highest-earning female musician, grossing $35 million, according to Forbes. This wasn’t her first time gracing the top 10, though — back in 2012, she also landed the #10 spot, bringing in $20 million, according to Billboard.
In 2023, Billboard listed Shakira as the 16th-highest-grossing Latin artist of all time.

How much does Shakira make from her concerts and tours?
A large part of Shakira’s wealth comes from her world tours, during which she sometimes sells out massive stadiums and arenas full of passionate fans eager to see her dance and sing live.
According to a 2020 report by Pollstar, she sold over 2.7 million tickets across 190 shows that grossed over $189 million between 2000 and 2020. This landed her the 19th spot on a list of female musicians ranked by touring revenue during that period. In 2023, Billboard reported a more modest touring revenue figure of $108.1 million across 120 shows.
In 2003, Shakira reportedly generated over $4 million from a single show on Valentine’s Day at Foro Sol in Mexico City. 15 years later, in 2018, Shakira grossed around $76.5 million from her El Dorado World Tour, according to Touring Data.
Related: RuPaul's net worth: Everything to know about the cultural icon and force behind 'Drag Race'
How much has Shakira made from her album sales?
According to a 2023 profile in Variety, Shakira has sold over 100 million records throughout her career. “Laundry Service,” the pop icon’s fifth studio album, was her most successful, selling over 13 million copies worldwide, according to TheRichest.
Exactly how much money Shakira has taken home from her album sales is unclear, but in 2008, it was widely reported that she signed a 10-year contract with LiveNation to the tune of between $70 and $100 million to release her subsequent albums and manage her tours.

How much did Shakira make from her Super Bowl and World Cup performances?
Shakira co-wrote one of her biggest hits, “Waka Waka (This Time for Africa),” after FIFA selected her to create the official anthem for the 2010 World Cup in South Africa. She performed the song, along with several of her existing fan-favorite tracks, during the event’s opening ceremonies. TheThings reported in 2023 that the song generated $1.4 million in revenue, citing Popnable for the figure.
A decade later, 2020’s Superbowl halftime show featured Shakira and Jennifer Lopez as co-headliners with guest performances by Bad Bunny and J Balvin. The 14-minute performance was widely praised as a high-energy celebration of Latin music and dance, but as is typical for Super Bowl shows, neither Shakira nor JLo was compensated beyond expenses and production costs.
The exposure value that comes with performing in the Super Bowl Halftime Show, though, is significant. It is typically the most-watched television event in the U.S. each year, and in 2020, a 30-second Super Bowl ad spot cost between $5 and $6 million.
How much did Shakira make as a coach on “The Voice?”
Shakira served as a team coach on the popular singing competition program “The Voice” during the show’s fourth and sixth seasons. On the show, celebrity musicians coach up-and-coming amateurs in a team-based competition that eventually results in a single winner. In 2012, The Hollywood Reporter wrote that Shakira’s salary as a coach on “The Voice” was $12 million.
Related: John Cena's net worth: The wrestler-turned-actor's investments, businesses, and more
How does Shakira spend her money?
Shakira doesn’t just make a lot of money — she spends it, too. Like many wealthy entertainers, she’s purchased her share of luxuries, but Barranquilla’s barefoot belly dancer is also a prolific philanthropist, having donated tens of millions to charitable causes throughout her career.
Private island
Back in 2006, she teamed up with Roger Waters of Pink Floyd fame and Spanish singer Alejandro Sanz to purchase Bonds Cay, a 550-acre island in the Bahamas, which was listed for $16 million at the time.
Along with her two partners in the purchase, Shakira planned to develop the island to feature housing, hotels, and an artists’ retreat designed to host a revolving cast of artists-in-residence. This plan didn’t come to fruition, though, and as of this article’s last update, the island was once again for sale on Vladi Private Islands.
Real estate and vehicles
Like most wealthy celebs, Shakira’s portfolio of high-end playthings also features an array of luxury properties and vehicles, including a home in Barcelona, a villa in Cyprus, a Miami mansion, and a rotating cast of Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
Philanthropy and charity
Shakira doesn’t just spend her massive wealth on herself; the “Queen of Latin Music” is also a dedicated philanthropist and regularly donates portions of her earnings to the Fundación Pies Descalzos, or “Barefoot Foundation,” a charity she founded in 1997 to “improve the education and social development of children in Colombia, which has suffered decades of conflict.” The foundation focuses on providing meals for children and building and improving educational infrastructure in Shakira’s hometown of Barranquilla as well as four other Colombian communities.
In addition to her efforts with the Fundación Pies Descalzos, Shakira has made a number of other notable donations over the years. In 2007, she diverted a whopping $40 million of her wealth to help rebuild community infrastructure in Peru and Nicaragua in the wake of a devastating 8.0 magnitude earthquake. Later, during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, Shakira donated a large supply of N95 masks for healthcare workers and ventilators for hospital patients to her hometown of Barranquilla.
Back in 2010, the UN honored Shakira with a medal to recognize her dedication to social justice, at which time the Director General of the International Labour Organization described her as a “true ambassador for children and young people.”

Shakira’s tax fraud scandal: How much did she pay?
In 2018, prosecutors in Spain initiated a tax evasion case against Shakira, alleging she lived primarily in Spain from 2012 to 2014 and therefore failed to pay around $14.4 million in taxes to the Spanish government. Spanish law requires anyone who is “domiciled” (i.e., living primarily) in Spain for more than half of the year to pay income taxes.
During the period in question, Shakira listed the Bahamas as her primary residence but did spend some time in Spain, as she was dating Gerard Piqué, a professional footballer and Spanish citizen. The couple’s first son, Milan, was also born in Barcelona during this period.
Shakira maintained that she spent far fewer than 183 days per year in Spain during each of the years in question. In an interview with Elle Magazine, the pop star opined that “Spanish tax authorities saw that I was dating a Spanish citizen and started to salivate. It's clear they wanted to go after that money no matter what."
Prosecutors in the case sought a fine of almost $26 million and a possible eight-year prison stint, but in November of 2023, Shakira took a deal to close the case, accepting a fine of around $8 million and a three-year suspended sentence to avoid going to trial. In reference to her decision to take the deal, Shakira stated, "While I was determined to defend my innocence in a trial that my lawyers were confident would have ruled in my favour [had the trial proceeded], I have made the decision to finally resolve this matter with the best interest of my kids at heart who do not want to see their mom sacrifice her personal well-being in this fight."
How much did the Shakira statue in Barranquilla cost?
In late 2023, a 21-foot-tall bronze likeness of Shakira was unveiled on a waterfront promenade in Barranquilla. The city’s then-mayor, Jaime Pumarejo, commissioned Colombian sculptor Yino Márquez to create the statue of the city’s treasured pop icon, along with a sculpture of the city’s coat of arms.
According to the New York Times, the two sculptures cost the city the equivalent of around $180,000. A plaque at the statue’s base reads, “A heart that composes, hips that don’t lie, an unmatched talent, a voice that moves the masses and bare feet that march for the good of children and humanity.”
Related: Taylor Swift net worth: The most successful entertainer joins the billionaire's club
bonds pandemic covid-19 real estate africa mexico spainInternational
Delta Air Lines adds a new route travelers have been asking for
The new Delta seasonal flight to the popular destination will run daily on a Boeing 767-300.

Those who have tried to book a flight from North America to Europe in the summer of 2023 know just how high travel demand to the continent has spiked.
At 2.93 billion, visitors to the countries making up the European Union had finally reached pre-pandemic levels last year while North Americans in particular were booking trips to both large metropolises such as Paris and Milan as well as smaller cities growing increasingly popular among tourists.
Related: A popular European city is introducing the highest 'tourist tax' yet
As a result, U.S.-based airlines have been re-evaluating their networks to add more direct routes to smaller European destinations that most travelers would have previously needed to reach by train or transfer flight with a local airline.
Shutterstock
Delta Air Lines: ‘Glad to offer customers increased choice…’
By the end of March, Delta Air Lines (DAL) will be restarting its route between New York’s JFK and Marco Polo International Airport in Venice as well as launching two new flights to Venice from Atlanta. One will start running this month while the other will be added during peak demand in the summer.
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
“As one of the most beautiful cities in the world, Venice is hugely popular with U.S. travelers, and our flights bring valuable tourism and trade opportunities to the city and the region as well as unrivalled opportunities for Venetians looking to explore destinations across the Americas,” Delta’s SVP for Europe Matteo Curcio said in a statement. “We’re glad to offer customers increased choice this summer with flights from New York and additional service from Atlanta.”
The JFK-Venice flight will run on a Boeing 767-300 (BA) and have 216 seats including higher classes such as Delta One, Delta Premium Select and Delta Comfort Plus.
Delta offers these features on the new flight
Both the New York and Atlanta flights are seasonal routes that will be pulled out of service in October. Both will run daily while the first route will depart New York at 8:55 p.m. and arrive in Venice at 10:15 a.m. local time on the way there, while leaving Venice at 12:15 p.m. to arrive at JFK at 5:05 p.m. on the way back.
According to Delta, this will bring its service to 17 flights from different U.S. cities to Venice during the peak summer period. As with most Delta flights at this point, passengers in all fare classes will have access to free Wi-Fi during the flight.
Those flying in Delta’s highest class or with access through airline status or a credit card will also be able to use the new Delta lounge that is part of the airline’s $12 billion terminal renovation and is slated to open to travelers in the coming months. The space will take up more than 40,000 square feet and have an outdoor terrace.
“Delta One customers can stretch out in a lie-flat seat and enjoy premium amenities like plush bedding made from recycled plastic bottles, more beverage options, and a seasonal chef-curated four-course meal,” Delta said of the new route. “[…] All customers can enjoy a wide selection of in-flight entertainment options and stay connected with Wi-Fi and enjoy free mobile messaging.”
stocks pandemic european europe-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International6 days ago
International6 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges
























