Uncategorized
Cantillon Overdrive… And The Bitcoin Breakout
Cantillon Overdrive… And The Bitcoin Breakout
Authored by Mark Jeftovic via BombThrower.com,
What we now call “The Cantillon Effect”…

Authored by Mark Jeftovic via BombThrower.com,
What we now call “The Cantillon Effect” was known far back as circa-1730, by at least one economist. It hasn’t been taken very seriously in modern times, especially here in the fiat age.
Named after its author, Richard Cantillon, in his “Essay on Economic Theory” (“Essai sur la Nature du Commerce en Général”) — it is his only surviving work and was published posthumously in 1755, more than 20 years after he was murdered by a former cook whom he had dismissed from his household. The disgruntled ex-employee, returned by night, robbed his home, then set it ablaze, with Cantillon — and the rest of his manuscripts, within.
The Essay On Economic Theory had been previously circulated in pamphlet form, which is why copies survived to be published to the world, and lays bare the dirty secret behind all fiat monetary schemes:
In a nutshell, when money is created or added to an economy, the people who receive it first, benefit, but they do so to the detriment of everybody else.
The early recipients of new money were able to spend it on accumulating more of the productive assets that society had to offer. But this also increased the money supply, which diluted the purchasing power of everybody else’s existing money.
The wealthy got to invest new money.
Everybody else had to spend more of their existing money.
So, while the rich got richer, it made it more expensive for the poor to stay alive.
The elites invariably believe the system works great. From inside their bubble it certainly seems that way. But it is unsustainable over the long haul. As the dynamic iterates, it accelerates, and it increases wealth disparity. If there was a nice, meaty middle-class in the economic bell curve, it wouldn’t last for long as the productive assets increasingly get hoovered up by a rentier class using new money.
Eventually wealth inequality hits a breaking point, and when that happens, all existing social contracts – real or implied – break down.
The French Revolution may be the first example of the Cantillon Effect’s consequences, after Cantillon himself detailed its underlying dynamics.
The distortions introduced from currency debasement are far reaching and take a long time to play out. But the tempo intensifies toward a “quickening” as it enters the end game, much like compound interest and bankruptcy (“gradually, then suddenly”). The rich become more imperious, the poor more resentful and then, finally, after generations of silent theft and economic repression, something sets off a phase shift — and then it’s show trials and guillotines.
In France’s case, the monetary missteps that set it on a course to Bastille Day went at least as far back as Louis XIV, the great-great-grandfather of the Sun King who would be left holding the bag (and his head in a bucket) nearly a century later.
In Guy Rowlands “The Financial Decline of a Great Power: War, Influence and Money in Louis XIV’s France“, we are told of “dimunitions” which devalued the coin of the realm by decree, (nevermind that it was gold and silver backed)…
The government would typically prepare an augmentation by decreeing diminutions—or abatements’—of the coins in circulation, a decision that did not require coins to be restamped or re-created. This was not primarily so the king could pull in more coins through taxation (denominated in Livres),” as any such gain would be cancelled out: a diminution would in fact also force the king to compensate his fisco-financiers and bankers for losses on their contracts and on the coins they held at the time. ‘
The main reason was so there could be huge leaps upward in the value of the coins to the level decreed by the subsequent augmentation, thus bringing in more seigniorage to the king. The government also hoped that a diminution, generating fear of further diminutions, would flush coin out into circulation, particularly for lending to the fisco-financiers.
That is why diminutions were announced in advance, with weeks or even months before the new, lower values would come into effect. This gave people a window in which to lend out their assets. There were indeed often several diminutions in a row: prior to the 1693 augmentation, the values of the coins were diminished four times; and prior to the great recoinage of 1709, diminutions were announced in March and November 1708 and on 16 March 1709.
The state never brought the coin values back down to the level they bad been before the previous augmentation, and this was important to ensure the public did not think the bottom of the valuation had been reached.”
Does any of this sound familiar?
Cantillon on steroids: The Fiat Era & Stakeholder Capitalism
“Let them eat brioche” — Marie Antoinette, 1789
“You will eat bugs, own nothing, and live in a pod” — The World Economic Forum, every day.
With the fiat era, starting in 1971, new money was no longer limited by the supply of gold, or whatever else was backing a currency. You could print the stuff right out of thin air now – which meant that instead of ostensibly enriching all members of society, with its “targeted inflation” for expanding the money supply, it would just accelerate the rate at which the underclass was being impoverished (which for a long time could be papered over with “hedonic adjustments” when reporting on it).
The Global Financial Crisis in 2008, followed by over a decade of ZIRP, NIRP, and QEternity, overclocked that process, and then Covid hit, when it went literally parabolic:
Via TradingEconomics
On its own, this may look like just another hockey stick graph. Most people don’t make the connection on exactly how this manifests in the real world (especially central bankers).
There is no subtler, no surer means of overturning the existing basis of society than to debauch the currency. The process engages all the hidden forces of economic law on the side of destruction, and does it in a manner which not one man in a million is able to diagnose.
— John Maynard Keynes
(Even fewer people realize that Keynes was a Marxist and his economic prescriptions, which form the basis of conventional economic theory to this day, would bring lead to socialism. This was intentional. Especially once you understand what socialism really is.)
This graph is just real estate, and as of 2020. That was before COVID, before lockdowns, before small businesses got shut down by decree while big box stores and Amazon stayed open and the Fed bought their bonds.
Let’s look at a couple of inflection points:
Via Pew Research
The graph above is from Pew Research. In 1971, the start of the Fiat Era, middle income households earned the bulk of the income pie at 62%. Along comes Nixon, who closed the gold window (“temporarily”), and it’s all downhill from there. All kinds of wealth inequality drivers can trace their genesis to that event in 1971.
Then when the bankers blew themselves up (again) in 2008, the bailouts happen (again) and we hit another inflection point: the era of ZIRP, NIRP and QEternity hits, and this is exactly where upper income households crossover the middle income earners. Again, this graph stops short of the Covid Era, at which point all of these trends accelerated.
Where does it leave things?
On the left: A tent city in BC Canada, on the right “Fentanyl zombies” roam downtown SF.
The bottom layers of the economic stratum are looking like a cross between Mad Max and a Zombie Apocalypse. Even worse, is that thanks to plunging income mobility, the underclass is growing. The middle class are falling into the poverty more often than ascending into wealth.
This Visual Capitalist chart looks at the number of people earning more than their parents by generational cohort. Remember, because of inflation everything is getting more expensive, but if each generation is earning less than their parents, they’re losing ground:
Unless you’re already wealthy – then everything is fine because your share of the pie is getting larger…
All Cantillon Schemes Require a Totalizing Ideology
As I mentioned recently in my article on how abandoning sound money perpetuates Forever Wars,
If there is a far-reaching, multi-generational global conspiracy – it is one that brainwashes the masses into trading their time, wealth and property for meaningless chits backed by nothing. Who needs global Communism?
In pre-Revolutionary France, it was By Divine Right. The king was chosen and appointed by God to govern the kingdom. This belief was used to justify the absolute power of the monarch and his authority over all aspects of French life. And the masses went along with it until the economics became so asymmetrical and unsustainable that the peasants revolted. They had no choice, the alternative was to starve to death.
Today’s totalizing ideology is a kind of euphemistically wrapped Technocratic Marxism. Klaus Schwab calls it “Stakeholder Capitalism”, George Gilder, perhaps more accurately, termed it Emergency Socialism in his latest book, Life After Capitalism.
It's called "Stakeholder Capitalism".
— Mark Jeftovic, The ₿itcoin Capitalist (@StuntPope) July 27, 2023
(...and you aren't a stakeholder ???? ) pic.twitter.com/pjyU37SL2o
Gilder only uses the phrase out once or twice in the book and never really expands on it.
Allow me.
Today’s Totalizing Ideology is that you, dear peasant, must ratchet your standard of living downwards. You will have to take up less space. You will have to consume less resources, pay more for everything and accept ever worsening living conditions because if you don’t, the world will end.
And nobody wants that, right?
In the meantime, your betters, the people who have it all under control and everything figured out, will continue to re-imagine your life, and the lives of your children, so that they can forestall the implosion of the global monetary system and finish hoovering up the remaining 5% of the global wealth that they don’t already own.
"The peasants have no bread". "Then let them eat bugs".
— Nick Griffin (@NickGriffinBU) September 22, 2023
Scene at Versailles as elitists who think you should own nothing, go nowhere & eat their processed crickets prepared to feast at taxpayers' expense.#vampireelite pic.twitter.com/zSeKw7KcqO
Which brings us to... Bitcoin.
If only there were some mechanism that was not only immune from dilution via inflation, but could actually reverse the Cantillon Effect.
Sure, there is gold – the age old monetary metal. I like gold and have been invested in it for nearly 30 years. Silver too. Everyone should have an allocation to gold and have some silver, including junk silver to have on-hand for sundries if (or when) your national currency collapses.
But Bitcoin, as distinct from other “cryptocurrencies”, is a very unique monetary asset, backed by energy, decentralized, hard-capped in supply, and largely impervious to capital controls in a way that is distinct from all other monetary assets.
To top it all off, Bitcoin exhibits a reverse Cantillon effect. Because Bitcoin is deflationary, it is becoming more valuable. It is increasing its purchasing power, as more wealth flows into the system and it does so for everybody hodling it. The difference between Bitcoin and Cantillonism is that the purchasing power isn’t declining as the currency units flow outward from the central spigot. It’s increasing for all units, at the same time.
Most people can’t wrap their head around this. Even the aforementioned George Gilder, concludes that Bitcoin can’t become the new global monetary standard because it is deflationary. And he did it in the chapter of his book called “Bitcoin Capitalism”. Heartbreaking.
But history has shown deflationary currencies not only work, economies thrive under them (see again, Sound Money Makes For Short Wars) – and Detlev S Schlichter wrote an entire book on why that’s the case.
“A monetary system with a money commodity of essentially fixed supply will experience secular deflation. A growing economy, with an entirely inflexible money supply will exhibit a tendency for prices to decline on trend, and for money’s purchasing [power] to steadily increase.
But the key question now, is why should this be a problem? We have already seen that historically secular deflation was rather minor and that it certainly never appeared to present any economic difficulties. No correlation between deflation or recession or stagnation is evident under commodity money systems. [T]here are no reasons on conceptual grounds to consider deflation to be a problem”
If there is any disparity, between time and value with Bitcoin, then it’s front loaded. People get into Bitcoin at the price they deserve, but there’s nothing stopping anybody from getting in whenever they want. With the Cantillion Effect, you have no control over new money creation, but yet you still have to live with the declining purchasing power instigated by other people.
With Bitcoin, even if you enter later, you are still on the escalator up, having your sats gain in purchasing power as more capital moves onto a Bitcoin Standard.
We may not have to fire up the guillotines in order to exit this particular episode of Cantillonism, (although we may fire them up for other reasons).
As more people exit the fiat system, the only people left to for the elites to dilute will be the remaining serfs who will get stuck inside the coming CBDC system.
More on that in a future post…
* * *
My forthcoming ebook The CBDC Survival Guide will give you the tools and the knowledge to navigate coming era of Monetary Apartheid. Bombthrower subscribers will get it free when it drops, sign up today.
The Bitcoin Capitalist: For Today’s Sovereign Individual provides actionable intelligence on the macro forces shaping Late Stage Globalism and a tactical toolkit for growing your wealth as it plays out. Try it today here.
Uncategorized
These Cities Have The Highest (And Lowest) Share Of Unaffordable Neighborhoods In 2024
These Cities Have The Highest (And Lowest) Share Of Unaffordable Neighborhoods In 2024
Authored by Sam Bourgi via CreditNews.com,
Homeownership…

Authored by Sam Bourgi via CreditNews.com,
Homeownership is one of the key pillars of the American dream. But for many families, the idyllic fantasy of a picket fence and backyard barbecues remains just that—a fantasy.
Thanks to elevated mortgage rates, sky-high house prices, and scarce inventory, millions of American families have been locked out of the opportunity to buy a home in many cities.
To shed light on America’s housing affordability crisis, Creditnews Research ranked the 50 most populous cities by the percentage of neighborhoods within reach for the typical married-couple household to buy a home in.
The study reveals a stark reality, with many cities completely out of reach for the most affluent household type. Not only that, the unaffordability has radically worsened in recent years.
Comparing how affordability has changed since Covid, Creditnews Research discovered an alarming pattern—indicating consistently more unaffordable housing in all but three cities.
Fortunately, there’s still hope for households seeking to put down roots in more affordable cities—especially for those looking beyond Los Angeles, New York, Boston, San Jone, and Miami.
The typical American family has a hard time putting down roots in many parts of the country. In 11 of the top 50 cities, at least 50% of neighborhoods are out of reach for the average married-couple household. The affordability gap has widened significantly since Covid; in fact, no major city has reported an improvement in affordability post-pandemic.
Sam Bourgi, Senior Analyst at Creditnews
Key findings
-
The most unaffordable cities are Los Angeles, Boston, St. Louis, and San Jose; in each city, 100% of neighborhoods are out of reach for for married-couple households earning a median income;
-
The most affordable cities are Cleveland, Hartford, and Memphis—in these cities, the typical family can afford all neighborhoods;
-
None of the top 50 cities by population saw an improvement in affordable neighborhoods post-pandemic;
-
California recorded the biggest spike in unaffordable neighborhoods since pre-Covid;
-
The share of unaffordable neighborhoods has increased the most since pre-Covid in San Jose (70 percentage points), San Diego (from 57.8 percentage points), and Riverside-San Bernardino (51.9 percentage points);
-
Only three cities have seen no change in housing affordability since pre-Covid: Cleveland, Memphis, and Hartford. They’re also the only cities that had 0% of unaffordable neighborhoods before Covid.
Cities with the highest share of unaffordable neighborhoods
With few exceptions, the most unaffordable cities for married-couple households tend to be located in some of the nation’s most expensive housing markets.
Four cities in the ranking have an unaffordability percentage of 100%—indicating that the median married-couple household couldn’t qualify for an average home in any neighborhood.
The following are the cities ranked from the least affordable to the most:
-
Los Angeles, CA: Housing affordability in Los Angeles has deteriorated over the last five years, as average incomes have failed to keep pace with rising property values and elevated mortgage rates. The median household income of married-couple families in LA is $117,056, but even at that rate, 100% of the city’s neighborhoods are unaffordable.
-
St. Louis, MO: It may be surprising to see St. Louis ranking among the most unaffordable housing markets for married-couple households. But a closer look reveals that the Mound City was unaffordable even before Covid. In 2019, 98% of the city’s neighborhoods were unaffordable—way worse than Los Angeles, Boston, or San Jose.
-
Boston, MA: Boston’s housing affordability challenges began long before Covid but accelerated after the pandemic. Before Covid, married couples earning a median income were priced out of 90.7% of Boston’s neighborhoods. But that figure has since jumped to 100%, despite a comfortable median household income of $172,223.
-
San Jose, CA: Nestled in Silicon Valley, San Jose has long been one of the most expensive cities for housing in America. But things have gotten far worse since Covid, as 100% of its neighborhoods are now out of reach for the average family. Perhaps the most shocking part is that the median household income for married-couple families is $188,403—much higher than the national average.
-
San Diego, CA: Another California city, San Diego, is among the most unaffordable places in the country. Despite boasting a median married-couple household income of $136,297, 95.6% of the city’s neighborhoods are unaffordable.
-
San Francisco, CA: San Francisco is another California city with a high married-couple median income ($211,585) but low affordability. The percentage of unaffordable neighborhoods for these homebuyers stands at 89.2%.
-
New York, NY: As one of the most expensive cities in America, New York is a difficult housing market for married couples with dual income. New York City’s share of unaffordable neighborhoods is 85.9%, marking a 33.4% rise from pre-Covid times.
-
Miami, FL: Partly due to a population boom post-Covid, Miami is now one of the most unaffordable cities for homebuyers. Roughly four out of five (79.4%) of Miami’s neighborhoods are out of reach price-wise for married-couple families. That’s a 34.7% increase from 2019.
-
Nashville, TN: With Nashville’s population growth rebounding to pre-pandemic levels, the city has also seen greater affordability challenges. In the Music City, 73.7% of neighborhoods are considered unaffordable for married-couple households—an increase of 11.9% from pre-Covid levels.
-
Richmond, VA: Rounding out the bottom 10 is Richmond, where 55.9% of the city’s 161 neighborhoods are unaffordable for married-couple households. That’s an 11.9% increase from pre-Covid levels.
Cities with the lowest share of unaffordable neighborhoods
All the cities in our top-10 ranking have less than 10% unaffordable neighborhoods—meaning the average family can qualify for a home in at least 90% of the city.
Interestingly, these cities are also outside the top 15 cities by population, and eight are in the bottom half.
The following are the cities ranked from the most affordable to the least:
-
Hartford, CT: Hartford ranks first with the percentage of unaffordable neighborhoods at 0%, unchanged since pre-Covid times. Married couples earning a median income of $135,612 can afford to live in any of the city’s 16 neighborhoods. Interestingly, Hartford is the smallest city to rank in the top 10.
-
Memphis, TN: Like Hartford, Memphis has 0% unaffordable neighborhoods, meaning any married couple earning a median income of $101,734 can afford an average homes in any of the city’s 12 neighborhoods. The percentage of unaffordable neighborhoods also stood at 0% before Covid.
-
Cleveland, OH: The Midwestern city of Cleveland is also tied for first, with the percentage of unaffordable neighborhoods at 0%. That means households with a median-couple income of $89,066 can qualify for an average home in all of the city’s neighborhoods. Cleveland is also among the three cities that have seen no change in unaffordability compared to 2019.
-
Minneapolis, MN: The largest city in the top 10, Minneapolis’ share of unaffordable neighborhoods stood at 2.41%, up slightly from 2019. Married couples earning the median income ($149,214) have access to the vast majority of the city’s 83 neighborhoods.
-
Baltimore, MD: Married-couple households in Baltimore earn a median income of $141,634. At that rate, they can afford to live in 97.3% of the city’s 222 neighborhoods, making only 2.7% of neighborhoods unaffordable. That’s up from 0% pre-Covid.
-
Louisville, KY: Louisville is a highly competitive market for married households. For married-couple households earning a median wage, only 3.6% of neighborhoods are unaffordable, up 11.9% from pre-Covid times.
-
Cincinnati, OH: The second Ohio city in the top 10 ranks close to Cleveland in population but has a much higher median married-couple household income of $129,324. Only 3.6% of the city’s neighborhoods are unaffordable, up slightly from pre-pandemic levels.
-
Indianapolis, IN: Another competitive Midwestern market, only 4.4% of Indianapolis is unaffordable, making the vast majority of the city’s 92 neighborhoods accessible to the average married couple. Still, the percentage of unaffordable neighborhoods before Covid was less than 1%.
-
Oklahoma City, OK: Before Covid, Oklahoma City had 0% neighborhoods unaffordable for married-couple households earning the median wage. It has since increased to 4.69%, which is still tiny compared to the national average.
-
Kansas City, MO: Kansas City has one of the largest numbers of neighborhoods in the top 50 cities. Its married-couple residents can afford to live in nearly 95% of them, making only 5.6% of neighborhoods out of reach. Like Indiana, Kansas City’s share of unaffordable neighborhoods was less than 1% before Covid.
The biggest COVID losers
What's particularly astonishing about the current housing market is just how quickly affordability has declined since Covid.
Even factoring in the market correction after the 2022 peak, the price of existing homes is still nearly one-third higher than before Covid. Mortgage rates have also more than doubled since early 2022.
Combined, the rising home prices and interest rates led to the worst mortgage affordability in more than 40 years.
Against this backdrop, it’s hardly surprising that unaffordability increased in 47 of the 50 cities studied and remained flat in the other three. No city reported improved affordability in 2024 compared to 2019.
The biggest increases are led by San Jose (70 percentage points), San Diego (57.8 percentage points), Riverside-San Bernardino (51.9 percentage points), Sacramento (43 percentage points), Orlando (37.4 percentage points), Miami (34.7 percentage points), and New York City (33.4 percentage points).
The following cities in our study are ranked by the largest percentage point change in unaffordable neighborhoods since pre-Covid:
Uncategorized
Your financial plan may be riskier without bitcoin
It might actually be riskier to not have bitcoin in your portfolio than it is to have a small allocation.

This article originally appeared in the Sound Advisory blog. Sound Advisory provide financial advisory services and are specialize in educating and guiding clients to thrive financially in a bitcoin-powered world. Click here to learn more.
“Belief is a wise wager. Granted that faith cannot be proved, what harm will come to you if you gamble on its truth and it proves false? If you gain, you gain all; if you lose, you lose nothing. Wager, then, without hesitation, that He exists.”
- Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal only lived to age 39 but became world-famous for many contributions in the fields of mathematics, physics, and theology. The above quote encapsulates Pascal’s wager—a philosophical argument for the Christian belief in the existence of God.
The argument's conclusion states that a rational person should live as though God exists. Even if the probability is low, the reward is worth the risk.
Pascal’s wager as a justification for bitcoin? Yes, I’m aware of the fallacies: false dichotomy, appeal to emotion, begging the question, etc. That is not the point. The point is that binary outcomes instigate extreme results, and the game theory of money suggests that it’s a winner-take-all game.
The Pascalian investor: A rational approach to bitcoin
Humanity’s adoption of “the best money over time” mimics a series of binary outcomes—A/B tests.
Throughout history, inferior forms of money have faded as better alternatives emerged (see India’s failed transition to a gold standard). And if bitcoin is trying to be the premier money of the future, it will either succeed or it won’t.
“If you ain’t first, you’re last.” -Ricky Bobby, Talladega Nights, on which monies succeed over time.
So, we can look at bitcoin success similarly to Pascal’s wager—let’s call it Satoshi’s wager. The translated points would go something like this:
- If you own bitcoin early and it becomes a globally valuable money, you gain immensely. ????
- If you own bitcoin and it fails, you’ve lost that value. ????
- If you don’t own bitcoin and it goes to zero, no pain and no gain. ????
- If you don’t own bitcoin and it succeeds, you will have missed out on the significant financial revolution of our lifetimes and fall comparatively behind. ????
If bitcoin is successful, it will be worth far more than it is today and have a massive impact on your financial future. If it fails, the losses are only limited to your exposure. The most that you could lose is the money that you invested.
It is hypothetically possible that bitcoin could be worth 100x more than it is today, but it can only possibly lose 1x its value as it goes to zero. The concept we’re discussing here is asymmetric upside - significant gains with relatively limited downside. In other words, the potential rewards of the investment outweigh the potential risks.
Bitcoin offers an asymmetric upside that makes it a wise investment for most portfolios. Even a small allocation provides potential protection against extreme currency debasement.
Salt, gasoline, and insurance

“Don’t over salt your steak, pour too much gas on the fire, or buy too much insurance.”
A little bit goes a long way, and you can easily overdo it. The same applies when looking at bitcoin in the context of a financial plan.
Bitcoin’s asymmetric upside gives it “insurance-like” qualities, and that insurance pays off very well in times of money printing. This was exemplified in 2020 when bitcoin's value increased over 300% in response to pandemic money printing, far outpacing stocks, gold, and bonds.
Bitcoin offers a similar asymmetric upside today. Bitcoin's supply is capped at 21 million coins, making it resistant to inflationary debasement. In contrast, the dollar's purchasing power consistently declines through unrestrained money printing. History has shown that societies prefer money that is hard to inflate.
If recent rampant inflation is uncontainable and the dollar system falters, bitcoin is well-positioned as a successor. This global monetary A/B test is still early, but given their respective sizes, a little bitcoin can go a long way. If it succeeds, early adopters will benefit enormously compared to latecomers. Of course, there are no guarantees, but the potential reward justifies reasonable exposure despite the risks.
Let’s imagine Nervous Nancy, an extremely conservative investor. She wants to invest but also take the least risk possible. She invests 100% of her money in short-term cash equivalents (short-term treasuries, money markets, CDs, maybe some cash in the coffee can). With this investment allocation, she’s nearly certain to get her initial investment back and receive a modest amount of interest as a gain. However, she has no guarantees that the investment returned to her will purchase the same amount as it used to. Inflation and money printing cause each dollar to be able to purchase less and less over time. Depending on the severity of the inflation, it might not buy anything at all. In other words, she didn’t lose any dollars, but the dollar lost purchasing power.
Now, let’s salt her portfolio with bitcoin.
99% short-term treasuries. 1% bitcoin.
With a 1% allocation, if bitcoin goes to zero overnight, she’ll have only lost a penny on the dollar, and her treasury interest will quickly fill the gap. Not at all catastrophic to her financial future.
However, if the hypothetical hyperinflationary scenario from above plays out and bitcoin grows 100x in purchasing power, she’s saved everything. Metaphorically, her entire dollar house burned down, and “bitcoin insurance” made her whole. Powerful. A little bitcoin salt goes a long way.
(When protecting against the existing system, it’s important to remember that you need to get your bitcoin out of the system. Keeping bitcoin on an exchange or with a counterparty will do you no good if that entity fails. If you view bitcoin as insurance, it’s essential to keep your bitcoin in cold storage and hold your keys. Otherwise, it’s someone else’s insurance.)
When all you have a hammer, everything looks like a…

A construction joke:
There are only three rules to construction: 1.) Always use the right tool for the job! 2.) A hammer is always the right tool! 3.) Anything can be a hammer!
Yeah. That’s what I thought, too. Slightly funny and mostly useless.
But if you spend enough time swinging a hammer, you’ll eventually realize it can be more than it first appears. Not everything is a nail. A hammer can tear down walls, break concrete, tap objects into place, and wiggle other things out. A hammer can create and destroy; it builds tall towers and humbles novice fingers. The use cases expand with the skill of the carpenter.
Like hammers, bitcoin is a monetary tool. And a 1-5% allocator to the asset typically sees a “speculative insurance” use case - valid. Bitcoin is speculative insurance, but it is not only speculative insurance. People invest and save in bitcoin for many different reasons.
I’ve seen people use bitcoin to pursue all of the following use cases:
- Hedging against a financial collapse (speculative insurance)
- Saving for family and future (long-term general savings and safety net)
- Growing a downpayment for a house (medium-term specific savings)
- Shooting for the moon in a manner equivalent to winning the lottery (gambling)
- Opting out of government-run, bank-controlled financial systems (financial optionality)
- Making a quick buck (short-term trading)
- Escaping a hostile country (wealth evacuation)
- Locking away wealth that can’t be confiscated (wealth preservation)
- As a means to influence opinions and gain followers (social status)
- Fix the money and fix the world (mission and purpose)
Keep this in mind when taking other people’s financial advice. They are often playing a different game than you. They have different goals, upbringings, worldviews, family dynamics, and circumstances. Even though they might use the same hammer as you, it could be for a completely different job.
Wrapping Up
A massive allocation to bitcoin may seem crazy to some people, yet perfectly reasonable to others. The same goes for having a 1% allocation.
But, given today’s macroeconomic environment and bitcoin’s trajectory, I find very few use cases where 0% bitcoin makes sense. By not owning bitcoin, you implicitly say that you are 100% certain it will fail and go to zero. Given its 14-year history so far, I’d recommend reducing your confidence. Nobody is 100% right forever. A little salt goes a long way. Your financial plan may be riskier without bitcoin. Diversify accordingly.
“We must learn our limits. We are all something, but none of us are everything.” - Blaise Pascal.
bonds pandemic stocks bitcoin link goldContact
Office: (208)-254-0142
Ste. 205
Eagle, ID 83616
Check the background of your financial professional on FINRA's BrokerCheck.The content is developed from sources believed to be providing accurate information. The information in this material is not intended as tax or legal advice. Please consult legal or tax professionals for specific information regarding your individual situation. Some of this material was developed and produced by FMG Suite to provide information on a topic that may be of interest. FMG Suite is not affiliated with the named representative, broker - dealer, state - or SEC - registered investment advisory firm. The opinions expressed and material provided are for general information, and should not be considered a solicitation for the purchase or sale of any security.
We take protecting your data and privacy very seriously. As of January 1, 2020 the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) suggests the following link as an extra measure to safeguard your data: Do not sell my personal information.
Copyright 2024 FMG Suite.
Sound Advisory, LLC (“SA”) is a registered investment advisor offering advisory services in the State of Idaho and in other jurisdictions where exempt. Registration does not imply a certain level of skill or training. The information on this site is not intended as tax, accounting, or legal advice, as an offer or solicitation of an offer to buy or sell, or as an endorsement of any company, security, fund, or other securities or non-securities offering. This information should not be relied upon as the sole factor in an investment-making decision. Past performance is no indication of future results. Investment in securities involves significant risk and has the potential for partial or complete loss of funds invested. It should not be assumed that any recommendations made will be profitable or equal any performance noted on this site.
The information on this site is provided “AS IS” and without warranties of any kind, either express or implied. To the fullest extent permissible pursuant to applicable laws, Sound Advisory LLC disclaims all warranties, express or implied, including, but not limited to, implied warranties of merchantability, non-infringement, and suitability for a particular purpose.
SA does not warrant that the information on this site will be free from error. Your use of the information is at your sole risk. Under no circumstances shall SA be liable for any direct, indirect, special or consequential damages that result from the use of, or the inability to use, the information provided on this site, even if SA or an SA authorized representative has been advised of the possibility of such damages. Information contained on this site should not be considered a solicitation to buy, an offer to sell, or a recommendation of any security in any jurisdiction where such offer, solicitation, or recommendation would be unlawful or unauthorized.
Uncategorized
The Question You Should Ask Whenever You’re Wrong
“Never bet on the end of the world. It only comes once, which is pretty long odds.” — Arthur Cashin, New York Stock Exchange Floor Manager (“Maxims…
“Never bet on the end of the world. It only comes once, which is pretty long odds.” — Arthur Cashin, New York Stock Exchange Floor Manager (“Maxims of Wall Street,” p. 110)
Since Joe Biden gave his State of the Union (or shall we say “Disunion”) speech last week, I’ve encountered a plethora of negative comments about the future of America.
Is the American Dream Over?
“If Biden is re-elected, it will be the end of the American Dream as we know it,” said one pundit on Fox News.
The critics are out in force. Supply-side economist Steve Moore writes, “Biden is intentionally trying to dismantle the American economy with his imbecile energy, climate change, crime, border, inflation, debt and high tax policies.”
Glenn Beck, the host of Blaze TV, recently warned that America may face multiple terrorist attacks in one day, similar to 9/11, given the open borders policy of the Biden Administration.
Recently, I attended a private meeting of political leaders and pundits who thought that President Biden’s address was the most polemical, shrill and divisive talk they had ever heard.
I’ve been watching State of the Union addresses all my adult life, by both Republicans and Democrats, and in many ways they are always polemical and divisive. What was amazing to me is how “sleepy” Joe Biden performed. He must have been well rested and jacked up with some pretty incredible drugs to do as well as he did.
President Biden did say some things that were crazy, such as when he asserted that voting for former president Donald Trump is a “vote against democracy.”
Hey, wasn’t it the Democrats who want to remove Trump from the November ballot in Colorado and other states? Talk about anti-democratic! I was glad to see the Supreme Court ruled 9-0 against the Colorado decision. Let the people decide. Isn’t that what democracy is all about?
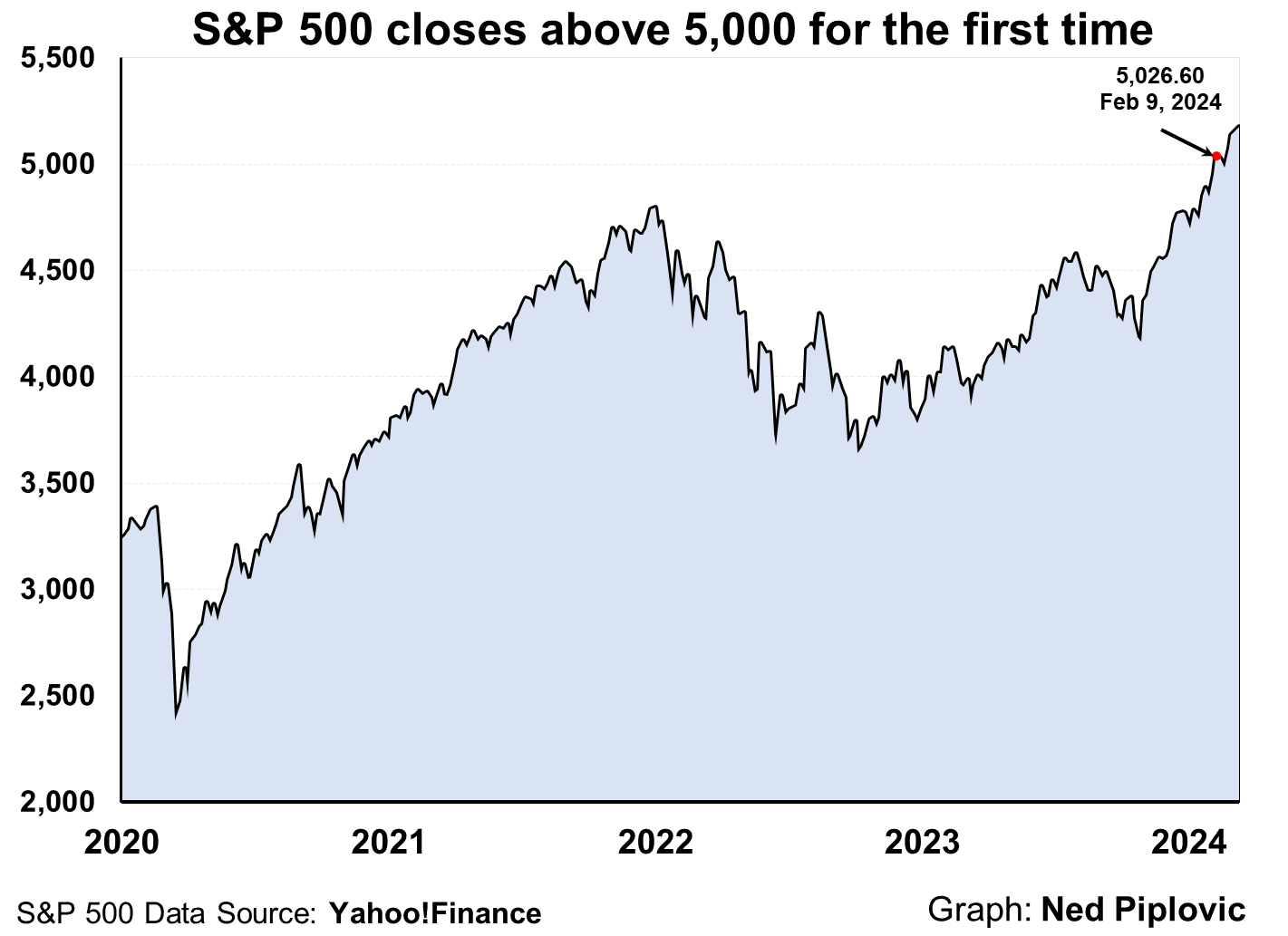
Why Then Is the Stock Market at an All-Time High?
Kevin Roberts, the new president of the Heritage Foundation, recently declared, “The American Dream is being threatened as never before!”
If that is true, why is the stock market at or near an all-time high? What are the prophets of doom and gloom missing?
That’s the question I always ask when I’m wrong about something:
“What am I missing?”
Wall Street is a good bellwether of what is going on the country. So far, the benefits outweigh the costs. The economy is recovering from the Covid pandemic, inflation is coming down, corporate profits are strong, new technologies are being introduced and there’s a strong movement to reverse the “cancel” and “woke” culture in the United States.
We have gridlock on Capitol Hill that is keeping a lot of bad legislation from becoming law. The Supreme Court has reversed many bad decisions by the lower courts.
We Remain Fully Invested
So, all is not lost after all. In my newsletter, Forecasts & Strategies, we remain fully invested, despite occasional corrections in the market.
We are also well diversified in some “contrarian” investments such as Bitcoin and gold, both of which continue to outperform and offset any selloffs in the stock market.
By remaining positive and fully invested, we have made good money in 2024.
The American Obituary Has Been Written Many Times
The American economy has been left for dead many times, only to be resuscitated with renewed vigor. We have survived civil and world wars, the Great Depression, the inflationary 1970s, terrorist attacks and more.
As J.P. Morgan once said, “The man who is a bear on the United States will eventually go broke” (“Maxims,” p. 111).
I encourage you to read my favorite J.P. Morgan story found on pp. 218-219 in “The Maxims of Wall Street.” See www.skousenbooks.com.
American exceptionalism is alive and well. We are still the Promised Land with millions wanting to live and work here.
Solving Our Unfunded Liability Problem: Look to Canada!
One serious problem in America is the irresponsible, out-of-control deficit spending and national debt, created by both Republican and Democratic leaders over the years. The trouble is getting worse, with rising interest rates to pay the debt and the growing unfunded liabilities from Social Security and Medicare.
Robert Poole of the Reason Foundation warns:
“The Congressional Budget Office (CBO)’s latest 10-year projection is frightening. CBO projects annual federal budget deficits to increase steadily, exceeding $2.5 trillion by 2034, assuming current policies continue… The federal government is projected to borrow an additional $20 trillion over the next decade, the CBO estimates.
“One driving factor is the impact of higher interest rates on the current $34 trillion (and growing) national debt… By 2034, annual interest expense is projected to be $1.6 trillion — more than one-fourth of all federal tax revenue.
“The Penn Wharton Budget Model suggests that the United States has about 20 years to fix this debt/deficit problem — ‘after which no amount of future tax increases or spending cuts could avoid the government defaulting on its debt.’
“On August 2, 2023, Fitch Ratings downgraded the federal government’s long-term debt rating from AAA to AA+. And on November 10, 2023, Moody’s Investors Service reduced its outlook on the U.S. credit rating from ‘stable’ to ‘negative.’ Standard & Poor’s did its downgrade in 2011. These are warning shots across the ship of state’s bow.”
Sounds ominous. What to do?
Canada faced a similar problem back in the mid-1990s. Deficits were getting out of hand, and the Canadian dollar was sinking. The Conservative Party and the Liberty Party of Canada worked together and resolved to cut government spending, lay off federal workers and then went on a supply-side tax-cutting program that resulted in economic growth and deficit reduction.
What about the unfunded liability problem, which causes national bankruptcy? Again, Canada offers an incredible example of solving the issue.
Last week, Andy Puzder and Terrence Keeley wrote an op-ed in The Wall Street Journal on the success of the Canadian social security system, which has earned a 9.3% annualized return over the past 10 years (versus almost zero return in our Social Security Trust Fund). They wrote:
“The Canada Pension Plan’s superiority stems from its asset allocation. The fund invests about 57% of its assets in equities and 12% in bonds; the rest is divided among real estate, infrastructure and credit. Over the past 10 years, the Canada Pension Plan has realized a 9.3% annualized net return. Similarly to how Social Security works, Canadian citizens pay into the program and are guaranteed lifetime benefits.”
At some point, the United States will need to imitate the Canadian model. Here is a chart on the difference between the two:

In sum, there are solutions to all of our problems — if we know where to look and remain optimistic.
Sound Advice from the ‘Investment Bible’
In my home, I have a whole section of my library devoted to dozens of books written by doomsayers and Cassandras, such as “The Coming Deflation”…. “How to Prosper During the Coming Bad Years”… “Bankruptcy 1995”… “The End of Inflation” and so on.
I’ve also collected a bunch of quotes on doomsayers and Cassandras in “The Maxims of Wall Street.”
Jim Woods, my colleague at Eagle Publishing, is a big fan.

Jim states, “I’ve always felt that a collection of wisdom from the best brains in that industry has been most special to me. And on this front, there is no better ‘how to’ anthology than the one by my friend, fellow Fast Money Alert co-editor and brilliant economist, Dr. Mark Skousen. The ‘Maxims of Wall Street’ is a collection of some of the greatest wisdom ever to flow from the biggest and brightest names on Wall Street. Great investors such as Jesse Livermore, Baron Rothschild, J.P. Morgan, Benjamin Graham, Warren Buffett, Peter Lynch and John Templeton are just a sneak peek at some of the names you’ll discover in this fantastic collection. Then, there is profundity from the likes of Ben Franklin, John D. Rockefeller, Joe Kennedy, Bernard Baruch, John Maynard Keynes, Steve Forbes and numerous other luminaries too copious to mention.”
If you don’t have an autographed copy of my collection of quotes, stories and wisdom of the world’s top traders and investors, please order a copy now.
It is in its 10th edition, having sold nearly 50,000 copies. It has been endorsed by Warren Buffett, Kevin O’Leary, Jack Bogle, Kim Githler, Bert Dohmen, Richard Band and Gene Epstein in Barron’s.
I offer it cheaply to my Skousen CAFÉ readers: Only $21 for the first copy, and all additional copies are $11 each (they make a great gift to clients, friends, relatives and your favorite broker or money manager). I sign and number each one, then mail it at no extra charge if you live in the United States. If you order an entire box (32 copies), the price is only $327. As Hetty Green, the first female millionaire, once said, “When I see a good thing going cheap, I buy a lot of it!”
To order, go to www.skousenbooks.com.
You Nailed it!
Friedrich Hayek Won the Nobel Prize 50 Years Ago
“Mises and Hayek articulated and vastly enriched the principles of Adam Smith at a crucial time in this century.” — Vernon Smith (2002 Nobel prize in economics)
March 23 is the anniversary of the passing of a giant in economics — the Austrian economist Friedrich Hayek (1899-1992).
He is most famous for his bestselling book “The Road to Serfdom,” written near the end of World War II, an admittedly a pessimistic book, warning the West that its move toward socialism, fascism and communism was indeed a “road to serfdom.”
Then, when he won the Nobel prize in economics in 1974, he warned again of the dangers of “accelerating inflation,” which he said, were “brought about by policies which the majority of economists recommended and even urged governments to pursue. We have indeed at the moment little cause for pride: as a profession we have made a mess of things.”
Fortunately, we have moved away from the road to serfdom, especially after the collapse of the Berlin Wall and the Soviet socialist central planning model.
But the road to freedom has been a checkered one, and we must always be alert to losing our liberties in the name of inequality, fairness and social justice.
Last month, Tom Woods interviewed me in honor of the 50th anniversary of Hayek’s winning the Nobel prize. Watch the interview here.

Mark Skousen, Friedrich Hayek and Gary North in Austria, 1985
I had the pleasure of interviewing Hayek for three hours in the Austrian alps in 1985. He was especially happy to hear I resurrected his macroeconomic model in developing gross output (GO). See www.grossoutput.com, a measure of Hayek’s triangles.
This week, Larry Reed, former president of the Foundation for Economic Education, wrote this wonderful tribute to Hayek.
Highly recommended.
Good investing, AEIOU,
Mark Skousen
The post The Question You Should Ask Whenever You’re Wrong appeared first on Stock Investor.
bonds pandemic equities bitcoin real estate canadian dollar gold-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International6 days ago
International6 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International6 days ago
International6 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges





























