PHILADELPHIA – After two years of considerable improvement, Americans’ knowledge of some basic facts about their government has fallen to earlier levels, with less than half of those surveyed able to name the three branches of government for the 2022 Annenberg Constitution Day Civics Survey.
The Annenberg Public Policy Center’s annual, nationally representative survey showed notable increases in 2020 and 2021 after tumultuous years that put the role of government and the three branches under a media spotlight. In those two years, the survey was run amid a pandemic and government health restrictions, two impeachment inquiries, a presidential election, an attempt to disrupt congressional certification of the electoral vote, criminal trials of the individuals charged in the assault on the U.S. Capitol, and waves of social justice protests, among other events.
The current survey, released for Constitution Day (Sept. 17), found the first drop in six years among those who could identify all three branches of government, and declines among those who could name the First Amendment rights, though knowledge remained high on some other questions. Additional findings on the Supreme Court will be released next month.
“When it comes to civics, knowledge is power,” said Kathleen Hall Jamieson, director of the Annenberg Public Policy Center of the University of Pennsylvania. “It’s troubling that so few know what rights we’re guaranteed by the First Amendment. We are unlikely to cherish, protect, and exercise rights if we don’t know that we have them.”
Highlights
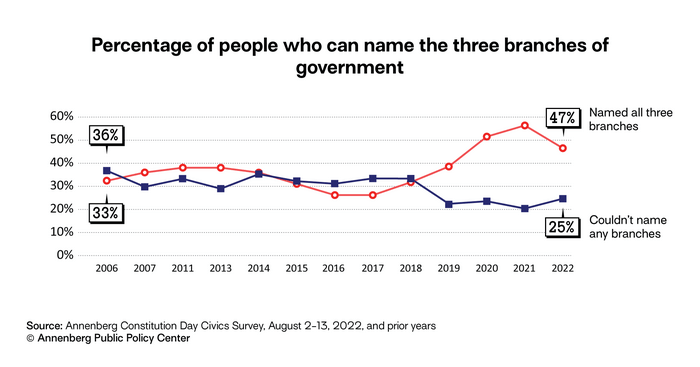
- Less than half of U.S. adults (47%) could name all three branches of government, down from 56% in 2021 and the first decline on this question since 2016.
- The number of respondents who could, unprompted, name each of the five freedoms guaranteed by the First Amendment also declined, sharply in some cases. For example, less than 1 in 4 people (24%) could name freedom of religion, down from 56% in 2021.
- Over half of Americans (51%) continue to assert incorrectly that Facebook is required to let all Americans express themselves freely on its platform under the First Amendment.
- But large numbers recognize other rights in the Bill of Rights and the veto process.
The Annenberg Constitution Day Civics Survey is a nationally representative survey conducted annually in advance of Constitution Day by the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania. This year’s survey of 1,113 U.S. adults was conducted by phone for APPC by independent research company SSRS on August 2-13, 2022. It has a margin of error of ± 3.6 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. The year-to-year changes reported here are statistically significant unless noted otherwise. For the questions and additional data, see the appendix and the methodology statement.
The three branches and how government works
The three branches: The survey found a significant drop in the percentage of respondents who named all three branches of government – executive, legislative, and judicial. This year, 47% named all three, down from 56% in 2021. One in 4 people (25%) could not name any, up from 20% in 2021.
The constitutionality of an act by the president: Asked who has final responsibility for determining whether an act by the president is constitutional if the president and the Supreme Court disagree – the president, Congress, or the court – less than half of Americans (46%) correctly said the Supreme Court, statistically unchanged from 2020 and 2021 (51%) but down significantly from 2019 (61%).
A 5-4 ruling: Asked what it means when the Supreme Court rules 5-4 in a case, just over half (55%) correctly chose “the decision is the law and needs to be followed,” down significantly from 61% in 2021. Others surveyed incorrectly said “the decision is sent back to Congress for reconsideration” (16%), “the decision is sent back to the federal court of appeals to be decided there” (16%), or they don’t know (13%).
Decline in knowing First Amendment rights
The First Amendment: When asked unprompted to name the protections specified in the First Amendment, the number of respondents who could identify them declined, at times steeply:
- Freedom of speech was cited by 63%, down from 74% in 2021 and 73% in 2020.
- Freedom of religion was named by 24%, down from 56% in 2021 and 47% in 2020.
- Freedom of the press was named by 20%, down from 50% in 2021 and 42% in 2020.
- Right of assembly was named by 16%, down from 30% in 2021 and 34% in 2020.
- Right to petition the government was named by 6%, down from 20% in 2021 and 14% in 2020.
One in 4 respondents (26%) said they can’t name any or don’t know, compared with 17% in 2021 and 19% in 2020.
The number of individuals who incorrectly named the right to bear arms – which is guaranteed under the Second Amendment, not the First – tripled to 9% from 3% in 2020 and 2021. In June, gun rights were in the news when the Supreme Court ruled to expand the right to carry guns in public places and when Congress passed gun safety legislation.
A large majority knows there is a personal right to own a gun: 82% say it is accurate to state that the Supreme Court has held that a citizen has a constitutional right to own a handgun (unchanged statistically from 83% in 2019).
Half think ‘freedom of speech’ applies to Facebook
Facebook and the First Amendment: Over half of those surveyed (51%, compared with 61% in 2021) incorrectly believe it’s accurate to state that the First Amendment’s protection of freedom of speech means that Facebook must permit all Americans to freely express themselves on Facebook pages. The First Amendment protects citizens from government censorship, but social media companies such as Facebook are private companies and courts have ruled private entities are not covered by it.
- What’s behind this: Nearly two-thirds of self-described conservatives (63%) think Facebook posts are covered by the First Amendment – as do half of self-described moderates (50%) and a smaller group of self-described liberals (41%).
Some civics knowledge indicators at high levels
The 2022 survey found that a strong majority knows the correct answer to some questions:
- Search and seizure: 78% know it is accurate to say that protection from “unreasonable searches and seizures” is guaranteed in the Bill of Rights.
- Religion: 76% know that under the Constitution, Congress cannot establish an official religion of the United States (statistically unchanged from 77% in 2016). And 88% know it is accurate to say that under the Constitution, U.S. citizens who are atheists have the same rights as other citizens (up from 79% in 2017).
- Overriding a veto: 76% know that under the Constitution, when the president vetoes legislation, the bill will become law if two-thirds of the members in each house of Congress vote to override the president (statistically unchanged from 73% in 2018).
And most can identify certain inaccurate claims, though substantial numbers are unsure:
- The president and the court: Most (73%) know it is inaccurate to say that under the Constitution a president can ignore a Supreme Court ruling if the president believes it is wrong (up from 65% in 2018), though 1 in 5 (22%) incorrectly thinks that is accurate.
- Testifying at trial: Most know that a judge cannot force a defendant to testify at trial: 63% know it is inaccurate to say that the Constitution allows a judge to insist that a defendant testify at his own trial (the same as in 2019), though nearly 1 in 3 people (32%) incorrectly thinks that a judge has that prerogative.
- Undocumented immigrants: Most respondents know that undocumented immigrants in the United States have some rights under the Constitution: 57% know it’s inaccurate to say that those who are in the United States illegally “do not have any rights” under the Constitution. But 40% think incorrectly that this is true. This has shifted in a positive direction since 2017, when the responses were nearly reversed (40% correctly knew it was inaccurate but 53% incorrectly said it was accurate). Those rights include education: The equal protection clause of the 14th Amendment has been applied by courts to say that undocumented children cannot be denied an education.
Civics education associated with knowledge
An APPC analysis found that taking a high school civics class continues to be associated with correct answers to civics knowledge questions, including knowledge of the three branches; knowledge of First Amendment rights; the meaning of a 5-4 Supreme Court decision; the Supreme Court having the final say on the constitutionality of a president’s actions; and knowing that Facebook is not covered by the First Amendment.
In 2022, nearly two-thirds (65%) of respondents with at least some high school education said they had taken a civics course in high school that focused on the Constitution or judicial system, about the same as in previous years we have asked this question. More than a third of those with at least some college education (36%) said they had taken a college course that focused on the U.S. system of government and the Constitution, significantly fewer than in 2021 but about the same as in 2019 (38%).
Constitution Day
The Annenberg Civics Knowledge Survey is released by APPC for Constitution Day, which celebrates the signing of the Constitution on Sept. 17, 1787. APPC’s activities to enhance civics education include Annenberg Classroom, which offers free resources for teaching the Constitution, and the Civics Renewal Network, a coalition of 39 nonpartisan, nonprofit organizations seeking to improve civics education by providing free, high-quality resources for teachers. Among those resources: CRN’s Constitution Day Toolkit for teachers and an Annenberg Classroom film on the First Amendment and student freedom of speech, one in a series of award-winning videos.
The Annenberg Public Policy Center was established in 1993 to educate the public and policy makers about communication’s role in advancing public understanding of political, science, and health issues at the local, state, and federal levels.
Method of Research
Survey