Why Increasing U.S. Dollar Strength Is A Risk For Bitcoin Price
Historical correlation between the U.S. dollar and bitcoin price indicates that current strengthening of the former could threaten the latter.
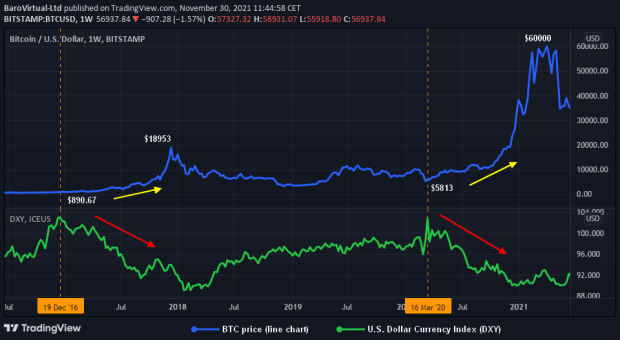
Historical correlation between the U.S. dollar and bitcoin price indicates that current strengthening of the former could threaten the latter.
For probably about two years now, it has been generally accepted in the cryptocurrency community that “BTC is an independent asset class,” which demonstrates that the first cryptocurrency performs well as an investment tool that hardly correlates with the economic cycle and is not even associated with other asset classes. On August 18, 2020, CoinShares even released a whole report on this, which mainly talked about the lack of correlation between bitcoin and commodities and traditional stocks.
But what about the correlation with the U.S. Dollar Currency Index (DXY)? Max Keiser was one of the first to draw our attention to bitcoin’s negative correlation with the U.S. dollar. In other words, when the U.S. dollar rises, then, as a rule, BTC tends to fall. I’ll also add that there is rarely a positive correlation between BTC and the U.S. dollar.
Still, if there is a positive correlation, it carries medium- and long-term risks for a stable upward trend in bitcoin.
Examples Of Negative Correlation Between BTC And DXY
In the chart above, we can see that the downtrend in the U.S. dollar, which began on December 19, 2016, at $103.10, led to a sharp rise in the price of BTC from $890 to $18,953, while the U.S. dollar fell to $89 by January 22, 2018. A similar situation was observed on March 16, 2020, when the U.S. dollar entered a brutal downtrend due to the U.S. financial government institutions’ not-entirely-rational monetary policy.
These two examples perfectly demonstrate the classic inverse correlation approach between bitcoin and the U.S. dollar. These are not the only examples of this statement; you can easily find other earlier examples through a trading charts provider.
Examples Of Positive Correlation Between BTC And DXY

As you can see from the chart above, a positive correlation leads to at least uncertainty and at most wild turbulence, including significant bearish corrections.
In the long term, the perceptible strengthening of the U.S. dollar between January 22, 2018, and March 16, 2020, had a very negative impact on the state of bitcoin. Actually, it seems that the periods marked on the chart were probably some of the worst milestones in bitcoin history, comparable to the first “crypto winter” of 2013 to 2015, as retail investors suffered colossal losses in the first place, just like other groups of traders.
Now, understanding from historical examples that the correlation between bitcoin and DXY exists, it is clear that this correlation really should be seriously monitored. Let’s move on to the factors behind the current strengthening of the U.S. dollar, which carries medium- and long-term risks to the outlook of bitcoin’s price cycle.
The Current State Of Bitcoin And DXY
First, let’s look at the technical picture of the correlation of the considered assets and determine what type of correlation is observed right now.

The chart above shows the second positive correlation between the U.S. dollar and bitcoin this year, which carries many risks for bitcoin.
From May 25 of this year, the U.S. dollar began a steady upward trend within the framework of a kind of accumulated consolidation from November 6, 2020, to September 3, 2021. Within the framework of this consolidation, there was also the first local positive correlation, which led to the collapse of bitcoin to the general negative signs of an impending correction on April 14, 2021. Also, the U.S. dollar has successfully overcome the resistance at $94.895 and has successfully consolidated above it, i.e., the DXY is still bullish.
Three key factors support the bullishness of the U.S. dollar, but with the potential to harm bitcoin for the foreseeable future:
1. Bullish formation on the DXY weekly chart:

The successful implementation of this pattern can bring very unpleasant surprises to bitcoin, as professional investors will weaken their positions in all risky assets, of course, which is also BTC. A successful breakout of the $100 mark will lead to a more severe reduction in long positions in bitcoin and its derivatives, including traditional stocks tools on BTC.
2. The number of transactions of foreign participants with the U.S. dollar:

Daily repurchase agreements (REPOs) for non-residents (brown line) has an upward trend, suggesting that the U.S. dollar is still demanded. I think that this is the main factor supporting the bullish sentiment of the U.S. dollar right now.
3. The state of dollar liquidity in the international market:

The TED spread reflects the demand for dollar liquidity in the global market in London, U.K. (LIBOR).
As you can see in the local size, starting from October 15, 2021, this indicator is growing, which indicates a steady demand for the dollar from foreign players, who are now profitable in maintaining the strengthening of the U.S. dollar. This mood prevails among foreign participants, including because the Federal Reserve, following a meeting on November 3, 2021, reduced the quantitative easing (QE) program, which, among other things, harms bitcoin in the medium- and long-term perspective.
I would also like to draw your attention to the fact that a new strain of COVID-19 may disrupt the Fed’s plans to slow down the “printing press.” Since a specific part of the growth of the U.S. dollar was based, among other things, on the expectations that the Fed will accelerate the pace of the stimulus program winding down, such negative news may cause particular uncertainty to form.
To summarize, it should be said that I wouldn’t want you to get the impression that the method we reviewed works 100% and without failures. I want to convey to the community that the historical data of a particular asset and the methods for comparing them is still of great value. In this regard, we have to monitor the correlation between bitcoin and the U.S. dollar, since this allows us to build a kind of defensive response system to protect our investment (trading) positions.
This is a guest post by Virtual Baro. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.
stocks covid-19 cryptocurrency bitcoin crypto btc crypto commoditiesSpread & Containment
There Goes The Fed’s Inflation Target: Goldman Sees Terminal Rate 100bps Higher At 3.5%
There Goes The Fed’s Inflation Target: Goldman Sees Terminal Rate 100bps Higher At 3.5%
Two years ago, we first said that it’s only a matter…
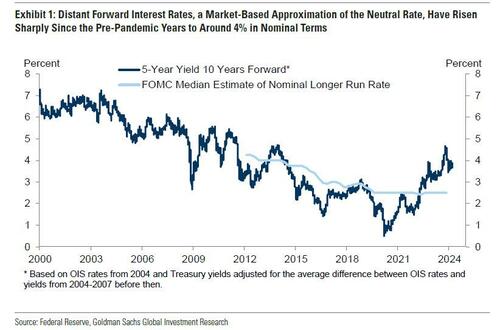
Two years ago, we first said that it's only a matter of time before the Fed admits it is unable to rsolve the so-called "last mile" of inflation and that as a result, the old inflation target of 2% is no longer viable.
At some point Fed will concede it has no control over supply. That's when we will start getting leaks of raising the inflation target
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) June 21, 2022
Then one year ago, we correctly said that while everyone was paying attention elsewhere, the inflation target had already been hiked to 2.8%... on the way to even more increases.
The new inflation target has been set to 2.8%. The rest is just narrative fill for the next 2 years. https://t.co/X1xYkecyPy
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) February 21, 2023
And while the Fed still pretends it can one day lower inflation to 2% even as it prepares to cut rates as soon as June, moments ago Goldman published a note from its economics team which had to balls to finally call a spade a spade, and concluded that - as party of the Fed's next big debate, i.e., rethinking the Neutral rate - both the neutral and terminal rate, a polite euphemism for the inflation target, are much higher than conventional wisdom believes, and that as a result Goldman is "penciling in a terminal rate of 3.25-3.5% this cycle, 100bp above the peak reached last cycle."
There is more in the full Goldman note, but below we excerpt the key fragments:
We argued last cycle that the long-run neutral rate was not as low as widely thought, perhaps closer to 3-3.5% in nominal terms than to 2-2.5%. We have also argued this cycle that the short-run neutral rate could be higher still because the fiscal deficit is much larger than usual—in fact, estimates of the elasticity of the neutral rate to the deficit suggest that the wider deficit might boost the short-term neutral rate by 1-1.5%. Fed economists have also offered another reason why the short-term neutral rate might be elevated, namely that broad financial conditions have not tightened commensurately with the rise in the funds rate, limiting transmission to the economy.
Over the coming year, Fed officials are likely to debate whether the neutral rate is still as low as they assumed last cycle and as the dot plot implies....
...Translation: raising the neutral rate estimate is also the first step to admitting that the traditional 2% inflation target is higher than previously expected. And once the Fed officially crosses that particular Rubicon, all bets are off.
... Their thinking is likely to be influenced by distant forward market rates, which have risen 1-2pp since the pre-pandemic years to about 4%; by model-based estimates of neutral, whose earlier real-time values have been revised up by roughly 0.5pp on average to about 3.5% nominal and whose latest values are little changed; and by their perception of how well the economy is performing at the current level of the funds rate.
The bank's conclusion:
We expect Fed officials to raise their estimates of neutral over time both by raising their long-run neutral rate dots somewhat and by concluding that short-run neutral is currently higher than long-run neutral. While we are fairly confident that Fed officials will not be comfortable leaving the funds rate above 5% indefinitely once inflation approaches 2% and that they will not go all the way back to 2.5% purely in the name of normalization, we are quite uncertain about where in between they will ultimately land.
Because the economy is not sensitive enough to small changes in the funds rate to make it glaringly obvious when neutral has been reached, the terminal or equilibrium rate where the FOMC decides to leave the funds rate is partly a matter of the true neutral rate and partly a matter of the perceived neutral rate. For now, we are penciling in a terminal rate of 3.25-3.5% this cycle, 100bps above the peak reached last cycle. This reflects both our view that neutral is higher than Fed officials think and our expectation that their thinking will evolve.
Not that this should come as a surprise: as a reminder, with the US now $35.5 trillion in debt and rising by $1 trillion every 100 days, we are fast approaching the Minsky Moment, which means the US has just a handful of options left: losing the reserve currency status, QEing the deficit and every new dollar in debt, or - the only viable alternative - inflating it all away. The only question we had before is when do "serious" economists make the same admission.
Meanwhile, nothing changes: total US debt jumps $57BN on March 15, to a record $34.543 trillion.
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) March 19, 2024
Three ways this ends: inflate it away, QE it all, or reserve status collapse
They now have.
And while we have discussed the staggering consequences of raising the inflation target by just 1% from 2% to 3% on everything from markets, to economic growth (instead of doubling every 35 years at 2% inflation target, prices would double every 23 years at 3%), and social cohesion, we will soon rerun the analysis again as the implications are profound. For now all you need to know is that with the US about to implicitly hit the overdrive of dollar devaluation, anything that is non-fiat will be much more preferable over fiat alternatives.
Much more in the full Goldman note available to pro subs in the usual place.
Spread & Containment
Household Net Interest Income Falls As Rates Spike
A Bloomberg article from this morning offered an excellent array of charts detailing the shifts in interest payment flows amid rising rates. The historical…
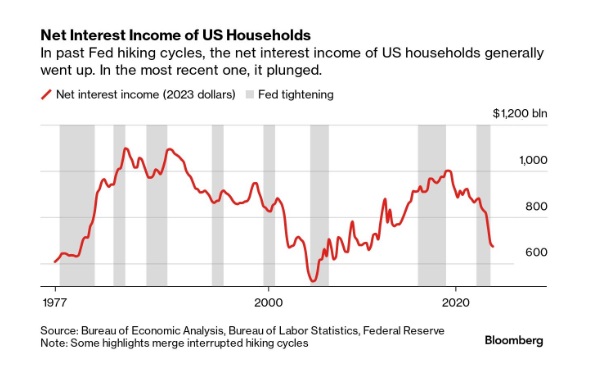
A Bloomberg article from this morning offered an excellent array of charts detailing the shifts in interest payment flows amid rising rates. The historical anomaly was both surprising and contradicted our priors.
10 Key Points:
- Historical Anomaly: This is the first time in the last fifty years that a Federal Reserve rate hike cycle has led to a significant drop in household net interest income.
- Interest Expense Increase: Since the Fed began raising rates in March 2022, Americans’ annual interest expenses on debts like mortgages and credit cards have surged by nearly $420 billion.
- Interest Income Lag: The increase in interest income during the same period was only about $280 billion, resulting in a net decline in household interest income, a departure from past trends.
- Consumer Debt Influence: The recent rate hikes impacted household finances more because of a higher proportion of consumer credit, which adjusts more quickly to rate changes, increasing interest costs.
- Banks and Savers: Banks have been slow to pass on higher interest rates to depositors, and the prolonged period of low rates before 2022 may have discouraged savers from actively seeking better returns.
- Shift in Wealth: There’s been a shift from interest-bearing assets to stocks, with dividends surpassing interest payments as a source of unearned income during the pandemic.
- Distributional Discrepancy: Higher interest rates benefit wealthier individuals who own interest-earning assets, whereas lower-income earners face the brunt of increased debt servicing costs, exacerbating economic inequality.
- Job Market Impact: Typically, Fed rate hikes affect households through the job market, as businesses cut costs, potentially leading to layoffs or wage suppression, though this hasn’t occurred yet in the current cycle.
- Economic Impact: The distribution of interest income and debt servicing means that rate increases transfer money from those more likely to spend (and thus stimulate the economy) to those less likely to increase consumption, potentially dampening economic activity.
- No Immediate Relief: Expectations for the Fed to reduce rates have diminished, indicating that high-interest expenses for households may persist.



Uncategorized
One more airline cracks down on lounge crowding in a way you won’t like
Qantas Airways is increasing the price of accessing its network of lounges by as much as 17%.

Over the last two years, multiple airlines have dealt with crowding in their lounges. While they are designed as a luxury experience for a small subset of travelers, high numbers of people taking a trip post-pandemic as well as the different ways they are able to gain access through status or certain credit cards made it difficult for some airlines to keep up with keeping foods stocked, common areas clean and having enough staff to serve bar drinks at the rate that customers expect them.
In the fall of 2023, Delta Air Lines (DAL) caught serious traveler outcry after announcing that it was cracking down on crowding by raising how much one needs to spend for lounge access and limiting the number of times one can enter those lounges.
Related: Competitors pushed Delta to backtrack on its lounge and loyalty program changes
Some airlines saw the outcry with Delta as their chance to reassure customers that they would not raise their fees while others waited for the storm to pass to quietly implement their own increases.
Shutterstock
This is how much more you'll have to pay for Qantas lounge access
Australia's flagship carrier Qantas Airways (QUBSF) is the latest airline to announce that it would raise the cost accessing the 24 lounges across the country as well as the 600 international lounges available at airports across the world through partner airlines.
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
Unlike other airlines which grant access primarily after reaching frequent flyer status, Qantas also sells it through a membership — starting from April 18, 2024, prices will rise from $600 Australian dollars ($392 USD) to $699 AUD ($456 USD) for one year, $1,100 ($718 USD) to $1,299 ($848 USD) for two years and $2,000 AUD ($1,304) to lock in the rate for four years.
Those signing up for lounge access for the first time also currently pay a joining fee of $99 AUD ($65 USD) that will rise to $129 AUD ($85 USD).
The airline also allows customers to purchase their membership with Qantas Points they collect through frequent travel; the membership fees are also being raised by the equivalent amount in points in what adds up to as much as 17% — from 308,000 to 399,900 to lock in access for four years.
Airline says hikes will 'cover cost increases passed on from suppliers'
"This is the first time the Qantas Club membership fees have increased in seven years and will help cover cost increases passed on from a range of suppliers over that time," a Qantas spokesperson confirmed to Simple Flying. "This follows a reduction in the membership fees for several years during the pandemic."
The spokesperson said the gains from the increases will go both towards making up for inflation-related costs and keeping existing lounges looking modern by updating features like furniture and décor.
While the price increases also do not apply for those who earned lounge access through frequent flyer status or change what it takes to earn that status, Qantas is also introducing even steeper increases for those renewing a membership or adding additional features such as spouse and partner memberships.
In some cases, the cost of these features will nearly double from what members are paying now.
stocks pandemic-

 Spread & Containment6 days ago
Spread & Containment6 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex





















