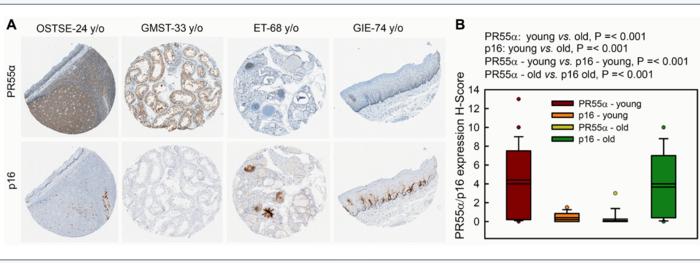
A team of researchers from UCLA has unveiled a first-of-its-kind stable and fully solid-state thermal transistor that uses an electric field to control a semiconductor device’s heat movement.
The group’s study, which will be published in the Nov. 3 issue of Science, details how the device works and its potential applications. With top speed and performance, the transistor could open new frontiers in heat management of computer chips through an atomic-level design and molecular engineering. The advance could also further the understanding of how heat is regulated in the human body.
“The precision control of how heat flows through materials has been a long-held but elusive dream for physicists and engineers,” said the study’s co-author Yongjie Hu, a professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering.” This new design principle takes a big leap toward that, as it manages the heat movement with the on-off switching of an electric field, just like how it has been done with electrical transistors for decades.”
Electrical transistors are the foundational building blocks of modern information technology. They were first developed by Bell Labs in the 1940s and have three terminals — a gate, a source and a sink. When an electrical field is applied through the gate, it regulates how electricity (in the form of electrons) moves through the chip. These semiconductor devices can amplify or switch electrical signals and power. But as they continue to shrink in size over the years, billions of transistors can fit on one chip, resulting in more heat generated from the movement of electrons, which affects chip performance. Conventional heat sinks passively draw heat away from hotspots, but it has remained a challenge to find a more dynamic control to actively regulate heat.
While there have been efforts in tuning thermal conductivity, their performances have suffered due to reliance on moving parts, ionic motions, or liquid solution components. This has resulted in slow switching speeds for heat movement on the order of minutes or far slower, creating issues in performance reliability as well as incompatibility with semiconductor manufacturing.
The new thermal transistor, which boasts a field effect (the modulation of the thermal conductivity of a material by the application of an external electric field) and a full solid state (no moving parts), offers high performance and compatibility with integrated circuits in semiconductor manufacturing processes. The team’s design incorporates the field effect on charge dynamics at an atomic interface to allow high performance using a negligible power to switch and amplify a heat flux continuously.
The UCLA team demonstrated electrically gated thermal transistors that achieved record-high performance with switching speed of more than 1 megahertz, or 1 million cycles per second. They also offered a 1,300% tunability in thermal conductance and reliable performance for more than 1 million switching cycles.
“This work is the result of a terrific collaboration in which we are able to leverage our detailed understanding of molecules and interfaces to make a major step forward in the control of important materials properties with the potential for real-world impact,” said co-author Paul Weiss, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry. “We have been able to improve both the speed and size of the thermal switching effect by orders of magnitude over what was previously possible.”
In the team’s proof-of-concept design, a self-assembled molecular interface is fabricated and acts as a conduit for heat movement. Switching an electrical field on and off through a third-terminal gate controls the thermal resistance across the atomic interfaces and thereby allowing heat to move through the material with precision.
The researchers validated the transistor’s performance with spectroscopy experiments and conducted first-principles theory computations that accounted for the field effects on the characteristics of atoms and molecules.
The study presents a scalable technology innovation for sustainable energy in chip manufacturing and performance. Hu suggested the concept also offers a new way to understand heat management in the human body.
“At the very fundamental level, the platform could provide insights for the molecular-level mechanisms for living cells,” Hu added.
Other authors on the paper — all from UCLA — include Man Li, Huan Wu, Erin Avery, Zihao Qin, Dominic Goronzy, Huu Duy Nguyen and Tianhan Liu. Hu and Weiss are also affiliated with the California NanoSystems Institute, as well as UCLA Samueli’s departments of Bioengineering and Materials Science and Engineering.
The research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation and the National Science Foundation. Technical support was provided by the UCLA Nanolab and the California NanoSystems Institute at UCLA. Computational resources were provided by the UCLA Institute for Digital Research and Education and by Advanced Cyberinfrastructure Coordination Ecosystem: Services & Support.
Journal
Science
DOI
10.1126/science.abo4297
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Electrically gated molecular thermal switch
Article Publication Date
3-Nov-2023
COI Statement
The authors declare no competing interests.