Uncategorized
The Subtle Art of Orange Pilling
Every Bitcoin user has very different reasons for using Bitcoin in the first place. That is something that everyone should consider when trying to orange…

Throughout the years, I have presented the case for Bitcoin to a lot of people from a wide range of backgrounds. The list includes curious cab drivers, financial advisors, young software developers, skeptical policymakers, voiceless activists, and once even an IMF employee.
Needless to say, most of these attempts ended up falling on deaf ears. So I started asking myself “why would this person in front of me care about Bitcoin?” and immediately realized that getting a response was particularly challenging because—even among Bitcoiners—there is no common understanding of what Bitcoin is in the first place. Is it “peer-to-peer electronic cash” as Satoshi originally defined it? Or should we consider it as “digital property” as Michael Saylor suggests? Or maybe listen to Gary Gensler and define it as a commodity?
As tempting as it is to look for a common definition for Bitcoin, doing so during a time when even the most simple linguistic choices are under scrutiny makes such a venture uninspiring and, frankly, pointless.
What I decided to do instead was understand what each of those people really cared about and how Bitcoin could fit into their view of the world rather than expecting them to understand a subject they are barely interested in. As the saying goes, “If the mountain will not come to Mohammed, Mohammed must go to the mountain.”
By doing so, I realized it was unreasonable to act like Morpheus and expect my interlocutors to take a big orange pill. After all, if that approach barely worked with Neo who was “the chosen one”, why would it work with my brother-in-law or with a stranger sitting next to me on the plane?
Because I’ve known for a while that Bitcoin’s nature is multifaceted, the very idea of one single entry point to a multifaceted concept did not sound right. Depending on where one lives, social status, professional background, set of beliefs, values, and environment, there will be a different (and smaller) orange pill that will be more appropriate for each person.
More categories may emerge in the future (Jason Lowery, for example, proposes a military interpretation of Bitcoin and the recent ordinals frenzy reminded us how valuable Bitcoin’s block space can be as its own use-case), but here are the four main buckets that I have identified so far—which represent four different set of problems that Bitcoin is solving for.
1 - Hard Money
In this sense, it’s more typical of a precious metal. Instead of the supply changing to keep the value the same, the supply is predetermined and the value changes —Satoshi Nakamoto
The first sets of problems that Bitcoin attempts to solve originate from a financial system that is broken in its most foundational aspects. For those not understanding, the problem can be described as having a similar nature (but, of course, different magnitude) to hyperinflation in Weimar Republic and Venezuela. The constant debasement of currencies (even the “mild” 2% inflation we all know about) has a tremendous societal impact, with those who are “close to the money printer” being the only winners—a phenomenon also known as the Cantillon Effect.
Unlike fiat money and commodities, such as gold, Bitcoin’s total supply is capped, which makes it the most scarce store of value in the history of mankind and, therefore, an ideal store of value in the long term.
For all those living in the half of the world that is experiencing double-digit inflation, this is a particularly interesting moment to understand how money printing and currency debasement can affect so many aspects of their lives. In fact, people who have lived through the 70s and those living in countries such as Venezuela, Lebanon, Zimbabwe, Argentina, and Turkey will be more receptive to the idea of Bitcoin as a way to preserve their purchasing power in inflationary environments.
This is arguably one of the most difficult aspects of Bitcoin to understand given the number of assumptions it requires us to challenge (e.g. “controlled inflation is good for the economy” or “fiat currencies are stable”). Yet, it’s arguably the most powerful orange pill that one could take.
2 - Superior Payment Network
Humans have invented the best financial tool in our history, and it’s an exciting time to be alive and use it — Jack Mallers
For the first time in human history, money and a payment network are integrated into one open and global system. Not only can Bitcoin serve as a store of value in the long term as explained above, but it also functions as a global medium of exchange that does not require any third party.
In a few seconds, money can be sent anywhere in the world by only paying a fraction of a cent. Compared to bank transfers, credit cards, and remittances, sending money through Bitcoin is significantly cheaper and faster.
People who don’t like bitcoin as a store of value can just use it as a payment system by converting it to the local currency at the two ends of the transaction. Why do that instead of using legacy systems? Perhaps to quickly send money during earthquakes and wars. Or to bypass remittance companies that take weeks to transfer money and charge up to 10% in fees.
The potential of Bitcoin just as a payment network extends to the most unthinkable areas. Micropayments have the potential to boost the creator economy and or solve the problems that have been haunting social networks.
3 - Freedom Technology
It would be a dark, dark world if Bitcoin didn't exist — Alex Gladstein
The two previous perspectives address the common criticism that “Bitcoin is useless”. But another common criticism—often paired with the former even though it directly contradicts it—is the fact that (just like cars, computers, and most technologies) Bitcoin is used by criminals.
As crazy as it might sound to many, that’s a feature, not a bug. Because in those instances where it’s ethnicity, religion, sex, or political views that determine whether one is a criminal, having a financial system that cannot be weaponized by the government is one of the best insurance policies you can wish for. That is particularly true for two-thirds of the global population that lives in backsliding democracies or autocratic regimes.
Those who care about freedom and human rights should be paying very close attention to this technology. Bitcoin has already provided lifeline support for individuals in need for over a decade. Wikileaks would have not been able to expose serious violations of human rights and civil liberties without Bitcoin. Similarly, many in North Korea, Iran, Afghanistan, Ukraine, Hong Kong, Belarus, Nigeria, and Russia also use Bitcoin as a tool to escape the control and government censorship.
As we move away from physical money and the potential for financial surveillance and censorship increases exponentially, the world will greatly benefit an additional set of checks and balances to limit the power of governments and corporations. Understanding this is very important for all those that are active in promoting individual freedom and human rights in the most authoritarian corners of the world.
4 - Energy Buyer Of Last Resort
It is a win-win-win for everybody. It's a win for the environment and an inarguable win for the economy — Dennis Porter
Lastly, there is a relatively small crowd of people who might be able to appreciate Bitcoin for a very different set of reasons. Bitcoin constitutes an unprecedented opportunity to build a cleaner, more resilient, and more efficient energy infrastructure. Bitcoin can mitigate the problem of intermittency—the demand/supply mismatch that occurs with renewable energy—and help with the $13B problem of congestion of the electric grid in rural areas.
Bitcoin miners can strengthen these grids and incentivize the deployment of more renewable energy by adapting to the fluctuations of power generation schedules since their rigs can be turned off at any moment without notice. Commonly referred to as “energy buyers of last resort”, Bitcoin miners are perfect for Demand Response programs. Last year, Bitcoin miners in Texas “returned up to 1,500 megawatts to the grid, enough to heat over 1.5 million small homes or keep 300 large hospitals fully operational”.
Bitcoin miners are also finding very creative ways to utilize energy that was previously wasted and many are arguing that Bitcoin is “the only available, practical and scalable technology when it comes to tackling the world’s most deadly greenhouse gas: methane.”
There’s (at least) four orange pills, and people don’t need to take them all.

One of the things I learned during my Bitcoin journey is that this is not a mono-functional technology like a washing-machine or an elevator. Because Bitcoin solves many different problems, its perceived value and utility will change significantly depending on who you talk to.
Those living in South Carolina might not care about censorship resistance or privacy as much as the local jobs that are created by a new Bitcoin company. The Turkish population might have not cared about Bitcoin as an inflation hedge (given the country’s situation, it should) during the earthquake earlier this year, but just needed a way to receive money as fast as possible. North Korean defectors like Yeonmi Park are not really interested in how Bitcoin micropayments can support artists online while they are being sold for less than $300 as sex slaves.
Listening and trying to understand who you are talking to is the most important thing you can do when presenting an idea. That is particularly true with Bitcoin, given the negative bias most people have towards it, how complex it is to understand, and how difficult it is to challenge some of the greatest assumptions that most people have.
This simple framework is an attempt to strategically identify the areas of interest of people who are new to Bitcoin and avoid overwhelming them with a big orange pill they might not be ready for.
Instead, by choosing between hard money, payment system, freedom technology, and energy buyer, I am now able to better structure conversations and elevator pitches when engaging with people and answering the usual “Uh! Tell me more about this Bitcoin thing!” question.
So go ahead, choose your orange pill and remember the most important question for Bitcoin is “why would one care about it?”
This is a guest post by Jesse Colzani. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.
bitcoin btc currencies commodities goldUncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemploymentUncategorized
Mortgage rates fall as labor market normalizes
Jobless claims show an expanding economy. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
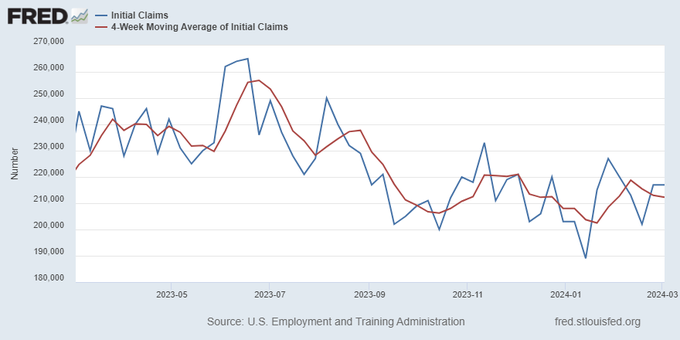
Everyone was waiting to see if this week’s jobs report would send mortgage rates higher, which is what happened last month. Instead, the 10-year yield had a muted response after the headline number beat estimates, but we have negative job revisions from previous months. The Federal Reserve’s fear of wage growth spiraling out of control hasn’t materialized for over two years now and the unemployment rate ticked up to 3.9%. For now, we can say the labor market isn’t tight anymore, but it’s also not breaking.
The key labor data line in this expansion is the weekly jobless claims report. Jobless claims show an expanding economy that has not lost jobs yet. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
From the Fed: In the week ended March 2, initial claims for unemployment insurance benefits were flat, at 217,000. The four-week moving average declined slightly by 750, to 212,250
Below is an explanation of how we got here with the labor market, which all started during COVID-19.
1. I wrote the COVID-19 recovery model on April 7, 2020, and retired it on Dec. 9, 2020. By that time, the upfront recovery phase was done, and I needed to model out when we would get the jobs lost back.
2. Early in the labor market recovery, when we saw weaker job reports, I doubled and tripled down on my assertion that job openings would get to 10 million in this recovery. Job openings rose as high as to 12 million and are currently over 9 million. Even with the massive miss on a job report in May 2021, I didn’t waver.
Currently, the jobs openings, quit percentage and hires data are below pre-COVID-19 levels, which means the labor market isn’t as tight as it once was, and this is why the employment cost index has been slowing data to move along the quits percentage.

3. I wrote that we should get back all the jobs lost to COVID-19 by September of 2022. At the time this would be a speedy labor market recovery, and it happened on schedule, too
Total employment data
4. This is the key one for right now: If COVID-19 hadn’t happened, we would have between 157 million and 159 million jobs today, which would have been in line with the job growth rate in February 2020. Today, we are at 157,808,000. This is important because job growth should be cooling down now. We are more in line with where the labor market should be when averaging 140K-165K monthly. So for now, the fact that we aren’t trending between 140K-165K means we still have a bit more recovery kick left before we get down to those levels.

From BLS: Total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 275,000 in February, and the unemployment rate increased to 3.9 percent, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Job gains occurred in health care, in government, in food services and drinking places, in social assistance, and in transportation and warehousing.
Here are the jobs that were created and lost in the previous month:

In this jobs report, the unemployment rate for education levels looks like this:
- Less than a high school diploma: 6.1%
- High school graduate and no college: 4.2%
- Some college or associate degree: 3.1%
- Bachelor’s degree or higher: 2.2%

Today’s report has continued the trend of the labor data beating my expectations, only because I am looking for the jobs data to slow down to a level of 140K-165K, which hasn’t happened yet. I wouldn’t categorize the labor market as being tight anymore because of the quits ratio and the hires data in the job openings report. This also shows itself in the employment cost index as well. These are key data lines for the Fed and the reason we are going to see three rate cuts this year.
recession unemployment covid-19 fed federal reserve mortgage rates recession recovery unemploymentUncategorized
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Last month we though that the January…
Last month we though that the January jobs report was the "most ridiculous in recent history" but, boy, were we wrong because this morning the Biden department of goalseeked propaganda (aka BLS) published the February jobs report, and holy crap was that something else. Even Goebbels would blush.
What happened? Let's take a closer look.
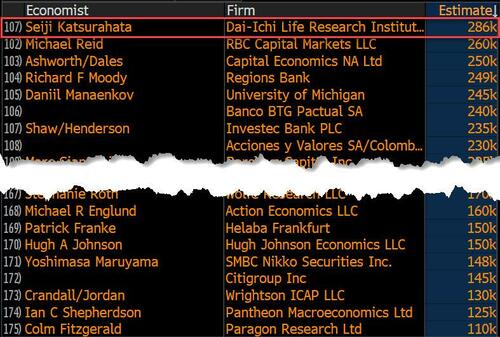
On the surface, it was (almost) another blockbuster jobs report, certainly one which nobody expected, or rather just one bank out of 76 expected. Starting at the top, the BLS reported that in February the US unexpectedly added 275K jobs, with just one research analyst (from Dai-Ichi Research) expecting a higher number.
Some context: after last month's record 4-sigma beat, today's print was "only" 3 sigma higher than estimates. Needless to say, two multiple sigma beats in a row used to only happen in the USSR... and now in the US, apparently.
Before we go any further, a quick note on what last month we said was "the most ridiculous jobs report in recent history": it appears the BLS read our comments and decided to stop beclowing itself. It did that by slashing last month's ridiculous print by over a third, and revising what was originally reported as a massive 353K beat to just 229K, a 124K revision, which was the biggest one-month negative revision in two years!
Of course, that does not mean that this month's jobs print won't be revised lower: it will be, and not just that month but every other month until the November election because that's the only tool left in the Biden admin's box: pretend the economic and jobs are strong, then revise them sharply lower the next month, something we pointed out first last summer and which has not failed to disappoint once.
In the past month the Biden department of goalseeking stuff higher before revising it lower, has revised the following data sharply lower:
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) August 30, 2023
- Jobs
- JOLTS
- New Home sales
- Housing Starts and Permits
- Industrial Production
- PCE and core PCE
To be fair, not every aspect of the jobs report was stellar (after all, the BLS had to give it some vague credibility). Take the unemployment rate, after flatlining between 3.4% and 3.8% for two years - and thus denying expectations from Sahm's Rule that a recession may have already started - in February the unemployment rate unexpectedly jumped to 3.9%, the highest since February 2022 (with Black unemployment spiking by 0.3% to 5.6%, an indicator which the Biden admin will quickly slam as widespread economic racism or something).
And then there were average hourly earnings, which after surging 0.6% MoM in January (since revised to 0.5%) and spooking markets that wage growth is so hot, the Fed will have no choice but to delay cuts, in February the number tumbled to just 0.1%, the lowest in two years...
... for one simple reason: last month's average wage surge had nothing to do with actual wages, and everything to do with the BLS estimate of hours worked (which is the denominator in the average wage calculation) which last month tumbled to just 34.1 (we were led to believe) the lowest since the covid pandemic...
... but has since been revised higher while the February print rose even more, to 34.3, hence why the latest average wage data was once again a product not of wages going up, but of how long Americans worked in any weekly period, in this case higher from 34.1 to 34.3, an increase which has a major impact on the average calculation.
While the above data points were examples of some latent weakness in the latest report, perhaps meant to give it a sheen of veracity, it was everything else in the report that was a problem starting with the BLS's latest choice of seasonal adjustments (after last month's wholesale revision), which have gone from merely laughable to full clownshow, as the following comparison between the monthly change in BLS and ADP payrolls shows. The trend is clear: the Biden admin numbers are now clearly rising even as the impartial ADP (which directly logs employment numbers at the company level and is far more accurate), shows an accelerating slowdown.
But it's more than just the Biden admin hanging its "success" on seasonal adjustments: when one digs deeper inside the jobs report, all sorts of ugly things emerge... such as the growing unprecedented divergence between the Establishment (payrolls) survey and much more accurate Household (actual employment) survey. To wit, while in January the BLS claims 275K payrolls were added, the Household survey found that the number of actually employed workers dropped for the third straight month (and 4 in the past 5), this time by 184K (from 161.152K to 160.968K).
This means that while the Payrolls series hits new all time highs every month since December 2020 (when according to the BLS the US had its last month of payrolls losses), the level of Employment has not budged in the past year. Worse, as shown in the chart below, such a gaping divergence has opened between the two series in the past 4 years, that the number of Employed workers would need to soar by 9 million (!) to catch up to what Payrolls claims is the employment situation.
There's more: shifting from a quantitative to a qualitative assessment, reveals just how ugly the composition of "new jobs" has been. Consider this: the BLS reports that in February 2024, the US had 132.9 million full-time jobs and 27.9 million part-time jobs. Well, that's great... until you look back one year and find that in February 2023 the US had 133.2 million full-time jobs, or more than it does one year later! And yes, all the job growth since then has been in part-time jobs, which have increased by 921K since February 2023 (from 27.020 million to 27.941 million).
Here is a summary of the labor composition in the past year: all the new jobs have been part-time jobs!
But wait there's even more, because now that the primary season is over and we enter the heart of election season and political talking points will be thrown around left and right, especially in the context of the immigration crisis created intentionally by the Biden administration which is hoping to import millions of new Democratic voters (maybe the US can hold the presidential election in Honduras or Guatemala, after all it is their citizens that will be illegally casting the key votes in November), what we find is that in February, the number of native-born workers tumbled again, sliding by a massive 560K to just 129.807 million. Add to this the December data, and we get a near-record 2.4 million plunge in native-born workers in just the past 3 months (only the covid crash was worse)!
The offset? A record 1.2 million foreign-born (read immigrants, both legal and illegal but mostly illegal) workers added in February!
Said otherwise, not only has all job creation in the past 6 years has been exclusively for foreign-born workers...

... but there has been zero job-creation for native born workers since June 2018!
This is a huge issue - especially at a time of an illegal alien flood at the southwest border...
... and is about to become a huge political scandal, because once the inevitable recession finally hits, there will be millions of furious unemployed Americans demanding a more accurate explanation for what happened - i.e., the illegal immigration floodgates that were opened by the Biden admin.
Which is also why Biden's handlers will do everything in their power to insure there is no official recession before November... and why after the election is over, all economic hell will finally break loose. Until then, however, expect the jobs numbers to get even more ridiculous.
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex


















