Uncategorized
The state of crypto in Western Europe: Swiss powerhouse and French unicorns
From taxes and legislation to the local startups and professional associations — all you need to know about blockchain and crypto in Western Europe….

From taxes and legislation to the local startups and professional associations — all you need to know about blockchain and crypto in Western Europe.
Despite the turbulence that broke out in the crypto market this summer, there is an important long-term marker that should be considered in any complex assessment — the combination of adoption and regulation. The latest report by EUBlockchain Observatory, named “EU Blockchain Ecosystem Developments,” tries to measure this combination within the European Union, combining the data on each and every member country from Portugal to Slovakia.
As the original report counts more than 200 pages, Cointelegraph prepared a summary with the intent to capture the most vital information about the state of crypto and blockchain in Europe. We started from a group of countries that are usually labeled as “Western European.”
Austria
Numbers: 50 blockchain solution providers, $48.72 million (50 million euros) in total funds raised
Regulation and legislation: A registry for Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) was established by the Financial Market Authority a year later, in 2020. Regulators have adopted an “overall non-restrictive approach” toward crypto and blockchain and crypto mining remains largely unregulated.
Taxes: As is the case in most European countries, digital currency exchange is VAT-exempt. Capital gains from the sale of crypto are subject to a progressive income tax that amounts to up to 55% for individuals and 25% for corporations, but digital taxation policies may apply if the digital currency generates interest income and thus qualifies as an investment asset.
Notable initiatives: In November 2019, the Austrian Blockchain Centre (ABC) was created to explore blockchain applications in the fields of finance, energy, logistics, public administration and the Internet of Things. ABC, currently involving more than 21 institutions and 54 companies in its public-private partnership model, aspires to become the world’s largest blockchain research center. Blockchain is also a key facilitator of the Smart City Vienna and Open Government Data initiatives.
Local players: Bitpanda, a Vienna-based trading platform, which market value exceeded $4 billion in 2021, Blockpit, a digital assets investment platform responsible for more than $500 million traded in 2017, and Conda, a crowd-investing platform for Austrian startups.
Belgium
Numbers: 47 blockchain solution providers, 992 blockchain professionals.
Regulation and legislation: According to the report, there are currently “no specific laws or regulations” in Belgium. In 2017, Financial Services and Markets Authority (FSMA) published a communication on an overview of the legislation and regulations that may apply to Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and crypto assets.
At the same time, FSMA maintains a red list of fraudulent crypto companies. Nevertheless, utility token offerings are considered “a regular option” to raise capital. The FSMA characterizes crypto assets as investment instruments given that they may provide rights to revenues or returns, a means of storage and exchange given their convertibility into other assets or a utility token if they provide access to certain products or services.
From May 2022, registration for VASPs and custodial wallets is obligatory. The providers must fulfill certain conditions including status as a legal entity and maintaining minimum capital of 50,000 euros.
Taxes: Tax stands at 33% on any cryptocurrency income, depending on how the individual is investing. A mere increase of value over time escapes taxation, but the investor is obliged to prove their holding strategy. There is no specification on the required holding time.
Notable initiatives: “Blockchain for Europe” represents international blockchain industry players at the EU level, with a primary focus on participation in the regulatory debate. HIVE Blockchain Society is a nonprofit blockchain association whose aim is to promote the understanding of distributed ledger technology and to inform the Belgian and international community about its developments.
Local players: Keyrock, a company that develops crypto-asset financial infrastructure by means of scalable, self-adaptive algorithmic technologies, Credix, a decentralized credit marketplace powered by Solana blockchain technology, and Delta, a Bitcoin (BTC) and cryptocurrency portfolio tracker app.
France
Numbers: 160+ blockchain startups, $175.4 million (180 million euros) of fundraised revenue
Regulation and legislation: France established a friendly legal framework for ICOs in 2016, allowing issuers to register cash vouchers directly into the blockchain. In 2017, the Financial Market Authority (AMF) launched the digital-asset fundraising support and research program UNICORN. France also authorizes the registration and transfer of unlisted securities using blockchain technology.
Taxes: The country’s highest administrative court reduced the tax burden on profits coming from cryptocurrencies and set a flat rate tax of 30%.
Notable initiatives: The public Deposits and Consignments Fund makes direct investments in crypto projects. The fund has invested $292.3 million (300 million euros) in blockchain and AI in the European Commission’s Investment Programme for the Future.
Community self-organization: The French Digital Asset Association (ADAN) operates as a professional lobbying group on behalf of the industry.
Local players: Ledger, leading global cryptocurrency hardware wallet provider, Coinhouse, a crypto asset management and transaction services company, providing staking, saving and custody services, and Sorare, a fantasy football gaming platform that uses blockchain technology based on Ethereum.
Germany
Numbers: 343 blockchain startups
Regulation and legislation: Since 2013, virtual currencies have been the “units of account.” In 2020, Germany introduced the concepts of “crypto asset” and “crypto custody.” The latter requires a license from the supervisory body BaFin. Virtual currencies are not considered legal tender in the country and are generally treated as investment assets or so-called “substitute currencies.”
Taxes: In May 2022, Germany’s Finance Ministry has released new cryptocurrency tax guidelines with no tax payable on gains from BTC and Ether (ETH) sold 12 months after acquisition.
Notable initiatives: In September 2020, the Deutsche Energie-Agentur announced the launch of the Future Energy Lab. It involves, among other things, the pilot projects related to the application of blockchain technology in the energy sector, such as the Blockchain Machine Identity Ledger (BMIL) and the Smart Contract Registry. The BMIL is a digital and decentralized directory for device identities.
The same year one of the four electricity transmission system operators in Germany announced a multi-year strategic partnership with Energy Web that will focus on testing and validating the technological promises of blockchain-based solutions.
Community self-organization: Established in 2017, the Blockchain Bundesverband is a non-profit association with more than 60 members. The association’s initiatives focus on education for decision-makers and the wider public. Based in Munich, the European Blockchain Association provides an independent, neutral platform for blockchain-related communities and organizations to discuss, develop and elaborate on shared work.
Local startups: Iota Foundation develops an open-source protocol that supports data and value transfer between devices and humans, and BitsCrunch, a crypto-analytics company.
The Netherlands
Numbers: 160+ blockchain startups, $360.5 million (370 million euros) of raised funds.
Regulation and legislation: The central bank and the Dutch Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) maintain a one-stop shop for regulatory information for startups called InnovationHub. There is also a regulatory sandbox for emerging technologies with a principles-based (rather than a rules-based) approach. Compliance is determined based on the intent of laws and regulations rather than their letter. A practice of partial authorizations, when a startup does not need to meet all the banking license criteria to obtain a license, is rather common.
Notable initiatives: During the COVID-19 pandemic, Tymlez launched a project to support the government’s transparency in medical supply chains through blockchain technology. There are projects in agriculture such as Blockchain for Agri-food, financed by the Dutch Ministry of Agriculture, Nature and Food Quality to improve supply chains.
Community self-organization: The report mentions meetup groups such as Blockchain Talks, Blockchain Netherlands, Food Integrity Blockchained, Permissionless Society Blockchains and Bitcoin Wednesday Amsterdam, as well as Ethereum Dev NL and Hyperledger Netherlands.
Local players: Bitfury provides mobile Bitcoin mining data centers, Aurus, a gold-backed cryptocurrency on the Ethereum blockchain, and Finturi, a blockchain-powered trade finance platform.
Switzerland
Numbers: $247.48 billion (254 billion euros) of the total valuation of the top 50 companies in 2021, 877 blockchain solution providers.
Regulation and legislation: In 2019, the Federal Council updated the existing framework conditions in relation to blockchain and crypto. In 2020, the Swiss Parliament passed the DLT blanket act, which selectively adapts 10 existing federal laws. In 2021, a license for DLT trading facilities was introduced.
According to the Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA), digital currencies are categorized based on their function and purpose as payment tokens, utility tokens and asset tokens.
Taxes: Tax rules vary between the individual cantons. Digital currencies are generally treated as foreign currencies for the purposes of wealth taxation. Their exchange value is determined by the Federal Tax administration at the end of the year. Capital gains on digital currencies are exempt from income tax for individuals. Purchases with digital currencies are VAT exempt.
Notable initiatives: Blockchain has been used for issuing digital self-sovereign identities and even voting on the regional level, while digital currencies are accepted for paying taxes and public services. The city of Zug, the capital of the so-called “Crypto Valley,” launched its blockchain-powered digital identity program in 2017. In 2021, the Swiss government started a public discussion on self-sovereign identities on the national level. In 2022, the city of Lugano acknowledged Bitcoin and Tether (USDT) as legal tender.
Community self-organization: The Crypto Valley Association and Blockchain Federation are the major public entities for blockchain enthusiasts and entrepreneurs. There are also popular communities like the Swiss Association of Crypto Investors and the Bitcoin Association.
Local players: Switzerland by far exceeds all the other nations in the list when it comes to globally acknowledged crypto companies. It’s enough to mention that such players as Cardano, Polkadot, Cardano, Solana, Cosmos and Tezos are based in this country.
Key takeaways
Discussing the report takeaways with Cointelegraph, Nikolaos Kostopoulos, senior blockchain consultant at Netcompany-Intrasoft and member of the EU Blockchain Observatory and Forum team, compared the European regulatory dialogue to the one that takes place in the United States, highlighting the role of France:
“French regulators and policymakers are seemingly winning the course for a comprehensive, objective and holistic effort to establish the framework for a growing blockchain and digital assets industry. This effort is already validated by the decision of leading players such as Binance and Crypto.com which are heavily investing in their French HQ as their EU base, but also the fact that France is home to a few of the biggest EU blockchain startups.”
While France’s regulatory efforts stay in a larger EU context, Switzerland still leads the way in terms of attracting startups and creating the most welcoming legal environment for them. Kostopoulos believes that this unique position can’t simply be explained by the country’s century-old tradition as a safe haven for big money.
“There are numerous reasons that constitute Switzerland more advanced and progressive in comparison to countries such as Belgium or France. The country has established procedures, progressive financial legislation, human resources and infrastructure to support a framework to accelerate financial innovation,” he said.
cryptocurrency bitcoin ethereum blockchain crypto btc pandemic covid-19 currencies crypto goldUncategorized
Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more
New Zillow research suggests the spring home shopping season may see a second wave this summer if mortgage rates fall
The post Homes listed for sale in…
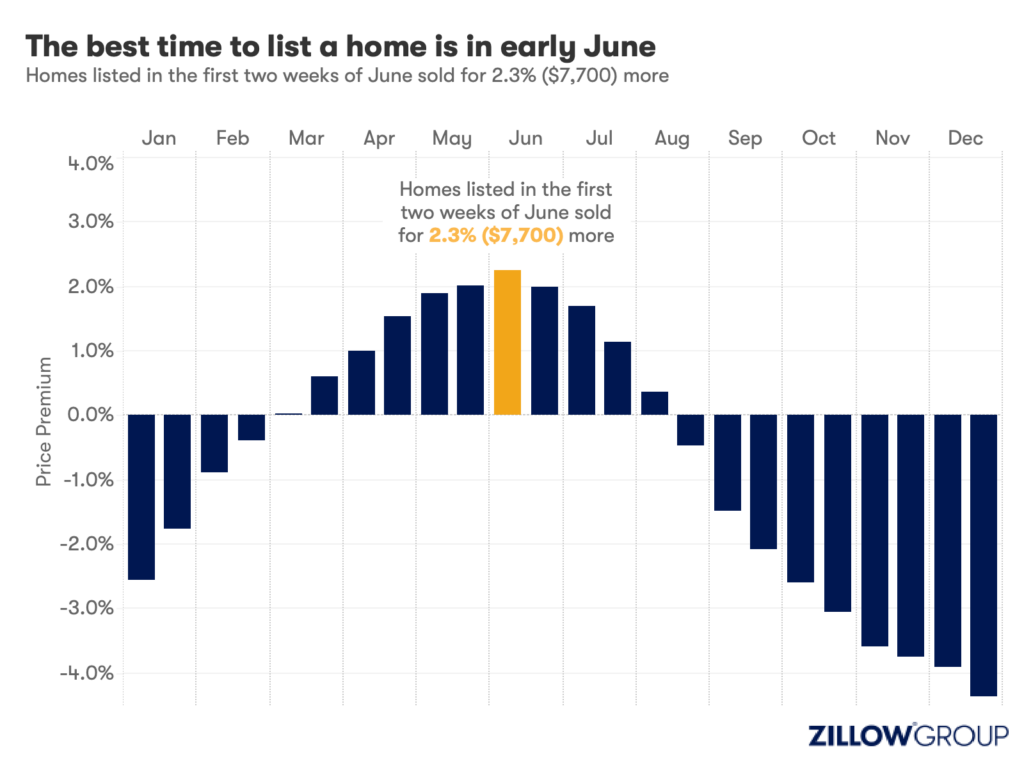
- A Zillow analysis of 2023 home sales finds homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more.
- The best time to list a home for sale is a month later than it was in 2019, likely driven by mortgage rates.
- The best time to list can be as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York and Philadelphia.
Spring home sellers looking to maximize their sale price may want to wait it out and list their home for sale in the first half of June. A new Zillow® analysis of 2023 sales found that homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more, a $7,700 boost on a typical U.S. home.
The best time to list consistently had been early May in the years leading up to the pandemic. The shift to June suggests mortgage rates are strongly influencing demand on top of the usual seasonality that brings buyers to the market in the spring. This home-shopping season is poised to follow a similar pattern as that in 2023, with the potential for a second wave if the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates midyear or later.
The 2.3% sale price premium registered last June followed the first spring in more than 15 years with mortgage rates over 6% on a 30-year fixed-rate loan. The high rates put home buyers on the back foot, and as rates continued upward through May, they were still reassessing and less likely to bid boldly. In June, however, rates pulled back a little from 6.79% to 6.67%, which likely presented an opportunity for determined buyers heading into summer. More buyers understood their market position and could afford to transact, boosting competition and sale prices.
The old logic was that sellers could earn a premium by listing in late spring, when search activity hit its peak. Now, with persistently low inventory, mortgage rate fluctuations make their own seasonality. First-time home buyers who are on the edge of qualifying for a home loan may dip in and out of the market, depending on what’s happening with rates. It is almost certain the Federal Reserve will push back any interest-rate cuts to mid-2024 at the earliest. If mortgage rates follow, that could bring another surge of buyers later this year.
Mortgage rates have been impacting affordability and sale prices since they began rising rapidly two years ago. In 2022, sellers nationwide saw the highest sale premium when they listed their home in late March, right before rates barreled past 5% and continued climbing.
Zillow’s research finds the best time to list can vary widely by metropolitan area. In 2023, it was as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York. Thirty of the top 35 largest metro areas saw for-sale listings command the highest sale prices between May and early July last year.
Zillow also found a wide range in the sale price premiums associated with homes listed during those peak periods. At the hottest time of the year in San Jose, homes sold for 5.5% more, a $88,000 boost on a typical home. Meanwhile, homes in San Antonio sold for 1.9% more during that same time period.
| Metropolitan Area | Best Time to List | Price Premium | Dollar Boost |
| United States | First half of June | 2.3% | $7,700 |
| New York, NY | First half of July | 2.4% | $15,500 |
| Los Angeles, CA | First half of May | 4.1% | $39,300 |
| Chicago, IL | First half of June | 2.8% | $8,800 |
| Dallas, TX | First half of June | 2.5% | $9,200 |
| Houston, TX | Second half of April | 2.0% | $6,200 |
| Washington, DC | Second half of June | 2.2% | $12,700 |
| Philadelphia, PA | First half of July | 2.4% | $8,200 |
| Miami, FL | First half of June | 2.3% | $12,900 |
| Atlanta, GA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $8,700 |
| Boston, MA | Second half of May | 3.5% | $23,600 |
| Phoenix, AZ | First half of June | 3.2% | $14,700 |
| San Francisco, CA | Second half of February | 4.2% | $50,300 |
| Riverside, CA | First half of May | 2.7% | $15,600 |
| Detroit, MI | First half of July | 3.3% | $7,900 |
| Seattle, WA | First half of June | 4.3% | $31,500 |
| Minneapolis, MN | Second half of May | 3.7% | $13,400 |
| San Diego, CA | Second half of April | 3.1% | $29,600 |
| Tampa, FL | Second half of June | 2.1% | $8,000 |
| Denver, CO | Second half of May | 2.9% | $16,900 |
| Baltimore, MD | First half of July | 2.2% | $8,200 |
| St. Louis, MO | First half of June | 2.9% | $7,000 |
| Orlando, FL | First half of June | 2.2% | $8,700 |
| Charlotte, NC | Second half of May | 3.0% | $11,000 |
| San Antonio, TX | First half of June | 1.9% | $5,400 |
| Portland, OR | Second half of April | 2.6% | $14,300 |
| Sacramento, CA | First half of June | 3.2% | $17,900 |
| Pittsburgh, PA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $4,700 |
| Cincinnati, OH | Second half of April | 2.7% | $7,500 |
| Austin, TX | Second half of May | 2.8% | $12,600 |
| Las Vegas, NV | First half of June | 3.4% | $14,600 |
| Kansas City, MO | Second half of May | 2.5% | $7,300 |
| Columbus, OH | Second half of June | 3.3% | $10,400 |
| Indianapolis, IN | First half of July | 3.0% | $8,100 |
| Cleveland, OH | First half of July | 3.4% | $7,400 |
| San Jose, CA | First half of June | 5.5% | $88,400 |
The post Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more appeared first on Zillow Research.
federal reserve pandemic home sales mortgage rates interest ratesUncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemploymentUncategorized
Mortgage rates fall as labor market normalizes
Jobless claims show an expanding economy. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
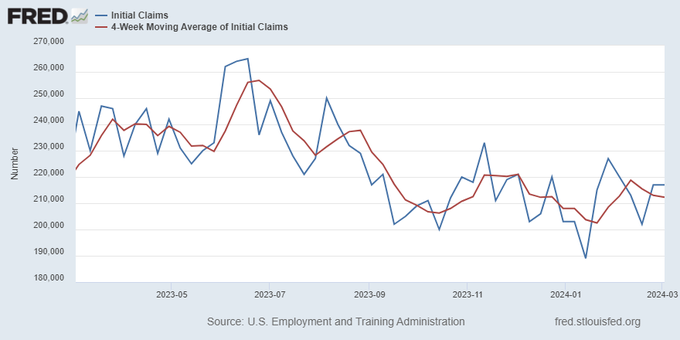
Everyone was waiting to see if this week’s jobs report would send mortgage rates higher, which is what happened last month. Instead, the 10-year yield had a muted response after the headline number beat estimates, but we have negative job revisions from previous months. The Federal Reserve’s fear of wage growth spiraling out of control hasn’t materialized for over two years now and the unemployment rate ticked up to 3.9%. For now, we can say the labor market isn’t tight anymore, but it’s also not breaking.
The key labor data line in this expansion is the weekly jobless claims report. Jobless claims show an expanding economy that has not lost jobs yet. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
From the Fed: In the week ended March 2, initial claims for unemployment insurance benefits were flat, at 217,000. The four-week moving average declined slightly by 750, to 212,250
Below is an explanation of how we got here with the labor market, which all started during COVID-19.
1. I wrote the COVID-19 recovery model on April 7, 2020, and retired it on Dec. 9, 2020. By that time, the upfront recovery phase was done, and I needed to model out when we would get the jobs lost back.
2. Early in the labor market recovery, when we saw weaker job reports, I doubled and tripled down on my assertion that job openings would get to 10 million in this recovery. Job openings rose as high as to 12 million and are currently over 9 million. Even with the massive miss on a job report in May 2021, I didn’t waver.
Currently, the jobs openings, quit percentage and hires data are below pre-COVID-19 levels, which means the labor market isn’t as tight as it once was, and this is why the employment cost index has been slowing data to move along the quits percentage.

3. I wrote that we should get back all the jobs lost to COVID-19 by September of 2022. At the time this would be a speedy labor market recovery, and it happened on schedule, too
Total employment data
4. This is the key one for right now: If COVID-19 hadn’t happened, we would have between 157 million and 159 million jobs today, which would have been in line with the job growth rate in February 2020. Today, we are at 157,808,000. This is important because job growth should be cooling down now. We are more in line with where the labor market should be when averaging 140K-165K monthly. So for now, the fact that we aren’t trending between 140K-165K means we still have a bit more recovery kick left before we get down to those levels.

From BLS: Total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 275,000 in February, and the unemployment rate increased to 3.9 percent, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Job gains occurred in health care, in government, in food services and drinking places, in social assistance, and in transportation and warehousing.
Here are the jobs that were created and lost in the previous month:

In this jobs report, the unemployment rate for education levels looks like this:
- Less than a high school diploma: 6.1%
- High school graduate and no college: 4.2%
- Some college or associate degree: 3.1%
- Bachelor’s degree or higher: 2.2%

Today’s report has continued the trend of the labor data beating my expectations, only because I am looking for the jobs data to slow down to a level of 140K-165K, which hasn’t happened yet. I wouldn’t categorize the labor market as being tight anymore because of the quits ratio and the hires data in the job openings report. This also shows itself in the employment cost index as well. These are key data lines for the Fed and the reason we are going to see three rate cuts this year.
recession unemployment covid-19 fed federal reserve mortgage rates recession recovery unemployment-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex



