International
The roots of Canada’s COVID-19 vaccine shortage go back decades
Behind Canada’s current COVID-19 vaccine shortage is a decades-long tale of unheeded warnings, missed opportunities and dismantled resources that was never going to end well.
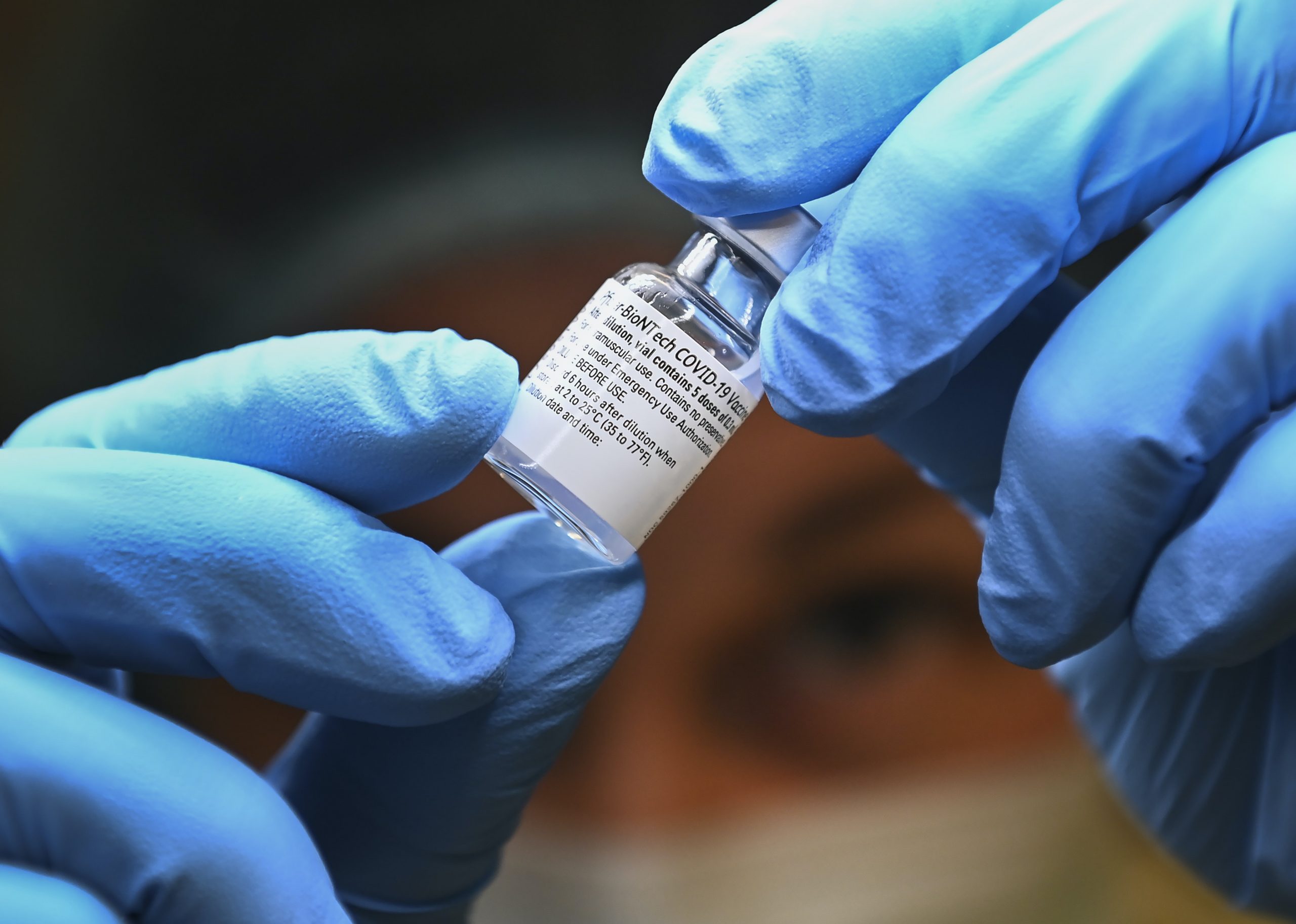

As of Feb. 5, Canada had administered 2.7 COVID-19 vaccination doses per 100 people compared to 61.7 for Israel and 16.2 for the United Kingdom. By contrast, Canada has signed contracts with seven different companies for a total of 234 million doses with options for tens of millions more.
What’s going on?
To understand the problem, we need to go back to the 1980s. At that time, the government-owned Connaught Labs was producing vaccines here in Canada and decision-making was in the public realm. But Connaught was partially privatized and then finally allowed to be sold to the French company Merieux (now part of Sanofi) by the Conservative government of Brian Mulroney.
Fast forward to the 2000s, when Québec-based vaccine manufacturer IAF BioChem went through a couple of sales and ended up being owned by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK).
Sanofi and GSK still make vaccines in Toronto and Ste-Foy, but decisions about what vaccines to produce are not in Canadian hands.
Unheeded warnings

It didn’t have to be that way. After the SARS outbreak in 2003, the report Learning from SARS led by Dr. David Naylor recommended that Canada develop a “national vaccine strategy” and prioritize the security of our vaccine supply. We got another warning about the need for a secure and steady supply of vaccines with the H1N1 pandemic of 2009 when there were production delays at the GSK plant in Ste-Foy.
Nobody seems to have been paying attention. As a result, when the COVID-19 pandemic started, Canada was left with few options.
COVID-19 response
Canada’s first attempt to ensure domestic production was a deal with the Chinese manufacturer CanSino Biologics in May 2020. Had that deal gone ahead, it would have involved trials at the Canadian Centre for Vaccinology at Dalhousie University and, if successful, subsequent domestic manufacturing. But within days of the agreement being announced, there were already troubles as the Chinese delayed sending the seed material for the vaccine and, ultimately, it never arrived.
Efforts to secure a domestically made supply then turned to upgrading the National Research Council (NRC) facility in Montréal and subsequently building an entirely new plant at a total cost of $170 million. In doing so, the government bypassed providing PnuVax, a biopharmaceutical company also located in Montréal, with any of the $600 million from Industry Canada’s Strategic Innovation Fund earmarked for the research or development of COVID-19 vaccines and therapies.
PnuVax had been renovated in 2012 to meet Health Canada standards and according to sources cited by the Globe and Mail, the company could have been ready to produce millions of doses of a COVID-19 vaccine by the end of 2020.

Prime Minister Justin Trudeau initially said the NRC facility would be up and running by November 2020 and producing 250,000 doses a month. However, in early February, Trudeau admitted that the NRC plant wouldn’t be ready until the summer of 2021, and with the need to outfit the facility for the Novavax vaccine and subsequent Health Canada inspections, there won’t be any vaccine coming from there until the end of 2021.
The failure of the CanSino deal and the delay in building the new NRC facility left Canada reliant on foreign sources of vaccine. The contracts for the vaccine were negotiated based on advice provided by the 18 member COVID-19 Vaccine Task Force set up by the NRC in June 2020.
Both the co-chairs of the task force have conflicts of interest with companies producing the vaccines and the terms of the contracts are being kept secret. Among other things, we don’t know what price Canada is paying for each vaccine, what the timeline for delivery is, whether there are penalties for delays and how the contracts are being enforced, if at all.
Complicating things even further, the contracts focused on large-scale delivery starting in April 2021 because of uncertainty back in the summer about when vaccines would be available.
Delayed deliveries
Now Canada is facing delays in vaccine delivery from both Pfizer and Moderna, the companies making the only two vaccines approved in Canada so far. The Pfizer plant in Belgium, where our vaccine comes from, is being retooled to increase production while the exact reasons for the Moderna delay are unclear. Moderna is shipping its vaccine to Canada through Belgium. (Both companies and the federal government have promised that the amounts scheduled for delivery by the end of March will be honoured.)

On top of having no domestic production and the delays, Canada is facing vaccine nationalism from other countries. U.S. President Joe Biden is sticking to an America-first position and not allowing the Pfizer plant in Michigan or the Moderna plant in New Hampshire to export any of their vaccines to Canada until all Americans have been vaccinated.
The European Union is also threatening to block the export of vaccines possibly affecting exports from Belgium, as it too is confronting delays in being able to vaccinate its citizens.
One response from Canada to all of this is to claim 1.9 million doses of the yet-to-be-approved AstraZeneca vaccine from COVAX, a facility primarily set up to ensure that low- and middle-income countries will have access to vaccines. Canada is the second-largest country donor to COVAX and is entitled to claim vaccines from COVAX, but is doing so when, as of Feb. 3, only four African countries have started vaccinating their citizens.
In an interview on CBC’s As It Happens, Karina Gould, Canada’s minister of international development, defended Canada’s move, a made-in-Canada form of vaccine nationalism.
Ensuring that Canadians would receive an effective vaccine quickly was never going to be a sure thing; there was always plenty of opportunity for something to go wrong. But the uncertainty involved has been compounded by a lack of government planning in the past, secrecy, a lack of international co-operation and poor government decision-making. Let’s hope we do better when the next pandemic comes around.
In 2017-2020, Joel Lexchin received payments for being on a panel at the American Diabetes Association, for talks at the Toronto Reference Library, for writing a brief in an action for side effects of a drug for Michael F. Smith, Lawyer and a second brief on the role of promotion in generating prescriptions for Goodmans LLP and from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research for presenting at a workshop on conflict-of-interest in clinical practice guidelines. He is currently a member of research groups that are receiving money from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. He is a member of the Foundation Board of Health Action International and the Board of Canadian Doctors for Medicare. He receives royalties from University of Toronto Press and James Lorimer & Co. Ltd. for books he has written.
disease control pandemic covid-19 vaccine canada europeanInternational
The next pandemic? It’s already here for Earth’s wildlife
Bird flu is decimating species already threatened by climate change and habitat loss.

I am a conservation biologist who studies emerging infectious diseases. When people ask me what I think the next pandemic will be I often say that we are in the midst of one – it’s just afflicting a great many species more than ours.
I am referring to the highly pathogenic strain of avian influenza H5N1 (HPAI H5N1), otherwise known as bird flu, which has killed millions of birds and unknown numbers of mammals, particularly during the past three years.
This is the strain that emerged in domestic geese in China in 1997 and quickly jumped to humans in south-east Asia with a mortality rate of around 40-50%. My research group encountered the virus when it killed a mammal, an endangered Owston’s palm civet, in a captive breeding programme in Cuc Phuong National Park Vietnam in 2005.
How these animals caught bird flu was never confirmed. Their diet is mainly earthworms, so they had not been infected by eating diseased poultry like many captive tigers in the region.
This discovery prompted us to collate all confirmed reports of fatal infection with bird flu to assess just how broad a threat to wildlife this virus might pose.
This is how a newly discovered virus in Chinese poultry came to threaten so much of the world’s biodiversity.
The first signs
Until December 2005, most confirmed infections had been found in a few zoos and rescue centres in Thailand and Cambodia. Our analysis in 2006 showed that nearly half (48%) of all the different groups of birds (known to taxonomists as “orders”) contained a species in which a fatal infection of bird flu had been reported. These 13 orders comprised 84% of all bird species.
We reasoned 20 years ago that the strains of H5N1 circulating were probably highly pathogenic to all bird orders. We also showed that the list of confirmed infected species included those that were globally threatened and that important habitats, such as Vietnam’s Mekong delta, lay close to reported poultry outbreaks.
Mammals known to be susceptible to bird flu during the early 2000s included primates, rodents, pigs and rabbits. Large carnivores such as Bengal tigers and clouded leopards were reported to have been killed, as well as domestic cats.
Our 2006 paper showed the ease with which this virus crossed species barriers and suggested it might one day produce a pandemic-scale threat to global biodiversity.
Unfortunately, our warnings were correct.
A roving sickness
Two decades on, bird flu is killing species from the high Arctic to mainland Antarctica.
In the past couple of years, bird flu has spread rapidly across Europe and infiltrated North and South America, killing millions of poultry and a variety of bird and mammal species. A recent paper found that 26 countries have reported at least 48 mammal species that have died from the virus since 2020, when the latest increase in reported infections started.
Not even the ocean is safe. Since 2020, 13 species of aquatic mammal have succumbed, including American sea lions, porpoises and dolphins, often dying in their thousands in South America. A wide range of scavenging and predatory mammals that live on land are now also confirmed to be susceptible, including mountain lions, lynx, brown, black and polar bears.
The UK alone has lost over 75% of its great skuas and seen a 25% decline in northern gannets. Recent declines in sandwich terns (35%) and common terns (42%) were also largely driven by the virus.
Scientists haven’t managed to completely sequence the virus in all affected species. Research and continuous surveillance could tell us how adaptable it ultimately becomes, and whether it can jump to even more species. We know it can already infect humans – one or more genetic mutations may make it more infectious.
At the crossroads
Between January 1 2003 and December 21 2023, 882 cases of human infection with the H5N1 virus were reported from 23 countries, of which 461 (52%) were fatal.
Of these fatal cases, more than half were in Vietnam, China, Cambodia and Laos. Poultry-to-human infections were first recorded in Cambodia in December 2003. Intermittent cases were reported until 2014, followed by a gap until 2023, yielding 41 deaths from 64 cases. The subtype of H5N1 virus responsible has been detected in poultry in Cambodia since 2014. In the early 2000s, the H5N1 virus circulating had a high human mortality rate, so it is worrying that we are now starting to see people dying after contact with poultry again.
It’s not just H5 subtypes of bird flu that concern humans. The H10N1 virus was originally isolated from wild birds in South Korea, but has also been reported in samples from China and Mongolia.
Recent research found that these particular virus subtypes may be able to jump to humans after they were found to be pathogenic in laboratory mice and ferrets. The first person who was confirmed to be infected with H10N5 died in China on January 27 2024, but this patient was also suffering from seasonal flu (H3N2). They had been exposed to live poultry which also tested positive for H10N5.
Species already threatened with extinction are among those which have died due to bird flu in the past three years. The first deaths from the virus in mainland Antarctica have just been confirmed in skuas, highlighting a looming threat to penguin colonies whose eggs and chicks skuas prey on. Humboldt penguins have already been killed by the virus in Chile.

How can we stem this tsunami of H5N1 and other avian influenzas? Completely overhaul poultry production on a global scale. Make farms self-sufficient in rearing eggs and chicks instead of exporting them internationally. The trend towards megafarms containing over a million birds must be stopped in its tracks.
To prevent the worst outcomes for this virus, we must revisit its primary source: the incubator of intensive poultry farms.
Diana Bell does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
genetic pandemic mortality spread deaths south korea south america europe uk chinaInternational
This is the biggest money mistake you’re making during travel
A retail expert talks of some common money mistakes travelers make on their trips.

Travel is expensive. Despite the explosion of travel demand in the two years since the world opened up from the pandemic, survey after survey shows that financial reasons are the biggest factor keeping some from taking their desired trips.
Airfare, accommodation as well as food and entertainment during the trip have all outpaced inflation over the last four years.
Related: This is why we're still spending an insane amount of money on travel
But while there are multiple tricks and “travel hacks” for finding cheaper plane tickets and accommodation, the biggest financial mistake that leads to blown travel budgets is much smaller and more insidious.
This is what you should (and shouldn’t) spend your money on while abroad
“When it comes to traveling, it's hard to resist buying items so you can have a piece of that memory at home,” Kristen Gall, a retail expert who heads the financial planning section at points-back platform Rakuten, told Travel + Leisure in an interview. “However, it's important to remember that you don't need every souvenir that catches your eye.”
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
According to Gall, souvenirs not only have a tendency to add up in price but also weight which can in turn require one to pay for extra weight or even another suitcase at the airport — over the last two months, airlines like Delta (DAL) , American Airlines (AAL) and JetBlue Airways (JBLU) have all followed each other in increasing baggage prices to in some cases as much as $60 for a first bag and $100 for a second one.
While such extras may not seem like a lot compared to the thousands one might have spent on the hotel and ticket, they all have what is sometimes known as a “coffee” or “takeout effect” in which small expenses can lead one to overspend by a large amount.
‘Save up for one special thing rather than a bunch of trinkets…’
“When traveling abroad, I recommend only purchasing items that you can't get back at home, or that are small enough to not impact your luggage weight,” Gall said. “If you’re set on bringing home a souvenir, save up for one special thing, rather than wasting your money on a bunch of trinkets you may not think twice about once you return home.”
Along with the immediate costs, there is also the risk of purchasing things that go to waste when returning home from an international vacation. Alcohol is subject to airlines’ liquid rules while certain types of foods, particularly meat and other animal products, can be confiscated by customs.
While one incident of losing an expensive bottle of liquor or cheese brought back from a country like France will often make travelers forever careful, those who travel internationally less frequently will often be unaware of specific rules and be forced to part with something they spent money on at the airport.
“It's important to keep in mind that you're going to have to travel back with everything you purchased,” Gall continued. “[…] Be careful when buying food or wine, as it may not make it through customs. Foods like chocolate are typically fine, but items like meat and produce are likely prohibited to come back into the country.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
stocks pandemic franceInternational
As the pandemic turns four, here’s what we need to do for a healthier future
On the fourth anniversary of the pandemic, a public health researcher offers four principles for a healthier future.

Anniversaries are usually festive occasions, marked by celebration and joy. But there’ll be no popping of corks for this one.
March 11 2024 marks four years since the World Health Organization (WHO) declared COVID-19 a pandemic.
Although no longer officially a public health emergency of international concern, the pandemic is still with us, and the virus is still causing serious harm.
Here are three priorities – three Cs – for a healthier future.
Clear guidance
Over the past four years, one of the biggest challenges people faced when trying to follow COVID rules was understanding them.
From a behavioural science perspective, one of the major themes of the last four years has been whether guidance was clear enough or whether people were receiving too many different and confusing messages – something colleagues and I called “alert fatigue”.
With colleagues, I conducted an evidence review of communication during COVID and found that the lack of clarity, as well as a lack of trust in those setting rules, were key barriers to adherence to measures like social distancing.
In future, whether it’s another COVID wave, or another virus or public health emergency, clear communication by trustworthy messengers is going to be key.
Combat complacency
As Maria van Kerkove, COVID technical lead for WHO, puts it there is no acceptable level of death from COVID. COVID complacency is setting in as we have moved out of the emergency phase of the pandemic. But is still much work to be done.
First, we still need to understand this virus better. Four years is not a long time to understand the longer-term effects of COVID. For example, evidence on how the virus affects the brain and cognitive functioning is in its infancy.
The extent, severity and possible treatment of long COVID is another priority that must not be forgotten – not least because it is still causing a lot of long-term sickness and absence.
Culture change
During the pandemic’s first few years, there was a question over how many of our new habits, from elbow bumping (remember that?) to remote working, were here to stay.
Turns out old habits die hard – and in most cases that’s not a bad thing – after all handshaking and hugging can be good for our health.
But there is some pandemic behaviour we could have kept, under certain conditions. I’m pretty sure most people don’t wear masks when they have respiratory symptoms, even though some health authorities, such as the NHS, recommend it.
Masks could still be thought of like umbrellas: we keep one handy for when we need it, for example, when visiting vulnerable people, especially during times when there’s a spike in COVID.
If masks hadn’t been so politicised as a symbol of conformity and oppression so early in the pandemic, then we might arguably have seen people in more countries adopting the behaviour in parts of east Asia, where people continue to wear masks or face coverings when they are sick to avoid spreading it to others.
Although the pandemic led to the growth of remote or hybrid working, presenteeism – going to work when sick – is still a major issue.
Encouraging parents to send children to school when they are unwell is unlikely to help public health, or attendance for that matter. For instance, although one child might recover quickly from a given virus, other children who might catch it from them might be ill for days.
Similarly, a culture of presenteeism that pressures workers to come in when ill is likely to backfire later on, helping infectious disease spread in workplaces.
At the most fundamental level, we need to do more to create a culture of equality. Some groups, especially the most economically deprived, fared much worse than others during the pandemic. Health inequalities have widened as a result. With ongoing pandemic impacts, for example, long COVID rates, also disproportionately affecting those from disadvantaged groups, health inequalities are likely to persist without significant action to address them.
Vaccine inequity is still a problem globally. At a national level, in some wealthier countries like the UK, those from more deprived backgrounds are going to be less able to afford private vaccines.
We may be out of the emergency phase of COVID, but the pandemic is not yet over. As we reflect on the past four years, working to provide clearer public health communication, avoiding COVID complacency and reducing health inequalities are all things that can help prepare for any future waves or, indeed, pandemics.
Simon Nicholas Williams has received funding from Senedd Cymru, Public Health Wales and the Wales Covid Evidence Centre for research on COVID-19, and has consulted for the World Health Organization. However, this article reflects the views of the author only, in his academic capacity at Swansea University, and no funding or organizational bodies were involved in the writing or content of this article.
vaccine treatment pandemic covid-19 spread social distancing uk world health organization-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex





















