Uncategorized
Switzerland’s Legacy Of Financial Freedom Makes It The Best Place For Bitcoin To Thrive
Switzerland values many of the core properties of Bitcoin and now the two are poised to create the future of financial sovereignty together.

This is an opinion editorial by Julian Liniger, the co-founder and CEO of bitcoin purchasing platform Relai.
As a Swiss citizen, it didn’t take me long to understand why Bitcoin is unique. Switzerland is a country that values lots of the critical aspects that Bitcoin offers to people. The small country in the middle of Europe encourages self sovereignty, privacy and financial literacy. The pioneering Swiss banking secrecy was codified in 1934. This regulation, along with its political neutrality and enduring stability, makes the country a “safe haven” for companies and institutions that deal with money.
However, there is one critical flaw: What’s the point of using the most trustworthy place in the world to store your money when the money itself is broken? Particularly in recent years, we have witnessed reckless behavior by governments and central banks across the globe. Tumbling from one crisis into the next one, it seems that no matter the obstacle, more liquidity has been (and continues to be) the solution from politicians. This is one of the reasons why price inflation is rising in developed nations, and is completely out of control in developing countries.
Bitcoin is a solution to this problem. Bitcoin is the ultimate pristine asset, capped at 21 million units, not centrally controlled, genuinely neutral and global. It’s a monetary good that can be best described as “digital gold.” And, on top of that, it will act as a foundational layer for a new global financial system.
I still remember my first real employment, which, ironically, was with one of the biggest national banks in Switzerland, called Raiffeisen. It was also when I first tried to understand how money and our financial system worked. I asked the bank employees and managers deep and intriguing questions, like probably no 21-year-old intern had before:
Why can the bank just create money out of thin air and lend it out to people for a profit?
What is fiat money backed by?
Why can banks just speculate with the savings of their customers and then get bailed out when they fuck up?
It always struck me how low on substance and high on bullshit the answers were and quickly, I realized that most of these bankers working for the money machine didn’t actually understand how it works. I came to the conclusion that the reason why it works in Switzerland was the high-quality standards, credibility and work ethics of the Swiss people, coupled with the country’s very stable regulatory and political system. These are clearly characteristics that set this nation apart from almost any other one in the world. And, for the same reasons, I think it is why Switzerland experiences among the lowest inflation rates and unemployment rates.
So, it has built the most fertile ground worldwide for the Bitcoin industry — and, finally, sound money — to flourish.
How Switzerland Is Beating The European Union
While Switzerland is in the middle of Europe, it always opted to stay sovereign. This also shows up in terms of the different approaches to regulating Bitcoin. One of the biggest differences between Swiss regulation and the European Union’s Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MICA) is the implementation of the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF) “travel rule.”
Switzerland’s travel rule, implemented by the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA), requires virtual asset service providers to verify the identity of the beneficiary of the transfer. Meanwhile, Europe’s version of the travel rule requires crypto asset service providers to apply enhanced due diligence measures when transactions involve self-custody wallets. What this means is that custodial services that operate in Europe will have to transfer huge amounts of data in order to comply with the much more demanding European travel rule.
Another one of the advantages of Switzerland is the “kassageschäft” framework. Originally used for exchanging physical coins and banknotes of national currencies, it also applies to Bitcoin. Therefore, you don’t need KYC/AML registration to exchange cash in Switzerland, and luckily it fits the digital age as well. In recent years, FINMA has lowered kassageschäft limits for bitcoin compared to physical coins and banknotes from 5,000 CHF per day to 1,000 CHF per day and now is trying to push the limits to 1,000 CHF per 30 days, a move that has been met with skepticism by Bitcoin companies in Switzerland. But, compared to other countries, the Swiss government has shown time again that it’s willing to talk and collaborate with Bitcoin companies to find the best solution for all.
Why Managing Risk Matters More Than Ever
One person’s asset is another person’s liability. This basic rule in the world of finance became very real for a lot of cryptocurrency investors in 2022. Some of the biggest (and in terms of marketing, the loudest) names in the industry collapsed last year, taking customer funds with them into the abyss.
But it was not only FTX, BlockFi and other crypto platforms that showed us that your assets are only yours as long as the respective third party says so. The banking crisis in Lebanon, rampant inflation combined with financial repression in Argentina and the loss of access to banking services because of political reasons around the world are very real. This all shows us one thing: counterparty risk matters, especially in the uncertain geopolitical future that we are heading into. We’ve seen that USD treasuries can be quickly frozen and sanctioned. The same goes for stocks or any other asset, including real estate, that people hold in other countries. While this has been the U.S.’s soft power of choice, investors have surely taken notice of the downsides of counterparty risks.
It matters more than ever that Switzerland is the most trusted place for money on the planet. It has always been open to innovation, technology and international finance. Furthermore, it is, both from a regulatory and political perspective, very decentralized and community driven. Switzerland consists of 26 autonomous cantons and offers its citizens true direct democracy. When taking a closer look, the similarities between Switzerland and Bitcoin are striking: Any Swiss citizens can start an initiative to change the federal constitution, and if they manage to collect at least 100,000 signatures, the whole country will vote for it, almost like a Bitcoin Improvement Proposal (BIP).
It should come as no surprise then that Switzerland plays a crucial role in the Bitcoin market today, known as a “crypto nation,” with Zug as the “Crypto Valley” and Lugano with the “Plan ₿” initiative, hosting hundreds of companies and thousands of employees working in this space.
Particularly Lugano, Switzerland’s ninth-largest city with a population of over 60,000 located in the Italian-speaking southern region, shows how Bitcoin innovation and adoption should be done: in a curious, open and grassroots way. Lugano Mayor Michele Foletti is not afraid to take the leap here, to show the world firsthand why the decentralized Swiss governance model enables projects like the advent of a bitcoin-focused city. More than 100 merchants, restaurants and bars accept bitcoin in Lugano. It’s expected that soon, taxes can be paid in bitcoin (and other cryptocurrencies), which means that it’s very easy to seamlessly delve into a new, open monetary network.
The Trust Crisis Is An Opportunity For Bitcoin And Switzerland
Public trust in institutions like (central) banks, politics and legacy media outlets is at its lowest point in decades. In particular, younger people are looking for new answers. According to a recent survey, 45% of millennials said they prefer bitcoin to stocks, gold or real estate. More than half (51%) of millennials said they have more faith in Bitcoin than in financial institutions.
This is bullish for Bitcoin. However, there are still obstacles. The tedious onboarding process, complicated user interfaces, lousy customer support and lack of self-custody solutions are still a reality for newbies interested in buying their first bitcoin. It’s clear what we have to do to get bitcoin in as many hands as possible: make buying and selling it easier. Get rid of all the hindrances, and allow anyone to stack sats in their own, self-hosted wallet, directly.
Bitcoin is about long-term thinking, about saving. And people are desperate for ways to save money that they can genuinely trust again, solutions that don't get eaten away by inflation or high fees, solutions that are ready for the digital age and that can’t be frozen or censored in any way.
I believe that Bitcoin is a force for good that can accelerate financial and, therefore human, freedom. Going forward, Satoshi Nakamoto’s invention will play an integral role not only as an asset without counterparty risk but also as an alternative financial layer that can host a wide range of services.
The Future Of Bitcoin-Only Is Bright, In Switzerland And Beyond
True to its history as a place that fosters financial innovation instead of killing it, Switzerland will thrive in a world that is increasingly embracing Bitcoin.
But despite the growing recognition and adoption of Bitcoin by the financial industry, it remains a bottom-up movement driven by its community of users, developers and enthusiasts. They are committed to the principles of decentralization, privacy and financial freedom and work to promote the use and adoption of bitcoin as a digital currency. The community is active in organizing meetups, forums and events where it can share its experiences and knowledge with others and work together to improve the technology.
Even in the European Union, where the will to innovate with Bitcoin seems less determined, Nakamoto’s innovation will thrive. With a coherent regulatory framework on the horizon, Bitcoin is set for a bright future in Europe — no matter how hard some politicians want to fight it. Despite an ongoing energy crisis and attacks on Bitcoin’s energy consumption, it’s clear that there will be demand for an asset like bitcoin. High price inflation, financial repression and a looming euro-based central bank digital currency will drive adoption and demand.
This is a guest post by Julian Liniger. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.
stocks cryptocurrency bitcoin crypto btc real estate currencies euro crypto goldUncategorized
Fast-food chain closes restaurants after Chapter 11 bankruptcy
Several major fast-food chains recently have struggled to keep restaurants open.

Competition in the fast-food space has been brutal as operators deal with inflation, consumers who are worried about the economy and their jobs and, in recent months, the falling cost of eating at home.
Add in that many fast-food chains took on more debt during the covid pandemic and that labor costs are rising, and you have a perfect storm of problems.
It's a situation where Restaurant Brands International (QSR) has suffered as much as any company.
Related: Wendy's menu drops a fan favorite item, adds something new
Three major Burger King franchise operators filed for bankruptcy in 2023, and the chain saw hundreds of stores close. It also saw multiple Popeyes franchisees move into bankruptcy, with dozens of locations closing.
RBI also stepped in and purchased one of its key franchisees.
"Carrols is the largest Burger King franchisee in the United States today, operating 1,022 Burger King restaurants in 23 states that generated approximately $1.8 billion of system sales during the 12 months ended Sept. 30, 2023," RBI said in a news release. Carrols also owns and operates 60 Popeyes restaurants in six states."
The multichain company made the move after two of its large franchisees, Premier Kings and Meridian, saw multiple locations not purchased when they reached auction after Chapter 11 bankruptcy filings. In that case, RBI bought select locations but allowed others to close.
Image source: Chen Jianli/Xinhua via Getty
Another fast-food chain faces bankruptcy problems
Bojangles may not be as big a name as Burger King or Popeye's, but it's a popular chain with more than 800 restaurants in eight states.
"Bojangles is a Carolina-born restaurant chain specializing in craveable Southern chicken, biscuits and tea made fresh daily from real recipes, and with a friendly smile," the chain says on its website. "Founded in 1977 as a single location in Charlotte, our beloved brand continues to grow nationwide."
Like RBI, Bojangles uses a franchise model, which makes it dependent on the financial health of its operators. The company ultimately saw all its Maryland locations close due to the financial situation of one of its franchisees.
Unlike. RBI, Bojangles is not public — it was taken private by Durational Capital Management LP and Jordan Co. in 2018 — which means the company does not disclose its financial information to the public.
That makes it hard to know whether overall softness for the brand contributed to the chain seeing its five Maryland locations after a Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing.
Bojangles has a messy bankruptcy situation
Even though the locations still appear on the Bojangles website, they have been shuttered since late 2023. The locations were operated by Salim Kakakhail and Yavir Akbar Durranni. The partners operated under a variety of LLCs, including ABS Network, according to local news channel WUSA9.
The station reported that the owners face a state investigation over complaints of wage theft and fraudulent W2s. In November Durranni and ABS Network filed for bankruptcy in New Jersey, WUSA9 reported.
"Not only do former employees say these men owe them money, WUSA9 learned the former owners owe the state, too, and have over $69,000 in back property taxes."
Former employees also say that the restaurant would regularly purchase fried chicken from Popeyes and Safeway when it ran out in their stores, the station reported.
Bojangles sent the station a comment on the situation.
"The franchisee is no longer in the Bojangles system," the company said. "However, it is important to note in your coverage that franchisees are independent business owners who are licensed to operate a brand but have autonomy over many aspects of their business, including hiring employees and payroll responsibilities."
Kakakhail and Durranni did not respond to multiple requests for comment from WUSA9.
bankruptcy pandemicUncategorized
Industrial Production Increased 0.1% in February
From the Fed: Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization
Industrial production edged up 0.1 percent in February after declining 0.5 percent in January. In February, the output of manufacturing rose 0.8 percent and the index for mining climbed 2.2 p…
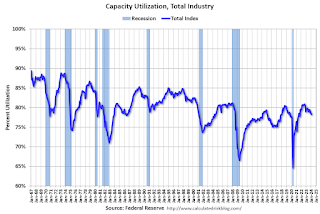
Industrial production edged up 0.1 percent in February after declining 0.5 percent in January. In February, the output of manufacturing rose 0.8 percent and the index for mining climbed 2.2 percent. Both gains partly reflected recoveries from weather-related declines in January. The index for utilities fell 7.5 percent in February because of warmer-than-typical temperatures. At 102.3 percent of its 2017 average, total industrial production in February was 0.2 percent below its year-earlier level. Capacity utilization for the industrial sector remained at 78.3 percent in February, a rate that is 1.3 percentage points below its long-run (1972–2023) average.Click on graph for larger image.
emphasis added
This graph shows Capacity Utilization. This series is up from the record low set in April 2020, and above the level in February 2020 (pre-pandemic).
Capacity utilization at 78.3% is 1.3% below the average from 1972 to 2022. This was below consensus expectations.
Note: y-axis doesn't start at zero to better show the change.
 The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.
The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.Industrial production increased to 102.3. This is above the pre-pandemic level.
Industrial production was above consensus expectations.
Uncategorized
Southwest and United Airlines have bad news for passengers
Both airlines are facing the same problem, one that could lead to higher airfares and fewer flight options.

Airlines operate in a market that's dictated by supply and demand: If more people want to fly a specific route than there are available seats, then tickets on those flights cost more.
That makes scheduling and predicting demand a huge part of maximizing revenue for airlines. There are, however, numerous factors that go into how airlines decide which flights to put on the schedule.
Related: Major airline faces Chapter 11 bankruptcy concerns
Every airport has only a certain number of gates, flight slots and runway capacity, limiting carriers' flexibility. That's why during times of high demand — like flights to Las Vegas during Super Bowl week — do not usually translate to airlines sending more planes to and from that destination.
Airlines generally do try to add capacity every year. That's become challenging as Boeing has struggled to keep up with demand for new airplanes. If you can't add airplanes, you can't grow your business. That's caused problems for the entire industry.
Every airline retires planes each year. In general, those get replaced by newer, better models that offer more efficiency and, in most cases, better passenger amenities.
If an airline can't get the planes it had hoped to add to its fleet in a given year, it can face capacity problems. And it's a problem that both Southwest Airlines (LUV) and United Airlines have addressed in a way that's inevitable but bad for passengers.
Image source: Kevin Dietsch/Getty Images
Southwest slows down its pilot hiring
In 2023, Southwest made a huge push to hire pilots. The airline lost thousands of pilots to retirement during the covid pandemic and it needed to replace them in order to build back to its 2019 capacity.
The airline successfully did that but will not continue that trend in 2024.
"Southwest plans to hire approximately 350 pilots this year, and no new-hire classes are scheduled after this month," Travel Weekly reported. "Last year, Southwest hired 1,916 pilots, according to pilot recruitment advisory firm Future & Active Pilot Advisors. The airline hired 1,140 pilots in 2022."
The slowdown in hiring directly relates to the airline expecting to grow capacity only in the low-single-digits percent in 2024.
"Moving into 2024, there is continued uncertainty around the timing of expected Boeing deliveries and the certification of the Max 7 aircraft. Our fleet plans remain nimble and currently differs from our contractual order book with Boeing," Southwest Airlines Chief Financial Officer Tammy Romo said during the airline's fourth-quarter-earnings call.
"We are planning for 79 aircraft deliveries this year and expect to retire roughly 45 700 and 4 800, resulting in a net expected increase of 30 aircraft this year."
That's very modest growth, which should not be enough of an increase in capacity to lower prices in any significant way.
United Airlines pauses pilot hiring
Boeing's (BA) struggles have had wide impact across the industry. United Airlines has also said it was going to pause hiring new pilots through the end of May.
United (UAL) Fight Operations Vice President Marc Champion explained the situation in a memo to the airline's staff.
"As you know, United has hundreds of new planes on order, and while we remain on path to be the fastest-growing airline in the industry, we just won't grow as fast as we thought we would in 2024 due to continued delays at Boeing," he said.
"For example, we had contractual deliveries for 80 Max 10s this year alone, but those aircraft aren't even certified yet, and it's impossible to know when they will arrive."
That's another blow to consumers hoping that multiple major carriers would grow capacity, putting pressure on fares. Until Boeing can get back on track, it's unlikely that competition between the large airlines will lead to lower fares.
In fact, it's possible that consumer demand will grow more than airline capacity which could push prices higher.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
bankruptcy pandemic stocks-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Spread & Containment2 days ago
Spread & Containment2 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex



















