International
Philadelphia bans supervised injection sites – evidence suggests keeping drug users on the street could do more harm than good
A group of academics look at the global evidence to examine the potential impact of safe injection sites in Philadelphia and the US.
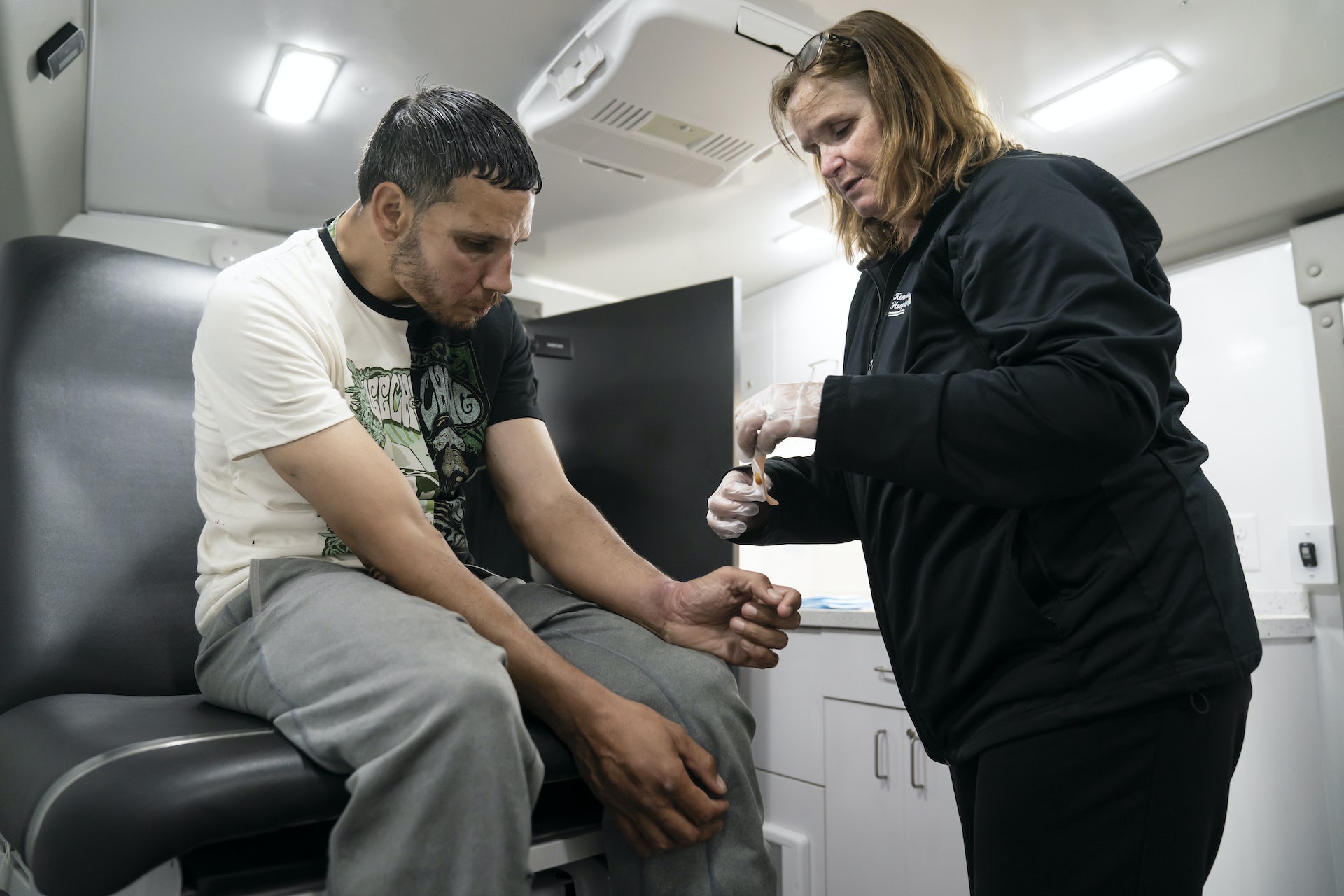
The United States remains tightly in the grasp of an ongoing, and escalating, crisis of deaths caused by opioid overdoses.
With a record-high 109,000 people dying in 2022, it is clear that something new needs to be done to reverse this trend.
Philadelphia is near the epicenter of the crisis. Some of the country’s largest open-air drug markets can be found in the Kensington neighborhood. Heroin, prescription opioids and fentanyl aren’t the only drugs of concern. Xylazine, a powerful non-opioid also known as tranq, has an overwhelming presence on the streets.
We are a group of Scandinavian and American researchers who have studied drug treatment and harm reduction, and we have been watching the situation in Philadelphia from a variety of perspectives.
A mixed response
A record 1,413 people died in Philadelphia from drug overdoses in 2022. The rate of drug-related deaths for Black residents more than doubled between 2018 and 2022, mirroring a problematic national trend.
In response, Philadelphia has adopted a multifaceted plan to stem the tide of overdoses.
But Philadelphia’s City Council has overwhelmingly rejected the establishment of supervised injection sites – a potentially impactful, evidence-based tool in this fight. Overriding the mayor’s veto on Sept. 28, 2023, council members have used zoning legislation to essentially prevent the opening of sites where people can take drugs under supervision across most of the city.
In May 2023, the Pennsylvania legislature also overwhelmingly voted to ban supervised injection sites in the entire state.
While much of the political discourse surrounding this decision has focused on protecting neighborhoods where drug activity happens in parks and on the streets, ample evidence suggests that banning supervised injection sites may instead jeopardize the people and communities the policy was intended to protect.
What is harm reduction?
Supervised injection sites are an example of harm reduction, a general approach to addressing addiction and other public health crises. Ranging from efforts aimed at reducing incidences of HIV to encouraging the safer consumption of alcohol, the concept has become integral to many global public health initiatives.
The goal of harm reduction is to minimize the negative effects associated with drug use and other risky behaviors rather than solely focusing on eliminating the activity. This approach acknowledges the difficulty in breaking addictive behaviors and the fact that some individuals won’t – or can’t – stop regardless of policy and social efforts.
For drug use, harm reduction takes many forms. These include encouraging nonjudgmental approaches toward people who use drugs among social service workers and health care personnel, needle exchange programs, distribution of drugs that reverse overdoses, testing drugs for safety – and, in many parts of the world, supervised injection sites.
Limitations in the United States
Supervised injection sites have been a particularly controversial approach to harm reduction not just in Philadelphia but across most of the U.S.
Only a few officially sanctioned supervised injection sites have emerged. Two opened in Manhattan in 2021 with support from the government of New York City, where research suggests they could save both lives and health care dollars. Rhode Island plans to open a third in Providence in spring 2024, permitted by state legislation. The legality of even these rare sites in the U.S. remains unclear under federal law, according to a 2011 study.
In the face of this uncertain legality, scant evidence from the U.S. is available. One unsanctioned site operating in secrecy was studied by academics. They found that 90% of users reported they would otherwise have been injecting in parks, streets or public restrooms, meaning the site averted over 2,300 public injections and safely disposed of at least 1,700 needles over two years.
Beyond this, policymakers have limited research in the U.S. to draw upon – and so it is informative to look abroad.
Globally, over 100 supervised injection sites are currently operating in 10 countries, including Canada and across Europe. Researchers have looked to experiences in Denmark and Norway, in particular, to study drug consumption rooms. Despite clear differences between Scandinavia and Philadelphia, the research and evidence highlight the potential impact of this form of harm reduction.
The evidence from Norway
In Norway, as in the U.S., harm-reduction efforts first began with opioid substitution therapy, meaning the provision of less dangerous drugs like methadone for opioid users.
When overdose rates kept rising, supervised injection sites where people who use drugs could get clean needles and be observed while using drugs were piloted in 2005 and made permanent by 2009.
The Norwegian Institute of Public Health collected data on the impact of the supervised injection site in Oslo. Just over 150 people used the site in 2005, the first year it opened. Two years later, demand had almost quadrupled. After just six months of operation, staff were recording over 900 injections per month, each diverted from the street. People using the facility told researchers their sense of human dignity improved.
Staff reported that the site allowed them to directly connect more people to social and health services. Other data shows that the presence of the site has reduced the use of ambulances and related public services, preserving those resources for the community.
Striking results in Denmark
The first official Danish supervised injection site opened its doors in Copenhagen in 2012, though underground versions had been operating for a few years.
Since then, several studies have shown the Copenhagen sites not only prevented many drug-related deaths, but improved overall health by successfully connecting people to substance abuse treatment and other health care services.
Staff were also successful at educating people about more hygienic injection techniques, thereby reducing infections and other drug-related complications that often lead to hospitalization. After the sites were opened, fewer people openly used drugs in Copenhagen’s parks and streets. Property values near the injection sites were unaffected.
An evaluation by the Danish Ministry of Health found that the number of needles and syringes discarded in the city’s public spaces was reduced by 70% to 80%, and residents in surrounding neighborhoods said their quality of life improved.
Copenhagen’s experience also highlights the essential fact that supervised injection sites alone aren’t a solution; they are only a part of an effective harm-reduction strategy and must be accompanied by social support and other programming.
For example, the Users’ Academy – or Brugernes Akademi in Danish – is a national nonprofit led by people who use drugs that offers a wide range of harm-reduction services directly to their peers. They run a needle exchange program through the mail and raise awareness regarding the legal rights of people who use drugs. They also operate a mobile health clinic that seeks to prevent diseases like hepatitis C and reduce barriers to health and social services.
An opportunity to investigate
Even in the face of the ongoing controversy in Philadelphia, new ideas are emerging.
Using the infusion of funding from national opioid settlements, Philadelphia could explore more politically acceptable approaches to harm reduction while collecting evidence and building support for a permanent supervised injection site.
In some European cities, mobile supervised injection sites have been adopted first. In Copenhagen, Fixelancen, an old ambulance, has been refurnished as a low-cost supervised injection site. It can service different areas of the city as the drug scene rapidly evolves, avoiding the focus and burden on a particular neighborhood. Such an approach could easily complement other mobile harm-reduction efforts already operating in Philadelphia.
Jannet van der Veen has received income from Brugernes Akademi.
Synøve Nygaard Andersen received funding from The Research Council of Norway (grant #288083).
Jordan Hyatt and Tony Joakim Ananiassen Sandset do not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and have disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
treatment testing therapy canada european europeGovernment
Chinese migration to US is nothing new – but the reasons for recent surge at Southern border are
A gloomier economic outlook in China and tightening state control have combined with the influence of social media in encouraging migration.
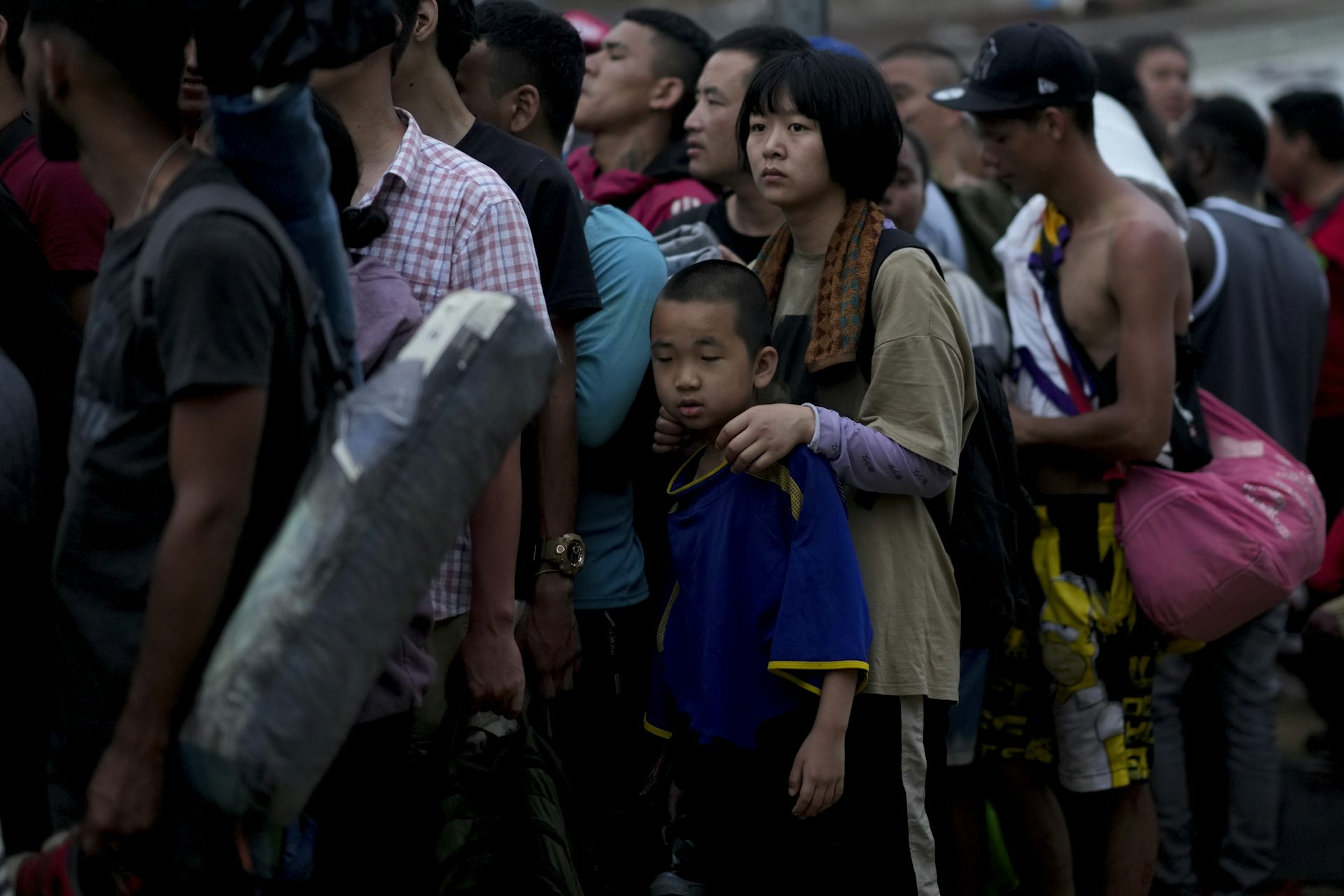

The brief closure of the Darien Gap – a perilous 66-mile jungle journey linking South American and Central America – in February 2024 temporarily halted one of the Western Hemisphere’s busiest migration routes. It also highlighted its importance to a small but growing group of people that depend on that pass to make it to the U.S.: Chinese migrants.
While a record 2.5 million migrants were detained at the United States’ southwestern land border in 2023, only about 37,000 were from China.
I’m a scholar of migration and China. What I find most remarkable in these figures is the speed with which the number of Chinese migrants is growing. Nearly 10 times as many Chinese migrants crossed the southern border in 2023 as in 2022. In December 2023 alone, U.S. Border Patrol officials reported encounters with about 6,000 Chinese migrants, in contrast to the 900 they reported a year earlier in December 2022.
The dramatic uptick is the result of a confluence of factors that range from a slowing Chinese economy and tightening political control by President Xi Jinping to the easy access to online information on Chinese social media about how to make the trip.
Middle-class migrants
Journalists reporting from the border have generalized that Chinese migrants come largely from the self-employed middle class. They are not rich enough to use education or work opportunities as a means of entry, but they can afford to fly across the world.
According to a report from Reuters, in many cases those attempting to make the crossing are small-business owners who saw irreparable damage to their primary or sole source of income due to China’s “zero COVID” policies. The migrants are women, men and, in some cases, children accompanying parents from all over China.
Chinese nationals have long made the journey to the United States seeking economic opportunity or political freedom. Based on recent media interviews with migrants coming by way of South America and the U.S.’s southern border, the increase in numbers seems driven by two factors.
First, the most common path for immigration for Chinese nationals is through a student visa or H1-B visa for skilled workers. But travel restrictions during the early months of the pandemic temporarily stalled migration from China. Immigrant visas are out of reach for many Chinese nationals without family or vocation-based preferences, and tourist visas require a personal interview with a U.S. consulate to gauge the likelihood of the traveler returning to China.
Social media tutorials
Second, with the legal routes for immigration difficult to follow, social media accounts have outlined alternatives for Chinese who feel an urgent need to emigrate. Accounts on Douyin, the TikTok clone available in mainland China, document locations open for visa-free travel by Chinese passport holders. On TikTok itself, migrants could find information on where to cross the border, as well as information about transportation and smugglers, commonly known as “snakeheads,” who are experienced with bringing migrants on the journey north.
With virtual private networks, immigrants can also gather information from U.S. apps such as X, YouTube, Facebook and other sites that are otherwise blocked by Chinese censors.
Inspired by social media posts that both offer practical guides and celebrate the journey, thousands of Chinese migrants have been flying to Ecuador, which allows visa-free travel for Chinese citizens, and then making their way over land to the U.S.-Mexican border.
This journey involves trekking through the Darien Gap, which despite its notoriety as a dangerous crossing has become an increasingly common route for migrants from Venezuela, Colombia and all over the world.
In addition to information about crossing the Darien Gap, these social media posts highlight the best places to cross the border. This has led to a large share of Chinese asylum seekers following the same path to Mexico’s Baja California to cross the border near San Diego.
Chinese migration to US is nothing new
The rapid increase in numbers and the ease of accessing information via social media on their smartphones are new innovations. But there is a longer history of Chinese migration to the U.S. over the southern border – and at the hands of smugglers.
From 1882 to 1943, the United States banned all immigration by male Chinese laborers and most Chinese women. A combination of economic competition and racist concerns about Chinese culture and assimilability ensured that the Chinese would be the first ethnic group to enter the United States illegally.
With legal options for arrival eliminated, some Chinese migrants took advantage of the relative ease of movement between the U.S. and Mexico during those years. While some migrants adopted Mexican names and spoke enough Spanish to pass as migrant workers, others used borrowed identities or paperwork from Chinese people with a right of entry, like U.S.-born citizens. Similarly to what we are seeing today, it was middle- and working-class Chinese who more frequently turned to illegal means. Those with money and education were able to circumvent the law by arriving as students or members of the merchant class, both exceptions to the exclusion law.
Though these Chinese exclusion laws officially ended in 1943, restrictions on migration from Asia continued until Congress revised U.S. immigration law in the Hart-Celler Act in 1965. New priorities for immigrant visas that stressed vocational skills as well as family reunification, alongside then Chinese leader Deng Xiaoping’s policies of “reform and opening,” helped many Chinese migrants make their way legally to the U.S. in the 1980s and 1990s.
Even after the restrictive immigration laws ended, Chinese migrants without the education or family connections often needed for U.S. visas continued to take dangerous routes with the help of “snakeheads.”
One notorious incident occurred in 1993, when a ship called the Golden Venture ran aground near New York, resulting in the drowning deaths of 10 Chinese migrants and the arrest and conviction of the snakeheads attempting to smuggle hundreds of Chinese migrants into the United States.
Existing tensions
Though there is plenty of precedent for Chinese migrants arriving without documentation, Chinese asylum seekers have better odds of success than many of the other migrants making the dangerous journey north.
An estimated 55% of Chinese asylum seekers are successful in making their claims, often citing political oppression and lack of religious freedom in China as motivations. By contrast, only 29% of Venezuelans seeking asylum in the U.S. have their claim granted, and the number is even lower for Colombians, at 19%.
The new halt on the migratory highway from the south has affected thousands of new migrants seeking refuge in the U.S. But the mix of push factors from their home country and encouragement on social media means that Chinese migrants will continue to seek routes to America.
And with both migration and the perceived threat from China likely to be features of the upcoming U.S. election, there is a risk that increased Chinese migration could become politicized, leaning further into existing tensions between Washington and Beijing.
Meredith Oyen does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
congress pandemic deaths south america mexico chinaGovernment
Is the National Guard a solution to school violence?
School board members in one Massachusetts district have called for the National Guard to address student misbehavior. Does their request have merit? A…

Every now and then, an elected official will suggest bringing in the National Guard to deal with violence that seems out of control.
A city council member in Washington suggested doing so in 2023 to combat the city’s rising violence. So did a Pennsylvania representative concerned about violence in Philadelphia in 2022.
In February 2024, officials in Massachusetts requested the National Guard be deployed to a more unexpected location – to a high school.
Brockton High School has been struggling with student fights, drug use and disrespect toward staff. One school staffer said she was trampled by a crowd rushing to see a fight. Many teachers call in sick to work each day, leaving the school understaffed.
As a researcher who studies school discipline, I know Brockton’s situation is part of a national trend of principals and teachers who have been struggling to deal with perceived increases in student misbehavior since the pandemic.
A review of how the National Guard has been deployed to schools in the past shows the guard can provide service to schools in cases of exceptional need. Yet, doing so does not always end well.
How have schools used the National Guard before?
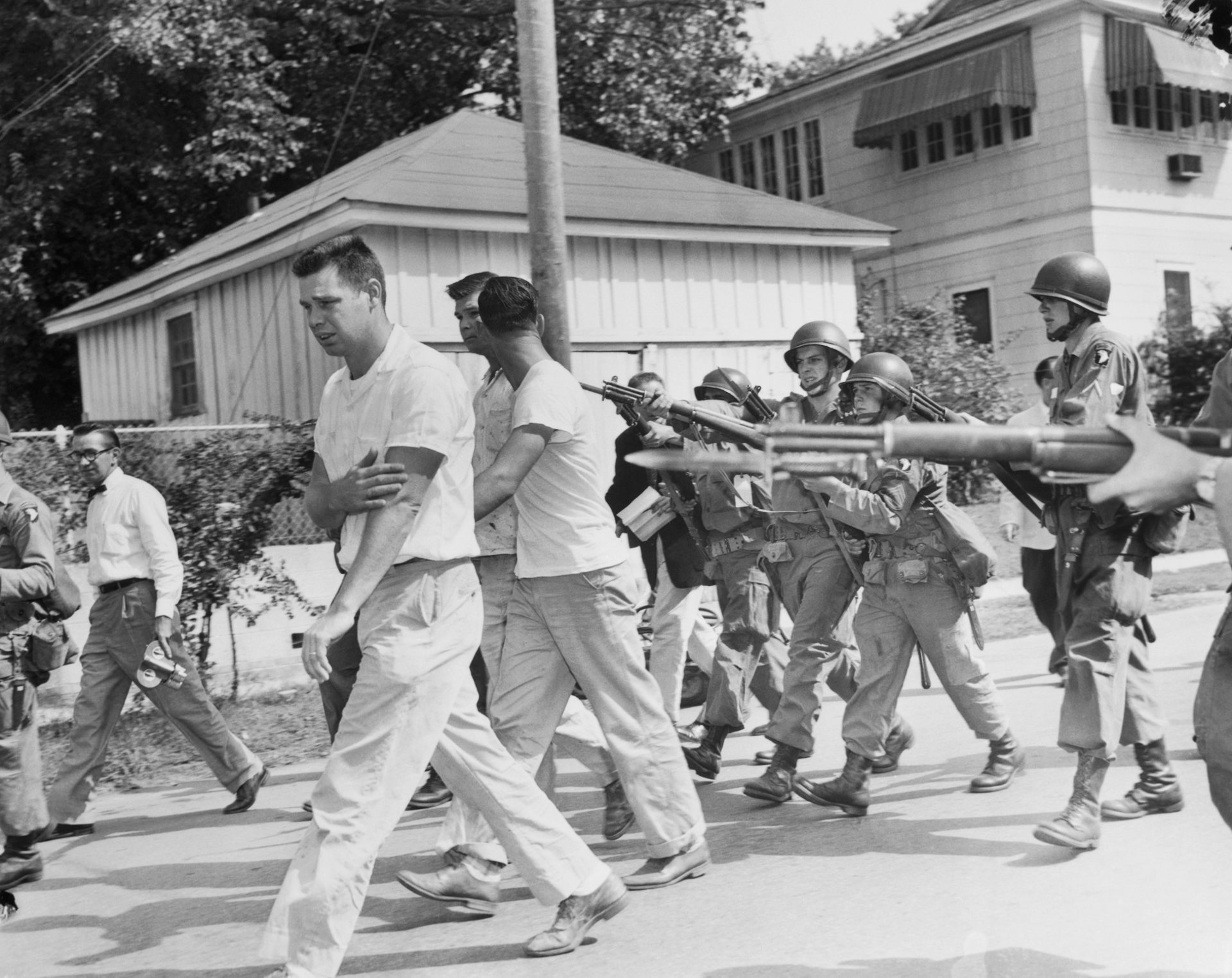
In 1957, the National Guard blocked nine Black students’ attempts to desegregate Central High School in Little Rock, Arkansas. While the governor claimed this was for safety, the National Guard effectively delayed desegregation of the school – as did the mobs of white individuals outside. Ironically, weeks later, the National Guard and the U.S. Army would enforce integration and the safety of the “Little Rock Nine” on orders from President Dwight Eisenhower.
One of the most tragic cases of the National Guard in an educational setting came in 1970 at Kent State University. The National Guard was brought to campus to respond to protests over American involvement in the Vietnam War. The guardsmen fatally shot four students.
In 2012, then-Sen. Barbara Boxer, a Democrat from California, proposed funding to use the National Guard to provide school security in the wake of the Sandy Hook school shooting. The bill was not passed.
More recently, the National Guard filled teacher shortages in New Mexico’s K-12 schools during the quarantines and sickness of the pandemic. While the idea did not catch on nationally, teachers and school personnel in New Mexico generally reported positive experiences.
Can the National Guard address school discipline?
The National Guard’s mission includes responding to domestic emergencies. Members of the guard are part-time service members who maintain civilian lives. Some are students themselves in colleges and universities. Does this mission and training position the National Guard to respond to incidents of student misbehavior and school violence?
On the one hand, New Mexico’s pandemic experience shows the National Guard could be a stopgap to staffing shortages in unusual circumstances. Similarly, the guards’ eventual role in ensuring student safety during school desegregation in Arkansas demonstrates their potential to address exceptional cases in schools, such as racially motivated mob violence. And, of course, many schools have had military personnel teaching and mentoring through Junior ROTC programs for years.
Those seeking to bring the National Guard to Brockton High School have made similar arguments. They note that staffing shortages have contributed to behavior problems.
One school board member stated: “I know that the first thought that comes to mind when you hear ‘National Guard’ is uniform and arms, and that’s not the case. They’re people like us. They’re educated. They’re trained, and we just need their assistance right now. … We need more staff to support our staff and help the students learn (and) have a safe environment.”
Yet, there are reasons to question whether calls for the National Guard are the best way to address school misconduct and behavior. First, the National Guard is a temporary measure that does little to address the underlying causes of student misbehavior and school violence.
Research has shown that students benefit from effective teaching, meaningful and sustained relationships with school personnel and positive school environments. Such educative and supportive environments have been linked to safer schools. National Guard members are not trained as educators or counselors and, as a temporary measure, would not remain in the school to establish durable relationships with students.
What is more, a military presence – particularly if uniformed or armed – may make students feel less welcome at school or escalate situations.
Schools have already seen an increase in militarization. For example, school police departments have gone so far as to acquire grenade launchers and mine-resistant armored vehicles.
Research has found that school police make students more likely to be suspended and to be arrested. Similarly, while a National Guard presence may address misbehavior temporarily, their presence could similarly result in students experiencing punitive or exclusionary responses to behavior.
Students deserve a solution other than the guard
School violence and disruptions are serious problems that can harm students. Unfortunately, schools and educators have increasingly viewed student misbehavior as a problem to be dealt with through suspensions and police involvement.
A number of people – from the NAACP to the local mayor and other members of the school board – have criticized Brockton’s request for the National Guard. Governor Maura Healey has said she will not deploy the guard to the school.
However, the case of Brockton High School points to real needs. Educators there, like in other schools nationally, are facing a tough situation and perceive a lack of support and resources.
Many schools need more teachers and staff. Students need access to mentors and counselors. With these resources, schools can better ensure educators are able to do their jobs without military intervention.
F. Chris Curran has received funding from the US Department of Justice, the Bureau of Justice Assistance, and the American Civil Liberties Union for work on school safety and discipline.
army governor pandemic mexicoInternational
Rand Paul Teases Senate GOP Leader Run – Musk Says “I Would Support”
Rand Paul Teases Senate GOP Leader Run – Musk Says "I Would Support"
Republican Kentucky Senator Rand Paul on Friday hinted that he may jump…

Republican Kentucky Senator Rand Paul on Friday hinted that he may jump into the race to become the next Senate GOP leader, and Elon Musk was quick to support the idea. Republicans must find a successor for periodically malfunctioning Mitch McConnell, who recently announced he'll step down in November, though intending to keep his Senate seat until his term ends in January 2027, when he'd be within weeks of turning 86.
So far, the announced field consists of two quintessential establishment types: John Cornyn of Texas and John Thune of South Dakota. While John Barrasso's name had been thrown around as one of "The Three Johns" considered top contenders, the Wyoming senator on Tuesday said he'll instead seek the number two slot as party whip.
Paul used X to tease his potential bid for the position which -- if the GOP takes back the upper chamber in November -- could graduate from Minority Leader to Majority Leader. He started by telling his 5.1 million followers he'd had lots of people asking him about his interest in running...
Thousands of people have been asking if I'd run for Senate leadership...
— Rand Paul (@RandPaul) March 8, 2024
...then followed up with a poll in which he predictably annihilated Cornyn and Thune, taking a 96% share as of Friday night, with the other two below 2% each.
????????️VOTE NOW ????️ ???? Who would you like to be the next Senate leader?
— Rand Paul (@RandPaul) March 8, 2024
Elon Musk was quick to back the idea of Paul as GOP leader, while daring Cornyn and Thune to follow Paul's lead by throwing their names out for consideration by the Twitter-verse X-verse.
I would support Rand Paul and suspect that other candidates will not actually run polls out of concern for the results, but let’s see if they will!
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 8, 2024
Paul has been a stalwart opponent of security-state mass surveillance, foreign interventionism -- to include shoveling billions of dollars into the proxy war in Ukraine -- and out-of-control spending in general. He demonstrated the latter passion on the Senate floor this week as he ridiculed the latest kick-the-can spending package:
This bill is an insult to the American people. The earmarks are all the wasteful spending that you could ever hope to see, and it should be defeated. Read more: https://t.co/Jt8K5iucA4 pic.twitter.com/I5okd4QgDg
— Senator Rand Paul (@SenRandPaul) March 8, 2024
In February, Paul used Senate rules to force his colleagues into a grueling Super Bowl weekend of votes, as he worked to derail a $95 billion foreign aid bill. "I think we should stay here as long as it takes,” said Paul. “If it takes a week or a month, I’ll force them to stay here to discuss why they think the border of Ukraine is more important than the US border.”
Don't expect a Majority Leader Paul to ditch the filibuster -- he's been a hardy user of the legislative delay tactic. In 2013, he spoke for 13 hours to fight the nomination of John Brennan as CIA director. In 2015, he orated for 10-and-a-half-hours to oppose extension of the Patriot Act.
Among the general public, Paul is probably best known as Capitol Hill's chief tormentor of Dr. Anthony Fauci, who was director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease during the Covid-19 pandemic. Paul says the evidence indicates the virus emerged from China's Wuhan Institute of Virology. He's accused Fauci and other members of the US government public health apparatus of evading questions about their funding of the Chinese lab's "gain of function" research, which takes natural viruses and morphs them into something more dangerous. Paul has pointedly said that Fauci committed perjury in congressional hearings and that he belongs in jail "without question."
Musk is neither the only nor the first noteworthy figure to back Paul for party leader. Just hours after McConnell announced his upcoming step-down from leadership, independent 2024 presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy, Jr voiced his support:
Mitch McConnell, who has served in the Senate for almost 40 years, announced he'll step down this November.
— Robert F. Kennedy Jr (@RobertKennedyJr) February 28, 2024
Part of public service is about knowing when to usher in a new generation. It’s time to promote leaders in Washington, DC who won’t kowtow to the military contractors or…
In a testament to the extent to which the establishment recoils at the libertarian-minded Paul, mainstream media outlets -- which have been quick to report on other developments in the majority leader race -- pretended not to notice that Paul had signaled his interest in the job. More than 24 hours after Paul's test-the-waters tweet-fest began, not a single major outlet had brought it to the attention of their audience.
That may be his strongest endorsement yet.
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex











