Uncategorized
Patient adherence – the key to restoring trust in pharma
Medication is a staple of modern medicine, with almost 50% of adults in the United States taking at
The post Patient adherence – the key to restoring…
Medication is a staple of modern medicine, with almost 50% of adults in the United States taking at least one prescription medication. Despite this, pharmaceutical companies have not won over public trust. A recent study found that only 48% of participants expressed trust in pharmaceutical companies. This lack of trust in such a crucial industry can lead to decreased compliance, poor treatment adherence, and negative health outcomes for patients.
The perceived lack of transparency in the pharmaceutical industry is a major contributor to the overall lack of trust. With the recent rapid rollout of Covid-19 vaccines, many people have raised questions about whether adequate research was conducted on these vaccines before approval. What people did not understand was that “fast tracking” approval does not limit the rigorous process involved in ensuring that a medication or vaccine is safe for market use. Additionally, when patients are prescribed medication, they are often unaware of the mechanism of action, potential side effects, interactions, and contraindications. Even when medical providers communicate this information to patients, it can be confusing or overwhelming, often leaving people feeling like they’ve been left in the dark. This feeling contributes to a deep mistrust in both specific branded medications and the pharmaceutical industry producing those medications.
Another factor that impacts trust in pharmaceutical companies is the discrepancy between the efficacy of medications in controlled clinical trials and their effectiveness in real-world use. This discrepancy can be caused by a variety of factors, however, one of the primary and most solvable ones is patient non-adherence to their medications. There are many reasons for patient non-adherence, including high medication costs, fear of potential side-effects, and forgetfulness, amongst others. However, the result of non-adherence is consistent. When patients do not take their medications according to the prescribed instructions, the drugs will not work as effectively as they did under the controlled conditions of a clinical trial. As patients observe this gap in the efficacy claimed by pharmaceutical companies compared to their personal experiences of lower effectiveness, their trust in specific drugs, clinical trial results, and pharmaceutical companies drops. This ultimately impacts patient perception of healthcare services in general.
Finally, the belief that pharmaceutical companies prioritise their bottom lines over the health and well-being of patients is probably the largest contributing factor to lack of trust in the industry. Given the high price tags placed on many medications, it’s easy to understand why patients often feel that they are being taken advantage of. This is especially understandable if they don’t have the means to pay for essential, potentially life-saving medications. As the relationship between pharmaceutical companies and patients breaks down, and patients feel that the industry is apathetic to their holistic wellbeing, they further disengage from interaction with the entirety of the healthcare ecosystem – including their providers, who prescribe the medications produced by pharmaceutical companies.
Adherence and education solutions – the glue between patient and pharma
In order to restore trust in the pharmaceutical industry, individual companies must invest in solutions that address the patient’s overall health – proving care is extended beyond the business interests of pharmaceutical companies. Patient-first mobile health solutions can help address the various issues that contribute to the lack of trust in the industry and improve the relationship between pharmaceutical companies, prescribers, and patients.
The first issue that adherence and education solutions can address is the perceived lack of transparency from the pharmaceutical industry. Many patient engagement applications have dedicated sections that educate patients about their prescribed medications and treatment protocols, providing them with necessary information about the mechanism of action, potential side effects, and contraindications of their medications. These explanations are provided in layman’s terms, often with videos that ease understanding and acceptability. By investing in patient education, pharmaceutical companies reduce the fear and uncertainty that many people experience when prescribed medication and dispel the perceived lack of transparency in the industry.
Patient engagement solutions can also help reduce the discrepancy between the efficacy of medications in clinical trials and their effectiveness in real-world use. By providing patients with tools and resources to help them better manage their medication regimens, such as reminders and tracking tools, pharmaceutical companies improve patient adherence, and close the gap between efficacy advertised based on clinical trial results, and personal real-world experience with medication effectiveness. As patients experience first-hand the effectiveness reported in clinical trials, trust in the validity of these trials and the intentions of the pharmaceutical companies that fund them improves.
Finally, adherence and education solutions help develop a holistic relationship between patient, provider, and pharma, so patients feel they are fully cared about and not simply walking wallets in the eyes of the pharmaceutical industry. Engagement apps dispel the notion that pharmaceutical companies are only focused on their bottom lines, by providing a source of real value to patients’ everyday lives, making them feel seen and recognised as individuals with unique lifestyles, needs, and treatment journeys. Patients experience a sense that there is a trusted voice that accompanies them, and this establishes a basis for trust and functions as a bridge between pharmaceutical companies and patients themselves.
Where are we going?
The industry is moving in the right direction to restore and strengthen patient trust. As pharmaceutical companies embrace digital solutions that engage patients, we expect to see a boom in patients becoming more empowered partners in managing their conditions (Participatory Health). We envision a future in which treatment will be comprised of a hybrid intervention model, utilising both digital disease management elements and medication elements together, to create better patient care and ultimately improved health outcomes. This dual model will empower patients to become more actively involved in their treatment decisions and will rebuild their trust in the pharmaceutical industry. Patients will live more healthily and take their medications. Pharma’s bottom line will improve. Trust between patients, physician prescribers, and pharmaceutical companies will be re-established. In this future, everyone wins – patients, pharma companies, physicians, and the overall healthcare ecosystem.
About the author
Yossi Bahagon, Chairman of Sweetch, has over 20 years’ experience in digital health. He is the founder of several digital health start-ups. Additionally, Bahagon founded a venture fund dedicated to digital health.
The post Patient adherence – the key to restoring trust in pharma appeared first on .
vaccine treatment clinical trials medication covid-19Uncategorized
Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more
New Zillow research suggests the spring home shopping season may see a second wave this summer if mortgage rates fall
The post Homes listed for sale in…
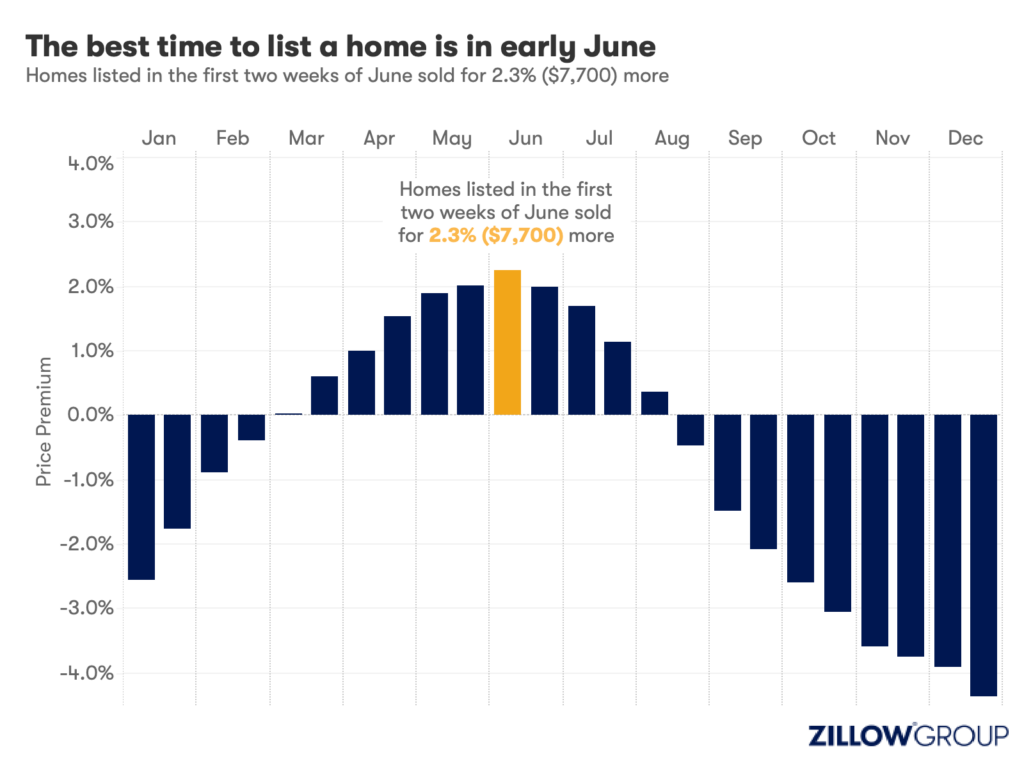
- A Zillow analysis of 2023 home sales finds homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more.
- The best time to list a home for sale is a month later than it was in 2019, likely driven by mortgage rates.
- The best time to list can be as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York and Philadelphia.
Spring home sellers looking to maximize their sale price may want to wait it out and list their home for sale in the first half of June. A new Zillow® analysis of 2023 sales found that homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more, a $7,700 boost on a typical U.S. home.
The best time to list consistently had been early May in the years leading up to the pandemic. The shift to June suggests mortgage rates are strongly influencing demand on top of the usual seasonality that brings buyers to the market in the spring. This home-shopping season is poised to follow a similar pattern as that in 2023, with the potential for a second wave if the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates midyear or later.
The 2.3% sale price premium registered last June followed the first spring in more than 15 years with mortgage rates over 6% on a 30-year fixed-rate loan. The high rates put home buyers on the back foot, and as rates continued upward through May, they were still reassessing and less likely to bid boldly. In June, however, rates pulled back a little from 6.79% to 6.67%, which likely presented an opportunity for determined buyers heading into summer. More buyers understood their market position and could afford to transact, boosting competition and sale prices.
The old logic was that sellers could earn a premium by listing in late spring, when search activity hit its peak. Now, with persistently low inventory, mortgage rate fluctuations make their own seasonality. First-time home buyers who are on the edge of qualifying for a home loan may dip in and out of the market, depending on what’s happening with rates. It is almost certain the Federal Reserve will push back any interest-rate cuts to mid-2024 at the earliest. If mortgage rates follow, that could bring another surge of buyers later this year.
Mortgage rates have been impacting affordability and sale prices since they began rising rapidly two years ago. In 2022, sellers nationwide saw the highest sale premium when they listed their home in late March, right before rates barreled past 5% and continued climbing.
Zillow’s research finds the best time to list can vary widely by metropolitan area. In 2023, it was as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York. Thirty of the top 35 largest metro areas saw for-sale listings command the highest sale prices between May and early July last year.
Zillow also found a wide range in the sale price premiums associated with homes listed during those peak periods. At the hottest time of the year in San Jose, homes sold for 5.5% more, a $88,000 boost on a typical home. Meanwhile, homes in San Antonio sold for 1.9% more during that same time period.
| Metropolitan Area | Best Time to List | Price Premium | Dollar Boost |
| United States | First half of June | 2.3% | $7,700 |
| New York, NY | First half of July | 2.4% | $15,500 |
| Los Angeles, CA | First half of May | 4.1% | $39,300 |
| Chicago, IL | First half of June | 2.8% | $8,800 |
| Dallas, TX | First half of June | 2.5% | $9,200 |
| Houston, TX | Second half of April | 2.0% | $6,200 |
| Washington, DC | Second half of June | 2.2% | $12,700 |
| Philadelphia, PA | First half of July | 2.4% | $8,200 |
| Miami, FL | First half of June | 2.3% | $12,900 |
| Atlanta, GA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $8,700 |
| Boston, MA | Second half of May | 3.5% | $23,600 |
| Phoenix, AZ | First half of June | 3.2% | $14,700 |
| San Francisco, CA | Second half of February | 4.2% | $50,300 |
| Riverside, CA | First half of May | 2.7% | $15,600 |
| Detroit, MI | First half of July | 3.3% | $7,900 |
| Seattle, WA | First half of June | 4.3% | $31,500 |
| Minneapolis, MN | Second half of May | 3.7% | $13,400 |
| San Diego, CA | Second half of April | 3.1% | $29,600 |
| Tampa, FL | Second half of June | 2.1% | $8,000 |
| Denver, CO | Second half of May | 2.9% | $16,900 |
| Baltimore, MD | First half of July | 2.2% | $8,200 |
| St. Louis, MO | First half of June | 2.9% | $7,000 |
| Orlando, FL | First half of June | 2.2% | $8,700 |
| Charlotte, NC | Second half of May | 3.0% | $11,000 |
| San Antonio, TX | First half of June | 1.9% | $5,400 |
| Portland, OR | Second half of April | 2.6% | $14,300 |
| Sacramento, CA | First half of June | 3.2% | $17,900 |
| Pittsburgh, PA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $4,700 |
| Cincinnati, OH | Second half of April | 2.7% | $7,500 |
| Austin, TX | Second half of May | 2.8% | $12,600 |
| Las Vegas, NV | First half of June | 3.4% | $14,600 |
| Kansas City, MO | Second half of May | 2.5% | $7,300 |
| Columbus, OH | Second half of June | 3.3% | $10,400 |
| Indianapolis, IN | First half of July | 3.0% | $8,100 |
| Cleveland, OH | First half of July | 3.4% | $7,400 |
| San Jose, CA | First half of June | 5.5% | $88,400 |
The post Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more appeared first on Zillow Research.
federal reserve pandemic home sales mortgage rates interest ratesUncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemploymentUncategorized
Mortgage rates fall as labor market normalizes
Jobless claims show an expanding economy. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
Everyone was waiting to see if this week’s jobs report would send mortgage rates higher, which is what happened last month. Instead, the 10-year yield had a muted response after the headline number beat estimates, but we have negative job revisions from previous months. The Federal Reserve’s fear of wage growth spiraling out of control hasn’t materialized for over two years now and the unemployment rate ticked up to 3.9%. For now, we can say the labor market isn’t tight anymore, but it’s also not breaking.
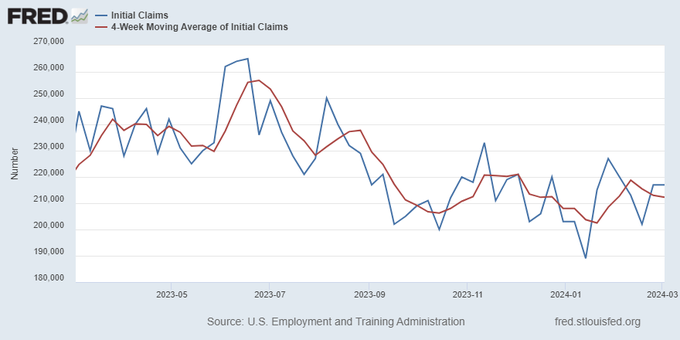
The key labor data line in this expansion is the weekly jobless claims report. Jobless claims show an expanding economy that has not lost jobs yet. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
From the Fed: In the week ended March 2, initial claims for unemployment insurance benefits were flat, at 217,000. The four-week moving average declined slightly by 750, to 212,250
Below is an explanation of how we got here with the labor market, which all started during COVID-19.
1. I wrote the COVID-19 recovery model on April 7, 2020, and retired it on Dec. 9, 2020. By that time, the upfront recovery phase was done, and I needed to model out when we would get the jobs lost back.
2. Early in the labor market recovery, when we saw weaker job reports, I doubled and tripled down on my assertion that job openings would get to 10 million in this recovery. Job openings rose as high as to 12 million and are currently over 9 million. Even with the massive miss on a job report in May 2021, I didn’t waver.
Currently, the jobs openings, quit percentage and hires data are below pre-COVID-19 levels, which means the labor market isn’t as tight as it once was, and this is why the employment cost index has been slowing data to move along the quits percentage.

3. I wrote that we should get back all the jobs lost to COVID-19 by September of 2022. At the time this would be a speedy labor market recovery, and it happened on schedule, too
Total employment data
4. This is the key one for right now: If COVID-19 hadn’t happened, we would have between 157 million and 159 million jobs today, which would have been in line with the job growth rate in February 2020. Today, we are at 157,808,000. This is important because job growth should be cooling down now. We are more in line with where the labor market should be when averaging 140K-165K monthly. So for now, the fact that we aren’t trending between 140K-165K means we still have a bit more recovery kick left before we get down to those levels.

From BLS: Total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 275,000 in February, and the unemployment rate increased to 3.9 percent, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Job gains occurred in health care, in government, in food services and drinking places, in social assistance, and in transportation and warehousing.
Here are the jobs that were created and lost in the previous month:

In this jobs report, the unemployment rate for education levels looks like this:
- Less than a high school diploma: 6.1%
- High school graduate and no college: 4.2%
- Some college or associate degree: 3.1%
- Bachelor’s degree or higher: 2.2%

Today’s report has continued the trend of the labor data beating my expectations, only because I am looking for the jobs data to slow down to a level of 140K-165K, which hasn’t happened yet. I wouldn’t categorize the labor market as being tight anymore because of the quits ratio and the hires data in the job openings report. This also shows itself in the employment cost index as well. These are key data lines for the Fed and the reason we are going to see three rate cuts this year.
recession unemployment covid-19 fed federal reserve mortgage rates recession recovery unemployment-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex



