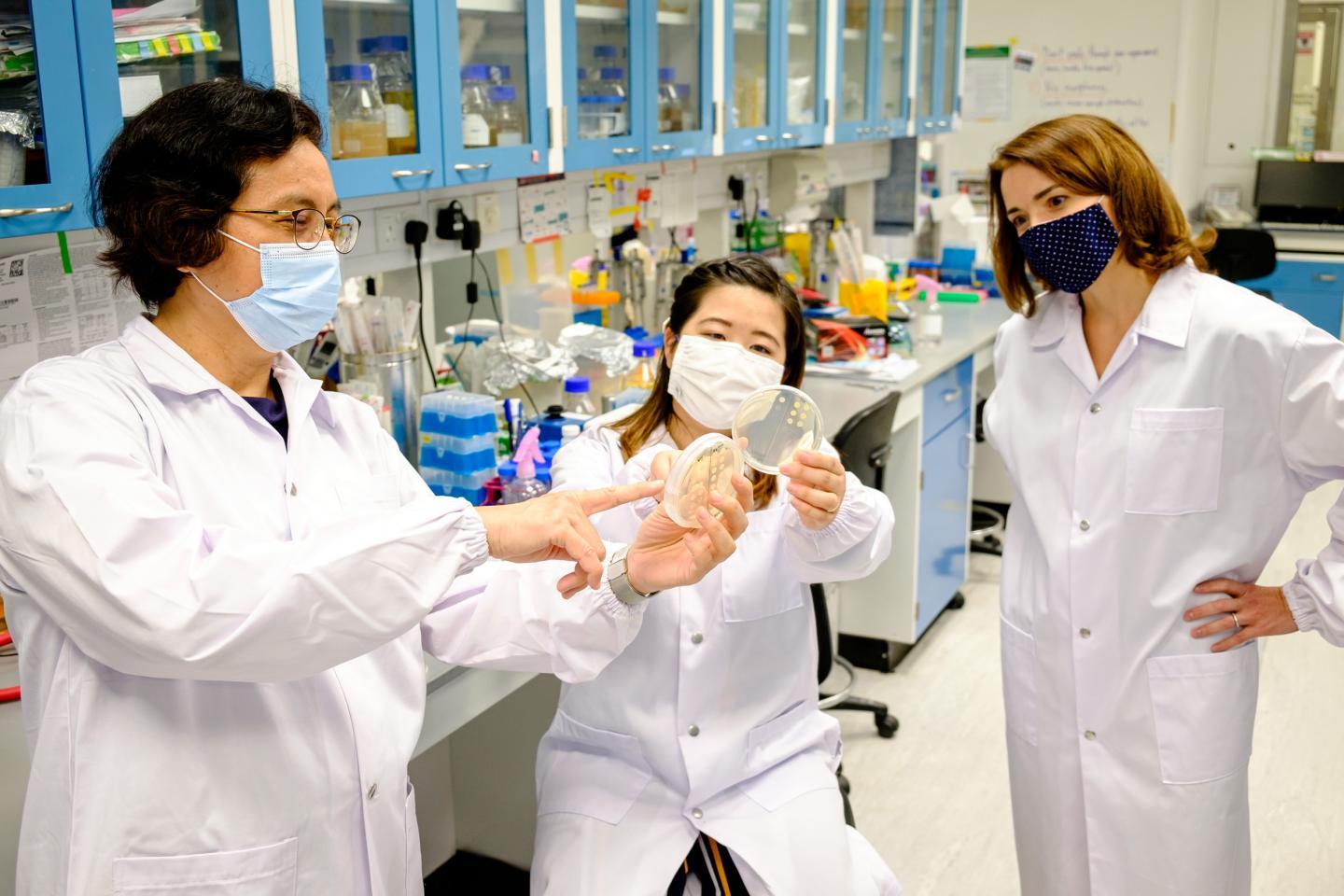
Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have developed a synthetic peptide that can make multidrug-resistant bacteria sensitive to antibiotics again when used together with traditional antibiotics, offering hope for the prospect of a combination treatment strategy to tackle certain antibiotic-tolerant infections.
On its own, the synthetic antimicrobial peptide can also kill bacteria that have grown resistant to antibiotics.
Every year, an estimated 700,000 people globally die of antibiotic-resistant diseases, according to the World Health Organisation. In the absence of new therapeutics, infections caused by resistant superbugs could kill an additional 10 million people each year worldwide by 2050, surpassing cancer[1]. Antibiotic resistance arises in bacteria when they can recognise and prevent drugs that would otherwise kill them, from passing through their cell wall.
This threat is accelerated by the developing COVID-19 pandemic, with patients admitted to hospitals often receiving antibiotics to keep secondary bacterial infections in check, amplifying the opportunity for resistant pathogens to emerge and spread[2].
The NTU Singapore team, led by Associate Professor Kimberly Kline and Professor Mary Chan, developed an antimicrobial peptide known as CSM5-K5 comprising repeated units of chitosan, a sugar found in crustacean shells that bears structural resemblance to the bacterial cell wall, and repeated units of the amino acid lysine.
The scientists believe that chitosan’s structural similarity to the bacterial cell wall helps the peptide interact with and embed itself in it, causing defects in the wall and membrane that eventually kill the bacteria.
The team tested the peptide on biofilms, which are slimy coats of bacteria that can cling onto surfaces such as living tissues or medical devices in hospitals, and which are difficult for traditional antibiotics to penetrate.
In both preformed biofilms in the lab and biofilms formed on wounds in mice, the NTU-developed peptide killed at least 90 per cent of the bacteria strains in four to five hours.
In separate experiments, when CSM5-K5 was used with antibiotics that the bacteria are otherwise resistant to, more bacteria was killed off as compared to when CSM5-K5 was used alone, suggesting that the peptide rendered the bacteria susceptible to antibiotics. The amount of antibiotics used in this combination therapy was also at a concentration lower than what is commonly prescribed.
The findings were published in the scientific journal ACS Infectious Diseases in May.
Assoc Prof Kimberly Kline, a Principal Investigator at the Singapore Centre for Environmental Life Sciences Engineering (SCELSE) at NTU, said: “Our findings show that our antimicrobial peptide is effective whether used alone or in combination with conventional antibiotics to fight multidrug-resistant bacteria. Its potency increases when used with antibiotics, restoring the bacteria’s sensitivity to drugs again. More importantly, we found that the bacteria we tested developed little to no resistance against our peptide, making it an effective and feasible addition to antibiotics as a viable combination treatment strategy as the world grapples with rising antibiotic resistance.”
Prof Mary Chan, director of NTU’s Centre of Antimicrobial Bioengineering, said: “While efforts are focussed on dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic, we should also remember that antibiotic resistance continues to be a growing problem, where secondary bacterial infections that develop in patients could complicate matters, posing a threat in the healthcare settings. For instance, viral respiratory infections could allow bacteria to enter the lungs more easily, leading to bacterial pneumonia, which is commonly associated with COVID-19.”
How the antimicrobial peptide works
Antimicrobial peptides, which carry a positive electric charge, typically work by binding to the negatively-charged bacterial membranes, disrupting the membrane and causing the bacteria to die eventually. The more positively charged a peptide is, the more efficient it is in binding to bacteria and thus killing them.
However, the peptide’s toxicity to the host also increases in line with the peptide’s positive charge – it damages the host organism’s cells as it kills bacteria. As a result, engineered antimicrobial peptides to date have met with limited success, said Assoc Prof Kline, who is also from the NTU School of Biological Sciences.
The peptide designed by the NTU team, called CSM5-K5, is able to cluster together to form nanoparticles when it is applied to bacteria biofilms. This clustering results in a more concentrated disruptive effect on the bacterial cell wall when compared to the activity of single chains of peptides, meaning it has high antibacterial activity but without causing undue damage to healthy cells (See Image 1 in Note to Editors).
To examine CSM5-K5’s efficacy on its own, the NTU scientists developed separate biofilms comprising methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, commonly known as the MRSA superbug; a highly virulent multidrug-resistant strain of Escherichia coli (MDR E. Coli); and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE). MRSA and VRE are classified as serious threats by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention[3].
In lab experiments, CSM5-K5 killed more than 99 per cent of the biofilm bacteria after four hours of treatment. In infected wounds on mice, the NTU-developed antimicrobial peptide killed more than 90 per cent of the bacteria.
When CSM5-K5 was used with conventional antibiotics, the NTU team found that the combination approach led to a further reduction in the bacteria in both lab-formed biofilms and infected wounds in mice as compared to when only CSM5-K5 was used, suggesting that the antimicrobial peptide made the bacteria sensitive to the drugs they would otherwise be resistant to.
More importantly, the NTU team found that the three strains of bacteria studied (MRSA, VRE and MDR E. coli) developed little to no resistance against CSM5-K5. While MRSA developed low-level resistance against CSM5-K5, this made MRSA more sensitive to the drug it is otherwise resistant to.
Prof Chan said: “Developing new drugs alone is no longer sufficient to fight difficult-to-treat bacterial infections, as bacteria continue to evolve and outsmart antibiotics/ It is important to look at innovative ways to tackle difficult-to-treat bacterial infections associated with antibiotic resistance and biofilms, such as tackling the bacteria’s defence mechanisms. A more effective and economic method to fight bacteria is through a combination therapy approach like ours.”
The next step forward for the team is to explore how such a combination therapy approach can be used for rare diseases or for wound dressing.
###
The research on the CSM5-K5 antimicrobial peptide was funded by NTU, the National Research Foundation, the Ministry of Education, and the Ministry of Health.
Note to Editors:
Paper ‘Combined Efficacy of an Antimicrobial Cationic Peptide Polymer With Conventional Antibiotics to Combat Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens’ published in ACS infectious diseases, 6(5), 1228-1237.
DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00016
Media contact:
Foo Jie Ying
Manager, Corporate Communications Office
Nanyang Technological University
Email: jieying@ntu.edu.sg
About Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
A research-intensive public university, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has 33,000 undergraduate and postgraduate students in the Engineering, Business, Science, Humanities, Arts, & Social Sciences, and Graduate colleges. It also has a medical school, the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, set up jointly with Imperial College London.
NTU is also home to world-class autonomous institutes – the National Institute of Education, S Rajaratnam School of International Studies, Earth Observatory of Singapore, and Singapore Centre for Environmental Life Sciences Engineering – and various leading research centres such as the Nanyang Environment & Water Research Institute (NEWRI) and Energy Research Institute @ NTU (ERI@N).
Ranked amongst the world’s top universities by QS, NTU has also been named the world’s top young university for the past seven years. The University’s main campus is frequently listed among the Top 15 most beautiful university campuses in the world and it has 57 Green Mark-certified (equivalent to LEED-certified) building projects, of which 95% are certified Green Mark Platinum. Apart from its main campus, NTU also has a campus in Singapore’s healthcare district.
For more information, visit http://www.