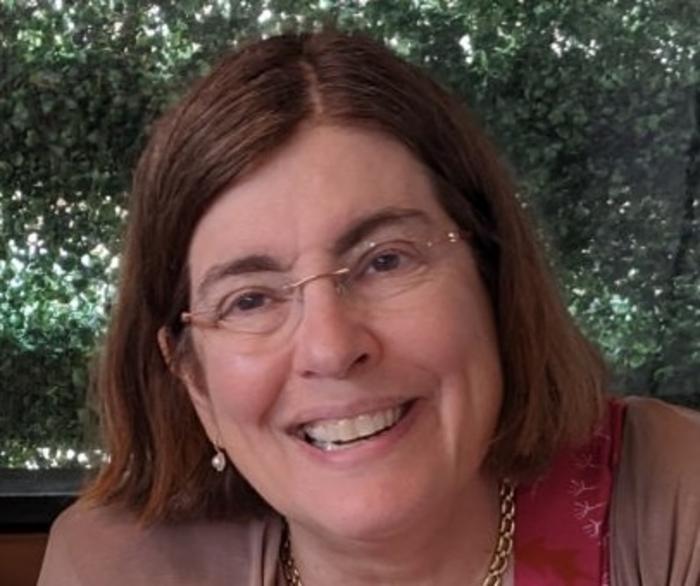
The Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) has appointed Etta D. Pisano, MD, FACR, senior portfolio lead, to build the agency’s clinical trial portfolio and lead the ARPA-H Advancing Clinical Trials Readiness Initiative under ARPA-H Resilient Systems Mission Office Director Jennifer Roberts.
The first radiologist to be appointed to such a role, Dr. Pisano is an internationally recognized expert in women’s health, breast cancer research, and the use of artificial intelligence in medical imaging applications.
“I am honored to be working for ARPA-H to identify and promote research that can improve healthcare quality, efficacy and delivery, and to improve patient care and access to clinical trials for all Americans, including women, rural residents, and the underserved,” said Dr. Pisano.
Dr. Pisano will continue to serve as study chair of the large-scale Tomosynthesis Mammographic Imaging Screening Trial (TMIST) for the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN). TMIST is led by ECOG-ACRIN with funding from the National Cancer Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health. She will also continue to serve as the American College of Radiology® (ACR®) Chief Research Officer (CRO). Dr. Pisano previously served as the principal investigator of the landmark Digital Mammographic Imaging Screening Trial (DMIST).
The TMIST breast cancer screening study is among the fastest growing National Cancer Institute (NCI) trials of the COVID-19 era. Under Dr. Pisano’s leadership, TMIST is assembling one of the most diverse cancer screening trial populations ever. Approximately 21% of TMIST U.S. participants are Black—more than double the average rate for Black participation in NCI-funded clinical trials (9%).
With ARPA-H, Dr. Pisano will work to build underserved and minority participation in clinical trials—including identifying and onboarding rural facilities and those outside of large academic medical centers—such as emerging retail healthcare sites.
These duties are also very consistent with the missions of ECOG-ACRIN and ACR, which include promoting the exploration and identification of next-generation technologies that can benefit patients and providers.
“This is a great opportunity for Etta, and I’m excited about the impact she will make on our approach to clinical trials,” said Mitchell D. Schnall, MD, PhD, group co-chair of ECOG-ACRIN.
About ECOG-ACRIN
The ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) is an expansive membership-based scientific organization that designs and conducts cancer research involving adults who have or are at risk of developing cancer. The Group comprises nearly 1400 member institutions and 21,000 research professionals in the United States and around the world. ECOG-ACRIN is known for advancing precision medicine and biomarker research through its leadership of major national clinical trials integrating cutting-edge genomic approaches. Member researchers and advocates collaborate across more than 40 scientific committees to design studies spanning the cancer care spectrum, from early detection to management of advanced disease. ECOG-ACRIN is funded primarily by the National Cancer Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health. Visit ecog-acrin.org, and follow us on X @eaonc, Facebook, LinkedIn, and Instagram.
Media Contact: Diane Dragaud, Director of Communications, communications@ecog-acrin.org.