Low-volatility equities under COVID-19
Low-volatility equities under COVID-19
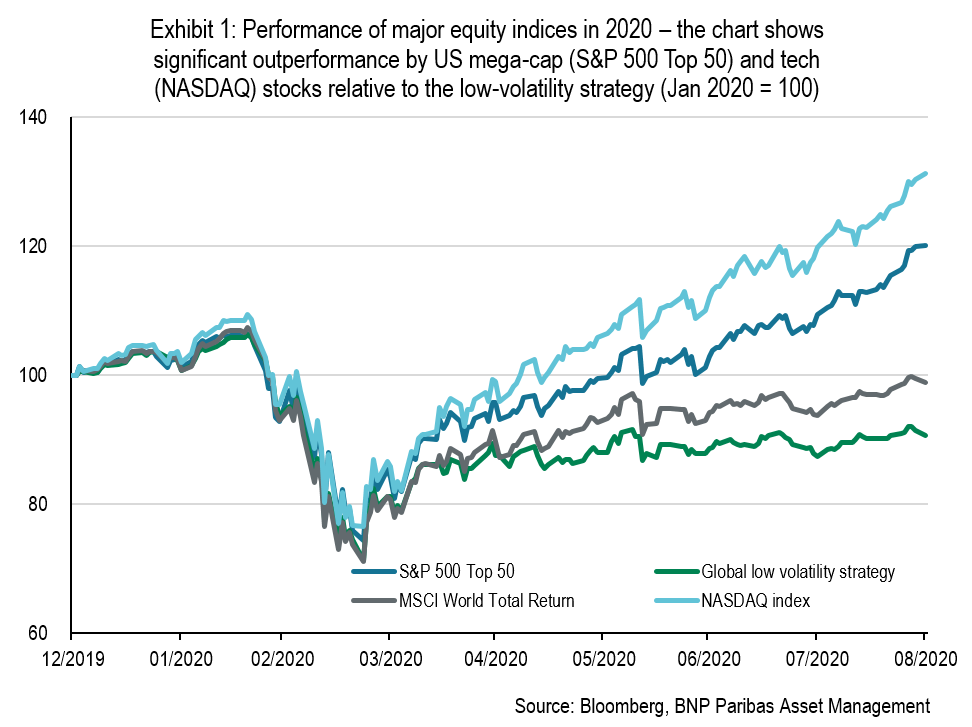
Many investors consider low-volatility stocks to be reliable defensive equity investments over the long term, delivering higher risk-adjusted returns than traditional market capitalisation indices.
However, in the short term, low-volatility strategies may encounter drawdowns, especially during periods of strong market rebounds and/or exceptional market conditions such as those seen since the start of the 2020 coronavirus crisis.
Why did low-volatility stocks underperform in 2020?
Movements in stock market indices have resembled a roller coaster this year. The first quarter saw the fastest market corrections in history: a -33.9% drawdown in the US S&P 500 index in just 23 days, and a -38.3% drawdown in the EuroSTOXX 50.
This was followed by an impressive rebound from April through August, bringing markets back to their highest levels ever (for the S&P 500, Dow Jones and NASDAQ indices).
With two thirds of the year behind us, we have seen two distinct periods:
- A risk-off environment in the first quarter as the COVID-19 pandemic triggered a shock with unprecedented consequences for the global economy
- An exceptional equity market recovery fuelled by highly accommodative central bank policies in the form of signficant injections of liquidity.
During the second phase, the market bounce was almost as rapid as the correction: Between April and August, the market rebounded by more than 50% (S&P 500 and MSCI World), led by the US information technology sector.
Challenging conditions for low-vol stocks
This context was challenging for low-volatility stocks. In the first quarter, they did relatively well thanks to their defensive characteristics. Their outperformance relative to market cap indices during the quarter was mainly due to their lower beta.
However, the alpha of low-volatility stocks was negative: the most defensive stocks, those with prudent business models and a low-volatility profile, were hit hard by the locking down of economies and the severe curtailment of economic activity.
We notably observed a short-term re-risking of defensive stocks and a high correlation between them, driving most defensive stocks to an unusual underperformance.

During the second phase, low-volatility stocks suffered from both their lower beta and a negative alpha. As global indices rebounded sharply, lower beta equity strategies delivered a lower performance and the alpha of low-volatility stocks was negative.
Equity indices were catapulted higher by high-beta, highly volatile stocks which rebounded very strongly from the lows. Given their notable presence in equity indices, the rebound was predominantly driven by US mega-cap and IT shares, which are typically not low-volatility stocks.[1]
Does the low-volatility anomaly belong to the past?
Our research leads us to believe that this is definitely the wrong conclusion to draw from recent events. Haugen & Heins first demonstrated the volatility anomaly in the 1970s in their renowned paper “On the Evidence Supporting the Existence of Risk Premiums in the Capital Market”. Since then, academic researchers have demonstrated that low-volatility anomaly works across regions, in emerging markets, through time, within equity sectors and even in other financial markets.
More recently, as our low-volatility strategy celebrated its 10th birthday, the Quantitative Research Group took the opportunity to run an out-of-sample test over this period. The results were decisive, providing evidence that the anomaly is even stronger. This paper shows that the low-volatility anomaly has not been arbitraged away.
Predicting the returns of low-volatility portfolios over short horizons, e.g. over a month or a quarter, is impossible, even assuming that portfolio constraints have no impact and that the portfolio is well balanced. Due to their defensive beta, we can say that low-volatility stock portfolios are likely to outperform the market capitalisation index when market returns are negative, but it is not certain they will.
Even if the alpha of low-volatility stocks is on average positive over the medium and long term – which explains their higher Sharpe ratios – a market fall may lead to underperformance.
Similarly, episodes of outperformance of low-volatility stock portfolios even when the market rises, as explained by the positive alpha of low-volatility stocks, should not be a surprise.
Robust alpha across cycles
Using a long-term simulation on the global equity universe, exhibit 2 shows that the low-volatility alpha has been robust since 1995. However, this solid spell was interrupted on three occasions: during the dot-com crisis of 1998-2002, the Great Financial Crisis of 2007-2009 and the COVID-19-crisis of 2020.
Each of these setbacks occurred after the low-volatility alpha had outperformed its historical trend over the preceding years. This suggests that such painful phases for investors might be seen as normalisation periods toward the long-term trend of the low-volatility alpha, which is only observed with hindsight.

Investors should be aware that the magnitude of the recent alpha underperformance is unfortunately not unprecedented. As suggested by exhibit 3, the drawdown of the low-volatility factor is similar to that of the tech bubble of 2000, but lower than in 2009, at the end of the Great Financial Crisis.

As such, the recent extraordinary 2020 COVID-19 related sell-off and rebound should not be regarded as marking the end of the low-volatility anomaly, but rather be considered as a one-off accident, unpredictable and exceptional in nature on a long-term profitable journey.
Take a long view on low-vol stocks
Investors should consider the benefits of low-volatility strategies over the long term. Rather than chasing short-term performance, we advocate long-term discipline that brings the power of compounding.
2020 is in many respects an exceptional year and one should not draw conclusions based on short-term unpredictable events.
Our quantitative research and investment teams continue to manage and improve our low-volatility strategies to deliver, over the long term, higher risk-adjusted returns than traditional market cap indices.
Any views expressed here are those of the author as of the date of publication, are based on available information, and are subject to change without notice. Individual portfolio management teams may hold different views and may take different investment decisions for different clients. This document does not constitute investment advice.
The value of investments and the income they generate may go down as well as up and it is possible that investors will not recover their initial outlay. Past performance is no guarantee for future returns.
Investing in emerging markets, or specialised or restricted sectors is likely to be subject to a higher-than-average volatility due to a high degree of concentration, greater uncertainty because less information is available, there is less liquidity or due to greater sensitivity to changes in market conditions (social, political and economic conditions).
Some emerging markets offer less security than the majority of international developed markets. For this reason, services for portfolio transactions, liquidation and conservation on behalf of funds invested in emerging markets may carry greater risk.
[1] The market capitalisation of the top-performing stocks is one of the highest ever seen in equity market history (22.6% of the S&P 500 market capitalisation is concentrated in five companies and 14.1% for the MSCI World; as of 31/07/2020).
Writen by Gregory Taïeb. The post Low-volatility equities under COVID-19 appeared first on Investors' Corner - The official blog of BNP Paribas Asset Management.
Government
Supreme Court Rules Public Officials May Block Their Constituents On Social Media
Supreme Court Rules Public Officials May Block Their Constituents On Social Media
Authored by Matthew Vadum via The Epoch Times (emphasis…

Authored by Matthew Vadum via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
Public officials may block people on social media in certain situations, the Supreme Court ruled unanimously on March 15.
At the same time, the court held that public officials who post about topics pertaining to their work on their personal social media accounts are acting on behalf of the government. But such officials can be found liable for violating the First Amendment only when they have been properly authorized by the government to communicate on its behalf.
The case is important because nowadays public officials routinely reach out to voters through social media on the same pages where they discuss personal matters unrelated to government business.
“When a government official posts about job-related topics on social media, it can be difficult to tell whether the speech is official or private,” Justice Amy Coney Barrett wrote for the nation’s highest court.
The case is separate from but brings to mind a lawsuit that several individuals previously filed against former President Donald Trump after he blocked them from accessing his social media account on Twitter, which was later renamed X. The Supreme Court dismissed that case, Biden v. Knight First Amendment Institute, in April 2021 as moot because President Trump had already left office.
At the time of the ruling, the then-Twitter had banned President Trump. When Elon Musk took over the company he reversed that policy.
The new decision in Lindke v. Freed was written by Justice Amy Coney Barrett.
Respondent James Freed, the city manager of Port Huron, Michigan, used a public Facebook account to communicate with his constituents. Petitioner Kevin Lindke, a resident of Port Huron, criticized the municipality’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic, including accusations of hypocrisy by local officials.
Mr. Freed blocked Mr. Lindke and others and removed their comments, according to Mr. Lindke’s petition.
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the 6th Circuit ruled for Mr. Freed, finding that he was acting only in a personal capacity and that his activities did not constitute governmental action.
Mr. Freed’s attorney, Victoria Ferres, said during oral arguments before the Supreme Court on Oct. 31, 2023, that her client didn’t give up his rights when using social media.
“This country’s 21 million government employees should have the right to talk publicly about their jobs on personal social media accounts like their private-sector counterparts.”
The position advocated by the other side would unfairly punish government officials, and “will result in uncertainty and self-censorship for this country’s government employees despite this Court repeatedly finding that government employees do not lose their rights merely by virtue of public employment,” she said.
In Lindke v. Freed, the Supreme Court found that a public official who prevents a person from comments on the official’s social media pages engages in governmental action under Section 1983 only if the official had “actual authority” to speak on the government’s behalf on a specific matter and if the official claimed to exercise that authority when speaking in the relevant social media posts.
Section 1983 refers to Title 42, U.S. Code, Section 1983, which allows people to sue government actors for deprivation of civil rights.
Justice Barrett wrote that according to the so-called state action doctrine, the test for “actual authority” must be “rooted in written law or longstanding custom to speak for the State.”
“That authority must extend to speech of the sort that caused the alleged rights deprivation. If the plaintiff cannot make this threshold showing of authority, he cannot establish state action.”
“For social-media activity to constitute state action, an official must not only have state authority—he must also purport to use it,” the justice continued.
“State officials have a choice about the capacity in which they choose to speak.”
Citing previous precedent, Justice Barrett wrote that generally a public employee claiming to speak on behalf of the government acts with state authority when he speaks “in his official capacity or” when he uses his speech to carry out “his responsibilities pursuant to state law.”
“If the public employee does not use his speech in furtherance of his official responsibilities, he is speaking in his own voice.”
The Supreme Court remanded the case to the 6th Circuit with instructions to vacate its judgment and ordered it to conduct “further proceedings consistent with this opinion.”
Also on March 15, the Supreme Court ruled on O’Connor-Ratcliff v. Garnier, a related case. The court’s sparse, unanimous opinion was unsigned.
Petitioners Michelle O’Connor-Ratcliff and T.J. Zane were two elected members of the Poway Unified School District Board of Trustees in California who used their personal Facebook and Twitter accounts to communicate with the public.
Respondents Christopher Garnier and Kimberly Garnier, parents of local students, “spammed Petitioners’ posts and tweets with repetitive comments and replies” so the school board members blocked the respondents from the accounts, according to the petition filed by Ms. O’Connor-Ratcliff and Mr. Zane.
But the Garniers said they were acting in good faith.
“The Garniers left comments exposing financial mismanagement by the former superintendent as well as incidents of racism,” the couple said in a brief.
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the 9th Circuit found in favor of the Garniers, holding that elected officials using social media accounts were participating in a public forum.
The Supreme Court ruled in a three-page opinion that because the 9th Circuit deviated from the standard the high court articulated in Lindke v. Freed, the 9th Circuit’s decision must be vacated.
The case was remanded to the 9th Circuit “for further proceedings consistent with our opinion” in the Lindke case, the Supreme Court stated.
International
Home buyers must now navigate higher mortgage rates and prices
Rates under 4% came and went during the Covid pandemic, but home prices soared. Here’s what buyers and sellers face as the housing season ramps up.

Springtime is spreading across the country. You can see it as daffodil, camellia, tulip and other blossoms start to emerge.
You can also see it in the increasing number of for sale signs popping up in front of homes, along with the painting, gardening and general sprucing up as buyers get ready to sell.
Which leads to two questions:
- How is the real estate market this spring?
- Where are mortgage rates?
What buyers and sellers face
The housing market is bedeviled with supply shortages, high prices and slow sales.
Mortgage rates are still high and may limit what a buyer can offer and a seller can expect.
Related: Analyst warns that a TikTok ban could lead to major trouble for Apple, Big Tech
And there's a factor not expected that may affect the sales process. Fixed commission rates on home sales are going away in July.
Reports this week and in a week will make the situation clearer for buyers and sellers.
The reports are:
- Housing starts from the U.S. Commerce Department due Tuesday. The consensus estimate is for a seasonally adjusted rate of about 1.4 million homes. These would include apartments, both rentals and condominiums.
- Existing home sales, due Thursday from the National Association of Realtors. The consensus estimate is for a seasonally adjusted sales rate of about 4 million homes. In 2023, some 4.1 million homes were sold, the worst sales rate since 1995.
- New-home sales and prices, due Monday from the Commerce Department. Analysts are expecting a sales rate of 661,000 homes (including condos), up 1.5% from a year ago.
Here is what buyers and sellers need to know about the situation.
Mortgage rates will stay above 5%
That's what most analysts believe. Right now, the rate on a 30-year mortgage is between 6.7% and 7%.
Rates peaked at 8% in October after the Federal Reserve signaled it was done raising interest rates.
The Freddie Mac Primary Mortgage Market Survey of March 14 was at 6.74%.
Freddie Mac buys mortgages from lenders and sells securities to investors. The effect is to replenish lenders' cash levels to make more loans.
A hotter-than-expected Producer Price Index released that day has pushed quotes to 7% or higher, according to data from Mortgage News Daily, which tracks mortgage markets.
TheStreet
On a median-priced home (price: $380,000) and a 20% down payment, that means a principal and interest rate payment of $2,022. The payment does not include taxes and insurance.
Last fall when the 30-year rate hit 8%, the payment would have been $2,230.
In 2021, the average rate was 2.96%, which translated into a payment of $1,275.
Short of a depression, that's a rate that won't happen in most of our lifetimes.
Most economists believe current rates will fall to around 6.3% by the end of the year, maybe lower, depending on how many times the Federal Reserve cuts rates this year.
If 6%, the payment on our median-priced home is $1,823.
But under 5%, absent a nasty recession, fuhgettaboutit.
Supply will be tight, keeping prices up
Two factors are affecting the supply of homes for sale in just about every market.
First: Homeowners who had been able to land a mortgage at 2.96% are very reluctant to sell because they would then have to find a home they could afford with, probably, a higher-cost mortgage.
More economic news:
- Fed members just hat-tipped what's next for interest rates
- Retail sales tumble clouds impact of inflation data
- Jobs report shocker: 353,000 hires crush forecasts, stokes inflation fears
Second, the combination of high prices and high mortgage rates are freezing out thousands of potential buyers, especially those looking for homes in lower price ranges.
Indeed, The Wall Street Journal noted that online brokerage Redfin said only about 20% of homes for sale in February were affordable for the typical household.
And here mortgage rates can play one last nasty trick. If rates fall, that means a buyer can afford to pay more. Sellers and their real-estate agents know this too, and may ask for a higher price.
Covid's last laugh: An inflation surge
Mortgage rates jumped to 8% or higher because since 2022 the Federal Reserve has been fighting to knock inflation down to 2% a year. Raising interest rates was the ammunition to battle rising prices.
In June 2022, the consumer price index was 9.1% higher than a year earlier.
The causes of the worst inflation since the 1970s were:
- Covid-19 pandemic, which caused the global economy to shut down in 2020. When Covid ebbed and people got back to living their lives, getting global supply chains back to normal operation proved difficult.
- Oil prices jumped to record levels because of the recovery from the pandemic recovery and Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
What the changes in commissions means
The long-standing practice of paying real-estate agents will be retired this summer, after the National Association of Realtors settled a long and bitter legal fight.
No longer will the seller necessarily pay 6% of the sale price to split between buyer and seller agents.
Both sellers and buyers will have to negotiate separately the services agents have charged for 100 years or more. These include pre-screening properties, writing sales contracts, and the like. The change will continue a trend of adding costs and complications to the process of buying or selling a home.
Already, interest rates are a complication. In addition, homeowners insurance has become very pricey, especially in communities vulnerable to hurricanes, tornadoes, and forest fires. Florida homeowners have seen premiums jump more than 102% in the last three years. A policy now costs three times more than the national average.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
recession depression pandemic covid-19 stocks fed federal reserve home sales mortgage rates real estate mortgages housing market recovery interest rates oil russia ukraine
Uncategorized
Default: San Francisco Four Seasons Hotel Investors $3 Million Late On Loan As Foreclosure Looms
Default: San Francisco Four Seasons Hotel Investors $3 Million Late On Loan As Foreclosure Looms
Westbrook Partners, which acquired the San…

Westbrook Partners, which acquired the San Francisco Four Seasons luxury hotel building, has been served a notice of default, as the developer has failed to make its monthly loan payment since December, and is currently behind by more than $3 million, the San Francisco Business Times reports.
Westbrook, which acquired the property at 345 California Center in 2019, has 90 days to bring their account current with its lender or face foreclosure.
Related
- Fed Fears "Notable" Financial System Vulnerability As Renowned CRE Investor Tells Team 'Stop All NYC Underwriting'
- The State Of Commercial Real Estate, In Charts
- "Who Could Be Next": Top Canadian Pension Fund Sells Manhattan Office Tower For $1, Sparking Firesale Panic
- "Heightened Risks": Goldman Points To Leading CRE Indicator That Shows Pain Train Not Over
As SF Gate notes, downtown San Francisco hotel investors have had a terrible few years - with interest rates higher than their pre-pandemic levels, and local tourism continuing to suffer thanks to the city's legendary mismanagement that has resulted in overlapping drug, crime, and homelessness crises (which SF Gate characterizes as "a negative media narrative).
Last summer, the owner of San Francisco’s Hilton Union Square and Parc 55 hotels abandoned its loan in the first major default. Industry insiders speculate that loan defaults like this may become more common given the difficult period for investors.
At a visitor impact summit in August, a senior director of hospitality analytics for the CoStar Group reported that there are 22 active commercial mortgage-backed securities loans for hotels in San Francisco maturing in the next two years. Of these hotel loans, 17 are on CoStar’s “watchlist,” as they are at a higher risk of default, the analyst said. -SF Gate
The 155-room Four Seasons San Francisco at Embarcadero currenly occupies the top 11 floors of the iconic skyscrper. After slow renovations, the hotel officially reopened in the summer of 2021.
"Regarding the landscape of the hotel community in San Francisco, the short term is a challenging situation due to high interest rates, fewer guests compared to pre-pandemic and the relatively high costs attached with doing business here," Alex Bastian, President and CEO of the Hotel Council of San Francisco, told SFGATE.
Heightened Risks
In January, the owner of the Hilton Financial District at 750 Kearny St. - Portsmouth Square's affiliate Justice Operating Company - defaulted on the property, which had a $97 million loan on the 544-room hotel taken out in 2013. The company says it proposed a loan modification agreement which was under review by the servicer, LNR Partners.
Meanwhile last year Park Hotels & Resorts gave up ownership of two properties, Parc 55 and Hilton Union Square - which were transferred to a receiver that assumed management.
In the third quarter of 2023, the most recent data available, the Hilton Financial District reported $11.1 million in revenue, down from $12.3 million from the third quarter of 2022. The hotel had a net operating loss of $1.56 million in the most recent third quarter.
Occupancy fell to 88% with an average daily rate of $218 in the third quarter compared with 94% and $230 in the same period of 2022. -SF Chronicle
According to the Chronicle, San Francisco's 2024 convention calendar is lighter than it was last year - in part due to key events leaving the city for cheaper, less crime-ridden places like Las Vegas.
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Spread & Containment5 days ago
Spread & Containment5 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex



















