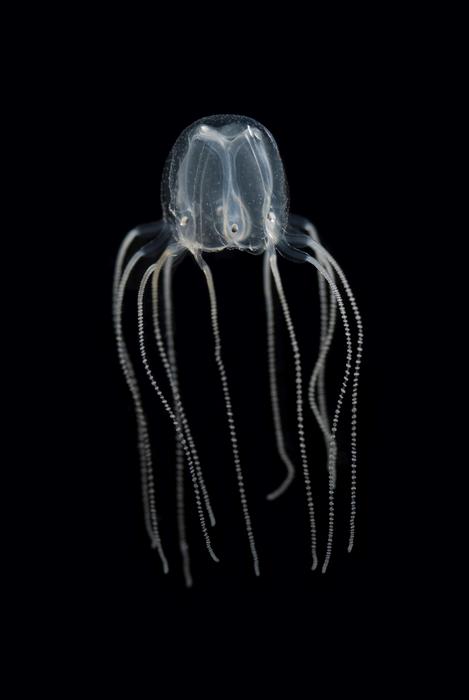
Jellyfish are more advanced than once thought. A new study from the University of Copenhagen has demonstrated that Caribbean box jellyfish can learn at a much more complex level than ever imagined – despite only having one thousand nerve cells and no centralized brain. The finding changes our fundamental understanding of the brain and could enlighten us about our own mysterious brains.
After more than 500 million years on Earth, the immense evolutionary success of jellyfish is undeniable. Still, we’ve always thought of them as simple creatures with very limited learning abilities.
The prevailing opinion is that more advanced nervous systems equate with more advanced learning potential in animals. Jellyfish and their relatives, collectively known as cnidarians, are considered to be the earliest living animals to develop nervous systems and to have fairly simple nervous systems and no centralized brain.
For more than a decade, neurobiologist Anders Garm has been researching box jellyfish, a group of jellyfish commonly known for being among the world’s most poisonous creatures. But these lethal jellies are interesting for another reason as well: it turns out that they are not quite as simple as once believed. And this shakes our entire understanding of what simple nervous systems are capable of.
“It was once presumed that jellyfish can only manage the simplest forms of learning, including habituation – i.e., the ability to get used to a certain stimulation, such as a constant sound or constant touch. Now, we see that jellyfish have a much more refined ability to learn, and that they can actually learn from their mistakes. And in doing so, modify their behavior,” says Anders Garm, an associate professor at the University of Copenhagen’s Department of Biology.
One of the most advanced attributes of a nervous system is the ability to change behavior as a result of experience – to remember and learn. The research team, headed by Jan Bielecki of Kiel University and Anders Garm, set out to test this ability in box jellyfish. The findings have just been published in the journal Current Biology.
A thousand nerve cells are more capable than once thought
The scientists studied the Caribbean box jellyfish, Tripedalia cystophora, a fingernail-sized medusa that lives in Caribbean mangrove swamps. Here, they use their impressive visual system including 24 eyes to hunt for tiny copepods among mangrove roots. While making for a good hunting grounds, the web of roots is also a dangerous place for soft-bodied jellies.
So, as the small box jellyfish approach the mangrove roots, they turn and swim away. Should they veer too soon, they won’t have enough time to catch any copepods. But if they turn too late, they risk bumping into the root and damaging their gelatinous bodies. Thus, assessing distances is crucial for them. And here, contrast is the key, as the researchers discovered:
“Our experiments show that contrast, i.e., how dark the root is in relation to the water, is used by the jellyfish to assess distances to roots, which allows them to swim away at just the right moment. Even more interesting is that the relationship between distance and contrast changes on a daily basis due to rainwater, algae and wave action,” says Anders Garm, who continues:
“We can see that as each new day of hunting begins, box jellyfish learn from the current contrasts by combining visual impressions and sensations during evasive manoeuvres that fail. So, despite having a mere one thousand nerve cells – our brains have roughly 100 billion – they can connect temporal convergences of various impressions and learn a connection – or what we call associative learning. And they actually learn about as quickly as advanced animals like fruit flies and mice.”
The new research results break with previous scientific perceptions of what animals with simple nervous systems are capable of:
“For fundamental neuroscience, this is pretty big news. It provides a new perspective on what can be done with a simple nervous system. This suggests that advanced learning may have been one of the most important evolutionary benefits of the nervous system from the very beginning,” says Anders Garm.
Seeking the brain cells where memory is housed
The research team has also shown where the learning is happening in these box jellyfish. This has given them unique opportunities for how to now study the precise changes that occur in a nerve cell when it is involved in advanced learning.
“We hope that this can become a supermodel system for looking at cellular processes in the advanced learning of all sorts of animals. We are now in the process of trying to pinpoint exactly which cells are involved in learning and memory formation. Upon doing so, we will be able to go in and look at what structural and physiological changes occur in the cells as learning takes place,” says Anders Garm.
If the scientists are able to pinpoint the exact mechanisms in jellyfish involved in learning, the next step will be to find out whether it applies specifically to jellies or if it can be found in all animals.
“Eventually, we will look for the same mechanisms in other animals, to see if this is how memory works in general,” says the researcher.
This kind of groundbreaking knowledge could be used for a wealth of purposes, according to Anders Garm:
“Understanding something as enigmatic and immensely complex as the brain is in itself an absolutely amazing thing. But there are unimaginably many useful possibilities. One major problem in the future will undoubtedly be various forms of dementia. I don’t claim that we are finding the cure for dementia, but if we can gain a better understanding of what memory is, which is a central problem in dementia, we may be able to lay a building block to better understand the disease and perhaps counteract it,” concludes the researcher.
FACT BOX: ABOUT TRIPEDALIA CYSTOPHORA
- Box jellyfish are a class of jellyfish known for being among the most poisonous animals in the world. They use their venom to catch fish and large shrimp. Tripedalia cystophora has a somewhat milder venom and feeds on tiny copepods.
- Box jellyfish do not have a centralized brain like most animals. Instead, they have four parallel brain-like structures, with approximately holds a thousand nerve cells in each. A human brain has approximately 100 billion nerve cells.
- Box jellyfish have twenty four eyes distributed among their four brain-like structures. Some of these eyes are image forming, providing box jellyfish with more complex vision than other types of jellyfish.
- To find their way through murky mangroves, four of Tripedalia cystophora’s eyes look up through the surface of the water and navigate using the mangrove canopies.
- Tripedalia cystophora is one of the smallest box jellyfish species, with a body of only about one centimeter in diameter. It lives in the Caribbean Sea and Central Indo-Pacific.
- Unlike many jellyfish species, Tripedalia cystophora actually mates as the male captures the female with its tentacles. A female’s eggs are then fertilized in their gut system, where they also develop into larvae.
[FACT BOX:] HOW THEY DID IT
The researchers replicated mangrove swamp conditions in the laboratory, where box jellyfish were placed in a behavioral arena. Here, the researchers manipulated jellyfish behavior by changing the contrast conditions to see what effect this had on their behavior.
They learned that jellyfish learning takes place through failed evasions. That is, they learn from misinterpreting contrast and bumping into roots. Here they combined the visual impression and mechanical shock they got whenever they bumped into a root – and in doing so, learned when to veer away.
“Our behavioural experiments demonstrate that three to five failed evasive manoeuvres are enough to change the jellyfish’s behaviour so that they no longer hit the roots. It is interesting that this is roughly the same repetition rate that a fruit fly or mouse needs to learn,” says Anders Garm.
The learning was further verified through electrophysiology and classical conditioning experiments, which also showed where in the jellyfish’s nervous system the learning takes place.
[FACT BOX:] ABOUT THE STUDY
The study was conducted by Jan Bielecki from Kiel University and Anders Garm, Sofie Katrine Dam Nielsen and Gösta Nachman from the Department of Biology, University of Copenhagen.
The study has just been published in the scientific journal Current Biology.
VIDEO LINK:
https://video.ku.dk/secret/88818429/e5f680af70640f1fd86e5d54e5e95f1a
Journal
Current Biology
DOI
10.1016/j.cub.2023.08.056
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Associative learning in the box jellyfish Tripedalia Cystophora
Article Publication Date
22-Sep-2023