Uncategorized
Infections from a diarrhoea-causing parasite are on the rise in the UK – but experts aren’t quite sure why
Infections from the Cryptosporidium parasite are five times higher than expected for this time of year.
Infections from a parasite which can cause long-lasting, severe diarrhoea has seen an “unprecedented and ongoing” surge across the UK. This increase in infections has been ongoing since mid-August.
Almost 500 cases of cryptosporidiosis in a week were reported at the end of September alone – five times more than the expected number for that time of year.
And this may just be the tip of the iceberg, as only about one-eighth of infections are ever reported.
While cases have started to fall, they’re still well above expected numbers. And the reasons why cases are so high this year is still unknown.
What is crypto?
Cryptosporidiosis (sometimes called crypto) is caused by the Cryptosporidium parasite.
There are several species of Cryptosporidium, most of which only rarely (if ever) cause disease in humans. There are two species which cause infections in humans: C parvum and C hominis.
C hominis almost exclusively causes infections in humans while C parvum causes infections in many different mammals – most typically cattle. But there is a subgroup of C parvum that has recently evolved into a form that generally only infects humans.
The main symptom of crypto is watery diarrhoea that can be accompanied by stomach cramps, dehydration, vomiting, fever or weight loss. Infections last about ten days on average, which is much longer than what you’d see with other infections, such as Salmonella or Campylobacter.
Crypto predominantly affects children, typically those of pre-school age. Children are most at risk due to their lack of immunity.

How do you contract it?
Crypto is caused by inadvertently ingesting faecal matter. The parasite can be spread through food, water and contact with an infected person or animal. Many crypto outbreaks have been caused by people drinking water that had become contaminated by human or animal faeces, or consuming unpasteurised milk or contaminated foods – typically salads.
Outbreaks have also been associated with farm visits, children’s day care centres and even swimming pools.
Most people recover from crypto without needing treatment. But sometimes crypto can cause severe disease, leading to weight loss and dehydration. Infections from the C hominis strain in particular can sometimes lead to long-term diarrhoea, irritable bowel syndrome, weight loss and fatigue.
People who are severely immune compromised – such as those with HIV/Aids or blood cancer – are also at greater risk of severe and potentially fatal infections.
There’s no vaccine against cryptosporidiosis. If you do catch crypto, make sure to drink plenty of water to replace lost fluids. People with more severe infections or people who are immunocompromised may be prescribed anti-parasitic drugs. While these don’t always work, they may help reduce the duration of symptoms.
What is behind the current outbreak?
The causes of the current surge in Cryptosporidium infections in the UK isn’t clear.
Prior to the pandemic, infections would be expected to rise in late summer and early autumn each year. But this year, the surge is especially large. Infections have surged in most parts of the UK, indicating it’s probably not due to a localised outbreak.
One explanation is that this surge is due to increased exposure.
About two-thirds of recently reported C hominis cases have been linked to overseas travel – mainly Spain. Around 80% of these C hominis cases reported swimming in the 14 days before becoming unwell.
In Spain, the towns of Tarazona and Zaragoza have both reported large waterborne outbreaks of crypto during late summer. But whether an outbreak in a part of Spain well away from the Mediterranean beaches most tourists head for could explain this surge is doubtful.
This also doesn’t account for some of the cases of crypto currently being reported, as foreign travel and swimming were much less frequent in recorded C parvum cases.
Another plausible explanation for this current wave is that our immunity to crypto has fallen as a result of COVID control measures. This means the parasite is able to infect more people than would normally be the case.
This would make sense, as lack of immunity was implicated in the high numbers of viral infections seen last year. Not to mention C hominis infections almost disappeared during the first two years of the pandemic due to COVID restrictions. C parvum infections also fell – but mainly only for the first few months after restrictions were introduced.
But if reduced immunity was the only explanation, then we’d expect to see increased case numbers elsewhere in Europe. Unfortunately, crypto infections are inconsistently reported across Europe making comparisons difficult. But among the UK’s neighbours, Ireland has certainly seen more cases this year than typical – even from pre-COVID years.
I suspect the explanation for the outbreak is a combination of the two. Reduced population immunity following a couple of years with very few infections led to increased infection rates. This then led to increased contamination of swimming pools – leading to yet more infections.
How can you protect yourself?
Although most infections in the current wave have been contracted while swimming, I wouldn’t encourage people to avoid swimming to protect themselves – not unless they have severe problems with immunity. But do try to avoid swallowing water while swimming.
If another bather has an accident in the pool, be sure to get out promptly to avoid swallowing water. Likewise, if you’re suffering from diarrhoea you should avoid swimming to protect other swimmers.
Paul Hunter is a member of several World Health Organization Expert Advisory committees relevant to this topic and a member of a scientidic advisory committee for Suez Environment. He receives funding from National Institute of Health Reseasrch and has recevied funding from The European Interreg programme.
crypto cryptoUncategorized
One city held a mass passport-getting event
A New Orleans congressman organized a way for people to apply for their passports en masse.

While the number of Americans who do not have a passport has dropped steadily from more than 80% in 1990 to just over 50% now, a lack of knowledge around passport requirements still keeps a significant portion of the population away from international travel.
Over the four years that passed since the start of covid-19, passport offices have also been dealing with significant backlog due to the high numbers of people who were looking to get a passport post-pandemic.
Related: Here is why it is (still) taking forever to get a passport
To deal with these concurrent issues, the U.S. State Department recently held a mass passport-getting event in the city of New Orleans. Called the "Passport Acceptance Event," the gathering was held at a local auditorium and invited residents of Louisiana’s 2nd Congressional District to complete a passport application on-site with the help of staff and government workers.
'Come apply for your passport, no appointment is required'
"Hey #LA02," Rep. Troy A. Carter Sr. (D-LA), whose office co-hosted the event alongside the city of New Orleans, wrote to his followers on Instagram (META) . "My office is providing passport services at our #PassportAcceptance event. Come apply for your passport, no appointment is required."
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
The event was held on March 14 from 10 a.m. to 1 p.m. While it was designed for those who are already eligible for U.S. citizenship rather than as a way to help non-citizens with immigration questions, it helped those completing the application for the first time fill out forms and make sure they have the photographs and identity documents they need. The passport offices in New Orleans where one would normally have to bring already-completed forms have also been dealing with lines and would require one to book spots weeks in advance.
These are the countries with the highest-ranking passports in 2024
According to Carter Sr.'s communications team, those who submitted their passport application at the event also received expedited processing of two to three weeks (according to the State Department's website, times for regular processing are currently six to eight weeks).
While Carter Sr.'s office has not released the numbers of people who applied for a passport on March 14, photos from the event show that many took advantage of the opportunity to apply for a passport in a group setting and get expedited processing.
Every couple of months, a new ranking agency puts together a list of the most and least powerful passports in the world based on factors such as visa-free travel and opportunities for cross-border business.
In January, global citizenship and financial advisory firm Arton Capital identified United Arab Emirates as having the most powerful passport in 2024. While the United States topped the list of one such ranking in 2014, worsening relations with a number of countries as well as stricter immigration rules even as other countries have taken strides to create opportunities for investors and digital nomads caused the American passport to slip in recent years.
A UAE passport grants holders visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to 180 of the world’s 198 countries (this calculation includes disputed territories such as Kosovo and Western Sahara) while Americans currently have the same access to 151 countries.
stocks pandemic covid-19 grantsUncategorized
Fast-food chain closes restaurants after Chapter 11 bankruptcy
Several major fast-food chains recently have struggled to keep restaurants open.

Competition in the fast-food space has been brutal as operators deal with inflation, consumers who are worried about the economy and their jobs and, in recent months, the falling cost of eating at home.
Add in that many fast-food chains took on more debt during the covid pandemic and that labor costs are rising, and you have a perfect storm of problems.
It's a situation where Restaurant Brands International (QSR) has suffered as much as any company.
Related: Wendy's menu drops a fan favorite item, adds something new
Three major Burger King franchise operators filed for bankruptcy in 2023, and the chain saw hundreds of stores close. It also saw multiple Popeyes franchisees move into bankruptcy, with dozens of locations closing.
RBI also stepped in and purchased one of its key franchisees.
"Carrols is the largest Burger King franchisee in the United States today, operating 1,022 Burger King restaurants in 23 states that generated approximately $1.8 billion of system sales during the 12 months ended Sept. 30, 2023," RBI said in a news release. Carrols also owns and operates 60 Popeyes restaurants in six states."
The multichain company made the move after two of its large franchisees, Premier Kings and Meridian, saw multiple locations not purchased when they reached auction after Chapter 11 bankruptcy filings. In that case, RBI bought select locations but allowed others to close.
Image source: Chen Jianli/Xinhua via Getty
Another fast-food chain faces bankruptcy problems
Bojangles may not be as big a name as Burger King or Popeye's, but it's a popular chain with more than 800 restaurants in eight states.
"Bojangles is a Carolina-born restaurant chain specializing in craveable Southern chicken, biscuits and tea made fresh daily from real recipes, and with a friendly smile," the chain says on its website. "Founded in 1977 as a single location in Charlotte, our beloved brand continues to grow nationwide."
Like RBI, Bojangles uses a franchise model, which makes it dependent on the financial health of its operators. The company ultimately saw all its Maryland locations close due to the financial situation of one of its franchisees.
Unlike. RBI, Bojangles is not public — it was taken private by Durational Capital Management LP and Jordan Co. in 2018 — which means the company does not disclose its financial information to the public.
That makes it hard to know whether overall softness for the brand contributed to the chain seeing its five Maryland locations after a Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing.
Bojangles has a messy bankruptcy situation
Even though the locations still appear on the Bojangles website, they have been shuttered since late 2023. The locations were operated by Salim Kakakhail and Yavir Akbar Durranni. The partners operated under a variety of LLCs, including ABS Network, according to local news channel WUSA9.
The station reported that the owners face a state investigation over complaints of wage theft and fraudulent W2s. In November Durranni and ABS Network filed for bankruptcy in New Jersey, WUSA9 reported.
"Not only do former employees say these men owe them money, WUSA9 learned the former owners owe the state, too, and have over $69,000 in back property taxes."
Former employees also say that the restaurant would regularly purchase fried chicken from Popeyes and Safeway when it ran out in their stores, the station reported.
Bojangles sent the station a comment on the situation.
"The franchisee is no longer in the Bojangles system," the company said. "However, it is important to note in your coverage that franchisees are independent business owners who are licensed to operate a brand but have autonomy over many aspects of their business, including hiring employees and payroll responsibilities."
Kakakhail and Durranni did not respond to multiple requests for comment from WUSA9.
bankruptcy pandemicUncategorized
Industrial Production Increased 0.1% in February
From the Fed: Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization
Industrial production edged up 0.1 percent in February after declining 0.5 percent in January. In February, the output of manufacturing rose 0.8 percent and the index for mining climbed 2.2 p…
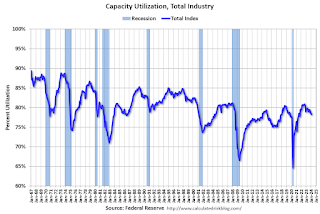
Industrial production edged up 0.1 percent in February after declining 0.5 percent in January. In February, the output of manufacturing rose 0.8 percent and the index for mining climbed 2.2 percent. Both gains partly reflected recoveries from weather-related declines in January. The index for utilities fell 7.5 percent in February because of warmer-than-typical temperatures. At 102.3 percent of its 2017 average, total industrial production in February was 0.2 percent below its year-earlier level. Capacity utilization for the industrial sector remained at 78.3 percent in February, a rate that is 1.3 percentage points below its long-run (1972–2023) average.Click on graph for larger image.
emphasis added
This graph shows Capacity Utilization. This series is up from the record low set in April 2020, and above the level in February 2020 (pre-pandemic).
Capacity utilization at 78.3% is 1.3% below the average from 1972 to 2022. This was below consensus expectations.
Note: y-axis doesn't start at zero to better show the change.
 The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.
The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.Industrial production increased to 102.3. This is above the pre-pandemic level.
Industrial production was above consensus expectations.
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Spread & Containment2 days ago
Spread & Containment2 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex



















