Uncategorized
From payments to DeFi: A closer look at the evolving stablecoin ecosystem
The stablecoin ecosystem has evolved significantly over the years, with new regulations and models shaping the landscape.
The rise…

The stablecoin ecosystem has evolved significantly over the years, with new regulations and models shaping the landscape.
The rise of digital currencies, exemplified by Bitcoin (BTC), brought a groundbreaking shift in the financial landscape.
However, it also brought to light a critical challenge: price volatility. Bitcoin and many other early cryptocurrencies exhibited extreme price fluctuations, making them difficult to use for everyday transactions or as a reliable store of value.
Users recognized the need for stability when dealing with digital assets, particularly when conducting business or holding assets for an extended period. This need for stability in the digital currency realm paved the way for the development of stablecoins.
As a result, stablecoins emerged to address the need for a reliable and consistent value in the digital currency space, employing various strategies such as asset pegging to fiat currencies or commodities and algorithmic mechanisms to achieve stability.
Stablecoins come in two primary categories, the first being collateralized stablecoins, like Tether (USDT), which are backed by real-world assets like fiat currencies or commodities, with each token linked to a specific asset to maintain stability.
The second type is algorithmic stablecoins, such as Dai (DAI) from MakerDAO, which don’t rely on physical collateral but instead use smart contracts and algorithms to manage supply and demand, striving to keep their price stable through decentralized governance and automated processes.
These stablecoins have since become integral components of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, enabling secure and stable digital transactions and opening up new possibilities for financial innovation. Here’s a closer look at some of the top stablecoins, how they came to be, and where they are now.
The birth of stablecoins
Tether (2014)
USDT launched in 2014 as a cryptocurrency created to bridge the gap between traditional fiat currencies and the digital currency ecosystem. It was founded by Tether, with Jan Ludovicus van der Velde serving as its CEO.
USDT was introduced during a time when the cryptocurrency market was growing rapidly but lacked a stable asset-backed digital currency.
Its unique selling point was its peg to the United States dollar. Each USDT token was designed to represent one U.S. dollar.
USDT faced early controversies and skepticism. One major concern was whether Tether held the dollar reserves it claimed to back its tokens. The company’s opaque financial practices and lack of regular audits fueled doubts within the cryptocurrency community. However, in recent times, Tether has published information about its reserves.
Tether claims to hold enough reserves to maintain a 1:1 peg to dollars, backing every USDT in circulation. This peg to a fiat currency was intended to provide users with a reliable and stable digital currency for various use cases, including trading and remittances.
According to a full reserve breakdown in 2023, Tether is backed by cash, cash equivalents secured loans, corporate bonds and other investments, including digital tokens.
A spokesperson for Tether told Cointelegraph, “Tether’s Q2 2023 assurance report highlights our prudent investment strategy. We have 85% in cash and cash equivalents, around $72.5 billion in U.S. Treasurys, along with smaller holdings in assets like gold and Bitcoin. We are gradually eliminating secured loans from our reserves. Last quarter, we added $850 million to our excess reserves, totaling about $3.3 billion, further bolstering Tether’s stability.”

Still, Tether’s role in the cryptocurrency market has drawn scrutiny. It has become widely used to transfer value between different cryptocurrency exchanges, allowing traders to avoid using traditional banking systems. Some critics alleged that Tether was used to manipulate cryptocurrency prices, particularly Bitcoin, by creating synthetic demand.
Despite these controversies, Tether remained one of the most widely used stablecoins in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, serving as a crucial tool for traders and investors navigating the volatile crypto markets.
Dai (2017)
DAI is a decentralized stablecoin that operates within the Ethereum blockchain ecosystem. It was created by the MakerDAO project, which was founded in 2014 with the goal of establishing a decentralized and algorithmic stablecoin solution.
Dai is not backed by a reserve of fiat currency. Instead, Dai is collateralized by a variety of cryptocurrencies, primarily Ether (ETH), which users lock up in a smart contract called a collateralized debt position (CDP).
Users who want to generate Dai deposit a certain amount of Ethereum into a CDP and then create DAI tokens based on the collateral’s value. The user can then use these DAI tokens as a stable medium of exchange or store of value.
Recent: Terrorist fundraising: Is crypto really to blame?
To ensure the stability of Dai, the MakerDAO system monitors the collateral’s value in the CDP. If the value of the collateral falls below a specified threshold (known as the liquidation ratio), the system can automatically sell the collateral to buy back Dai tokens and stabilize its value.
Additionally, the stability mechanisms of Dai have evolved over time. In addition to Ethereum, MakerDAO has introduced multicollateral Dai (MCD), allowing users to collateralize a wider range of assets, further diversifying the system and reducing its dependency on a single cryptocurrency. This evolution has made Dai more resilient and adaptable to market changes.
USD Coin (2018)
USD Coin (USDC) was launched in September 2018 as a joint venture between two well-known cryptocurrency companies, Circle and Coinbase. The stablecoin is also managed by Centre, a consortium co-founded by the two companies.
However, Circle and Coinbase dissolved Centre, the group responsible for overseeing USDC since 2018, in August 2023. As a result, Circle was given sole governance of USDC.
The coin temporarily lost its 1:1 peg with the U.S. dollar in March 2023 when Silicon Valley Bank, where Circle held $3.3 billion of its currency reserves, collapsed due to a liquidity crisis. While the coin briefly dipped to $0.87, Circle later confirmed that it was able to withdraw its reserves from SVB, restoring the 1:1 peg, but not without a blow to user confidence.
USDC’s primary purpose is to provide a digital representation of the U.S. dollar, making it easier for users to transact in the cryptocurrency space while avoiding the price volatility associated with other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Each USDC token is meant to be backed by a corresponding amount of dollars held in reserve, which is regularly audited to maintain transparency and trust within the ecosystem.

USDC operates on the Ethereum blockchain as an ERC-20 token. However, it has since expanded to other blockchains like Alogrand, Stellar, Base and Optimism to increase its scalability and reduce transaction costs. This interoperability has broadened its use cases beyond just the Ethereum network, making it accessible to a more extensive range of users and applications.
Within the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, USDC is used in many ways. First, it functions as a source of liquidity in decentralized exchanges like Uniswap and Curve. Users provide USDC to these platforms, becoming liquidity providers and earning a share of the transaction fees generated by these pools. This offers a way to generate passive income from USDC holdings.
Additionally, USDC can be used as collateral for borrowing on DeFi lending platforms such as Compound and Aave. Users lock up their USDC assets as collateral, allowing them to borrow other cryptocurrencies or stablecoins. This enables leverage and liquidity without traditional intermediaries, and it also lets users earn interest on their USDC deposits while using them as collateral.
Furthermore, DeFi enthusiasts often engage in yield farming and staking using USDC. By participating in liquidity pools or staking their USDC tokens, users can receive rewards, typically in the form of governance tokens or interest.
TrueUSD (2018)
TrueUSD (TUSD) was released in March 2018 by TrustToken, a blockchain technology company focusing on creating asset-backed tokens.
The coin has wavered from its 1:1 peg to the dollar at several points, one of the more recent incidents being when Prime Trust, a technology partner to the stablecoin, announced it was pausing TUSD mints.
Announcement:
— TrueUSD (@tusdio) June 10, 2023
TUSD mints via Prime Trust are paused for further notification.
Thanks for your understanding and we are sorry for any inconvenience. Please contact support@trueusd.com for any further questions.
In October 2023, the project came under fire as a hack at one of its third-party vendors potentially compromised the Know Your Customer data of TUSD users. TrueUSD quickly noted the reserves themselves were secure and never put at risk.
TrueUSD is often used in cryptocurrency trading and investment as a way to park funds during market volatility, offering traders a safe haven from crypto price fluctuations.
Binance USD (2019)
Binance USD (BUSD) is a collateralized stablecoin issued by Binance, one of the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchanges. It was introduced to the cryptocurrency market in September 2019.
The value of BUSD is intended to remain close to 1:1 with the U.S. dollar, meaning that 1 BUSD is generally equivalent to 1 U.S. dollar. To achieve this stability, Binance holds equivalent amounts of U.S. dollars in reserve to back the BUSD tokens in circulation.
This reserve is regularly audited to ensure that it matches the total supply of BUSD, thus maintaining the coin’s peg to the U.S. dollar. This transparency and asset backing are essential for instilling trust among users and investors.
BUSD can be used for various purposes within the cryptocurrency space. Traders often use it as a stable medium to park their funds when they want to exit volatile cryptocurrency positions temporarily. It is also employed in trading pairs on Binance and other exchanges, allowing traders to move in and out of positions with ease.
Moreover, BUSD has found applications outside the trading world. It is commonly used in decentralized finance platforms and yield farming protocols like PancakeSwap as a stable asset to provide liquidity or collateralize loans. However, recently, Binance has started to wind down support for the BUSD stablecoin and plans to stop the support for BUSD entirely by 2024.
This decision was made due to its issuer, Paxos, being ordered to stop the minting of BUSD by the New York Department of Financial Services.
TerraUSD (2020)
TerraClassicUSD (USTC) — formerly known as TerraUSD (UST) — is a stablecoin released in 2018 that was algorithmically stabilized rather than being backed by a reserve of traditional assets like fiat-collateralized stablecoins.
USTC distinguished itself by operating on a unique algorithmic mechanism that used incentives and disincentives to keep its value close to $1. One of the key features of USTC was its use of Luna (LUNA), the native cryptocurrency of the Terra blockchain, as collateral.
When USTC’s price deviated from its $1 target, a mechanism called the Terra Stability Reserve came into play. If TerraUSD was trading above $1, users could mint new TerraUSD by locking up Luna as collateral. Conversely, when TerraUSD was trading below $1, users could redeem it for Luna at a profit, effectively balancing the supply and demand to bring the price back to its target.
On May 7, 2022, USTC depegged from the dollar after a series of trades took advantage of a “shallow” pool on the decentralized exchange 3pool, causing the coin to lose its peg to the dollar.
Efforts to restore the peg worked briefly but were ultimately unsuccessful. During the same period, the complementary token, LUNA, originally intended to provide price stability to UST, suffered a dramatic decline, plummeting from $80 to $0.005.
The following day, on May 25, Terra’s network validators voted in favor of a transformative proposal presented by Do Kwon, one of the project’s co-founders. This proposal sought to launch a new blockchain called Terra 2.0, which would notably exclude a stablecoin component.
Under this plan, previous holders of LUNA and UST would receive the new blockchain’s native token, Terra (LUNA2), based on the amount of these tokens they held. This transition aimed to recalibrate the Terra ecosystem and diversify its offerings.
Importantly, the original Terra blockchain would continue to function alongside Terra 2.0, and its token would be renamed to Luna Classic (LUNC), while TerraUSD was rebranded as TerraClassicUSD or USTC.
Overall, this saga called into question the practicality and stability of algorithmically balanced stablecoins, as user trust in such ecosystems and $50 billion in value evaporated.
The evolving landscape of stablecoin projects
Regulatory changes are a significant factor influencing the stablecoin landscape. Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing stablecoins due to financial stability, consumer protection and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance concerns. In October, U.S. Federal Reserve Board Governor Michelle Bowman argued against the use of stablecoins due to their low level of regulation.
Some countries are actively working on regulatory frameworks to address stablecoin issuance and usage within their jurisdictions. These regulations may require stablecoin issuers to adhere to specific reserve and reporting requirements. For example, Singapore requires stablecoins to maintain minimum base capital and liquid assets to reduce the risk of insolvency.
In July, the Financial Stability Board (FSB), which monitors and makes regulations regarding the global financial system, created a cryptocurrency regulatory proposal. The FSB suggested that global stablecoin issuers establish a governance body and that the minimum reserve asset ratio be set at 1:1 unless the issuer “is subject to adequate prudential requirements” like commercial bank standards.
Stablecoin projects themselves have also been evolving along with changing legal and economic conditions.
Competition among stablecoin projects has increased transparency, with many issuers providing regular audits and attestation reports to prove their asset backing and stability. Cross-chain interoperability is also a growing trend, allowing stablecoins to move seamlessly between blockchain networks.
Tether’s spokesperson said, “The potential advantages and challenges of stablecoins moving seamlessly between different blockchain networks are significant [...] This capability enhances interoperability, allowing users to transact across various ecosystems, fostering a more interconnected blockchain space. Additionally, it grants access to unique features and applications on different blockchains, enabling users to leverage the strengths of each network for specific use cases.”
Magazine: Ethereum restaking: Blockchain innovation or dangerous house of cards?
DeFi is another industry where stablecoins are growing in popularity. Flex Yang, founder of Hope.money, a stablecoin protocol backed by crypto-native reserves, told Cointelegraph, “Stablecoins also play a pivotal role in the DeFi ecosystem, enabling users to engage in lending, borrowing, trading and earning interest without exposing themselves to the volatility of other cryptocurrencies. For instance, staking USDT for a year can result in an annualized return of approximately 6%.”
Stablecoins also enable yield farming and liquidity provisioning in DeFi. Users can provide liquidity to decentralized exchanges and automated market makers by pairing stablecoins with other cryptocurrencies. This process, known as liquidity provisioning, allows users to earn fees and incentives while maintaining the stability of their assets.
As stablecoins play a crucial role in the broader cryptocurrency and financial landscape, expect ongoing innovation, partnerships and adaptation to market dynamics.
bonds corporate bonds cryptocurrency bitcoin ethereum blockchain crypto btc currencies crypto commodities goldUncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemploymentUncategorized
Mortgage rates fall as labor market normalizes
Jobless claims show an expanding economy. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
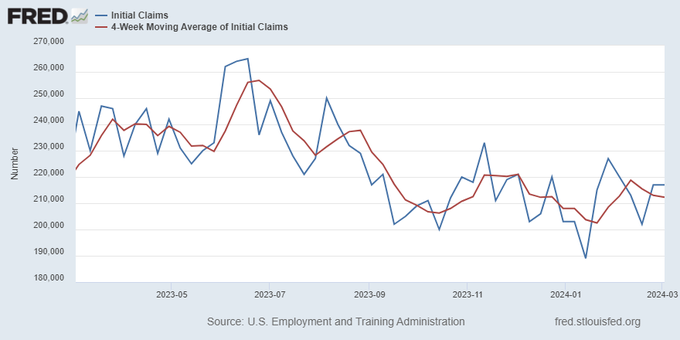
Everyone was waiting to see if this week’s jobs report would send mortgage rates higher, which is what happened last month. Instead, the 10-year yield had a muted response after the headline number beat estimates, but we have negative job revisions from previous months. The Federal Reserve’s fear of wage growth spiraling out of control hasn’t materialized for over two years now and the unemployment rate ticked up to 3.9%. For now, we can say the labor market isn’t tight anymore, but it’s also not breaking.
The key labor data line in this expansion is the weekly jobless claims report. Jobless claims show an expanding economy that has not lost jobs yet. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
From the Fed: In the week ended March 2, initial claims for unemployment insurance benefits were flat, at 217,000. The four-week moving average declined slightly by 750, to 212,250
Below is an explanation of how we got here with the labor market, which all started during COVID-19.
1. I wrote the COVID-19 recovery model on April 7, 2020, and retired it on Dec. 9, 2020. By that time, the upfront recovery phase was done, and I needed to model out when we would get the jobs lost back.
2. Early in the labor market recovery, when we saw weaker job reports, I doubled and tripled down on my assertion that job openings would get to 10 million in this recovery. Job openings rose as high as to 12 million and are currently over 9 million. Even with the massive miss on a job report in May 2021, I didn’t waver.
Currently, the jobs openings, quit percentage and hires data are below pre-COVID-19 levels, which means the labor market isn’t as tight as it once was, and this is why the employment cost index has been slowing data to move along the quits percentage.

3. I wrote that we should get back all the jobs lost to COVID-19 by September of 2022. At the time this would be a speedy labor market recovery, and it happened on schedule, too
Total employment data
4. This is the key one for right now: If COVID-19 hadn’t happened, we would have between 157 million and 159 million jobs today, which would have been in line with the job growth rate in February 2020. Today, we are at 157,808,000. This is important because job growth should be cooling down now. We are more in line with where the labor market should be when averaging 140K-165K monthly. So for now, the fact that we aren’t trending between 140K-165K means we still have a bit more recovery kick left before we get down to those levels.

From BLS: Total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 275,000 in February, and the unemployment rate increased to 3.9 percent, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Job gains occurred in health care, in government, in food services and drinking places, in social assistance, and in transportation and warehousing.
Here are the jobs that were created and lost in the previous month:

In this jobs report, the unemployment rate for education levels looks like this:
- Less than a high school diploma: 6.1%
- High school graduate and no college: 4.2%
- Some college or associate degree: 3.1%
- Bachelor’s degree or higher: 2.2%

Today’s report has continued the trend of the labor data beating my expectations, only because I am looking for the jobs data to slow down to a level of 140K-165K, which hasn’t happened yet. I wouldn’t categorize the labor market as being tight anymore because of the quits ratio and the hires data in the job openings report. This also shows itself in the employment cost index as well. These are key data lines for the Fed and the reason we are going to see three rate cuts this year.
recession unemployment covid-19 fed federal reserve mortgage rates recession recovery unemploymentUncategorized
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Last month we though that the January…
Last month we though that the January jobs report was the "most ridiculous in recent history" but, boy, were we wrong because this morning the Biden department of goalseeked propaganda (aka BLS) published the February jobs report, and holy crap was that something else. Even Goebbels would blush.
What happened? Let's take a closer look.
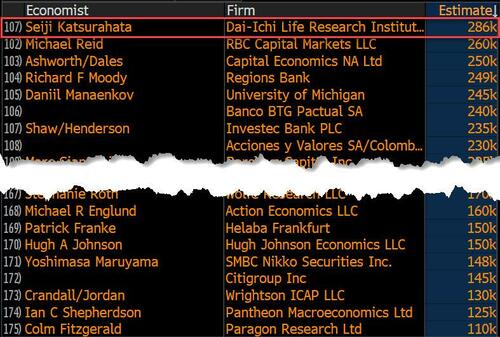
On the surface, it was (almost) another blockbuster jobs report, certainly one which nobody expected, or rather just one bank out of 76 expected. Starting at the top, the BLS reported that in February the US unexpectedly added 275K jobs, with just one research analyst (from Dai-Ichi Research) expecting a higher number.
Some context: after last month's record 4-sigma beat, today's print was "only" 3 sigma higher than estimates. Needless to say, two multiple sigma beats in a row used to only happen in the USSR... and now in the US, apparently.
Before we go any further, a quick note on what last month we said was "the most ridiculous jobs report in recent history": it appears the BLS read our comments and decided to stop beclowing itself. It did that by slashing last month's ridiculous print by over a third, and revising what was originally reported as a massive 353K beat to just 229K, a 124K revision, which was the biggest one-month negative revision in two years!
Of course, that does not mean that this month's jobs print won't be revised lower: it will be, and not just that month but every other month until the November election because that's the only tool left in the Biden admin's box: pretend the economic and jobs are strong, then revise them sharply lower the next month, something we pointed out first last summer and which has not failed to disappoint once.
In the past month the Biden department of goalseeking stuff higher before revising it lower, has revised the following data sharply lower:
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) August 30, 2023
- Jobs
- JOLTS
- New Home sales
- Housing Starts and Permits
- Industrial Production
- PCE and core PCE
To be fair, not every aspect of the jobs report was stellar (after all, the BLS had to give it some vague credibility). Take the unemployment rate, after flatlining between 3.4% and 3.8% for two years - and thus denying expectations from Sahm's Rule that a recession may have already started - in February the unemployment rate unexpectedly jumped to 3.9%, the highest since February 2022 (with Black unemployment spiking by 0.3% to 5.6%, an indicator which the Biden admin will quickly slam as widespread economic racism or something).
And then there were average hourly earnings, which after surging 0.6% MoM in January (since revised to 0.5%) and spooking markets that wage growth is so hot, the Fed will have no choice but to delay cuts, in February the number tumbled to just 0.1%, the lowest in two years...
... for one simple reason: last month's average wage surge had nothing to do with actual wages, and everything to do with the BLS estimate of hours worked (which is the denominator in the average wage calculation) which last month tumbled to just 34.1 (we were led to believe) the lowest since the covid pandemic...
... but has since been revised higher while the February print rose even more, to 34.3, hence why the latest average wage data was once again a product not of wages going up, but of how long Americans worked in any weekly period, in this case higher from 34.1 to 34.3, an increase which has a major impact on the average calculation.
While the above data points were examples of some latent weakness in the latest report, perhaps meant to give it a sheen of veracity, it was everything else in the report that was a problem starting with the BLS's latest choice of seasonal adjustments (after last month's wholesale revision), which have gone from merely laughable to full clownshow, as the following comparison between the monthly change in BLS and ADP payrolls shows. The trend is clear: the Biden admin numbers are now clearly rising even as the impartial ADP (which directly logs employment numbers at the company level and is far more accurate), shows an accelerating slowdown.
But it's more than just the Biden admin hanging its "success" on seasonal adjustments: when one digs deeper inside the jobs report, all sorts of ugly things emerge... such as the growing unprecedented divergence between the Establishment (payrolls) survey and much more accurate Household (actual employment) survey. To wit, while in January the BLS claims 275K payrolls were added, the Household survey found that the number of actually employed workers dropped for the third straight month (and 4 in the past 5), this time by 184K (from 161.152K to 160.968K).
This means that while the Payrolls series hits new all time highs every month since December 2020 (when according to the BLS the US had its last month of payrolls losses), the level of Employment has not budged in the past year. Worse, as shown in the chart below, such a gaping divergence has opened between the two series in the past 4 years, that the number of Employed workers would need to soar by 9 million (!) to catch up to what Payrolls claims is the employment situation.
There's more: shifting from a quantitative to a qualitative assessment, reveals just how ugly the composition of "new jobs" has been. Consider this: the BLS reports that in February 2024, the US had 132.9 million full-time jobs and 27.9 million part-time jobs. Well, that's great... until you look back one year and find that in February 2023 the US had 133.2 million full-time jobs, or more than it does one year later! And yes, all the job growth since then has been in part-time jobs, which have increased by 921K since February 2023 (from 27.020 million to 27.941 million).
Here is a summary of the labor composition in the past year: all the new jobs have been part-time jobs!
But wait there's even more, because now that the primary season is over and we enter the heart of election season and political talking points will be thrown around left and right, especially in the context of the immigration crisis created intentionally by the Biden administration which is hoping to import millions of new Democratic voters (maybe the US can hold the presidential election in Honduras or Guatemala, after all it is their citizens that will be illegally casting the key votes in November), what we find is that in February, the number of native-born workers tumbled again, sliding by a massive 560K to just 129.807 million. Add to this the December data, and we get a near-record 2.4 million plunge in native-born workers in just the past 3 months (only the covid crash was worse)!
The offset? A record 1.2 million foreign-born (read immigrants, both legal and illegal but mostly illegal) workers added in February!
Said otherwise, not only has all job creation in the past 6 years has been exclusively for foreign-born workers...

... but there has been zero job-creation for native born workers since June 2018!
This is a huge issue - especially at a time of an illegal alien flood at the southwest border...
... and is about to become a huge political scandal, because once the inevitable recession finally hits, there will be millions of furious unemployed Americans demanding a more accurate explanation for what happened - i.e., the illegal immigration floodgates that were opened by the Biden admin.
Which is also why Biden's handlers will do everything in their power to insure there is no official recession before November... and why after the election is over, all economic hell will finally break loose. Until then, however, expect the jobs numbers to get even more ridiculous.
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire




































