International
‘Follow The Science’: A Potent Source Of Authority For Politicians
‘Follow The Science’: A Potent Source Of Authority For Politicians
Authored by Nathan Worcester via The Epoch Times,
To hear the way some politicians talk, when it comes to COVID-19, they’re all “following the science,” not to mention…

Authored by Nathan Worcester via The Epoch Times,
To hear the way some politicians talk, when it comes to COVID-19, they’re all “following the science,” not to mention “the data.”
“Look at the data. Follow the science. Listen to the experts. Be smart,” now-former New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo wrote on Twitter in May 2020, after “Two Weeks to Flatten the Curve” had fully transitioned to “The New Normal.”
“We’ve been operating on facts and data and science from the very beginning,” said Illinois Gov. J.B. Pritzker in a campaign ad titled simply “Follow The Science.”
President Joe Biden has frequently appealed to “the science.” In an executive order announcing a vaccine mandate for federal workers, for instance, he said his administration used “the best available data and science-based public health measures.” In an article criticizing Biden’s move to push vaccine boosters in September, StatNews’s Lev Facher described “Follow the Science” as “a mantra” for the administration.
White House chief medical adviser on COVID-19 Dr. Anthony Fauci stands at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in Bethesda, Md., on Feb. 11, 2021. (Saul Loeb/AFP via Getty Images)
“The science” emerged long before 2020 as a potent source of authority for politicians. Yet while the scientific method is a powerful tool for advancing human potential, the belief that it alone can guide us is an example of “scientism.”
Scientism is, in the words of public intellectual Scott Masson, “the belief that moral or evaluative judgments are merely subjective and that only the ‘hard’ sciences—think physics, chemistry, or biology—furnish legitimate objective knowledge.” While few American politicians would openly endorse this position, the actions many have taken during the COVID-19 pandemic reflect scientism in deed, if not in word.
Scientism lets politicians off the hook for their decisions. They didn’t really make a decision—they merely “followed the science.”
As a scientistic credo, “Follow the science” doesn’t just abrogate leaders’ accountability as decision-makers. It also does violence to the nature of science, which seldom offers the clear-cut, politically useful conclusions that politicians want.
People wearing face masks stand in line as they wait to be vaccinated at the Sydney Olympic Park Vaccination Centre at Homebush in Sydney, Australia, on Aug. 16, 2021. (David Gray/AFP via Getty Images)
A popular meme contrasts the “scientific method” with the “science worshiper’s method.” While the former moves in a rigorous, self-correcting way toward results that may or may not align with a specific hypothesis, the latter constructs a model and then only accepts the data that will confirm that model.
At its most extreme, “following the science” is inflexibly dogmatic. When less inflexible, “following the science” can lead to sudden, sharp changes in public policy, often in the face of other evidence and goals separate from the COVID-19 response—for example, avoiding other health problems or economic disruption traceable to such policies.
Masking
In the case of masking, “following the science” has led to a series of dramatic reversals.
Surgeon General Jerome Adams speaks to members of Congress in Washington on Sept. 9, 2020. (Michael Reynolds/Pool/AFP via Getty Images)
In February 2020, U.S. Surgeon General Jerome Adams wrote on Twitter that Americans should “STOP BUYING MASKS!” as they were “not effective.”
In March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) maintained that healthy individuals didn’t need to wear masks.
Yet as mask production ramped up in the United States, U.S. public health authorities changed their tune. In early April, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended that Americans consider wearing cloth masks.
By June 2020, WHO recommended that healthy members of the general public wear masks in situations where physical distancing wasn’t possible, citing new scientific evidence on transmission.
A man enters the headquarters of the World Health Organization in Geneva, Switzerland, on June 15, 2021. (Sean Gallup/Getty Images)
In 2021, the CDC repeatedly shifted on masking. In July 2021, it reversed a May recommendation that vaccinated people need not wear masks, drawing rebukes from Republican governors.
Some experts believe that such shifts mark a significant departure from our understanding of masking before the pandemic.
“When it comes to the point of certain interventions that are sort of weakly supported, and if you go back and look at everything that was published before 2020, and come to this completely different conclusion if you read the things that published later on in 2020, about masks or the ability of lockdowns to stop and end spread indefinitely—long-term lockdowns that have devastating collateral damage—and that type of thing. And then you realize how politicized this really has become,” immunologist Steven Templeton, a professor at Indiana University, formerly with the CDC, said in an interview with The Epoch Times’ EpochTV.
One of the most politicized issues is the masking of young children. While advocates have argued that children could be major transmitters of COVID-19, opponents have argued that children are neither major vectors of the disease nor vulnerable to serious illness or death. They have also pointed out the understudied developmental and physiological risks of masking young children.
A pupil wearing a face mask attends a class in a file photo. (JEAN-CHRISTOPHE VERHAEGEN/AFP via Getty Images)
One 2021 preprint found no correlation between mask mandates and COVID-19 case rates among students and faculty across schools in Florida, New York, and Massachusetts, though the authors included caveats about how well their findings could be generalized.
Still, for many schools, “following the science” has led to universal mask mandates. Portland Public Schools, for example, requires the masking of children at all times and places, indoor or outdoor, and irrespective of vaccination status, “except when eating, drinking or playing a musical wind instrument.”
You realize how politicized this really has become.
— Steven Templeton, professor at Indiana University
In one instance, guerilla footage showed kindergartners “eating” while sitting outside on buckets in 40-degree weather while socially distanced from playmates.
In cases such as these, “following the science” has the look and feel of political theater.
Men wearing protective suits make their way at a bus stop at Narita international airport on the first day of closed borders to prevent the spread of the new Omicron variant amid the pandemic in Narita, east of Tokyo, Japan, Nov. 30, 2021. (Kim Kyung-Hoon/Reuters)
Omicron and Beyond
The Omicron variant of COVID-19 hasn’t yet caused a surge in serious COVID-19 cases. Yet as soon as the new strain made international headlines, governments across the world were ready to “follow the science,” or at least take some sort of action in its name.
The United States, the UK, and other countries have banned travel from many countries in southern Africa, where Omicron was first detected. Japan, meanwhile, barred entry of all foreign nationals.
WHO and other scientists and physicians argued that these bans weren’t warranted, in part because they would do little to slow the variant’s spread.
As the new strain made international headlines, governments across the world were ready to ‘Follow the Science.’
The CEO of Pfizer, too, has speculated that the variant could push up the debut of its latest booster, telling CNBC, “I think we will need a fourth dose.”
For now, however, the new variant appears to be mild. To date, Omicron doesn’t seem to have caused a single verifiable death.
World Health Organization (WHO) Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus attends a news conference organized by the Geneva Association of United Nations Correspondents (ACANU) amid the COVID-19 outbreak, caused by the novel coronavirus, at the WHO headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, on July 3, 2020. (Fabrice Coffrini/Pool via Reuters)
When asked by The Epoch Times if Omicron had led to a single confirmed fatality, a WHO spokesperson sent its weekly epidemiological update for Dec. 7.
According to that guide: “All of the 212 confirmed cases identified in 18 European Union countries for which there was information available on severity were asymptomatic or mild. While South Africa saw an 82 percent increase in hospital admissions due to COVID-19 (from 502 to 912) during the week 28 November–4 December 2021, it is not yet known the proportion of these with the Omicron variant.”
In addition, the WHO spokesperson said, “For Omicron, we have not had any deaths reported, but it is still early in the clinical course of disease and this may change.”
The CDC didn’t immediately respond to a request for comment from The Epoch Times on whether there were any confirmed Omicron deaths.
Other examples abound. For instance, while data show vaccinated individuals are significantly less likely to die of COVID-19 than the unvaccinated, “following the science” to preapproved conclusions may prematurely foreclose or minimize serious concerns about vaccine safety, particularly in relation to heart inflammation or other cardiovascular disease.
In September testimony before the FDA in its evaluation of the Pfizer booster, entrepreneur Steve Kirsch said that Pfizer’s vaccines kill more people than they save, citing Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) data, among other information.
Just days ago, physicians and scientists in the UK reportedly warned that post-pandemic stress disorder is driving a rise in heart attacks and other cardiovascular issues, including among younger patients.
Some commentators speculated that the rise could be related to vaccines.
Candace Owens wrote on Twitter in response to the story: “I’ve just learned that the sudden increase in heart-related illnesses is likely due to **checks Big Pharma notes** Post-Pandemic Stress Disorder. Nothing to see here!”
Following Science, Not ‘Following the Science’
While New York and New York City have pursued hardline policies, including the city’s vaccine pass system applicable to children as young as 5, the state of Florida has blocked mandates and prioritized individual choice.
Today, case rates in Florida are lower than in New York, likely in part because of the disease’s seasonality. Moreover, while Floridians are on average older than New York residents, suggesting that they should be more vulnerable to COVID-19, the death rate per 100,000 is still lower in that state than in New York, according to NBC News. New York City itself has had more than 34,000 deaths, due partly to major early clusters in nursing homes in the city.
People visit Clearwater Beach after Governor Ron DeSantis opened the beaches at 7 a.m. on May 4, 2020 in Clearwater, Fla. (Mike Ehrmann/Getty Images)
The Senate’s Dec. 8 vote to block Biden’s OSHA vaccine mandate for large employers, which came soon after the 6th Circuit Court overruled the same mandate, could signal the resilience of checks and balances against compulsion in the name of “the science.”
Elsewhere in the world, “following the science,” often in spite of other scientific evidence, is leading to more draconian policies.
New Brunswick, Canada, has permitted grocery stores to exclude the unvaccinated, violating the basic human right to food articulated in Article 25 of The Universal Declaration of Human Rights as well as Article 11 of the International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights.
Canadian and American flags fly near the Ambassador Bridge at the Canada–U.S. border crossing in Windsor, Ont., in a file photo. (The Canadian Press/Rob Gurdebeke)
Numerous studies have raised questions about whether vaccination stems transmission, with some suggesting that vaccinated people with suppressed symptoms of the disease may even be major drivers of new infection. Regardless, “the science” demands greater sacrifices by the day.
Good science can and should inform our judgments as well as those of politicians. But unthinking gestures toward “the science” don’t shield any of us from responsibility—though as Jeffrey A. Tucker of The Brownstone Institute points out, the bureaucrats whose banalities enforce our new scientistic consensuses shirk any blame for its self-evident failures.
International
Copper Soars, Iron Ore Tumbles As Goldman Says “Copper’s Time Is Now”
Copper Soars, Iron Ore Tumbles As Goldman Says "Copper’s Time Is Now"
After languishing for the past two years in a tight range despite recurring…
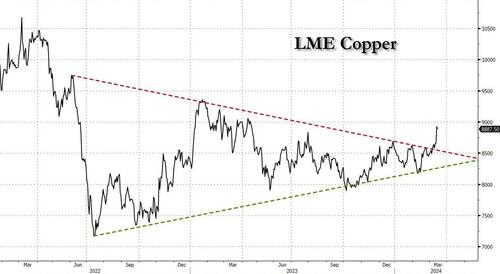
After languishing for the past two years in a tight range despite recurring speculation about declining global supply, copper has finally broken out, surging to the highest price in the past year, just shy of $9,000 a ton as supply cuts hit the market; At the same time the price of the world's "other" most important mined commodity has diverged, as iron ore has tumbled amid growing demand headwinds out of China's comatose housing sector where not even ghost cities are being built any more.
Copper surged almost 5% this week, ending a months-long spell of inertia, as investors focused on risks to supply at various global mines and smelters. As Bloomberg adds, traders also warmed to the idea that the worst of a global downturn is in the past, particularly for metals like copper that are increasingly used in electric vehicles and renewables.
Yet the commodity crash of recent years is hardly over, as signs of the headwinds in traditional industrial sectors are still all too obvious in the iron ore market, where futures fell below $100 a ton for the first time in seven months on Friday as investors bet that China’s years-long property crisis will run through 2024, keeping a lid on demand.
Indeed, while the mood surrounding copper has turned almost euphoric, sentiment on iron ore has soured since the conclusion of the latest National People’s Congress in Beijing, where the CCP set a 5% goal for economic growth, but offered few new measures that would boost infrastructure or other construction-intensive sectors.
As a result, the main steelmaking ingredient has shed more than 30% since early January as hopes of a meaningful revival in construction activity faded. Loss-making steel mills are buying less ore, and stockpiles are piling up at Chinese ports. The latest drop will embolden those who believe that the effects of President Xi Jinping’s property crackdown still have significant room to run, and that last year’s rally in iron ore may have been a false dawn.
Meanwhile, as Bloomberg notes, on Friday there were fresh signs that weakness in China’s industrial economy is hitting the copper market too, with stockpiles tracked by the Shanghai Futures Exchange surging to the highest level since the early days of the pandemic. The hope is that headwinds in traditional industrial areas will be offset by an ongoing surge in usage in electric vehicles and renewables.
And while industrial conditions in Europe and the US also look soft, there’s growing optimism about copper usage in India, where rising investment has helped fuel blowout growth rates of more than 8% — making it the fastest-growing major economy.
In any case, with the demand side of the equation still questionable, the main catalyst behind copper’s powerful rally is an unexpected tightening in global mine supplies, driven mainly by last year’s closure of a giant mine in Panama (discussed here), but there are also growing worries about output in Zambia, which is facing an El Niño-induced power crisis.
On Wednesday, copper prices jumped on huge volumes after smelters in China held a crisis meeting on how to cope with a sharp drop in processing fees following disruptions to supplies of mined ore. The group stopped short of coordinated production cuts, but pledged to re-arrange maintenance work, reduce runs and delay the startup of new projects. In the coming weeks investors will be watching Shanghai exchange inventories closely to gauge both the strength of demand and the extent of any capacity curtailments.
“The increase in SHFE stockpiles has been bigger than we’d anticipated, but we expect to see them coming down over the next few weeks,” Colin Hamilton, managing director for commodities research at BMO Capital Markets, said by phone. “If the pace of the inventory builds doesn’t start to slow, investors will start to question whether smelters are actually cutting and whether the impact of weak construction activity is starting to weigh more heavily on the market.”
* * *
Few have been as happy with the recent surge in copper prices as Goldman's commodity team, where copper has long been a preferred trade (even if it may have cost the former team head Jeff Currie his job due to his unbridled enthusiasm for copper in the past two years which saw many hedge fund clients suffer major losses).
As Goldman's Nicholas Snowdon writes in a note titled "Copper's time is now" (available to pro subscribers in the usual place)...
... there has been a "turn in the industrial cycle." Specifically according to the Goldman analyst, after a prolonged downturn, "incremental evidence now points to a bottoming out in the industrial cycle, with the global manufacturing PMI in expansion for the first time since September 2022." As a result, Goldman now expects copper to rise to $10,000/t by year-end and then $12,000/t by end of Q1-25.’
Here are the details:
Previous inflexions in global manufacturing cycles have been associated with subsequent sustained industrial metals upside, with copper and aluminium rising on average 25% and 9% over the next 12 months. Whilst seasonal surpluses have so far limited a tightening alignment at a micro level, we expect deficit inflexions to play out from quarter end, particularly for metals with severe supply binds. Supplemented by the influence of anticipated Fed easing ahead in a non-recessionary growth setting, another historically positive performance factor for metals, this should support further upside ahead with copper the headline act in this regard.
Goldman then turns to what it calls China's "green policy put":
Much of the recent focus on the “Two Sessions” event centred on the lack of significant broad stimulus, and in particular the limited property support. In our view it would be wrong – just as in 2022 and 2023 – to assume that this will result in weak onshore metals demand. Beijing’s emphasis on rapid growth in the metals intensive green economy, as an offset to property declines, continues to act as a policy put for green metals demand. After last year’s strong trends, evidence year-to-date is again supportive with aluminium and copper apparent demand rising 17% and 12% y/y respectively. Moreover, the potential for a ‘cash for clunkers’ initiative could provide meaningful right tail risk to that healthy demand base case. Yet there are also clear metal losers in this divergent policy setting, with ongoing pressure on property related steel demand generating recent sharp iron ore downside.
Meanwhile, Snowdon believes that the driver behind Goldman's long-running bullish view on copper - a global supply shock - continues:
Copper’s supply shock progresses. The metal with most significant upside potential is copper, in our view. The supply shock which began with aggressive concentrate destocking and then sharp mine supply downgrades last year, has now advanced to an increasing bind on metal production, as reflected in this week's China smelter supply rationing signal. With continued positive momentum in China's copper demand, a healthy refined import trend should generate a substantial ex-China refined deficit this year. With LME stocks having halved from Q4 peak, China’s imminent seasonal demand inflection should accelerate a path into extreme tightness by H2. Structural supply underinvestment, best reflected in peak mine supply we expect next year, implies that demand destruction will need to be the persistent solver on scarcity, an effect requiring substantially higher pricing than current, in our view. In this context, we maintain our view that the copper price will surge into next year (GSe 2025 $15,000/t average), expecting copper to rise to $10,000/t by year-end and then $12,000/t by end of Q1-25’
Another reason why Goldman is doubling down on its bullish copper outlook: gold.
The sharp rally in gold price since the beginning of March has ended the period of consolidation that had been present since late December. Whilst the initial catalyst for the break higher came from a (gold) supportive turn in US data and real rates, the move has been significantly amplified by short term systematic buying, which suggests less sticky upside. In this context, we expect gold to consolidate for now, with our economists near term view on rates and the dollar suggesting limited near-term catalysts for further upside momentum. Yet, a substantive retracement lower will also likely be limited by resilience in physical buying channels. Nonetheless, in the midterm we continue to hold a constructive view on gold underpinned by persistent strength in EM demand as well as eventual Fed easing, which should crucially reactivate the largely for now dormant ETF buying channel. In this context, we increase our average gold price forecast for 2024 from $2,090/toz to $2,180/toz, targeting a move to $2,300/toz by year-end.
Much more in the full Goldman note available to pro subs.
International
The millions of people not looking for work in the UK may be prioritising education, health and freedom
Economic inactivity is not always the worst option.

Around one in five British people of working age (16-64) are now outside the labour market. Neither in work nor looking for work, they are officially labelled as “economically inactive”.
Some of those 9.2 million people are in education, with many students not active in the labour market because they are studying full-time. Others are older workers who have chosen to take early retirement.
But that still leaves a large number who are not part of the labour market because they are unable to work. And one key driver of economic inactivity in recent years has been illness.
This increase in economic inactivity – which has grown since before the pandemic – is not just harming the economy, but also indicative of a deeper health crisis.
For those suffering ill health, there are real constraints on access to work. People with health-limiting conditions cannot just slot into jobs that are available. They need help to address the illnesses they have, and to re-engage with work through organisations offering supportive and healthy work environments.
And for other groups, such as stay-at-home parents, businesses need to offer flexible work arrangements and subsidised childcare to support the transition from economic inactivity into work.
The government has a role to play too. Most obviously, it could increase investment in the NHS. Rising levels of poor health are linked to years of under-investment in the health sector and economic inactivity will not be tackled without more funding.
Carrots and sticks
For the time being though, the UK government appears to prefer an approach which mixes carrots and sticks. In the March 2024 budget, for example, the chancellor cut national insurance by 2p as a way of “making work pay”.
But it is unclear whether small tax changes like this will have any effect on attracting the economically inactive back into work.
Jeremy Hunt also extended free childcare. But again, questions remain over whether this is sufficient to remove barriers to work for those with parental responsibilities. The high cost and lack of availability of childcare remain key weaknesses in the UK economy.
The benefit system meanwhile has been designed to push people into work. Benefits in the UK remain relatively ungenerous and hard to access compared with other rich countries. But labour shortages won’t be solved by simply forcing the economically inactive into work, because not all of them are ready or able to comply.
It is also worth noting that work itself may be a cause of bad health. The notion of “bad work” – work that does not pay enough and is unrewarding in other ways – can lead to economic inactivity.
There is also evidence that as work has become more intensive over recent decades, for some people, work itself has become a health risk.
The pandemic showed us how certain groups of workers (including so-called “essential workers”) suffered more ill health due to their greater exposure to COVID. But there are broader trends towards lower quality work that predate the pandemic, and these trends suggest improving job quality is an important step towards tackling the underlying causes of economic inactivity.
Freedom
Another big section of the economically active population who cannot be ignored are those who have retired early and deliberately left the labour market behind. These are people who want and value – and crucially, can afford – a life without work.
Here, the effects of the pandemic can be seen again. During those years of lockdowns, furlough and remote working, many of us reassessed our relationship with our jobs. Changed attitudes towards work among some (mostly older) workers can explain why they are no longer in the labour market and why they may be unresponsive to job offers of any kind.

And maybe it is from this viewpoint that we should ultimately be looking at economic inactivity – that it is actually a sign of progress. That it represents a move towards freedom from the drudgery of work and the ability of some people to live as they wish.
There are utopian visions of the future, for example, which suggest that individual and collective freedom could be dramatically increased by paying people a universal basic income.
In the meantime, for plenty of working age people, economic inactivity is a direct result of ill health and sickness. So it may be that the levels of economic inactivity right now merely show how far we are from being a society which actually supports its citizens’ wellbeing.
David Spencer has received funding from the ESRC.
uk pandemicInternational
Illegal Immigrants Leave US Hospitals With Billions In Unpaid Bills
Illegal Immigrants Leave US Hospitals With Billions In Unpaid Bills
By Autumn Spredemann of The Epoch Times
Tens of thousands of illegal…

By Autumn Spredemann of The Epoch Times
Tens of thousands of illegal immigrants are flooding into U.S. hospitals for treatment and leaving billions in uncompensated health care costs in their wake.
The House Committee on Homeland Security recently released a report illustrating that from the estimated $451 billion in annual costs stemming from the U.S. border crisis, a significant portion is going to health care for illegal immigrants.
With the majority of the illegal immigrant population lacking any kind of medical insurance, hospitals and government welfare programs such as Medicaid are feeling the weight of these unanticipated costs.
Apprehensions of illegal immigrants at the U.S. border have jumped 48 percent since the record in fiscal year 2021 and nearly tripled since fiscal year 2019, according to Customs and Border Protection data.
Last year broke a new record high for illegal border crossings, surpassing more than 3.2 million apprehensions.
And with that sea of humanity comes the need for health care and, in most cases, the inability to pay for it.
In January, CEO of Denver Health Donna Lynne told reporters that 8,000 illegal immigrants made roughly 20,000 visits to the city’s health system in 2023.
The total bill for uncompensated care costs last year to the system totaled $140 million, said Dane Roper, public information officer for Denver Health. More than $10 million of it was attributed to “care for new immigrants,” he told The Epoch Times.
Though the amount of debt assigned to illegal immigrants is a fraction of the total, uncompensated care costs in the Denver Health system have risen dramatically over the past few years.
The total uncompensated costs in 2020 came to $60 million, Mr. Roper said. In 2022, the number doubled, hitting $120 million.
He also said their city hospitals are treating issues such as “respiratory illnesses, GI [gastro-intenstinal] illnesses, dental disease, and some common chronic illnesses such as asthma and diabetes.”
“The perspective we’ve been trying to emphasize all along is that providing healthcare services for an influx of new immigrants who are unable to pay for their care is adding additional strain to an already significant uncompensated care burden,” Mr. Roper said.
He added this is why a local, state, and federal response to the needs of the new illegal immigrant population is “so important.”
Colorado is far from the only state struggling with a trail of unpaid hospital bills.

Dr. Robert Trenschel, CEO of the Yuma Regional Medical Center situated on the Arizona–Mexico border, said on average, illegal immigrants cost up to three times more in human resources to resolve their cases and provide a safe discharge.
“Some [illegal] migrants come with minor ailments, but many of them come in with significant disease,” Dr. Trenschel said during a congressional hearing last year.
“We’ve had migrant patients on dialysis, cardiac catheterization, and in need of heart surgery. Many are very sick.”
He said many illegal immigrants who enter the country and need medical assistance end up staying in the ICU ward for 60 days or more.
A large portion of the patients are pregnant women who’ve had little to no prenatal treatment. This has resulted in an increase in babies being born that require neonatal care for 30 days or longer.
Dr. Trenschel told The Epoch Times last year that illegal immigrants were overrunning healthcare services in his town, leaving the hospital with $26 million in unpaid medical bills in just 12 months.
ER Duty to Care
The Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act of 1986 requires that public hospitals participating in Medicare “must medically screen all persons seeking emergency care … regardless of payment method or insurance status.”
The numbers are difficult to gauge as the policy position of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is that it “will not require hospital staff to ask patients directly about their citizenship or immigration status.”
In southern California, again close to the border with Mexico, some hospitals are struggling with an influx of illegal immigrants.
American patients are enduring longer wait times for doctor appointments due to a nursing shortage in the state, two health care professionals told The Epoch Times in January.
A health care worker at a hospital in Southern California, who asked not to be named for fear of losing her job, told The Epoch Times that “the entire health care system is just being bombarded” by a steady stream of illegal immigrants.
“Our healthcare system is so overwhelmed, and then add on top of that tuberculosis, COVID-19, and other diseases from all over the world,” she said.

A newly-enacted law in California provides free healthcare for all illegal immigrants residing in the state. The law could cost taxpayers between $3 billion and $6 billion per year, according to recent estimates by state and federal lawmakers.
In New York, where the illegal immigration crisis has manifested most notably beyond the southern border, city and state officials have long been accommodating of illegal immigrants’ healthcare costs.
Since June 2014, when then-mayor Bill de Blasio set up The Task Force on Immigrant Health Care Access, New York City has worked to expand avenues for illegal immigrants to get free health care.
“New York City has a moral duty to ensure that all its residents have meaningful access to needed health care, regardless of their immigration status or ability to pay,” Mr. de Blasio stated in a 2015 report.
The report notes that in 2013, nearly 64 percent of illegal immigrants were uninsured. Since then, tens of thousands of illegal immigrants have settled in the city.
“The uninsured rate for undocumented immigrants is more than three times that of other noncitizens in New York City (20 percent) and more than six times greater than the uninsured rate for the rest of the city (10 percent),” the report states.
The report states that because healthcare providers don’t ask patients about documentation status, the task force lacks “data specific to undocumented patients.”
Some health care providers say a big part of the issue is that without a clear path to insurance or payment for non-emergency services, illegal immigrants are going to the hospital due to a lack of options.
“It’s insane, and it has been for years at this point,” Dana, a Texas emergency room nurse who asked to have her full name omitted, told The Epoch Times.
Working for a major hospital system in the greater Houston area, Dana has seen “a zillion” migrants pass through under her watch with “no end in sight.” She said many who are illegal immigrants arrive with treatable illnesses that require simple antibiotics. “Not a lot of GPs [general practitioners] will see you if you can’t pay and don’t have insurance.”
She said the “undocumented crowd” tends to arrive with a lot of the same conditions. Many find their way to Houston not long after crossing the southern border. Some of the common health issues Dana encounters include dehydration, unhealed fractures, respiratory illnesses, stomach ailments, and pregnancy-related concerns.
“This isn’t a new problem, it’s just worse now,” Dana said.

Medicaid Factor
One of the main government healthcare resources illegal immigrants use is Medicaid.
All those who don’t qualify for regular Medicaid are eligible for Emergency Medicaid, regardless of immigration status. By doing this, the program helps pay for the cost of uncompensated care bills at qualifying hospitals.
However, some loopholes allow access to the regular Medicaid benefits. “Qualified noncitizens” who haven’t been granted legal status within five years still qualify if they’re listed as a refugee, an asylum seeker, or a Cuban or Haitian national.
Yet the lion’s share of Medicaid usage by illegal immigrants still comes through state-level benefits and emergency medical treatment.
A Congressional report highlighted data from the CMS, which showed total Medicaid costs for “emergency services for undocumented aliens” in fiscal year 2021 surpassed $7 billion, and totaled more than $5 billion in fiscal 2022.
Both years represent a significant spike from the $3 billion in fiscal 2020.
An employee working with Medicaid who asked to be referred to only as Jennifer out of concern for her job, told The Epoch Times that at a state level, it’s easy for an illegal immigrant to access the program benefits.
Jennifer said that when exceptions are sent from states to CMS for approval, “denial is actually super rare. It’s usually always approved.”
She also said it comes as no surprise that many of the states with the highest amount of Medicaid spending are sanctuary states, which tend to have policies and laws that shield illegal immigrants from federal immigration authorities.
Moreover, Jennifer said there are ways for states to get around CMS guidelines. “It’s not easy, but it can and has been done.”
The first generation of illegal immigrants who arrive to the United States tend to be healthy enough to pass any pre-screenings, but Jennifer has observed that the subsequent generations tend to be sicker and require more access to care. If a family is illegally present, they tend to use Emergency Medicaid or nothing at all.
The Epoch Times asked Medicaid Services to provide the most recent data for the total uncompensated care that hospitals have reported. The agency didn’t respond.
Continue reading over at The Epoch Times
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Spread & Containment3 days ago
Spread & Containment3 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex



































