Financial Stability Risks Grow as War Complicates Push to Contain Inflation
While no systemic event has materialized so far, the balance of risks has tilted more firmly to the downside.
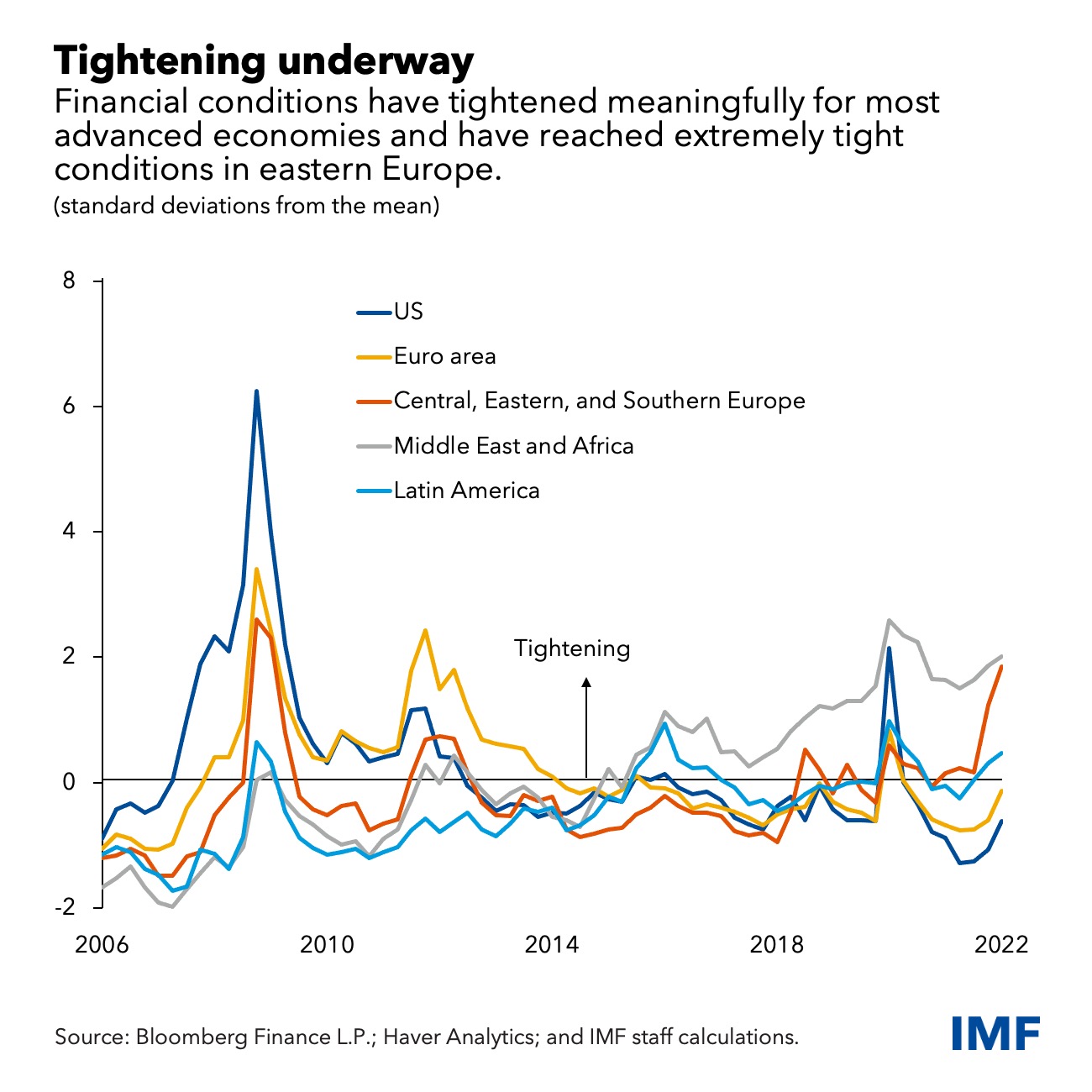
While no systemic event has materialized, the balance of risks has tilted more firmly to the downside.
emerging markets pandemic crypto real estate currencies us dollar crypto commodities commodity markets oil
Government
Problems After COVID-19 Vaccination More Prevalent Among Naturally Immune: Study
Problems After COVID-19 Vaccination More Prevalent Among Naturally Immune: Study
Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis…
Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
People who recovered from COVID-19 and received a COVID-19 shot were more likely to suffer adverse reactions, researchers in Europe are reporting.
Participants in the study were more likely to experience an adverse reaction after vaccination regardless of the type of shot, with one exception, the researchers found.
Across all vaccine brands, people with prior COVID-19 were 2.6 times as likely after dose one to suffer an adverse reaction, according to the new study. Such people are commonly known as having a type of protection known as natural immunity after recovery.
People with previous COVID-19 were also 1.25 times as likely after dose 2 to experience an adverse reaction.
The findings held true across all vaccine types following dose one.
Of the female participants who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, for instance, 82 percent who had COVID-19 previously experienced an adverse reaction after their first dose, compared to 59 percent of females who did not have prior COVID-19.
The only exception to the trend was among males who received a second AstraZeneca dose. The percentage of males who suffered an adverse reaction was higher, 33 percent to 24 percent, among those without a COVID-19 history.
“Participants who had a prior SARS-CoV-2 infection (confirmed with a positive test) experienced at least one adverse reaction more often after the 1st dose compared to participants who did not have prior COVID-19. This pattern was observed in both men and women and across vaccine brands,” Florence van Hunsel, an epidemiologist with the Netherlands Pharmacovigilance Centre Lareb, and her co-authors wrote.
There were only slightly higher odds of the naturally immune suffering an adverse reaction following receipt of a Pfizer or Moderna booster, the researchers also found.
The researchers performed what’s known as a cohort event monitoring study, following 29,387 participants as they received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine. The participants live in a European country such as Belgium, France, or Slovakia.
Overall, three-quarters of the participants reported at least one adverse reaction, although some were minor such as injection site pain.
Adverse reactions described as serious were reported by 0.24 percent of people who received a first or second dose and 0.26 percent for people who received a booster. Different examples of serious reactions were not listed in the study.
Participants were only specifically asked to record a range of minor adverse reactions (ADRs). They could provide details of other reactions in free text form.
“The unsolicited events were manually assessed and coded, and the seriousness was classified based on international criteria,” researchers said.
The free text answers were not provided by researchers in the paper.
“The authors note, ‘In this manuscript, the focus was not on serious ADRs and adverse events of special interest.’” Yet, in their highlights section they state, “The percentage of serious ADRs in the study is low for 1st and 2nd vaccination and booster.”
Dr. Joel Wallskog, co-chair of the group React19, which advocates for people who were injured by vaccines, told The Epoch Times: “It is intellectually dishonest to set out to study minor adverse events after COVID-19 vaccination then make conclusions about the frequency of serious adverse events. They also fail to provide the free text data.” He added that the paper showed “yet another study that is in my opinion, deficient by design.”
Ms. Hunsel did not respond to a request for comment.
She and other researchers listed limitations in the paper, including how they did not provide data broken down by country.
The paper was published by the journal Vaccine on March 6.
The study was funded by the European Medicines Agency and the Dutch government.
No authors declared conflicts of interest.
Some previous papers have also found that people with prior COVID-19 infection had more adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination, including a 2021 paper from French researchers. A U.S. study identified prior COVID-19 as a predictor of the severity of side effects.
Some other studies have determined COVID-19 vaccines confer little or no benefit to people with a history of infection, including those who had received a primary series.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention still recommends people who recovered from COVID-19 receive a COVID-19 vaccine, although a number of other health authorities have stopped recommending the shot for people who have prior COVID-19.
Another New Study
In another new paper, South Korean researchers outlined how they found people were more likely to report certain adverse reactions after COVID-19 vaccination than after receipt of another vaccine.
The reporting of myocarditis, a form of heart inflammation, or pericarditis, a related condition, was nearly 20 times as high among children as the reporting odds following receipt of all other vaccines, the researchers found.
The reporting odds were also much higher for multisystem inflammatory syndrome or Kawasaki disease among adolescent COVID-19 recipients.
Researchers analyzed reports made to VigiBase, which is run by the World Health Organization.
“Based on our results, close monitoring for these rare but serious inflammatory reactions after COVID-19 vaccination among adolescents until definitive causal relationship can be established,” the researchers wrote.
The study was published by the Journal of Korean Medical Science in its March edition.
Limitations include VigiBase receiving reports of problems, with some reports going unconfirmed.
Funding came from the South Korean government. One author reported receiving grants from pharmaceutical companies, including Pfizer.
Uncategorized
Key shipping company files for Chapter 11 bankruptcy
The Illinois-based general freight trucking company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy to reorganize.

The U.S. trucking industry has had a difficult beginning of the year for 2024 with several logistics companies filing for bankruptcy to seek either a Chapter 7 liquidation or Chapter 11 reorganization.
The Covid-19 pandemic caused a lot of supply chain issues for logistics companies and also created a shortage of truck drivers as many left the business for other occupations. Shipping companies, in the meantime, have had extreme difficulty recruiting new drivers for thousands of unfilled jobs.
Related: Tesla rival’s filing reveals Chapter 11 bankruptcy is possible
Freight forwarder company Boateng Logistics joined a growing list of shipping companies that permanently shuttered their businesses as the firm on Feb. 22 filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy with plans to liquidate.
The Carlsbad, Calif., logistics company filed its petition in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of California listing assets up to $50,000 and and $1 million to $10 million in liabilities. Court papers said it owed millions of dollars in liabilities to trucking, logistics and factoring companies. The company filed bankruptcy before any creditors could take legal action.
Lawsuits force companies to liquidate in bankruptcy
Lawsuits, however, can force companies to file bankruptcy, which was the case for J.J. & Sons Logistics of Clint, Texas, which on Jan. 22 filed for Chapter 7 liquidation in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Western District of Texas. The company filed bankruptcy four days before the scheduled start of a trial for a wrongful death lawsuit filed by the family of a former company truck driver who had died from drowning in 2016.
California-based logistics company Wise Choice Trans Corp. shut down operations and filed for Chapter 7 liquidation on Jan. 4 in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Northern District of California, listing $1 million to $10 million in assets and liabilities.
The Hayward, Calif., third-party logistics company, founded in 2009, provided final mile, less-than-truckload and full truckload services, as well as warehouse and fulfillment services in the San Francisco Bay Area.
The Chapter 7 filing also implemented an automatic stay against all legal proceedings, as the company listed its involvement in four legal actions that were ongoing or concluded. Court papers reportedly did not list amounts for damages.
In some cases, debtors don't have to take a drastic action, such as a liquidation, and can instead file a Chapter 11 reorganization.
Shutterstock
Nationwide Cargo seeks to reorganize its business
Nationwide Cargo Inc., a general freight trucking company that also hauls fresh produce and meat, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Northern District of Illinois with plans to reorganize its business.
The East Dundee, Ill., shipping company listed $1 million to $10 million in assets and $10 million to $50 million in liabilities in its petition and said funds will not be available to pay unsecured creditors. The company operates with 183 trucks and 171 drivers, FreightWaves reported.
Nationwide Cargo's three largest secured creditors in the petition were Equify Financial LLC (owed about $3.5 million,) Commercial Credit Group (owed about $1.8 million) and Continental Bank NA (owed about $676,000.)
The shipping company reported gross revenue of about $34 million in 2022 and about $40 million in 2023. From Jan. 1 until its petition date, the company generated $9.3 million in gross revenue.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
bankruptcy pandemic covid-19 stocksUncategorized
Key shipping company files Chapter 11 bankruptcy
The Illinois-based general freight trucking company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy to reorganize.

The U.S. trucking industry has had a difficult beginning of the year for 2024 with several logistics companies filing for bankruptcy to seek either a Chapter 7 liquidation or Chapter 11 reorganization.
The Covid-19 pandemic caused a lot of supply chain issues for logistics companies and also created a shortage of truck drivers as many left the business for other occupations. Shipping companies, in the meantime, have had extreme difficulty recruiting new drivers for thousands of unfilled jobs.
Related: Tesla rival’s filing reveals Chapter 11 bankruptcy is possible
Freight forwarder company Boateng Logistics joined a growing list of shipping companies that permanently shuttered their businesses as the firm on Feb. 22 filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy with plans to liquidate.
The Carlsbad, Calif., logistics company filed its petition in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of California listing assets up to $50,000 and and $1 million to $10 million in liabilities. Court papers said it owed millions of dollars in liabilities to trucking, logistics and factoring companies. The company filed bankruptcy before any creditors could take legal action.
Lawsuits force companies to liquidate in bankruptcy
Lawsuits, however, can force companies to file bankruptcy, which was the case for J.J. & Sons Logistics of Clint, Texas, which on Jan. 22 filed for Chapter 7 liquidation in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Western District of Texas. The company filed bankruptcy four days before the scheduled start of a trial for a wrongful death lawsuit filed by the family of a former company truck driver who had died from drowning in 2016.
California-based logistics company Wise Choice Trans Corp. shut down operations and filed for Chapter 7 liquidation on Jan. 4 in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Northern District of California, listing $1 million to $10 million in assets and liabilities.
The Hayward, Calif., third-party logistics company, founded in 2009, provided final mile, less-than-truckload and full truckload services, as well as warehouse and fulfillment services in the San Francisco Bay Area.
The Chapter 7 filing also implemented an automatic stay against all legal proceedings, as the company listed its involvement in four legal actions that were ongoing or concluded. Court papers reportedly did not list amounts for damages.
In some cases, debtors don't have to take a drastic action, such as a liquidation, and can instead file a Chapter 11 reorganization.
Shutterstock
Nationwide Cargo seeks to reorganize its business
Nationwide Cargo Inc., a general freight trucking company that also hauls fresh produce and meat, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Northern District of Illinois with plans to reorganize its business.
The East Dundee, Ill., shipping company listed $1 million to $10 million in assets and $10 million to $50 million in liabilities in its petition and said funds will not be available to pay unsecured creditors. The company operates with 183 trucks and 171 drivers, FreightWaves reported.
Nationwide Cargo's three largest secured creditors in the petition were Equify Financial LLC (owed about $3.5 million,) Commercial Credit Group (owed about $1.8 million) and Continental Bank NA (owed about $676,000.)
The shipping company reported gross revenue of about $34 million in 2022 and about $40 million in 2023. From Jan. 1 until its petition date, the company generated $9.3 million in gross revenue.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
bankruptcy pandemic covid-19 stocks-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Spread & Containment2 days ago
Spread & Containment2 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A





















