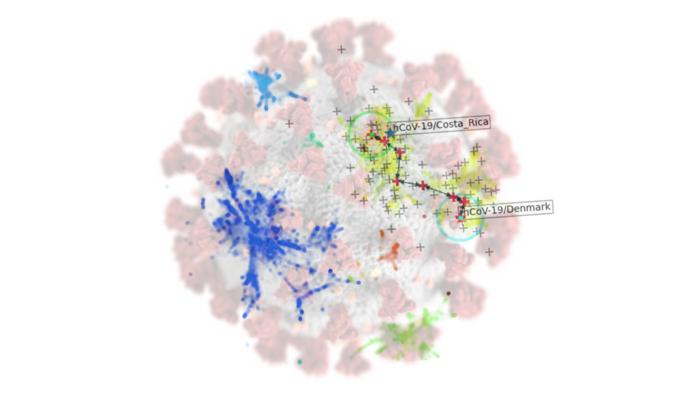
Scientists at The Universities of Manchester and Oxford have developed an AI framework that can identify and track new and concerning COVID-19 variants and could help with other infections in the future.
The framework combines dimension reduction techniques and a new explainable clustering algorithm called CLASSIX, developed by mathematicians at The University of Manchester. This enables the quick identification of groups of viral genomes that might present a risk in the future from huge volumes of data.
The study, presented this week in the journal PNAS, could support traditional methods of tracking viral evolution, such as phylogenetic analysis, which currently require extensive manual curation.
Roberto Cahuantzi, a researcher at The University of Manchester and first and corresponding author of the paper, said: “Since the emergence of COVID-19, we have seen multiple waves of new variants, heightened transmissibility, evasion of immune responses, and increased severity of illness.
“Scientists are now intensifying efforts to pinpoint these worrying new variants, such as alpha, delta and omicron, at the earliest stages of their emergence. If we can find a way to do this quickly and efficiently, it will enable us to be more proactive in our response, such as tailored vaccine development and may even enable us to eliminate the variants before they become established.”
Like many other RNA viruses, COVID-19 has a high mutation rate and short time between generations meaning it evolves extremely rapidly. This means identifying new strains that are likely to be problematic in the future requires considerable effort.
Currently, there are almost 16 million sequences available on the GISAID database (the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data), which provides access to genomic data of influenza viruses.
Mapping the evolution and history of all COVID-19 genomes from this data is currently done using extremely large amounts of computer and human time.
The described method allows automation of such tasks. The researchers processed 5.7 million high-coverage sequences in only one to two days on a standard modern laptop; this would not be possible for existing methods, putting identification of concerning pathogen strains in the hands of more researchers due to reduced resource needs.
Thomas House, Professor of Mathematical Sciences at The University of Manchester, said: “The unprecedented amount of genetic data generated during the pandemic demands improvements to our methods to analyse it thoroughly. The data is continuing to grow rapidly but without showing a benefit to curating this data, there is a risk that it will be removed or deleted.
“We know that human expert time is limited, so our approach should not replace the work of humans all together but work alongside them to enable the job to be done much quicker and free our experts for other vital developments.”
The proposed method works by breaking down genetic sequences of the COVID-19 virus into smaller “words” (called 3-mers) represented as numbers by counting them. Then, it groups similar sequences together based on their word patterns using machine learning techniques.
Stefan Güttel, Professor of Applied Mathematics at the University of Manchester, said: “The clustering algorithm CLASSIX we developed is much less computationally demanding than traditional methods and is fully explainable, meaning that it provides textual and visual explanations of the computed clusters.”
Roberto Cahuantzi added: “Our analysis serves as a proof of concept, demonstrating the potential use of machine learning methods as an alert tool for the early discovery of emerging major variants without relying on the need to generate phylogenies.
“Whilst phylogenetics remains the ‘gold standard’ for understanding the viral ancestry, these machine learning methods can accommodate several orders of magnitude more sequences than the current phylogenetic methods and at a low computational cost.”
Journal
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
DOI
10.1073/pnas.2317284121
Article Title
Unsupervised identification of significant lineages of SARS-CoV-2 through scalable machine learning methods