Uncategorized
Donald Trump: how COVID-19 killed his hope of re-election – new research
A survey of US voters shows that – on their most important issue, COVID-19 – the US president fared particularly badly.

When Donald Trump tested positive for COVID-19 on October 2 and was hospitalised a day later it was widely assumed this would put a major crimp in his re-election campaign. In the event, the US president recovered quite quickly and returned to the campaign trail with gusto after a typically bullish photo-op as he arrived back at the White House.
But survey evidence – initial findings from which are published here for the first time – shows that, despite having apparently triumphed over the virus, he did not escape the grasp of COVID-19 and that his handling of the pandemic played a crucial role in his defeat in the November 3 election.
COVID-19’s horrific toll on human life and its devastating effects on millions of people’s economic and psychological wellbeing have become omnipresent realities. So it’s hardly surprising that the University of Texas at Dallas’ national Cometrends survey, which was conducted in the two weeks before the presidential election, indicates that the pandemic was the dominant issue on many voters’ minds.

As the first graph, above, shows, 62% of 2,500 respondents cited the COVID crisis as one of the top three issues facing the country, while 39% said it was the single most important. No other issue – not even the ailing economy – was chosen as most important by one person in five.
The salience of the pandemic as an issue was a major problem for Trump because an overwhelming number of voters judged that he had mishandled the crisis. As the second graph, below, shows, two-thirds of the Cometrends survey respondents said that they disapproved of the president’s response, while only one person in four approved. When given another chance to comment on his pandemic performance later in the survey, 51% said it had been “bad” or “terrible” and only 38% said “good” or “excellent”.

These dismal ratings for the president on coronavirus were quite opposite to those for the economy – among people who thought the economy was the most important issue, 69% approved of the job the president was doing and only 25% disapproved. Although this was good news for Trump, only a relatively small minority (17%) of voters gave the economy top billing as their most important issue. Moreover, he could not rely on various other issues to improve his job approval rating – across all issues other than the pandemic, only 41% approved of the president’s performance compared with 50% who disapproved.

The third graph, above, shows clearly that if electors were not that concerned about the pandemic they were more likely to vote for Trump as president. But if they gave the issue the top priority they were much less likely to do so. The graph illustrates the impact of COVID-19 on voting for the president, while at the same time statistically taking into account a number of other factors that influence voting behaviour.
The latter include attitudes to the economy, the environment, healthcare, law and order and race relations, as well as other important measures such as identifications with the Democratic and Republican parties, liberal-conservative ideological views and socio-demographic characteristics. The probability of voting for Trump is only 42% among voters who thought COVID-19 was the most important issue but 53% among those who prioritised some other issue in the top three.
This pattern is the opposite for that of the economy. More than three-quarters of voters who gave top priority to the economy supported Trump. That number fell to less than one in three among those for whom economic conditions were not a major concern.
These numbers are nearly identical to those for the large group of potential swing voters who think of themselves as political independents and have no attachment to either of the parties. Independents giving top priority to the pandemic made up nearly 13% of the voters in the Cometrends survey and, other things being equal, the probability of them voting for Trump was very mediocre, at just slightly over 40%.
Game-changing virus
As he was preparing for the 2020 campaign, Trump repeatedly emphasised that his case for re-election was strengthened by his demonstrated ability to deliver economic prosperity. Soaring stock prices and record low unemployment numbers for many groups of voters including ethnic and racial minorities, women and young people were helping the president to make his case. Then the pandemic came along and profoundly changed America and the election-year issue agenda.
As the election date of November 3 approached, most people focusing on the economy as the number one priority continued to give Trump high marks. But these people were now a distinct minority of the electorate. COVID-19 had become the dominant issue for millions of Americans and our survey evidence strongly indicates that most of them judged Trump very harshly for how he was handling the crisis. In many cases, those adverse judgements translated into votes for Trump’s opponent, Joe Biden.
Trump may have recovered physically from COVID-19. But his prospects of re-election took a body blow that he would not recover from.
Paul Whiteley receives funding from the British Academy and the Economic and Social Research Council.
Harold D Clarke has received funding from the National Science Foundation (US).
Karl Ho receives funding from Hong Kong Research Grants Council, Taiwan Ministry of Education, Taiwan Fellowship.
Marianne Stewart receives funding from National Science Foundaton (US).
Uncategorized
Fast-food chain closes restaurants after Chapter 11 bankruptcy
Several major fast-food chains recently have struggled to keep restaurants open.

Competition in the fast-food space has been brutal as operators deal with inflation, consumers who are worried about the economy and their jobs and, in recent months, the falling cost of eating at home.
Add in that many fast-food chains took on more debt during the covid pandemic and that labor costs are rising, and you have a perfect storm of problems.
It's a situation where Restaurant Brands International (QSR) has suffered as much as any company.
Related: Wendy's menu drops a fan favorite item, adds something new
Three major Burger King franchise operators filed for bankruptcy in 2023, and the chain saw hundreds of stores close. It also saw multiple Popeyes franchisees move into bankruptcy, with dozens of locations closing.
RBI also stepped in and purchased one of its key franchisees.
"Carrols is the largest Burger King franchisee in the United States today, operating 1,022 Burger King restaurants in 23 states that generated approximately $1.8 billion of system sales during the 12 months ended Sept. 30, 2023," RBI said in a news release. Carrols also owns and operates 60 Popeyes restaurants in six states."
The multichain company made the move after two of its large franchisees, Premier Kings and Meridian, saw multiple locations not purchased when they reached auction after Chapter 11 bankruptcy filings. In that case, RBI bought select locations but allowed others to close.
Image source: Chen Jianli/Xinhua via Getty
Another fast-food chain faces bankruptcy problems
Bojangles may not be as big a name as Burger King or Popeye's, but it's a popular chain with more than 800 restaurants in eight states.
"Bojangles is a Carolina-born restaurant chain specializing in craveable Southern chicken, biscuits and tea made fresh daily from real recipes, and with a friendly smile," the chain says on its website. "Founded in 1977 as a single location in Charlotte, our beloved brand continues to grow nationwide."
Like RBI, Bojangles uses a franchise model, which makes it dependent on the financial health of its operators. The company ultimately saw all its Maryland locations close due to the financial situation of one of its franchisees.
Unlike. RBI, Bojangles is not public — it was taken private by Durational Capital Management LP and Jordan Co. in 2018 — which means the company does not disclose its financial information to the public.
That makes it hard to know whether overall softness for the brand contributed to the chain seeing its five Maryland locations after a Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing.
Bojangles has a messy bankruptcy situation
Even though the locations still appear on the Bojangles website, they have been shuttered since late 2023. The locations were operated by Salim Kakakhail and Yavir Akbar Durranni. The partners operated under a variety of LLCs, including ABS Network, according to local news channel WUSA9.
The station reported that the owners face a state investigation over complaints of wage theft and fraudulent W2s. In November Durranni and ABS Network filed for bankruptcy in New Jersey, WUSA9 reported.
"Not only do former employees say these men owe them money, WUSA9 learned the former owners owe the state, too, and have over $69,000 in back property taxes."
Former employees also say that the restaurant would regularly purchase fried chicken from Popeyes and Safeway when it ran out in their stores, the station reported.
Bojangles sent the station a comment on the situation.
"The franchisee is no longer in the Bojangles system," the company said. "However, it is important to note in your coverage that franchisees are independent business owners who are licensed to operate a brand but have autonomy over many aspects of their business, including hiring employees and payroll responsibilities."
Kakakhail and Durranni did not respond to multiple requests for comment from WUSA9.
bankruptcy pandemicUncategorized
Industrial Production Increased 0.1% in February
From the Fed: Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization
Industrial production edged up 0.1 percent in February after declining 0.5 percent in January. In February, the output of manufacturing rose 0.8 percent and the index for mining climbed 2.2 p…
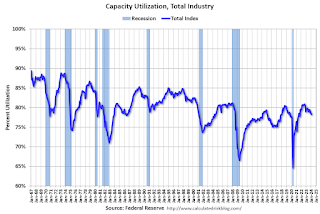
Industrial production edged up 0.1 percent in February after declining 0.5 percent in January. In February, the output of manufacturing rose 0.8 percent and the index for mining climbed 2.2 percent. Both gains partly reflected recoveries from weather-related declines in January. The index for utilities fell 7.5 percent in February because of warmer-than-typical temperatures. At 102.3 percent of its 2017 average, total industrial production in February was 0.2 percent below its year-earlier level. Capacity utilization for the industrial sector remained at 78.3 percent in February, a rate that is 1.3 percentage points below its long-run (1972–2023) average.Click on graph for larger image.
emphasis added
This graph shows Capacity Utilization. This series is up from the record low set in April 2020, and above the level in February 2020 (pre-pandemic).
Capacity utilization at 78.3% is 1.3% below the average from 1972 to 2022. This was below consensus expectations.
Note: y-axis doesn't start at zero to better show the change.
 The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.
The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.Industrial production increased to 102.3. This is above the pre-pandemic level.
Industrial production was above consensus expectations.
Uncategorized
Southwest and United Airlines have bad news for passengers
Both airlines are facing the same problem, one that could lead to higher airfares and fewer flight options.

Airlines operate in a market that's dictated by supply and demand: If more people want to fly a specific route than there are available seats, then tickets on those flights cost more.
That makes scheduling and predicting demand a huge part of maximizing revenue for airlines. There are, however, numerous factors that go into how airlines decide which flights to put on the schedule.
Related: Major airline faces Chapter 11 bankruptcy concerns
Every airport has only a certain number of gates, flight slots and runway capacity, limiting carriers' flexibility. That's why during times of high demand — like flights to Las Vegas during Super Bowl week — do not usually translate to airlines sending more planes to and from that destination.
Airlines generally do try to add capacity every year. That's become challenging as Boeing has struggled to keep up with demand for new airplanes. If you can't add airplanes, you can't grow your business. That's caused problems for the entire industry.
Every airline retires planes each year. In general, those get replaced by newer, better models that offer more efficiency and, in most cases, better passenger amenities.
If an airline can't get the planes it had hoped to add to its fleet in a given year, it can face capacity problems. And it's a problem that both Southwest Airlines (LUV) and United Airlines have addressed in a way that's inevitable but bad for passengers.
Image source: Kevin Dietsch/Getty Images
Southwest slows down its pilot hiring
In 2023, Southwest made a huge push to hire pilots. The airline lost thousands of pilots to retirement during the covid pandemic and it needed to replace them in order to build back to its 2019 capacity.
The airline successfully did that but will not continue that trend in 2024.
"Southwest plans to hire approximately 350 pilots this year, and no new-hire classes are scheduled after this month," Travel Weekly reported. "Last year, Southwest hired 1,916 pilots, according to pilot recruitment advisory firm Future & Active Pilot Advisors. The airline hired 1,140 pilots in 2022."
The slowdown in hiring directly relates to the airline expecting to grow capacity only in the low-single-digits percent in 2024.
"Moving into 2024, there is continued uncertainty around the timing of expected Boeing deliveries and the certification of the Max 7 aircraft. Our fleet plans remain nimble and currently differs from our contractual order book with Boeing," Southwest Airlines Chief Financial Officer Tammy Romo said during the airline's fourth-quarter-earnings call.
"We are planning for 79 aircraft deliveries this year and expect to retire roughly 45 700 and 4 800, resulting in a net expected increase of 30 aircraft this year."
That's very modest growth, which should not be enough of an increase in capacity to lower prices in any significant way.
United Airlines pauses pilot hiring
Boeing's (BA) struggles have had wide impact across the industry. United Airlines has also said it was going to pause hiring new pilots through the end of May.
United (UAL) Fight Operations Vice President Marc Champion explained the situation in a memo to the airline's staff.
"As you know, United has hundreds of new planes on order, and while we remain on path to be the fastest-growing airline in the industry, we just won't grow as fast as we thought we would in 2024 due to continued delays at Boeing," he said.
"For example, we had contractual deliveries for 80 Max 10s this year alone, but those aircraft aren't even certified yet, and it's impossible to know when they will arrive."
That's another blow to consumers hoping that multiple major carriers would grow capacity, putting pressure on fares. Until Boeing can get back on track, it's unlikely that competition between the large airlines will lead to lower fares.
In fact, it's possible that consumer demand will grow more than airline capacity which could push prices higher.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
bankruptcy pandemic stocks-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Spread & Containment2 days ago
Spread & Containment2 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex



















