Uncategorized
Cybercrime insurance is making the ransomware problem worse
In a viscous cycle, it’s also becoming harder to get cyberinsurance.

Cybercrime insurance is making the ransomware problem worse During the COVID-19 pandemic, there was another outbreak in cyberspace: a digital epidemic driven by ransomware.
Several organisations worldwide fell victim to cyber-extortionists who stole data either to sell to other criminals or held it as a ransom for a profit. The sheer number of attacks indicates that cyber security and anti-ransomware defences did not work or have limited effectiveness.
Businesses are turning to cyberinsurance companies in desperation to protect themselves from attack. But the growth of the cyberinsurance market is only encouraging criminals to target companies that have extortion insurance.
A 2021 study from the University of Leeds found there was a massive acceleration in major cyber-attacks on organisations during the pandemic. The paper also showed a “shift in offender tactics which scale up levels of fear in victims … such tactics include a shift towards naming and shaming victims, the theft of commercially sensitive data and attacks targeting organisations which provide services to other organisations.”
A report by global cybersecurity firm Sophos found that 66% of organisations surveyed, from across 31 countries, were hit with ransomware in 2021, up from 37% in 2020. The average ransom paid increased nearly fivefold to US$812,360 (£706,854). Insurance companies often opt to pay the ransoms that cybercriminals demand – 82% of UK companies pay up.
Where are the attacks coming from
According to US think tank the Council on Foreign Relations 22 countries are suspected of sponsoring cyberattacks, including the United States.
And a new black market in which cybercriminals provide products and services to other cybercriminals is flourishing and driving the surge in ransomware attacks. So-called ransomware allows everyone from teenagers to skilled amateurs to professional criminals to rent malware, encryption tools, and even Bitcoin wallets.
It is like a criminal renting a gun from another criminal who manufactured it.
In July 2020, three teenagers hacked Twitter. The attack resulted in the hijacking of 130 accounts – some of which included high-profile targets including Joe Biden, Barack Obama, Apple, Elon Musk and Bill Gates. The bitcoin accounts associated with their ransomware scam received more than 400 transfers totalling over US$100,000 (£87,000).

What’s the problem with insurance?
The past few years have seen a surge in specialist cybercrime insurance policies. The global cybercrime insurance market is predicted to grow from US$7 billion in gross written premiums (GWP) in 2020 to US$20.6 billion by 2025.
Insurers need to do more to discourage incompetent security practices. Car drivers must pass theory and practical driving tests. But cyberinsurance policies rarely audit the IT security of an organisation before the policy is finalised.
A standardised ISO norm (quality management standards internationally agreed by experts) for software did not exist until 2015. It means customers have no way of judging the security standards of anything produced before 2015. Even now, some of the risk assessments a software would go through in its lifetime could be less rigorous than for the kettle in our home. And ISO testing is voluntary.
The market lacks understanding of large-scale, sophisticated, cyber-attacks. The insurance sector works by determining the probability of an incident happening and the impact it would have. The cyberinsurance market struggles to forecast the likelihood of cyber-attacks because changes in digital technology can be so unpredictable. Attackers’ capabilities and intentions shift rapidly.
Most insurers currently have no long-term data for cyberincidents or ransomware. This has led to underfunded cyberinsurance programs, which rely heavily on optimistic financial models.
As a result it is getting more difficult to secure cyberinsurance as the growing number of claims is forcing valuers to be more discerning in the clients they accept. Lloyds of London released new rules in December 2021 stating that underwriters will no longer cover damage caused by “war or a cyberoperation that is carried out in the course of the war”.
Insurance premiums increased by 22% in 2020 and a further 32% in 2021 across 38 countries. The cost incurred by the business gets passed on to customers. The ransomware demand will contribute to the overall rise in living costs as ransomware costs are being passed on to the customers.
As part of my work with the Northern Cloud Crime Centre, I looked at the effectiveness of laws in the UK to regulate criminal activity in the Cloud. I found the cybercrime legislation in the UK has failed to keep pace with technological and market developments over the past 30 years. The Computer Misuse Act 1990 needs updating to make it more effective at policing cybercrime. If we cannot fix the situation, it will threaten jobs and investment in the UK.
What is the solution
Ransomware attacks are so effective because they exploit human weaknesses and organisations’ lack of technological defences.
Law enforcement authorities advise ransomware victims not to pay the ransom because it encourages further attacks and fuels a vicious cycle.
But prevention is the best solution. Organisations need to put more effort into developing security measures such as a multifactor authentication system. Managers also need to carry out penetration testing, where a cybersecurity expert searches for vulnerabilities in a computer system.
Businesses are legally obliged to have a fire plan in place. The time has come for mandatory ransomware and phishing resilience testing. The insurance industry needs to set minimum security requirements as part of the risk assessment. Organisations need greater transparency regarding what security they do and do not have in place.
Consensus is growing among researchers that solid cybersecurity can’t be achieved with technology alone because a human errors are to blame for a huge amount of incidents. The UK government is proposing new laws to regulate cybersecurity standards. But these laws won’t work if it doesn’t invest in public education about phishing threats.
Cybercrime insurance can help minimise business disruption, provide financial protection, and even help with legal and regulatory actions after a cyberincident. But it will not solve the problems that created the vulnerability to an attack in the first place.
Part of the research for this article was carried out as Co-I of EPSRC funded CRITiCaL - Combatting cRiminals In The Cloud (EPSRC) June 2015 - May 2022. https://northerncloudcrimecentre.org/ https://essl.leeds.ac.uk/education-social-sciences-law/dir-record/research-projects/350/critical-combatting-criminals-in-the-cloud
bitcoin pandemic covid-19Uncategorized
NY Fed Finds Medium, Long-Term Inflation Expectations Jump Amid Surge In Stock Market Optimism
NY Fed Finds Medium, Long-Term Inflation Expectations Jump Amid Surge In Stock Market Optimism
One month after the inflation outlook tracked…
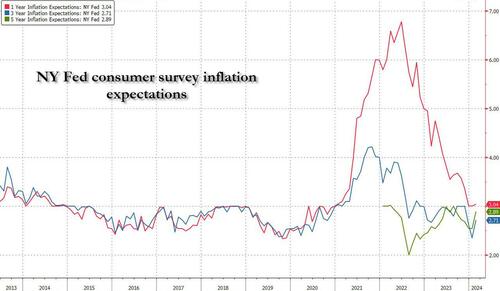
One month after the inflation outlook tracked by the NY Fed Consumer Survey extended their late 2023 slide, with 3Y inflation expectations in January sliding to a record low 2.4% (from 2.6% in December), even as 1 and 5Y inflation forecasts remained flat, moments ago the NY Fed reported that in February there was a sharp rebound in longer-term inflation expectations, rising to 2.7% from 2.4% at the three-year ahead horizon, and jumping to 2.9% from 2.5% at the five-year ahead horizon, while the 1Y inflation outlook was flat for the 3rd month in a row, stuck at 3.0%.
The increases in both the three-year ahead and five-year ahead measures were most pronounced for respondents with at most high school degrees (in other words, the "really smart folks" are expecting deflation soon). The survey’s measure of disagreement across respondents (the difference between the 75th and 25th percentile of inflation expectations) decreased at all horizons, while the median inflation uncertainty—or the uncertainty expressed regarding future inflation outcomes—declined at the one- and three-year ahead horizons and remained unchanged at the five-year ahead horizon.
Going down the survey, we find that the median year-ahead expected price changes increased by 0.1 percentage point to 4.3% for gas; decreased by 1.8 percentage points to 6.8% for the cost of medical care (its lowest reading since September 2020); decreased by 0.1 percentage point to 5.8% for the cost of a college education; and surprisingly decreased by 0.3 percentage point for rent to 6.1% (its lowest reading since December 2020), and remained flat for food at 4.9%.
We find the rent expectations surprising because it is happening just asking rents are rising across the country.
At the same time as consumers erroneously saw sharply lower rents, median home price growth expectations remained unchanged for the fifth consecutive month at 3.0%.
Turning to the labor market, the survey found that the average perceived likelihood of voluntary and involuntary job separations increased, while the perceived likelihood of finding a job (in the event of a job loss) declined. "The mean probability of leaving one’s job voluntarily in the next 12 months also increased, by 1.8 percentage points to 19.5%."
Mean unemployment expectations - or the mean probability that the U.S. unemployment rate will be higher one year from now - decreased by 1.1 percentage points to 36.1%, the lowest reading since February 2022. Additionally, the median one-year-ahead expected earnings growth was unchanged at 2.8%, remaining slightly below its 12-month trailing average of 2.9%.
Turning to household finance, we find the following:
- The median expected growth in household income remained unchanged at 3.1%. The series has been moving within a narrow range of 2.9% to 3.3% since January 2023, and remains above the February 2020 pre-pandemic level of 2.7%.
- Median household spending growth expectations increased by 0.2 percentage point to 5.2%. The increase was driven by respondents with a high school degree or less.
- Median year-ahead expected growth in government debt increased to 9.3% from 8.9%.
- The mean perceived probability that the average interest rate on saving accounts will be higher in 12 months increased by 0.6 percentage point to 26.1%, remaining below its 12-month trailing average of 30%.
- Perceptions about households’ current financial situations deteriorated somewhat with fewer respondents reporting being better off than a year ago. Year-ahead expectations also deteriorated marginally with a smaller share of respondents expecting to be better off and a slightly larger share of respondents expecting to be worse off a year from now.
- The mean perceived probability that U.S. stock prices will be higher 12 months from now increased by 1.4 percentage point to 38.9%.
- At the same time, perceptions and expectations about credit access turned less optimistic: "Perceptions of credit access compared to a year ago deteriorated with a larger share of respondents reporting tighter conditions and a smaller share reporting looser conditions compared to a year ago."
Also, a smaller percentage of consumers, 11.45% vs 12.14% in prior month, expect to not be able to make minimum debt payment over the next three months
Last, and perhaps most humorous, is the now traditional cognitive dissonance one observes with these polls, because at a time when long-term inflation expectations jumped, which clearly suggests that financial conditions will need to be tightened, the number of respondents expecting higher stock prices one year from today jumped to the highest since November 2021... which incidentally is just when the market topped out during the last cycle before suffering a painful bear market.
Uncategorized
Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more
New Zillow research suggests the spring home shopping season may see a second wave this summer if mortgage rates fall
The post Homes listed for sale in…
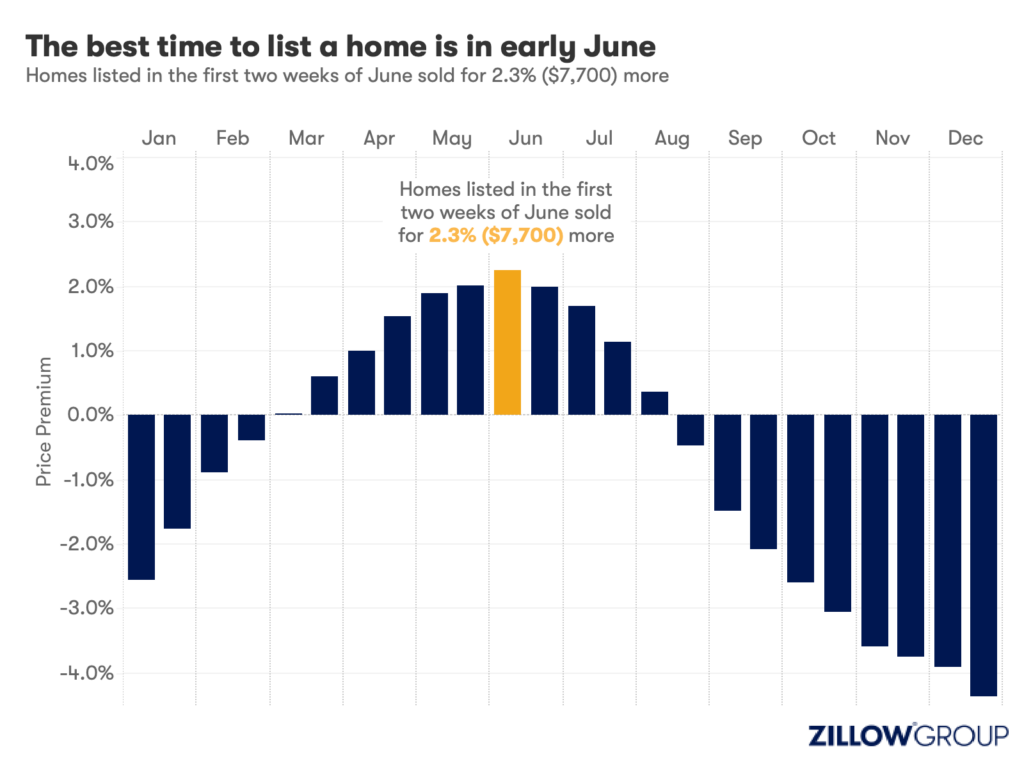
- A Zillow analysis of 2023 home sales finds homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more.
- The best time to list a home for sale is a month later than it was in 2019, likely driven by mortgage rates.
- The best time to list can be as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York and Philadelphia.
Spring home sellers looking to maximize their sale price may want to wait it out and list their home for sale in the first half of June. A new Zillow® analysis of 2023 sales found that homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more, a $7,700 boost on a typical U.S. home.
The best time to list consistently had been early May in the years leading up to the pandemic. The shift to June suggests mortgage rates are strongly influencing demand on top of the usual seasonality that brings buyers to the market in the spring. This home-shopping season is poised to follow a similar pattern as that in 2023, with the potential for a second wave if the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates midyear or later.
The 2.3% sale price premium registered last June followed the first spring in more than 15 years with mortgage rates over 6% on a 30-year fixed-rate loan. The high rates put home buyers on the back foot, and as rates continued upward through May, they were still reassessing and less likely to bid boldly. In June, however, rates pulled back a little from 6.79% to 6.67%, which likely presented an opportunity for determined buyers heading into summer. More buyers understood their market position and could afford to transact, boosting competition and sale prices.
The old logic was that sellers could earn a premium by listing in late spring, when search activity hit its peak. Now, with persistently low inventory, mortgage rate fluctuations make their own seasonality. First-time home buyers who are on the edge of qualifying for a home loan may dip in and out of the market, depending on what’s happening with rates. It is almost certain the Federal Reserve will push back any interest-rate cuts to mid-2024 at the earliest. If mortgage rates follow, that could bring another surge of buyers later this year.
Mortgage rates have been impacting affordability and sale prices since they began rising rapidly two years ago. In 2022, sellers nationwide saw the highest sale premium when they listed their home in late March, right before rates barreled past 5% and continued climbing.
Zillow’s research finds the best time to list can vary widely by metropolitan area. In 2023, it was as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York. Thirty of the top 35 largest metro areas saw for-sale listings command the highest sale prices between May and early July last year.
Zillow also found a wide range in the sale price premiums associated with homes listed during those peak periods. At the hottest time of the year in San Jose, homes sold for 5.5% more, a $88,000 boost on a typical home. Meanwhile, homes in San Antonio sold for 1.9% more during that same time period.
| Metropolitan Area | Best Time to List | Price Premium | Dollar Boost |
| United States | First half of June | 2.3% | $7,700 |
| New York, NY | First half of July | 2.4% | $15,500 |
| Los Angeles, CA | First half of May | 4.1% | $39,300 |
| Chicago, IL | First half of June | 2.8% | $8,800 |
| Dallas, TX | First half of June | 2.5% | $9,200 |
| Houston, TX | Second half of April | 2.0% | $6,200 |
| Washington, DC | Second half of June | 2.2% | $12,700 |
| Philadelphia, PA | First half of July | 2.4% | $8,200 |
| Miami, FL | First half of June | 2.3% | $12,900 |
| Atlanta, GA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $8,700 |
| Boston, MA | Second half of May | 3.5% | $23,600 |
| Phoenix, AZ | First half of June | 3.2% | $14,700 |
| San Francisco, CA | Second half of February | 4.2% | $50,300 |
| Riverside, CA | First half of May | 2.7% | $15,600 |
| Detroit, MI | First half of July | 3.3% | $7,900 |
| Seattle, WA | First half of June | 4.3% | $31,500 |
| Minneapolis, MN | Second half of May | 3.7% | $13,400 |
| San Diego, CA | Second half of April | 3.1% | $29,600 |
| Tampa, FL | Second half of June | 2.1% | $8,000 |
| Denver, CO | Second half of May | 2.9% | $16,900 |
| Baltimore, MD | First half of July | 2.2% | $8,200 |
| St. Louis, MO | First half of June | 2.9% | $7,000 |
| Orlando, FL | First half of June | 2.2% | $8,700 |
| Charlotte, NC | Second half of May | 3.0% | $11,000 |
| San Antonio, TX | First half of June | 1.9% | $5,400 |
| Portland, OR | Second half of April | 2.6% | $14,300 |
| Sacramento, CA | First half of June | 3.2% | $17,900 |
| Pittsburgh, PA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $4,700 |
| Cincinnati, OH | Second half of April | 2.7% | $7,500 |
| Austin, TX | Second half of May | 2.8% | $12,600 |
| Las Vegas, NV | First half of June | 3.4% | $14,600 |
| Kansas City, MO | Second half of May | 2.5% | $7,300 |
| Columbus, OH | Second half of June | 3.3% | $10,400 |
| Indianapolis, IN | First half of July | 3.0% | $8,100 |
| Cleveland, OH | First half of July | 3.4% | $7,400 |
| San Jose, CA | First half of June | 5.5% | $88,400 |
The post Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more appeared first on Zillow Research.
federal reserve pandemic home sales mortgage rates interest ratesUncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemployment-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex











