Burger King Stock (QSR) has been rising for 3 consecutive weeks: here is where to buy it
The price of the Burger King Stock (QSR) has been rising for the last 3 consecutive months on increased digital sales. To help stock investors interested…

The price of the Burger King Stock (QSR) has been rising for the last 3 consecutive months on increased digital sales.
To help stock investors interested in investing in Burger King, Invezz has created a brief article on what it is and where to buy it.
To find out more, please continue reading.
Where to trade Burger King Stock
Saxo Markets
Access 40,000+ instruments – across 10+ asset classes – to trade, hedge and invest from a single account. With prices as low as 0.4 pips for currency pairs and 0.01 USD per share.
Register with Saxo Markets instantly
Admirals
Admirals is a multi-award-winning online financial broker offering competitive spreads and low commission charges. Admirals offers trading in Forex and CFDs on multiple products, including energies, stocks, bonds, ETFs, indices, and metals. Admirals offers a wide range of free webinars, seminars and videos. Clients can choose from a wide range of account options depending on their trading and instrument preferences
Register with Admirals instantly
What is Burger King Stock?
Burger King Stock is the stock of Burger King, which is among the restaurant chains owned by Restaurant Brands International Inc. (RBI). The Burger stock currently trades under the ticker of its parent company (NYSE: QSR) on the New York Stock exchange.
In a nutshell, Restaurant Brands International Inc. (RBI) is a Canadian-American multinational company that operates several restaurant chains including Burger King, Tim Hortons, and Popeyes.
Burger King is approximated to receive over 11 million people who dine in its restaurants around the world. And with such numbers, it has become one of the most sought-after stocks in the market.
Should I buy QSR stock today?
If you are looking for a tech stock that has been on the decline since Covid struck but has started rising again as things get back to normal, then the QSR stock could be a good choice.
Nevertheless, new variants of Covid-19 viruses are being detected now and then around the world and any serious outbreak would send the stock to its knees again.
Burger King Stock (QSR) price prediction
After falling between mid-June, 2021 and the end of January 2022, the QSR stock has started rising again and analysts expect it to retest $65 by the end of the first quarter of 2022.
$QSR stock social media coverage
The post Burger King Stock (QSR) has been rising for 3 consecutive weeks: here is where to buy it appeared first on Invezz.
bonds covid-19 stocksGovernment
Looking Back At COVID’s Authoritarian Regimes
After having moved from Canada to the United States, partly to be wealthier and partly to be freer (those two are connected, by the way), I was shocked,…

After having moved from Canada to the United States, partly to be wealthier and partly to be freer (those two are connected, by the way), I was shocked, in March 2020, when President Trump and most US governors imposed heavy restrictions on people’s freedom. The purpose, said Trump and his COVID-19 advisers, was to “flatten the curve”: shut down people’s mobility for two weeks so that hospitals could catch up with the expected demand from COVID patients. In her book Silent Invasion, Dr. Deborah Birx, the coordinator of the White House Coronavirus Task Force, admitted that she was scrambling during those two weeks to come up with a reason to extend the lockdowns for much longer. As she put it, “I didn’t have the numbers in front of me yet to make the case for extending it longer, but I had two weeks to get them.” In short, she chose the goal and then tried to find the data to justify the goal. This, by the way, was from someone who, along with her task force colleague Dr. Anthony Fauci, kept talking about the importance of the scientific method. By the end of April 2020, the term “flatten the curve” had all but disappeared from public discussion.
Now that we are four years past that awful time, it makes sense to look back and see whether those heavy restrictions on the lives of people of all ages made sense. I’ll save you the suspense. They didn’t. The damage to the economy was huge. Remember that “the economy” is not a term used to describe a big machine; it’s a shorthand for the trillions of interactions among hundreds of millions of people. The lockdowns and the subsequent federal spending ballooned the budget deficit and consequent federal debt. The effect on children’s learning, not just in school but outside of school, was huge. These effects will be with us for a long time. It’s not as if there wasn’t another way to go. The people who came up with the idea of lockdowns did so on the basis of abstract models that had not been tested. They ignored a model of human behavior, which I’ll call Hayekian, that is tested every day.
These are the opening two paragraphs of my latest Defining Ideas article, “Looking Back at COVID’s Authoritarian Regimes,” Defining Ideas, March 14, 2024.
Another excerpt:
That wasn’t the only uncertainty. My daughter Karen lived in San Francisco and made her living teaching Pilates. San Francisco mayor London Breed shut down all the gyms, and so there went my daughter’s business. (The good news was that she quickly got online and shifted many of her clients to virtual Pilates. But that’s another story.) We tried to see her every six weeks or so, whether that meant our driving up to San Fran or her driving down to Monterey. But were we allowed to drive to see her? In that first month and a half, we simply didn’t know.
Read the whole thing, which is longer than usual.
(0 COMMENTS) budget deficit coronavirus covid-19 white house fauci trump canadaUncategorized
The hostility Black women face in higher education carries dire consequences
9 Black women who were working on or recently earned their PhDs told a researcher they felt isolated and shut out.

Isolated. Abused. Overworked.
These are the themes that emerged when I invited nine Black women to chronicle their professional experiences and relationships with colleagues as they earned their Ph.D.s at a public university in the Midwest. I featured their writings in the dissertation I wrote to get my Ph.D. in curriculum and instruction.
The women spoke of being silenced.
“It’s not just the beating me down that is hard,” one participant told me about constantly having her intelligence questioned. “It is the fact that it feels like I’m villainized and made out to be the problem for trying to advocate for myself.”
The women told me they did not feel like they belonged. They spoke of routinely being isolated by peers and potential mentors.
One participant told me she felt that peer community, faculty mentorship and cultural affinity spaces were lacking.
Because of the isolation, participants often felt that they were missing out on various opportunities, such as funding and opportunities to get their work published.
Participants also discussed the ways they felt they were duped into taking on more than their fair share of work.
“I realized I had been tricked into handling a two- to four-person job entirely by myself,” one participant said of her paid graduate position. “This happened just about a month before the pandemic occurred so it very quickly got swept under the rug.”
Why it matters
The hostility that Black women face in higher education can be hazardous to their health. The women in my study told me they were struggling with depression, had thought about suicide and felt physically ill when they had to go to campus.
Other studies have found similar outcomes. For instance, a 2020 study of 220 U.S. Black college women ages 18-48 found that even though being seen as a strong Black woman came with its benefits – such as being thought of as resilient, hardworking, independent and nurturing – it also came at a cost to their mental and physical health.
These kinds of experiences can take a toll on women’s bodies and can result in poor maternal health, cancer, shorter life expectancy and other symptoms that impair their ability to be well.
I believe my research takes on greater urgency in light of the recent death of Antoinette “Bonnie” Candia-Bailey, who was vice president of student affairs at Lincoln University. Before she died by suicide, she reportedly wrote that she felt she was suffering abuse and that the university wasn’t taking her mental health concerns seriously.
What other research is being done
Several anthologies examine the negative experiences that Black women experience in academia. They include education scholars Venus Evans-Winters and Bettina Love’s edited volume, “Black Feminism in Education,” which examines how Black women navigate what it means to be a scholar in a “white supremacist patriarchal society.” Gender and sexuality studies scholar Stephanie Evans analyzes the barriers that Black women faced in accessing higher education from 1850 to 1954. In “Black Women, Ivory Tower,” African American studies professor Jasmine Harris recounts her own traumatic experiences in the world of higher education.
What’s next
In addition to publishing the findings of my research study, I plan to continue exploring the depths of Black women’s experiences in academia, expanding my research to include undergraduate students, as well as faculty and staff.
I believe this research will strengthen this field of study and enable people who work in higher education to develop and implement more comprehensive solutions.
The Research Brief is a short take on interesting academic work.
Ebony Aya received funding from the Black Collective Foundation in 2022 to support the work of the Aya Collective.
depression pandemicUncategorized
US Economic Growth Still Expected To Slow In Q1 GDP Report
A new round of nowcasts continue to estimate that US economic activity will downshift in next month’s release of first-quarter GDP data. Today’s revised…
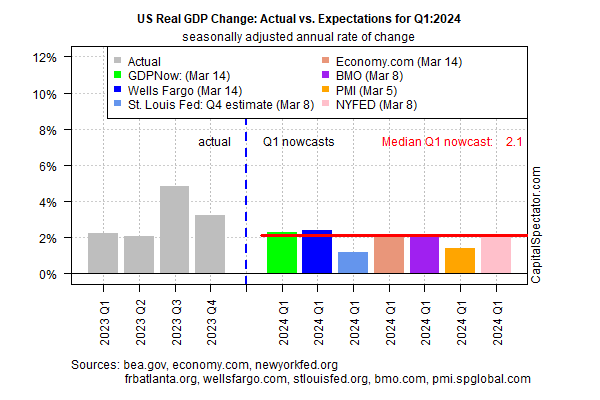
A new round of nowcasts continue to estimate that US economic activity will downshift in next month’s release of first-quarter GDP data. Today’s revised estimate is based on the median for a set of nowcasts compiled by CapitalSpectator.com.
Output for the January-through-March period is currently projected to soften to a 2.1% increase (seasonally adjusted annual rate). The estimate reflects a substantially softer rise vs. Q4’s strong 3.2% advance, which in turn marks a downshift from Q3’s red-hot 4.9% increase, according to government data.
Today’s revised Q1 estimate was essentially unchanged from the previous Q1 nowcast (published on Mar. 7). At this late date in the current quarter, the odds are relatively high that the current median estimate is a reasonable guesstimate for the actual GDP data that the Bureau of Economic Analysis will publish in late-April.
GDP rising at roughly a 2% pace marks another slowdown from recent quarters, but if the current nowcast is correct it suggests that recession risk remains low. The question is whether the slowdown persists into Q2 and beyond. Given the expected deceleration in growth on tap for Q1, the economy may be flirting with a tipping point for recession later in the year. It’s premature to make such a forecast with high confidence, but it’s a scenario that’s increasingly plausible, albeit speculatively so for now.
Yesterday’s release of retail sales numbers for February aligns with the possibility that even softer growth is coming. Although spending rebounded last month after January’s steep decline, the bounce was lowr than expected.
“The modest rebound in retail sales in February suggests that consumer spending growth slowed in early 2024,” says Michael Pearce, Oxford Economics deputy chief US economist.

Reviewing retail spending on a year-over-year basis provides a clearer view of the softer-growth profile. The pace edged up to 1.5% last month vs. the year-earlier level, but that’s close to the slowest increase in the post-pandemic recovery.

Despite emerging signs of slowing growth, relief for the economy in the form of interest-rate cuts may be further out in time than recently expected, due to the latest round of sticky inflation news this week.
“When the Fed is contemplating a series of rate cuts and is confronted by suddenly slower economic growth and suddenly brisker inflation, they will respond to the new news on the inflation side every time,” says Chris Low, chief economist at FHN Financial. “After all, this is not the first time in the past couple of years consumers have paused spending for a couple of months to catch their breath.”
How is recession risk evolving? Monitor the outlook with a subscription to:
The US Business Cycle Risk Report
recession pandemic economic growth fed recession gdp recovery consumer spending
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Spread & Containment2 days ago
Spread & Containment2 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A





















