Uncategorized
Blockchain improves charity transparency — But is it right for everyone?
Can blockchain technology actually help to improve transparency within charities?
In 2021, the Australian branch of the Red Cross…
Can blockchain technology actually help to improve transparency within charities?
In 2021, the Australian branch of the Red Cross received $90 million to aid the victims of the bushfires that plagued various regions of New South Wales and Victoria.
However, the organization soon came under fire for its lack of transparency when it revealed that it would only distribute around one-third of the intended funds on immediate assistance and that it could take up to three years to distribute the total amount.
One resident who lost his home to the fires told local media, “They made a lot of promises that they’re going to this, that and other, (but) I’ve received nothing, I have no idea where the money is going.”
This one example highlights a common problem among charities: The processes for distributing charitable giving are often obscured by bureaucracy and prone to mismanagement. Without robust accountability mechanisms, charities risk mismanaging or misusing funds and, at worst, committing outright fraud.
Jack Vinijtrongjit, CEO of AAG — a venture capital firm that heads the AAG Charity DAO — told Cointelegraph, “Statistically, a lot of money goes to waste when it comes to charity. For example, in some cases, only fifty cents out of a dollar ends up at the destination. Very few can achieve efficiency in the 83% range, like Oxfam.”
Blockchain technology can provide tangible benefits for both donors and charities. It offers greater accountability and transparency for contributors, enabling them to follow their donations and see the results of their generosity.
How blockchain can provide transparency
Blockchain technology provides real-time tracking of donations and transactions. This level of transparency helps to build trust and confidence among donors, as they can verify that their funds are being used for the intended purpose.
In addition, it allows charities to provide donors with a detailed breakdown of their contributions, showing how each dollar is allocated to various projects or initiatives. Vinijtrongjit said, “With blockchain, the fund flow can be seen easily, and if the organization expects people to keep donating, they need to make sure as many funds as possible are delivered as intended.”

He said this transparency can reduce fraud and misuse of funds, as “there can be cases where corrupt local officials would take the funds and misuse them.”
Blockchain technology also has the important property of being immutable. A blockchain record or transaction cannot be changed or removed without the agreement of all nodes in the network. Because of its immutability, the charity’s financial records, donation histories and other data are safe from alteration.
Recent: Central banks want to look under crypto’s hood — Is this a positive sign?
This function is especially important for nonprofit organizations since it guarantees that any donations made to their cause will be permanently documented and easily audited by third parties.
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, are another valuable aspect of blockchain technology for charities. These contracts can be used to automate processes such as distributing funds or verifying the completion of specific tasks.
Smart contracts help ensure that funds are used for their designated purposes, as they only release funds when predefined conditions are met. This enhances transparency by eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of misusing funds.
Charities using blockchain technology
One notable example of a charity using blockchain technology is the United Nations World Food Programme’s (WFP) Building Blocks project. WFP deployed blockchain when providing food assistance to Syrian refugees in Jordan.
Each transaction, from food purchases to distribution, was recorded on a blockchain, allowing refugees to access their entitlements via a biometrically verified account.
The World Food Programme also extended its use of blockchain to Yemen, where it employed the technology to provide food assistance to vulnerable populations amid the ongoing Yemeni civil war. By providing digital vouchers through blockchain, the WFP could ensure that aid reached those in need while minimizing the risk of diversion or fraud.
In 2022, Binance launched the Ukraine Emergency Relief Fund, a cryptocurrency-focused crowdfunding platform that allowed people to make contributions to emergency relief efforts aimed at assisting refugees and children in need. This initiative also aims to provide crucial logistical support — including food, fuel and essential supplies — for refugees on the ground. Additionally, Binance donated 16,042 BNB (BNB), equal to $6 million at the time, to the fund.
Donations can be tracked via the official fundraising page, which shows a list of donors, the amount donated by each donor, the total amount raised, and allocations. For example, 2.5 million Binance USD (BUSD) (worth $2.5 million) was allocated to UNICEF and Mercy Corps each, out of the $11.3 million raised so far.

Smaller charities such as GiveDirectly have also adopted blockchain technology. GiveDirectly, which recently provided direct cash transfers to survivors of the earthquake in Morocco and children living in poverty in Flint, Michigan, uses blockchain to record and verify every transaction.
Key considerations for charities
For charities looking to incorporate blockchain technology, there are several best practices to follow. First, it is imperative to establish clear objectives when integrating blockchain into charitable operations.
These objectives should be well-defined, including enhancing transparency, streamlining administrative processes or optimizing aid distribution.
Selecting the most suitable blockchain platform is of paramount importance. Choices like Ethereum or Hyperledger should be made judiciously, considering factors such as scalability, security and the unique requirements of the charitable organization.
Marina Zibareva, a spokesperson for Binance Charity — a nonprofit organization that uses blockchain technology for crypto donations — told Cointelegraph, “Charities need to adhere to some critical best practices when adopting blockchain technology to improve transparency in charitable operations. Among these is gaining a comprehensive understanding of how blockchain and cryptocurrency function. Acquiring this foundational knowledge is a pivotal first step in the integration process.”
Understanding how blockchain technology works is important for charities since blockchain technology isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. There are different implementations and platforms, each with unique features. For instance, layer-2 networks like Polygon have faster speeds and lower transaction costs. To select the most suitable solution, charities must understand these differences and how they align with their specific goals and donor preferences.
Jerry Lopez, founder and CEO of Philcoin — a blockchain-based philanthropy platform — told Cointelegraph:
“It is important for the organization to conduct an internal analysis to assess capabilities and resources. Is the organization ready for innovation and/or adaptation? Are the main stakeholders ready for the shift?”
“This sounds like an obvious point, but it’s essential. Charitable organizations can be slower to accept change. Understanding what’s necessary to make the leap to blockchain solutions will require additional resources and investments to ensure credible, trusted and functioning solutions are implemented,” he said.
Lopez also stressed the importance of the organization knowing if it’s “fully committed to seeing through the transition,” which can take time, research, understanding and a dedicated team to help manage and oversee the development. “Very often, organizations will learn through trial and error,” Lopez said.
Good security practices and maintaining data accuracy are fundamental principles to building and maintaining trust with both donors and beneficiaries. This involves the continuous upkeep of precise, up-to-date records on the blockchain. Regular audits and verification of transactions are essential measures to prevent errors or fraudulent activities.
Zibareva said, “Charities must prioritize security as they venture into the blockchain realm. Adopting cutting-edge security measures and technologies is vital to safeguard the system’s integrity. Putting safety at the forefront ensures the protection of the organization and its donors from potential fraud and bolsters the overall trust in the transparency mechanisms in place.”
Adhering to data protection regulations and preserving the privacy of sensitive beneficiary information are nonnegotiable elements. These data security considerations should be balanced with the necessity of allowing accessibility for verification purposes.
Planning for scalability is another critical aspect, particularly when anticipating a growing volume of transactions and beneficiaries over time. The long-term sustainability of the blockchain infrastructure should be a central concern, ensuring that it can adapt to the evolving needs of the charitable organization.
Zibareva added that charities “should evaluate their technical readiness, considering their capacity to manage cryptocurrency wallets and other blockchain-related infrastructures.”
“By comparing their operational needs with blockchain’s capabilities and leveraging expert insights, charitable organizations can decide whether blockchain integration aligns with their transparency goals.”
It’s also necessary for charities to assess whether their community (donors, partners, etc.) are ready to accept using blockchain platforms for charitable purposes.
Lopez said, “Is the community ready to accept blockchain? How will blockchain solutions impact the supplier chain, for example? Is the community able to accept, receive or interact with the new solutions, or will this require additional infrastructure, education, training and development to ensure the full charitable cycle is onboarded?”
The adoption of blockchain technology in the charitable sector is a complex process that goes beyond just the technology itself. It involves organizational preparedness, supplier relationships and the broader community’s ability to adapt. Transparency in charities is a noble goal, but it requires a comprehensive and well-planned approach to ensure that the full potential of blockchain is realized without leaving any stakeholders behind.
What else can charities do to increase transparency?
While blockchain technology can indeed help track the flow of funds, it can be combined with additional organizational processes to ensure that charitable donations are used effectively.
Vinijtrongjit said, “I don’t believe blockchain alone can help fix these issues since tracking the use of funds is much more complex. For example, local charities at the destination may be forced to use a vendor overcharging them as part of the corruption scheme. An independent audit must still be carried out, but at least blockchain can be used to ensure the fund gets to the destination.”
Magazine: Ethereum restaking: Blockchain innovation or dangerous house of cards?
Independent audits are another important aspect of ensuring transparency, as they can thoroughly examine a charity’s financial records, operations and compliance with regulations. They provide an objective evaluation of the organization’s financial health and adherence to best practices.
Vinijtrongjit also believes that organizations must fully adopt blockchain in every part of their operations, as charities providing comprehensive, accessible and regular reports that detail their activities and financial information can be beneficial.
This includes information such as the allocation of funds and the amount of money raised, which can be gathered from the blockchain and added to these reports. Vinijtrongjit said:
“This will be like providing insights to the potential donors so they can decide not just what cause to contribute to but also based on how well the organization can carry out the mission.”cryptocurrency ethereum blockchain crypto bnb crypto
Uncategorized
NY Fed Finds Medium, Long-Term Inflation Expectations Jump Amid Surge In Stock Market Optimism
NY Fed Finds Medium, Long-Term Inflation Expectations Jump Amid Surge In Stock Market Optimism
One month after the inflation outlook tracked…
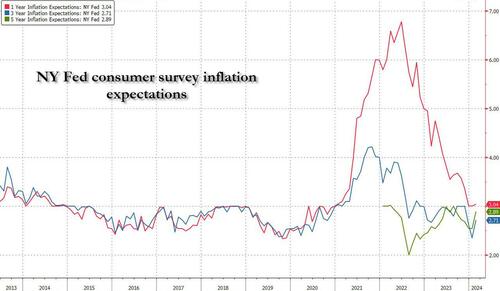
One month after the inflation outlook tracked by the NY Fed Consumer Survey extended their late 2023 slide, with 3Y inflation expectations in January sliding to a record low 2.4% (from 2.6% in December), even as 1 and 5Y inflation forecasts remained flat, moments ago the NY Fed reported that in February there was a sharp rebound in longer-term inflation expectations, rising to 2.7% from 2.4% at the three-year ahead horizon, and jumping to 2.9% from 2.5% at the five-year ahead horizon, while the 1Y inflation outlook was flat for the 3rd month in a row, stuck at 3.0%.
The increases in both the three-year ahead and five-year ahead measures were most pronounced for respondents with at most high school degrees (in other words, the "really smart folks" are expecting deflation soon). The survey’s measure of disagreement across respondents (the difference between the 75th and 25th percentile of inflation expectations) decreased at all horizons, while the median inflation uncertainty—or the uncertainty expressed regarding future inflation outcomes—declined at the one- and three-year ahead horizons and remained unchanged at the five-year ahead horizon.
Going down the survey, we find that the median year-ahead expected price changes increased by 0.1 percentage point to 4.3% for gas; decreased by 1.8 percentage points to 6.8% for the cost of medical care (its lowest reading since September 2020); decreased by 0.1 percentage point to 5.8% for the cost of a college education; and surprisingly decreased by 0.3 percentage point for rent to 6.1% (its lowest reading since December 2020), and remained flat for food at 4.9%.
We find the rent expectations surprising because it is happening just asking rents are rising across the country.
At the same time as consumers erroneously saw sharply lower rents, median home price growth expectations remained unchanged for the fifth consecutive month at 3.0%.
Turning to the labor market, the survey found that the average perceived likelihood of voluntary and involuntary job separations increased, while the perceived likelihood of finding a job (in the event of a job loss) declined. "The mean probability of leaving one’s job voluntarily in the next 12 months also increased, by 1.8 percentage points to 19.5%."
Mean unemployment expectations - or the mean probability that the U.S. unemployment rate will be higher one year from now - decreased by 1.1 percentage points to 36.1%, the lowest reading since February 2022. Additionally, the median one-year-ahead expected earnings growth was unchanged at 2.8%, remaining slightly below its 12-month trailing average of 2.9%.
Turning to household finance, we find the following:
- The median expected growth in household income remained unchanged at 3.1%. The series has been moving within a narrow range of 2.9% to 3.3% since January 2023, and remains above the February 2020 pre-pandemic level of 2.7%.
- Median household spending growth expectations increased by 0.2 percentage point to 5.2%. The increase was driven by respondents with a high school degree or less.
- Median year-ahead expected growth in government debt increased to 9.3% from 8.9%.
- The mean perceived probability that the average interest rate on saving accounts will be higher in 12 months increased by 0.6 percentage point to 26.1%, remaining below its 12-month trailing average of 30%.
- Perceptions about households’ current financial situations deteriorated somewhat with fewer respondents reporting being better off than a year ago. Year-ahead expectations also deteriorated marginally with a smaller share of respondents expecting to be better off and a slightly larger share of respondents expecting to be worse off a year from now.
- The mean perceived probability that U.S. stock prices will be higher 12 months from now increased by 1.4 percentage point to 38.9%.
- At the same time, perceptions and expectations about credit access turned less optimistic: "Perceptions of credit access compared to a year ago deteriorated with a larger share of respondents reporting tighter conditions and a smaller share reporting looser conditions compared to a year ago."
Also, a smaller percentage of consumers, 11.45% vs 12.14% in prior month, expect to not be able to make minimum debt payment over the next three months
Last, and perhaps most humorous, is the now traditional cognitive dissonance one observes with these polls, because at a time when long-term inflation expectations jumped, which clearly suggests that financial conditions will need to be tightened, the number of respondents expecting higher stock prices one year from today jumped to the highest since November 2021... which incidentally is just when the market topped out during the last cycle before suffering a painful bear market.
Uncategorized
Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more
New Zillow research suggests the spring home shopping season may see a second wave this summer if mortgage rates fall
The post Homes listed for sale in…
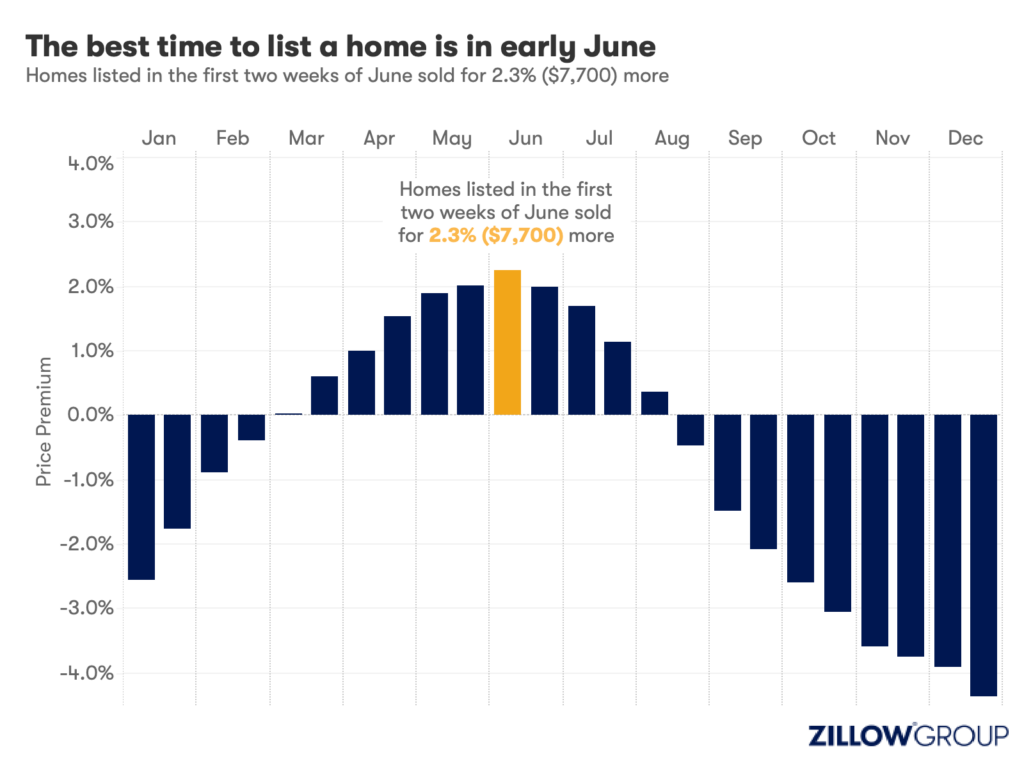
- A Zillow analysis of 2023 home sales finds homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more.
- The best time to list a home for sale is a month later than it was in 2019, likely driven by mortgage rates.
- The best time to list can be as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York and Philadelphia.
Spring home sellers looking to maximize their sale price may want to wait it out and list their home for sale in the first half of June. A new Zillow® analysis of 2023 sales found that homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more, a $7,700 boost on a typical U.S. home.
The best time to list consistently had been early May in the years leading up to the pandemic. The shift to June suggests mortgage rates are strongly influencing demand on top of the usual seasonality that brings buyers to the market in the spring. This home-shopping season is poised to follow a similar pattern as that in 2023, with the potential for a second wave if the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates midyear or later.
The 2.3% sale price premium registered last June followed the first spring in more than 15 years with mortgage rates over 6% on a 30-year fixed-rate loan. The high rates put home buyers on the back foot, and as rates continued upward through May, they were still reassessing and less likely to bid boldly. In June, however, rates pulled back a little from 6.79% to 6.67%, which likely presented an opportunity for determined buyers heading into summer. More buyers understood their market position and could afford to transact, boosting competition and sale prices.
The old logic was that sellers could earn a premium by listing in late spring, when search activity hit its peak. Now, with persistently low inventory, mortgage rate fluctuations make their own seasonality. First-time home buyers who are on the edge of qualifying for a home loan may dip in and out of the market, depending on what’s happening with rates. It is almost certain the Federal Reserve will push back any interest-rate cuts to mid-2024 at the earliest. If mortgage rates follow, that could bring another surge of buyers later this year.
Mortgage rates have been impacting affordability and sale prices since they began rising rapidly two years ago. In 2022, sellers nationwide saw the highest sale premium when they listed their home in late March, right before rates barreled past 5% and continued climbing.
Zillow’s research finds the best time to list can vary widely by metropolitan area. In 2023, it was as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York. Thirty of the top 35 largest metro areas saw for-sale listings command the highest sale prices between May and early July last year.
Zillow also found a wide range in the sale price premiums associated with homes listed during those peak periods. At the hottest time of the year in San Jose, homes sold for 5.5% more, a $88,000 boost on a typical home. Meanwhile, homes in San Antonio sold for 1.9% more during that same time period.
| Metropolitan Area | Best Time to List | Price Premium | Dollar Boost |
| United States | First half of June | 2.3% | $7,700 |
| New York, NY | First half of July | 2.4% | $15,500 |
| Los Angeles, CA | First half of May | 4.1% | $39,300 |
| Chicago, IL | First half of June | 2.8% | $8,800 |
| Dallas, TX | First half of June | 2.5% | $9,200 |
| Houston, TX | Second half of April | 2.0% | $6,200 |
| Washington, DC | Second half of June | 2.2% | $12,700 |
| Philadelphia, PA | First half of July | 2.4% | $8,200 |
| Miami, FL | First half of June | 2.3% | $12,900 |
| Atlanta, GA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $8,700 |
| Boston, MA | Second half of May | 3.5% | $23,600 |
| Phoenix, AZ | First half of June | 3.2% | $14,700 |
| San Francisco, CA | Second half of February | 4.2% | $50,300 |
| Riverside, CA | First half of May | 2.7% | $15,600 |
| Detroit, MI | First half of July | 3.3% | $7,900 |
| Seattle, WA | First half of June | 4.3% | $31,500 |
| Minneapolis, MN | Second half of May | 3.7% | $13,400 |
| San Diego, CA | Second half of April | 3.1% | $29,600 |
| Tampa, FL | Second half of June | 2.1% | $8,000 |
| Denver, CO | Second half of May | 2.9% | $16,900 |
| Baltimore, MD | First half of July | 2.2% | $8,200 |
| St. Louis, MO | First half of June | 2.9% | $7,000 |
| Orlando, FL | First half of June | 2.2% | $8,700 |
| Charlotte, NC | Second half of May | 3.0% | $11,000 |
| San Antonio, TX | First half of June | 1.9% | $5,400 |
| Portland, OR | Second half of April | 2.6% | $14,300 |
| Sacramento, CA | First half of June | 3.2% | $17,900 |
| Pittsburgh, PA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $4,700 |
| Cincinnati, OH | Second half of April | 2.7% | $7,500 |
| Austin, TX | Second half of May | 2.8% | $12,600 |
| Las Vegas, NV | First half of June | 3.4% | $14,600 |
| Kansas City, MO | Second half of May | 2.5% | $7,300 |
| Columbus, OH | Second half of June | 3.3% | $10,400 |
| Indianapolis, IN | First half of July | 3.0% | $8,100 |
| Cleveland, OH | First half of July | 3.4% | $7,400 |
| San Jose, CA | First half of June | 5.5% | $88,400 |
The post Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more appeared first on Zillow Research.
federal reserve pandemic home sales mortgage rates interest ratesUncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemployment-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex











