Government
Worker strikes and union elections surged in 2022 – could it mark a turning point for organized labor?
Workers have filed the most union petitions since 2015 and the number of strikes have surged, but whether this turns into a sustained increase in membership…
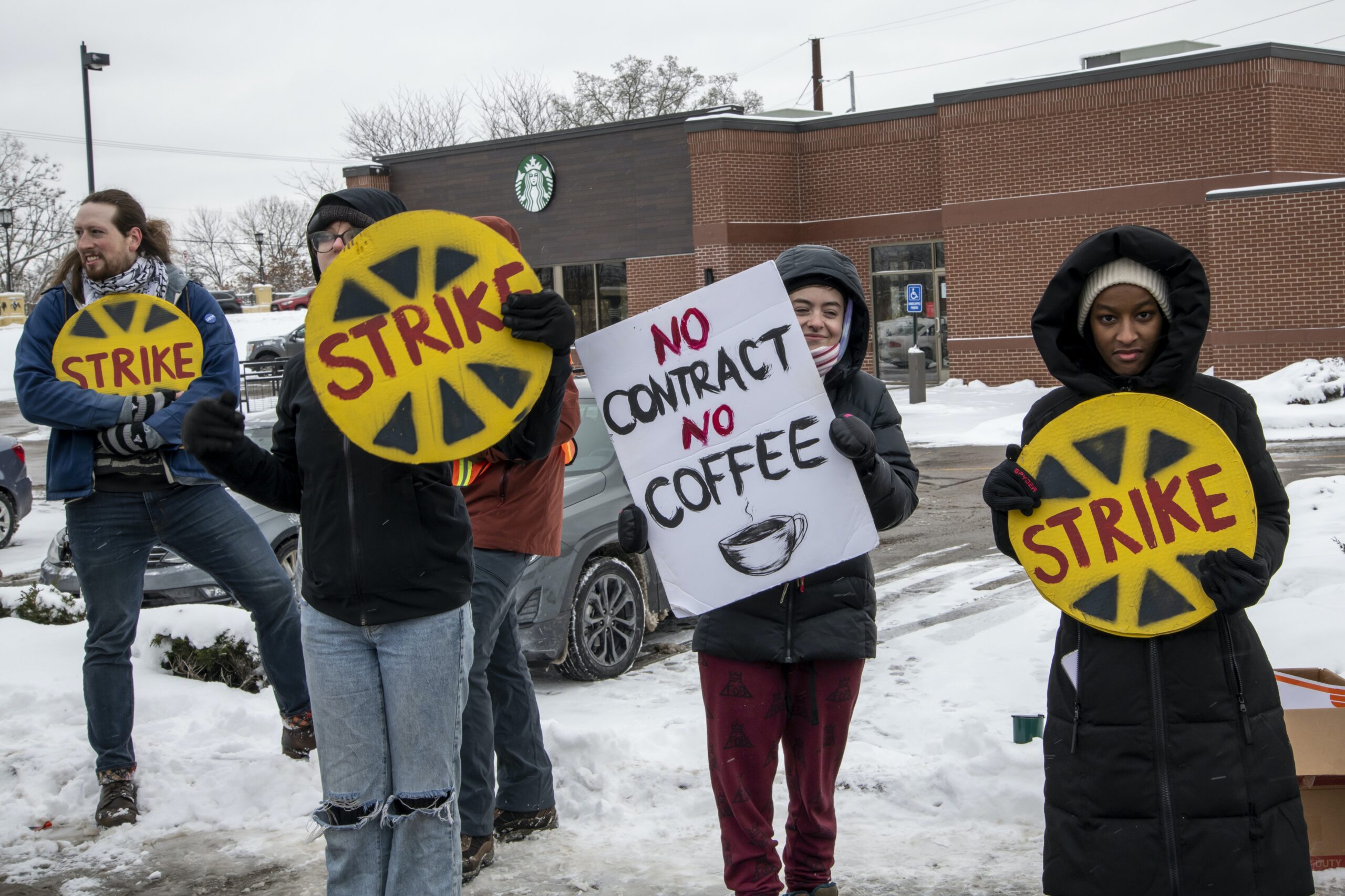
Workers organized and took to the picket line in increased numbers in 2022 to demand better pay and working conditions, leading to optimism among labor leaders and advocates that they’re witnessing a turnaround in labor’s sagging fortunes.
Teachers, journalists and baristas were among the tens of thousands of workers who went on strike – and it took an act of Congress to prevent 115,000 railroad employees from walking out as well. In total, there have been at least 20 major work stoppages involving at least 1,000 workers each in 2022, up from 16 in 2021, and hundreds more that were smaller.
At the same time, workers at Starbucks, Amazon, Apple and dozens of other companies filed over 2,000 petitions to form unions during the year – the most since 2015. Workers won 76% of the 1,363 elections that were held.
Historically, however, these figures are pretty tepid. The number of major work stoppages has been plunging for decades, from nearly 200 as recently as 1980, while union elections typically exceeded 5,000 a year before the 1980s. As of 2021, union membership was at about the lowest level on record, at 10.3%. In the 1950s, over 1 in 3 workers belonged to a union.
As a labor scholar, I agree that the evidence shows a surge in union activism. The obvious question is: Do these developments manifest a tipping point?
Signs of increased union activism
First, let’s take a closer look at 2022.
The most noteworthy sign of labor’s revival has been the rise in the number of petitions filed with the National Labor Relations Board. In fiscal year 2022, which ended in September, workers filed 2,072 petitions, up 63% from the previous year. Starbucks workers alone filed 354 of these petitions, winning the vast majority of the elections held. In addition, employees at companies historically deemed untouchable by unions, including Apple, Microsoft and Wells Fargo, also scored wins.
The increase in strike activity is also important. And while the major strikes that involve 1,000 or more employees and are tracked by the Bureau of Labor Statistics arouse the greatest attention, they represent only the tip of the iceberg.
The bureau recorded 20 major strikes in 2022, which is about 25% more than the average of 16 a year over the past two decades. Examples of these major strikes include the recent one-day New York Times walkout, two strikes in California involving more than 3,000 workers at health care company Kaiser Permanente, 2,100 workers at Frontier Communications and 48,000 workers at the University of California.
Since 2021, Cornell University has been keeping track of any labor action, however small, and found that there were a total of 385 strikes in calendar year 2022, up from 270 in the previous year. In total, these reported strikes have occurred in nearly 600 locations in 19 states., signifying the geographic breadth of activism.
Historical parallels
Of course, these figures are still quite low by historical standards.
I believe two previous spikes in the early 20th century offer some clues as to whether recent events could lead to sustained gains in union membership.
From 1934 to 1939, union membership soared from 7.6% to 19.2%. A few years later, from 1941 to 1945, membership climbed from 20% to 27%.
Both spikes occurred during periods of national and global upheaval. The first spike came in the latter half of the Great Depression, when unemployment in the U.S. reached as high as a quarter of the workforce. Economic deprivation and a lack of workplace protections led to widespread political and social activism and sweeping efforts to organize workers in response. It also contributed to the enactment of the National Labor Relations Act in 1935, which stimulated organizing in the industrial sector.
The second jump came as the U.S. mobilized the economy to fight a two-front war in Europe and Asia. National economic mobilization to support the war led to growth in manufacturing employment, where unions had been making substantial gains. Government wartime policy encouraged unionization as part of a bargain for industrial peace during the war.
Inequality and pandemic heroes
Today’s situation is a far cry from the economic misery of the Great Depression or the social upheaval of a global war, but there are some parallels worth exploring.
Overall unemployment may be near record lows, but economic inequality is higher than it was during the Depression. The top 10% of households hold over 68% of the wealth in the U.S. In 1936, this was about 47%.
In addition, the top 0.1% of wage earners experienced a nearly 390% increase in real wages from 1979 to 2020, versus a meager 28.2% pay hike for the bottom 90%. And employment in manufacturing, where unions had gained a stronghold in the 1940s and 1950s, slipped over 33% from 1979 to 2022.
Another parallel to the two historical precedents concerns national mobilization. The pandemic required a massive response in early 2020, as workers in industries deemed essential, such as health care, public safety and food and agriculture, bore the brunt of its impact, earning them the label “heroes” for their efforts. In such an environment, workers began to appreciate more the protections they derived from unions for occupational safety and health, eventually helping birth much-hyped recent labor trends like the “great resignation” and “quiet quitting.”
A stacked deck
Ultimately, however, the deck is still heavily stacked against unions, with unsupportive labor laws and very few employers showing real receptivity to having a unionized workforce.
And unions are limited in how much they can change public policy or the structure of the U.S. economy that makes unionization difficult. Reforming labor law through legislation has remained elusive, and the results of the 2022 midterms are not likely to make it any easier.
This makes me unconvinced that recent signs of progress represent a turning point.
An ace up labor’s sleeve may be public sentiment. Support for labor is at its highest since 1965, with 71% saying they approve of unions, according to a Gallup poll in August. And workers themselves are increasingly showing an interest in joining them. In 2017, 48% of workers polled said they would vote for union representation, up from 32% in 1995, the last time this question was asked.
Future success may depend on unions’ ability to tap into their growing popularity and emulate the recent wins at Starbucks and Amazon, as well as the successful “Fight for $15” campaign, which since 2012 has helped pass $15 minimum wage laws in a dozen states and Washington, D.C.
The odds may be steep, but the seeds of opportunity are there if labor is able to exploit them.
Marick Masters does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
depression unemployment pandemic congress unemployment europeGovernment
Rand Paul Teases Senate GOP Leader Run – Musk Says “I Would Support”
Rand Paul Teases Senate GOP Leader Run – Musk Says "I Would Support"
Republican Kentucky Senator Rand Paul on Friday hinted that he may jump…

Republican Kentucky Senator Rand Paul on Friday hinted that he may jump into the race to become the next Senate GOP leader, and Elon Musk was quick to support the idea. Republicans must find a successor for periodically malfunctioning Mitch McConnell, who recently announced he'll step down in November, though intending to keep his Senate seat until his term ends in January 2027, when he'd be within weeks of turning 86.
So far, the announced field consists of two quintessential establishment types: John Cornyn of Texas and John Thune of South Dakota. While John Barrasso's name had been thrown around as one of "The Three Johns" considered top contenders, the Wyoming senator on Tuesday said he'll instead seek the number two slot as party whip.
Paul used X to tease his potential bid for the position which -- if the GOP takes back the upper chamber in November -- could graduate from Minority Leader to Majority Leader. He started by telling his 5.1 million followers he'd had lots of people asking him about his interest in running...
Thousands of people have been asking if I'd run for Senate leadership...
— Rand Paul (@RandPaul) March 8, 2024
...then followed up with a poll in which he predictably annihilated Cornyn and Thune, taking a 96% share as of Friday night, with the other two below 2% each.
????????️VOTE NOW ????️ ???? Who would you like to be the next Senate leader?
— Rand Paul (@RandPaul) March 8, 2024
Elon Musk was quick to back the idea of Paul as GOP leader, while daring Cornyn and Thune to follow Paul's lead by throwing their names out for consideration by the Twitter-verse X-verse.
I would support Rand Paul and suspect that other candidates will not actually run polls out of concern for the results, but let’s see if they will!
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 8, 2024
Paul has been a stalwart opponent of security-state mass surveillance, foreign interventionism -- to include shoveling billions of dollars into the proxy war in Ukraine -- and out-of-control spending in general. He demonstrated the latter passion on the Senate floor this week as he ridiculed the latest kick-the-can spending package:
This bill is an insult to the American people. The earmarks are all the wasteful spending that you could ever hope to see, and it should be defeated. Read more: https://t.co/Jt8K5iucA4 pic.twitter.com/I5okd4QgDg
— Senator Rand Paul (@SenRandPaul) March 8, 2024
In February, Paul used Senate rules to force his colleagues into a grueling Super Bowl weekend of votes, as he worked to derail a $95 billion foreign aid bill. "I think we should stay here as long as it takes,” said Paul. “If it takes a week or a month, I’ll force them to stay here to discuss why they think the border of Ukraine is more important than the US border.”
Don't expect a Majority Leader Paul to ditch the filibuster -- he's been a hardy user of the legislative delay tactic. In 2013, he spoke for 13 hours to fight the nomination of John Brennan as CIA director. In 2015, he orated for 10-and-a-half-hours to oppose extension of the Patriot Act.
Among the general public, Paul is probably best known as Capitol Hill's chief tormentor of Dr. Anthony Fauci, who was director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease during the Covid-19 pandemic. Paul says the evidence indicates the virus emerged from China's Wuhan Institute of Virology. He's accused Fauci and other members of the US government public health apparatus of evading questions about their funding of the Chinese lab's "gain of function" research, which takes natural viruses and morphs them into something more dangerous. Paul has pointedly said that Fauci committed perjury in congressional hearings and that he belongs in jail "without question."
Musk is neither the only nor the first noteworthy figure to back Paul for party leader. Just hours after McConnell announced his upcoming step-down from leadership, independent 2024 presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy, Jr voiced his support:
Mitch McConnell, who has served in the Senate for almost 40 years, announced he'll step down this November.
— Robert F. Kennedy Jr (@RobertKennedyJr) February 28, 2024
Part of public service is about knowing when to usher in a new generation. It’s time to promote leaders in Washington, DC who won’t kowtow to the military contractors or…
In a testament to the extent to which the establishment recoils at the libertarian-minded Paul, mainstream media outlets -- which have been quick to report on other developments in the majority leader race -- pretended not to notice that Paul had signaled his interest in the job. More than 24 hours after Paul's test-the-waters tweet-fest began, not a single major outlet had brought it to the attention of their audience.
That may be his strongest endorsement yet.
Government
The Great Replacement Loophole: Illegal Immigrants Score 5-Year Work Benefit While “Waiting” For Deporation, Asylum
The Great Replacement Loophole: Illegal Immigrants Score 5-Year Work Benefit While "Waiting" For Deporation, Asylum
Over the past several…
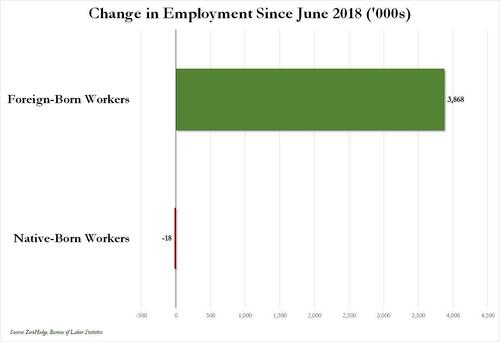
Over the past several months we've pointed out that there has been zero job creation for native-born workers since the summer of 2018...
... and that since Joe Biden was sworn into office, most of the post-pandemic job gains the administration continuously brags about have gone foreign-born (read immigrants, mostly illegal ones) workers.
And while the left might find this data almost as verboten as FBI crime statistics - as it directly supports the so-called "great replacement theory" we're not supposed to discuss - it also coincides with record numbers of illegal crossings into the United States under Biden.
In short, the Biden administration opened the floodgates, 10 million illegal immigrants poured into the country, and most of the post-pandemic "jobs recovery" went to foreign-born workers, of which illegal immigrants represent the largest chunk.

'But Tyler, illegal immigrants can't possibly work in the United States whilst awaiting their asylum hearings,' one might hear from the peanut gallery. On the contrary: ever since Biden reversed a key aspect of Trump's labor policies, all illegal immigrants - even those awaiting deportation proceedings - have been given carte blanche to work while awaiting said proceedings for up to five years...
... something which even Elon Musk was shocked to learn.
Wow, learn something new every day https://t.co/8MDtEEZGam
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 10, 2024
Which leads us to another question: recall that the primary concern for the Biden admin for much of 2022 and 2023 was soaring prices, i.e., relentless inflation in general, and rising wages in particular, which in turn prompted even Goldman to admit two years ago that the diabolical wage-price spiral had been unleashed in the US (diabolical, because nothing absent a major economic shock, read recession or depression, can short-circuit it once it is in place).
Well, there is one other thing that can break the wage-price spiral loop: a flood of ultra-cheap illegal immigrant workers. But don't take our word for it: here is Fed Chair Jerome Powell himself during his February 60 Minutes interview:
PELLEY: Why was immigration important?
POWELL: Because, you know, immigrants come in, and they tend to work at a rate that is at or above that for non-immigrants. Immigrants who come to the country tend to be in the workforce at a slightly higher level than native Americans do. But that's largely because of the age difference. They tend to skew younger.
PELLEY: Why is immigration so important to the economy?
POWELL: Well, first of all, immigration policy is not the Fed's job. The immigration policy of the United States is really important and really much under discussion right now, and that's none of our business. We don't set immigration policy. We don't comment on it.
I will say, over time, though, the U.S. economy has benefited from immigration. And, frankly, just in the last, year a big part of the story of the labor market coming back into better balance is immigration returning to levels that were more typical of the pre-pandemic era.
PELLEY: The country needed the workers.
POWELL: It did. And so, that's what's been happening.
Translation: Immigrants work hard, and Americans are lazy. But much more importantly, since illegal immigrants will work for any pay, and since Biden's Department of Homeland Security, via its Citizenship and Immigration Services Agency, has made it so illegal immigrants can work in the US perfectly legally for up to 5 years (if not more), one can argue that the flood of illegals through the southern border has been the primary reason why inflation - or rather mostly wage inflation, that all too critical component of the wage-price spiral - has moderated in in the past year, when the US labor market suddenly found itself flooded with millions of perfectly eligible workers, who just also happen to be illegal immigrants and thus have zero wage bargaining options.
None of this is to suggest that the relentless flood of immigrants into the US is not also driven by voting and census concerns - something Elon Musk has been pounding the table on in recent weeks, and has gone so far to call it "the biggest corruption of American democracy in the 21st century", but in retrospect, one can also argue that the only modest success the Biden admin has had in the past year - namely bringing inflation down from a torrid 9% annual rate to "only" 3% - has also been due to the millions of illegals he's imported into the country.
We would be remiss if we didn't also note that this so often carries catastrophic short-term consequences for the social fabric of the country (the Laken Riley fiasco being only the latest example), not to mention the far more dire long-term consequences for the future of the US - chief among them the trillions of dollars in debt the US will need to incur to pay for all those new illegal immigrants Democrat voters and low-paid workers. This is on top of the labor revolution that will kick in once AI leads to mass layoffs among high-paying, white-collar jobs, after which all those newly laid off native-born workers hoping to trade down to lower paying (if available) jobs will discover that hardened criminals from Honduras or Guatemala have already taken them, all thanks to Joe Biden.
Spread & Containment
‘I couldn’t stand the pain’: the Turkish holiday resort that’s become an emergency dental centre for Britons who can’t get treated at home
The crisis in NHS dentistry is driving increasing numbers abroad for treatment. Here are some of their stories.

It’s a hot summer day in the Turkish city of Antalya, a Mediterranean resort with golden beaches, deep blue sea and vibrant nightlife. The pool area of the all-inclusive resort is crammed with British people on sun loungers – but they aren’t here for a holiday. This hotel is linked to a dental clinic that organises treatment packages, and most of these guests are here to see a dentist.
From Norwich, two women talk about gums and injections. A man from Wales holds a tissue close to his mouth and spits blood – he has just had two molars extracted.
The dental clinic organises everything for these dental “tourists” throughout their treatment, which typically lasts from three to 15 days. The stories I hear of what has caused them to travel to Turkey are strikingly similar: all have struggled to secure dental treatment at home on the NHS.
“The hotel is nice and some days I go to the beach,” says Susan*, a hairdresser in her mid-30s from Norwich. “But really, we aren’t tourists like in a proper holiday. We come here because we have no choice. I couldn’t stand the pain.”

This is Susan’s second visit to Antalya. She explains that her ordeal started two years earlier:
I went to an NHS dentist who told me I had gum disease … She did some cleaning to my teeth and gums but it got worse. When I ate, my teeth were moving … the gums were bleeding and it was very painful. I called to say I was in pain but the clinic was not accepting NHS patients any more.
The only option the dentist offered Susan was to register as a private patient:
I asked how much. They said £50 for x-rays and then if the gum disease got worse, £300 or so for extraction. Four of them were moving – imagine: £1,200 for losing your teeth! Without teeth I’d lose my clients, but I didn’t have the money. I’m a single mum. I called my mum and cried.
Susan’s mother told her about a friend of hers who had been to Turkey for treatment, then together they found a suitable clinic:
The prices are so much cheaper! Tooth extraction, x-rays, consultations – it all comes included. The flight and hotel for seven days cost the same as losing four teeth in Norwich … I had my lower teeth removed here six months ago, now I’ve got implants … £2,800 for everything – hotel, transfer, treatments. I only paid the flights separately.
In the UK, roughly half the adult population suffers from periodontitis – inflammation of the gums caused by plaque bacteria that can lead to irreversible loss of gums, teeth, and bone. Regular reviews by a dentist or hygienist are required to manage this condition. But nine out of ten dental practices cannot offer NHS appointments to new adult patients, while eight in ten are not accepting new child patients.
Some UK dentists argue that Britons who travel abroad for treatment do so mainly for cosmetic procedures. They warn that dental tourism is dangerous, and that if their treatment goes wrong, dentists in the UK will be unable to help because they don’t want to be responsible for further damage. Susan shrugs this off:
Dentists in England say: ‘If you go to Turkey, we won’t touch you [afterwards].’ But I don’t worry because there are no appointments at home anyway. They couldn’t help in the first place, and this is why we are in Turkey.
‘How can we pay all this money?’
As a social anthropologist, I travelled to Turkey a number of times in 2023 to investigate the crisis of NHS dentistry, and the journeys abroad that UK patients are increasingly making as a result. I have relatives in Istanbul and have been researching migration and trading patterns in Turkey’s largest city since 2016.
In August 2023, I visited the resort in Antalya, nearly 400 miles south of Istanbul. As well as Susan, I met a group from a village in Wales who said there was no provision of NHS dentistry back home. They had organised a two-week trip to Turkey: the 12-strong group included a middle-aged couple with two sons in their early 20s, and two couples who were pensioners. By going together, Anya tells me, they could support each other through their different treatments:
I’ve had many cavities since I was little … Before, you could see a dentist regularly – you didn’t even think about it. If you had pain or wanted a regular visit, you phoned and you went … That was in the 1990s, when I went to the dentist maybe every year.
Anya says that once she had children, her family and work commitments meant she had no time to go to the dentist. Then, years later, she started having serious toothache:
Every time I chewed something, it hurt. I ate soups and soft food, and I also lost weight … Even drinking was painful – tea: pain, cold water: pain. I was taking paracetamol all the time! I went to the dentist to fix all this, but there were no appointments.
Anya was told she would have to wait months, or find a dentist elsewhere:
A private clinic gave me a list of things I needed done. Oh my God, almost £6,000. My husband went too – same story. How can we pay all this money? So we decided to come to Turkey. Some people we know had been here, and others in the village wanted to come too. We’ve brought our sons too – they also need to be checked and fixed. Our whole family could be fixed for less than £6,000.
By the time they travelled, Anya’s dental problems had turned into a dental emergency. She says she could not live with the pain anymore, and was relying on paracetamol.
In 2023, about 6 million adults in the UK experienced protracted pain (lasting more than two weeks) caused by toothache. Unintentional paracetamol overdose due to dental pain is a significant cause of admissions to acute medical units. If left untreated, tooth infections can spread to other parts of the body and cause life-threatening complications – and on rare occasions, death.
In February 2024, police were called to manage hundreds of people queuing outside a newly opened dental clinic in Bristol, all hoping to be registered or seen by an NHS dentist. One in ten Britons have admitted to performing “DIY dentistry”, of which 20% did so because they could not find a timely appointment. This includes people pulling out their teeth with pliers and using superglue to repair their teeth.
In the 1990s, dentistry was almost entirely provided through NHS services, with only around 500 solely private dentists registered. Today, NHS dentist numbers in England are at their lowest level in a decade, with 23,577 dentists registered to perform NHS work in 2022-23, down 695 on the previous year. Furthermore, the precise division of NHS and private work that each dentist provides is not measured.
The COVID pandemic created longer waiting lists for NHS treatment in an already stretched public service. In Bridlington, Yorkshire, people are now reportedly having to wait eight-to-nine years to get an NHS dental appointment with the only remaining NHS dentist in the town.
In his book Patients of the State (2012), Argentine sociologist Javier Auyero describes the “indignities of waiting”. It is the poor who are mostly forced to wait, he writes. Queues for state benefits and public services constitute a tangible form of power over the marginalised. There is an ethnic dimension to this story, too. Data suggests that in the UK, patients less likely to be effective in booking an NHS dental appointment are non-white ethnic groups and Gypsy or Irish travellers, and that it is particularly challenging for refugees and asylum-seekers to access dental care.

This article is part of Conversation Insights
The Insights team generates long-form journalism derived from interdisciplinary research. The team is working with academics from different backgrounds who have been engaged in projects aimed at tackling societal and scientific challenges.
In 2022, I experienced my own dental emergency. An infected tooth was causing me debilitating pain, and needed root canal treatment. I was advised this would cost £71 on the NHS, plus £307 for a follow-up crown – but that I would have to wait months for an appointment. The pain became excruciating – I could not sleep, let alone wait for months. In the same clinic, privately, I was quoted £1,300 for the treatment (more than half my monthly income at the time), or £295 for a tooth extraction.
I did not want to lose my tooth because of lack of money. So I bought a flight to Istanbul immediately for the price of the extraction in the UK, and my tooth was treated with root canal therapy by a private dentist there for £80. Including the costs of travelling, the total was a third of what I was quoted to be treated privately in the UK. Two years on, my treated tooth hasn’t given me any more problems.
A better quality of life
Not everyone is in Antalya for emergency procedures. The pensioners from Wales had contacted numerous clinics they found on the internet, comparing prices, treatments and hotel packages at least a year in advance, in a carefully planned trip to get dental implants – artificial replacements for tooth roots that help support dentures, crowns and bridges.

In Turkey, all the dentists I speak to (most of whom cater mainly for foreigners, including UK nationals) consider implants not a cosmetic or luxurious treatment, but a development in dentistry that gives patients who are able to have the procedure a much better quality of life. This procedure is not available on the NHS for most of the UK population, and the patients I meet in Turkey could not afford implants in private clinics back home.
Paul is in Antalya to replace his dentures, which have become uncomfortable and irritating to his gums, with implants. He says he couldn’t find an appointment to see an NHS dentist. His wife Sonia went through a similar procedure the year before and is very satisfied with the results, telling me: “Why have dentures that you need to put in a glass overnight, in the old style? If you can have implants, I say, you’re better off having them.”
Most of the dental tourists I meet in Antalya are white British: this city, known as the Turkish Riviera, has developed an entire economy catering to English-speaking tourists. In 2023, more than 1.3 million people visited the city from the UK, up almost 15% on the previous year.
Read more: NHS dentistry is in crisis – are overseas dentists the answer?
In contrast, the Britons I meet in Istanbul are predominantly from a non-white ethnic background. Omar, a pensioner of Pakistani origin in his early 70s, has come here after waiting “half a year” for an NHS appointment to fix the dental bridge that is causing him pain. Omar’s son had been previously for a hair transplant, and was offered a free dental checkup by the same clinic, so he suggested it to his father. Having worked as a driver for a manufacturing company for two decades in Birmingham, Omar says he feels disappointed to have contributed to the British economy for so long, only to be “let down” by the NHS:
At home, I must wait and wait and wait to get a bridge – and then I had many problems with it. I couldn’t eat because the bridge was uncomfortable and I was in pain, but there were no appointments on the NHS. I asked a private dentist and they recommended implants, but they are far too expensive [in the UK]. I started losing weight, which is not a bad thing at the beginning, but then I was worrying because I couldn’t chew and eat well and was losing more weight … Here in Istanbul, I got dental implants – US$500 each, problem solved! In England, each implant is maybe £2,000 or £3,000.
In the waiting area of another clinic in Istanbul, I meet Mariam, a British woman of Iraqi background in her late 40s, who is making her second visit to the dentist here. Initially, she needed root canal therapy after experiencing severe pain for weeks. Having been quoted £1,200 in a private clinic in outer London, Mariam decided to fly to Istanbul instead, where she was quoted £150 by a dentist she knew through her large family. Even considering the cost of the flight, Mariam says the decision was obvious:
Dentists in England are so expensive and NHS appointments so difficult to find. It’s awful there, isn’t it? Dentists there blamed me for my rotten teeth. They say it’s my fault: I don’t clean or I ate sugar, or this or that. I grew up in a village in Iraq and didn’t go to the dentist – we were very poor. Then we left because of war, so we didn’t go to a dentist … When I arrived in London more than 20 years ago, I didn’t speak English, so I still didn’t go to the dentist … I think when you move from one place to another, you don’t go to the dentist unless you are in real, real pain.
In Istanbul, Mariam has opted not only for the urgent root canal treatment but also a longer and more complex treatment suggested by her consultant, who she says is a renowned doctor from Syria. This will include several extractions and implants of back and front teeth, and when I ask what she thinks of achieving a “Hollywood smile”, Mariam says:
Who doesn’t want a nice smile? I didn’t come here to be a model. I came because I was in pain, but I know this doctor is the best for implants, and my front teeth were rotten anyway.
Dentists in the UK warn about the risks of “overtreatment” abroad, but Mariam appears confident that this is her opportunity to solve all her oral health problems. Two of her sisters have already been through a similar treatment, so they all trust this doctor.

The UK’s ‘dental deserts’
To get a fuller understanding of the NHS dental crisis, I’ve also conducted 20 interviews in the UK with people who have travelled or were considering travelling abroad for dental treatment.
Joan, a 50-year-old woman from Exeter, tells me she considered going to Turkey and could have afforded it, but that her back and knee problems meant she could not brave the trip. She has lost all her lower front teeth due to gum disease and, when I meet her, has been waiting 13 months for an NHS dental appointment. Joan tells me she is living in “shame”, unable to smile.
In the UK, areas with extremely limited provision of NHS dental services – known as as “dental deserts” – include densely populated urban areas such as Portsmouth and Greater Manchester, as well as many rural and coastal areas.
In Felixstowe, the last dentist taking NHS patients went private in 2023, despite the efforts of the activist group Toothless in Suffolk to secure better access to NHS dentists in the area. It’s a similar story in Ripon, Yorkshire, and in Dumfries & Galloway, Scotland, where nearly 25,000 patients have been de-registered from NHS dentists since 2021.
Data shows that 2 million adults must travel at least 40 miles within the UK to access dental care. Branding travel for dental care as “tourism” carries the risk of disguising the elements of duress under which patients move to restore their oral health – nationally and internationally. It also hides the immobility of those who cannot undertake such journeys.
The 90-year-old woman in Dumfries & Galloway who now faces travelling for hours by bus to see an NHS dentist can hardly be considered “tourism” – nor the Ukrainian war refugees who travelled back from West Sussex and Norwich to Ukraine, rather than face the long wait to see an NHS dentist.
Many people I have spoken to cannot afford the cost of transport to attend dental appointments two hours away – or they have care responsibilities that make it impossible. Instead, they are forced to wait in pain, in the hope of one day securing an appointment closer to home.

‘Your crisis is our business’
The indignities of waiting in the UK are having a big impact on the lives of some local and foreign dentists in Turkey. Some neighbourhoods are rapidly changing as dental and other health clinics, usually in luxurious multi-storey glass buildings, mushroom. In the office of one large Istanbul medical complex with sections for hair transplants and dentistry (plus one linked to a hospital for more extensive cosmetic surgery), its Turkish owner and main investor tells me:
Your crisis is our business, but this is a bazaar. There are good clinics and bad clinics, and unfortunately sometimes foreign patients do not know which one to choose. But for us, the business is very good.
This clinic only caters to foreign patients. The owner, an architect by profession who also developed medical clinics in Brazil, describes how COVID had a major impact on his business:
When in Europe you had COVID lockdowns, Turkey allowed foreigners to come. Many people came for ‘medical tourism’ – we had many patients for cosmetic surgery and hair transplants. And that was when the dental business started, because our patients couldn’t see a dentist in Germany or England. Then more and more patients started to come for dental treatments, especially from the UK and Ireland. For them, it’s very, very cheap here.
The reasons include the value of the Turkish lira relative to the British pound, the low cost of labour, the increasing competition among Turkish clinics, and the sheer motivation of dentists here. While most dentists catering to foreign patients are from Turkey, others have arrived seeking refuge from war and violence in Syria, Iraq, Afghanistan, Iran and beyond. They work diligently to rebuild their lives, careers and lost wealth.
Regardless of their origin, all dentists in Turkey must be registered and certified. Hamed, a Syrian dentist and co-owner of a new clinic in Istanbul catering to European and North American patients, tells me:
I know that you say ‘Syrian’ and people think ‘migrant’, ‘refugee’, and maybe think ‘how can this dentist be good?’ – but Syria, before the war, had very good doctors and dentists. Many of us came to Turkey and now I have a Turkish passport. I had to pass the exams to practise dentistry here – I study hard. The exams are in Turkish and they are difficult, so you cannot say that Syrian doctors are stupid.
Hamed talks excitedly about the latest technology that is coming to his profession: “There are always new materials and techniques, and we cannot stop learning.” He is about to travel to Paris to an international conference:
I can say my techniques are very advanced … I bet I put more implants and do more bone grafting and surgeries every week than any dentist you know in England. A good dentist is about practice and hand skills and experience. I work hard, very hard, because more and more patients are arriving to my clinic, because in England they don’t find dentists.

While there is no official data about the number of people travelling from the UK to Turkey for dental treatment, investors and dentists I speak to consider that numbers are rocketing. From all over the world, Turkey received 1.2 million visitors for “medical tourism” in 2022, an increase of 308% on the previous year. Of these, about 250,000 patients went for dentistry. One of the most renowned dental clinics in Istanbul had only 15 British patients in 2019, but that number increased to 2,200 in 2023 and is expected to reach 5,500 in 2024.
Like all forms of medical care, dental treatments carry risks. Most clinics in Turkey offer a ten-year guarantee for treatments and a printed clinical history of procedures carried out, so patients can show this to their local dentists and continue their regular annual care in the UK. Dental treatments, checkups and maintaining a good oral health is a life-time process, not a one-off event.
Many UK patients, however, are caught between a rock and a hard place – criticised for going abroad, yet unable to get affordable dental care in the UK before and after their return. The British Dental Association has called for more action to inform these patients about the risks of getting treated overseas – and has warned UK dentists about the legal implications of treating these patients on their return. But this does not address the difficulties faced by British patients who are being forced to go abroad in search of affordable, often urgent dental care.
A global emergency
The World Health Organization states that the explosion of oral disease around the world is a result of the “negligent attitude” that governments, policymakers and insurance companies have towards including oral healthcare under the umbrella of universal healthcare. It as if the health of our teeth and mouth is optional; somehow less important than treatment to the rest of our body. Yet complications from untreated tooth decay can lead to hospitalisation.
The main causes of oral health diseases are untreated tooth decay, severe gum disease, toothlessness, and cancers of the lip and oral cavity. Cases grew during the pandemic, when little or no attention was paid to oral health. Meanwhile, the global cosmetic dentistry market is predicted to continue growing at an annual rate of 13% for the rest of this decade, confirming the strong relationship between socioeconomic status and access to oral healthcare.
In the UK since 2018, there have been more than 218,000 admissions to hospital for rotting teeth, of which more than 100,000 were children. Some 40% of children in the UK have not seen a dentist in the past 12 months. The role of dentists in prevention of tooth decay and its complications, and in the early detection of mouth cancer, is vital. While there is a 90% survival rate for mouth cancer if spotted early, the lack of access to dental appointments is causing cases to go undetected.
The reasons for the crisis in NHS dentistry are complex, but include: the real-term cuts in funding to NHS dentistry; the challenges of recruitment and retention of dentists in rural and coastal areas; pay inequalities facing dental nurses, most of them women, who are being badly hit by the cost of living crisis; and, in England, the 2006 Dental Contract that does not remunerate dentists in a way that encourages them to continue seeing NHS patients.
The UK is suffering a mass exodus of the public dentistry workforce, with workers leaving the profession entirely or shifting to the private sector, where payments and life-work balance are better, bureaucracy is reduced, and prospects for career development look much better. A survey of general dental practitioners found that around half have reduced their NHS work since the pandemic – with 43% saying they were likely to go fully private, and 42% considering a career change or taking early retirement.
Reversing the UK’s dental crisis requires more commitment to substantial reform and funding than the “recovery plan” announced by Victoria Atkins, the secretary of state for health and social care, on February 7.
The stories I have gathered show that people travelling abroad for dental treatment don’t see themselves as “tourists” or vanity-driven consumers of the “Hollywood smile”. Rather, they have been forced by the crisis in NHS dentistry to seek out a service 1,500 miles away in Turkey that should be a basic, affordable right for all, on their own doorstep.
*Names in this article have been changed to protect the anonymity of the interviewees.

For you: more from our Insights series:
GP crisis: how did things go so wrong, and what needs to change?
Insomnia: how chronic sleep problems can lead to a spiralling decline in mental health
To hear about new Insights articles, join the hundreds of thousands of people who value The Conversation’s evidence-based news. Subscribe to our newsletter.
Diana Ibanez Tirado receives funding from the School of Global Studies, University of Sussex.
pound pandemic treatment therapy spread recovery iran brazil european europe uk germany ukraine world health organization-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex























