Government
Why “Science Denial”?
Why "Science Denial"?
Authored by Sheldon Richman via The Libertarian Institute,
In a new book two professors of psychology, Gale Sinatra and Barbara Hofer, seek to explain why what they call "science denial" is rampant today and how…

Authored by Sheldon Richman via The Libertarian Institute,
In a new book two professors of psychology, Gale Sinatra and Barbara Hofer, seek to explain why what they call "science denial" is rampant today and how dangerous it is. They also give their account in a strange conversation with Michael Shermer, the editor of Skeptic magazine, from whom we might have expected a tad more "skepticism" or at least some devil’s advocacy.
The views of all three are in some ways vague and even confused, but the condescension toward the unenlightened rubes who disagree with them on certain scientific controversies–primarily climate- and COVID-19-related–couldn’t have been more clear.
While Sinatra and Hofer smear a large and diverse group of people as "science deniers," they undercut their own claim when they admit that no one actually rejects science per se. So their sensational but misleading title and broad statements are designed not to inform but rather to sell books to their progressive-minded audience. The rubes they are talking about, the authors admit, go to doctors, take prescribed medicines, fly on airplanes, etc. That hardly sounds like general science denial.
So what’s the problem? What the authors have in mind is doubt about or rejection of particular scientific claims. They are willing to apply the label "cafeteria deniers." But why not call them "cafeteria skeptics"? Or would that hit Shermer too close to home?
My purpose is not to defend or criticize any particular scientific claim in dispute. Some are backed by strong evidence, while others have little or no evidence behind them. Laymen ought to exercise care in (tentatively) deciding who among the contending scientists are likely to be right. Here I only want to raise a big reason for doubt that the authors and Shermer ignore.
But first, to demonstrate authors’ and Shermer’s sloppiness (which may be too charitable an interpretation of what they’re doing), please note that early on they embrace the allegedly near-unanimous (97 percent) consensus among climate scientists on ominous manmade global warming. Their point is that anyone who would take a position contrary to such an overwhelming consensus would have to be a jerk.
In fact, that so-called consensus was cobbled together by examining just the abstracts of a selection of climate scientists’ journal articles over a certain period. Only a third of those papers expressed an explicit or implicit view on whether manmade global warming was happening. Of those, 97 percent agreed on–well, something. But what? What they all apparently agreed on was that an unspecified amount of warming has occurred and that human activity has had an unspecified degree of responsibility.
Notice that no magnitudes and no net assessment of harms and benefits are implied in that sentence whatsoever. By that low bar, most if not all climate scientists and laymen in the realist-optimist camp are part of the consensus! That a good deal of the force out of the consensus proclamation, wouldn’t you say?
Yet this "consensus" is decisive for climate alarmists Sinatra, Hofer, and Shermer. (If you think humility is a virtue in scientists, don’t look for it in these writers.) Shermer says what impressed him is that all those in the 97 percent "converged" on that view (again, what view?) "independently," while the others, he says, converged on no particular theory about the climate. Has he looked into the facts? Or does he go along with whatever is called a consensus by the news media? Is this is how he decides on matters outside his specialty? They’re growing a strange crop of skeptics these days.
Here is the problem: when the authors and Shermer call someone a "climate change (or just a climate) denier," they are making a slickly illegitimate move; for what’s being denied is not climate change or warming between 1850 and 1998, but a looming climate catastrophe, natural or manmade. Catastrophe denial does not equal climate-change denial. No one–no one!–thinks that climate does not change. Well, actually one group does seem to think this: the alarmists who imply or say outright that except for human activity, climate would not change (or not change very much). But that of course is absurd. The concept change is baked into the concept climate. The only sense in which the climate is not changing today is that it never stops changing.
Sinatra, Hofer, and Shermer spent an hour and a half talking about "science denial," with no disagreement among them. In all the time none of them mentioned the word politicization, that is, the perverse incentives from government meddling in scientific research. They discussed lots of possible reasons for "denial"–like confirmation bias and other well-known cognitive biases–but it seems never to have occurred to any of them that some people are more inclined to distrust particular scientific claims these days than previously because they have observed that purportedly objective claims (and not just about scientific matters) are used to advance political causes. Sinatra, Hofer, and Shermer have no trouble believing that so-called deniers have hidden political and cultural agendas, but they show no sign of suspecting that those who make the claims, along with the politicians who translate them into coercive government policy, may also have political and cultural agendas–and often not so hidden.
This seems like a serious shortcoming. While Sinatra and Hofer acknowledge that scientists are human beings and subject to the same imperfections as everyone else–envy, greed, ambition, a desire for peer approval, etc.–they assure us that these faults are rooted out by an internal checks-and-balance system. Because of these, no threat to science can arise from within, but only from outside, that is, from "deniers."
That, however, isn’t how it works out. Checks and balances on paper often bear little relationship to checks and balances in practice. (This is true of constitutions too.) For example, the peer-review process for academic publication and promotion has become incestuous "pal review." Paradigms are protected against challenges and patched up through ad hoc salvage operations when a paradigm’s shortcomings are exposed.
Moreover, politicians are naturally inclined toward research that identifies "crises" that allegedly only government can address. As H. L. Mencken pointed out, “The whole aim of practical politics is to keep the populace alarmed (and hence clamorous to be led to safety) by an endless series of hobgoblins, most of them imaginary.”
In need of government grants to secure promotion and tenure at their universities, many scientists are inclined to give the politicians what they want. Those are the ones who will get the money, at any rate. An orthodoxy arises, and independent thinkers, no matter how qualified, are marginalized and smeared as, say, "science deniers." (The obvious association with the properly stigmatized term Holocaust deniers is no coincidence.) It’s happened repeatedly before. It’s happening now. (Again, I don’t mean that every scientific claim that is criticized is necessarily wrong.)
Politicians demand research that goes in one direction, and some scientists are happy to supply it. The politicians then use the research to justify expanded power (the Green New Deal and economic shutdown in a pandemic), which stimulates further research in that direction. I’m not saying that every participant is a cynic, but it is fun to be near the action. To borrow a trope from the analysis of the military-industrial complex, it’s a self-licking ice-cream cone. And all of this is further amplified by the 24/7 news media, which will always prefer reports of looming disasters to good news, and of course the social networks, which are the lookout for "misinformation."
If you want to see how politicization can create doubters, here’s one case apart from scientific controversies: Russiagate. For years the American people were assured by most of the "objective" mainstream media, fed by “public-spirited” leaks and retired government spies working as dispassionate commentators, that the allegedly nonpolitical intelligence apparatus had solid evidence that Vladimir Putin had rigged the 2016 election to put his puppet Donald Trump in the White House. None of that was true, as shown by the massive FBI investigation led by a sainted special counsel. Don’t you think that a good portion of the American people realize that this establishment campaign was intended to drive Trump from office or at least cripple his presidency, effectively reversing the election? (One need not be a Trump fan–I’m certainly not–to see this.) Germane to my point, if that kind of gross abuse can occur in one matter, why can’t it be occurring in other matters?
A key part of the politicization of science is government finance of research, which Sinatra and Hofer predictably want more of. As I noted recently, in his 1961 farewell speech President Dwight Eisenhower warned about the emerging government-science complex, which he said was just as dangerous as the military-industrial complex.
If climate alarmists regard private support for research as tainted by self-interest, the rest of us are entitled to regard government support as similarly tainted. Sinatra, Hofer, and Shermer really should grow up and embrace what Public Choice political economist James Buchanan called "politics without romance."
Maybe if politics had not tainted institutional science, fewer people would distrust so many of its claims. Politics is the craft of winning and maintaining power by assembling self-serving coalitions in order to impose costs on everyone else. Some people have justifiably come to assume that many government-financed scientific claims are formulated for that purpose.
If I’m right, then the use of science to advance an interventionist political agenda has sown very distrust the authors and Shermer abhor. Laymen should certainly be discriminating when they judge scientific claims, and real consensuses should be taken into account. But that does not exonerate the scientists who have actively fed policymakers’ efforts to control our lives.
Government
Survey Shows Declining Concerns Among Americans About COVID-19
Survey Shows Declining Concerns Among Americans About COVID-19
A new survey reveals that only 20% of Americans view covid-19 as "a major threat"…
A new survey reveals that only 20% of Americans view covid-19 as "a major threat" to the health of the US population - a sharp decline from a high of 67% in July 2020.
What's more, the Pew Research Center survey conducted from Feb. 7 to Feb. 11 showed that just 10% of Americans are concerned that they will catch the disease and require hospitalization.
"This data represents a low ebb of public concern about the virus that reached its height in the summer and fall of 2020, when as many as two-thirds of Americans viewed COVID-19 as a major threat to public health," reads the report, which was published March 7.
According to the survey, half of the participants understand the significance of researchers and healthcare providers in understanding and treating long COVID - however 27% of participants consider this issue less important, while 22% of Americans are unaware of long COVID.
What's more, while Democrats were far more worried than Republicans in the past, that gap has narrowed significantly.
"In the pandemic’s first year, Democrats were routinely about 40 points more likely than Republicans to view the coronavirus as a major threat to the health of the U.S. population. This gap has waned as overall levels of concern have fallen," reads the report.
More via the Epoch Times;
The survey found that three in ten Democrats under 50 have received an updated COVID-19 vaccine, compared with 66 percent of Democrats ages 65 and older.
Moreover, 66 percent of Democrats ages 65 and older have received the updated COVID-19 vaccine, while only 24 percent of Republicans ages 65 and older have done so.
“This 42-point partisan gap is much wider now than at other points since the start of the outbreak. For instance, in August 2021, 93 percent of older Democrats and 78 percent of older Republicans said they had received all the shots needed to be fully vaccinated (a 15-point gap),” it noted.
COVID-19 No Longer an Emergency
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently issued its updated recommendations for the virus, which no longer require people to stay home for five days after testing positive for COVID-19.
The updated guidance recommends that people who contracted a respiratory virus stay home, and they can resume normal activities when their symptoms improve overall and their fever subsides for 24 hours without medication.
“We still must use the commonsense solutions we know work to protect ourselves and others from serious illness from respiratory viruses, this includes vaccination, treatment, and staying home when we get sick,” CDC director Dr. Mandy Cohen said in a statement.
The CDC said that while the virus remains a threat, it is now less likely to cause severe illness because of widespread immunity and improved tools to prevent and treat the disease.
“Importantly, states and countries that have already adjusted recommended isolation times have not seen increased hospitalizations or deaths related to COVID-19,” it stated.
The federal government suspended its free at-home COVID-19 test program on March 8, according to a website set up by the government, following a decrease in COVID-19-related hospitalizations.
According to the CDC, hospitalization rates for COVID-19 and influenza diseases remain “elevated” but are decreasing in some parts of the United States.
International
Rand Paul Teases Senate GOP Leader Run – Musk Says “I Would Support”
Rand Paul Teases Senate GOP Leader Run – Musk Says "I Would Support"
Republican Kentucky Senator Rand Paul on Friday hinted that he may jump…

Republican Kentucky Senator Rand Paul on Friday hinted that he may jump into the race to become the next Senate GOP leader, and Elon Musk was quick to support the idea. Republicans must find a successor for periodically malfunctioning Mitch McConnell, who recently announced he'll step down in November, though intending to keep his Senate seat until his term ends in January 2027, when he'd be within weeks of turning 86.
So far, the announced field consists of two quintessential establishment types: John Cornyn of Texas and John Thune of South Dakota. While John Barrasso's name had been thrown around as one of "The Three Johns" considered top contenders, the Wyoming senator on Tuesday said he'll instead seek the number two slot as party whip.
Paul used X to tease his potential bid for the position which -- if the GOP takes back the upper chamber in November -- could graduate from Minority Leader to Majority Leader. He started by telling his 5.1 million followers he'd had lots of people asking him about his interest in running...
Thousands of people have been asking if I'd run for Senate leadership...
— Rand Paul (@RandPaul) March 8, 2024
...then followed up with a poll in which he predictably annihilated Cornyn and Thune, taking a 96% share as of Friday night, with the other two below 2% each.
????????️VOTE NOW ????️ ???? Who would you like to be the next Senate leader?
— Rand Paul (@RandPaul) March 8, 2024
Elon Musk was quick to back the idea of Paul as GOP leader, while daring Cornyn and Thune to follow Paul's lead by throwing their names out for consideration by the Twitter-verse X-verse.
I would support Rand Paul and suspect that other candidates will not actually run polls out of concern for the results, but let’s see if they will!
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 8, 2024
Paul has been a stalwart opponent of security-state mass surveillance, foreign interventionism -- to include shoveling billions of dollars into the proxy war in Ukraine -- and out-of-control spending in general. He demonstrated the latter passion on the Senate floor this week as he ridiculed the latest kick-the-can spending package:
This bill is an insult to the American people. The earmarks are all the wasteful spending that you could ever hope to see, and it should be defeated. Read more: https://t.co/Jt8K5iucA4 pic.twitter.com/I5okd4QgDg
— Senator Rand Paul (@SenRandPaul) March 8, 2024
In February, Paul used Senate rules to force his colleagues into a grueling Super Bowl weekend of votes, as he worked to derail a $95 billion foreign aid bill. "I think we should stay here as long as it takes,” said Paul. “If it takes a week or a month, I’ll force them to stay here to discuss why they think the border of Ukraine is more important than the US border.”
Don't expect a Majority Leader Paul to ditch the filibuster -- he's been a hardy user of the legislative delay tactic. In 2013, he spoke for 13 hours to fight the nomination of John Brennan as CIA director. In 2015, he orated for 10-and-a-half-hours to oppose extension of the Patriot Act.
Among the general public, Paul is probably best known as Capitol Hill's chief tormentor of Dr. Anthony Fauci, who was director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease during the Covid-19 pandemic. Paul says the evidence indicates the virus emerged from China's Wuhan Institute of Virology. He's accused Fauci and other members of the US government public health apparatus of evading questions about their funding of the Chinese lab's "gain of function" research, which takes natural viruses and morphs them into something more dangerous. Paul has pointedly said that Fauci committed perjury in congressional hearings and that he belongs in jail "without question."
Musk is neither the only nor the first noteworthy figure to back Paul for party leader. Just hours after McConnell announced his upcoming step-down from leadership, independent 2024 presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy, Jr voiced his support:
Mitch McConnell, who has served in the Senate for almost 40 years, announced he'll step down this November.
— Robert F. Kennedy Jr (@RobertKennedyJr) February 28, 2024
Part of public service is about knowing when to usher in a new generation. It’s time to promote leaders in Washington, DC who won’t kowtow to the military contractors or…
In a testament to the extent to which the establishment recoils at the libertarian-minded Paul, mainstream media outlets -- which have been quick to report on other developments in the majority leader race -- pretended not to notice that Paul had signaled his interest in the job. More than 24 hours after Paul's test-the-waters tweet-fest began, not a single major outlet had brought it to the attention of their audience.
That may be his strongest endorsement yet.
Government
The Great Replacement Loophole: Illegal Immigrants Score 5-Year Work Benefit While “Waiting” For Deporation, Asylum
The Great Replacement Loophole: Illegal Immigrants Score 5-Year Work Benefit While "Waiting" For Deporation, Asylum
Over the past several…
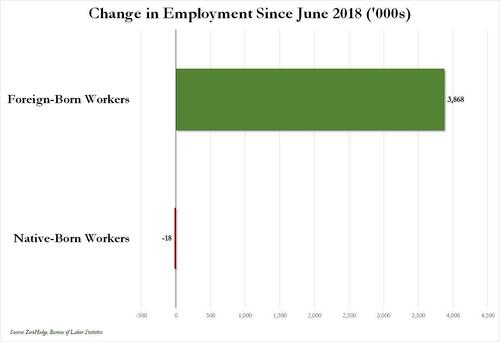
Over the past several months we've pointed out that there has been zero job creation for native-born workers since the summer of 2018...
... and that since Joe Biden was sworn into office, most of the post-pandemic job gains the administration continuously brags about have gone foreign-born (read immigrants, mostly illegal ones) workers.
And while the left might find this data almost as verboten as FBI crime statistics - as it directly supports the so-called "great replacement theory" we're not supposed to discuss - it also coincides with record numbers of illegal crossings into the United States under Biden.
In short, the Biden administration opened the floodgates, 10 million illegal immigrants poured into the country, and most of the post-pandemic "jobs recovery" went to foreign-born workers, of which illegal immigrants represent the largest chunk.

'But Tyler, illegal immigrants can't possibly work in the United States whilst awaiting their asylum hearings,' one might hear from the peanut gallery. On the contrary: ever since Biden reversed a key aspect of Trump's labor policies, all illegal immigrants - even those awaiting deportation proceedings - have been given carte blanche to work while awaiting said proceedings for up to five years...
... something which even Elon Musk was shocked to learn.
Wow, learn something new every day https://t.co/8MDtEEZGam
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 10, 2024
Which leads us to another question: recall that the primary concern for the Biden admin for much of 2022 and 2023 was soaring prices, i.e., relentless inflation in general, and rising wages in particular, which in turn prompted even Goldman to admit two years ago that the diabolical wage-price spiral had been unleashed in the US (diabolical, because nothing absent a major economic shock, read recession or depression, can short-circuit it once it is in place).
Well, there is one other thing that can break the wage-price spiral loop: a flood of ultra-cheap illegal immigrant workers. But don't take our word for it: here is Fed Chair Jerome Powell himself during his February 60 Minutes interview:
PELLEY: Why was immigration important?
POWELL: Because, you know, immigrants come in, and they tend to work at a rate that is at or above that for non-immigrants. Immigrants who come to the country tend to be in the workforce at a slightly higher level than native Americans do. But that's largely because of the age difference. They tend to skew younger.
PELLEY: Why is immigration so important to the economy?
POWELL: Well, first of all, immigration policy is not the Fed's job. The immigration policy of the United States is really important and really much under discussion right now, and that's none of our business. We don't set immigration policy. We don't comment on it.
I will say, over time, though, the U.S. economy has benefited from immigration. And, frankly, just in the last, year a big part of the story of the labor market coming back into better balance is immigration returning to levels that were more typical of the pre-pandemic era.
PELLEY: The country needed the workers.
POWELL: It did. And so, that's what's been happening.
Translation: Immigrants work hard, and Americans are lazy. But much more importantly, since illegal immigrants will work for any pay, and since Biden's Department of Homeland Security, via its Citizenship and Immigration Services Agency, has made it so illegal immigrants can work in the US perfectly legally for up to 5 years (if not more), one can argue that the flood of illegals through the southern border has been the primary reason why inflation - or rather mostly wage inflation, that all too critical component of the wage-price spiral - has moderated in in the past year, when the US labor market suddenly found itself flooded with millions of perfectly eligible workers, who just also happen to be illegal immigrants and thus have zero wage bargaining options.
None of this is to suggest that the relentless flood of immigrants into the US is not also driven by voting and census concerns - something Elon Musk has been pounding the table on in recent weeks, and has gone so far to call it "the biggest corruption of American democracy in the 21st century", but in retrospect, one can also argue that the only modest success the Biden admin has had in the past year - namely bringing inflation down from a torrid 9% annual rate to "only" 3% - has also been due to the millions of illegals he's imported into the country.
We would be remiss if we didn't also note that this so often carries catastrophic short-term consequences for the social fabric of the country (the Laken Riley fiasco being only the latest example), not to mention the far more dire long-term consequences for the future of the US - chief among them the trillions of dollars in debt the US will need to incur to pay for all those new illegal immigrants Democrat voters and low-paid workers. This is on top of the labor revolution that will kick in once AI leads to mass layoffs among high-paying, white-collar jobs, after which all those newly laid off native-born workers hoping to trade down to lower paying (if available) jobs will discover that hardened criminals from Honduras or Guatemala have already taken them, all thanks to Joe Biden.
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex





















