Announced today, a new Centre for Doctoral Training (CDT) has been funded by a grant of over £9 million from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) to help train the next, diverse generation of research leaders in data visualization.
A collaboration between City, University of London and the University of Warwick, the EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Diversity in Data Visualization (DIVERSE CDT) will train 60 PhD students, in cohorts of 12 students, beginning in October 2025. The set-up phase will begin in July 2024.
The funding announcement is part of a wider UK Research & Innovation (UKRI) announcement of the UK’s biggest-ever investment in engineering and physical sciences postgraduate skills, totalling more than £1 billion.
DIVERSE CDT will be supported by 19 partner organisations, including the Natural History Museum, the Ordnance Survey, and the Centre for Applied Education Research.
Data Visualization is the practice of designing, developing and evaluating representations of complex data – the kinds of data that lie at the heart of every organization – to enable more people to make real-world use of a source of information which is otherwise challenging to access.
Data visualization can be used to synthesise complex data into a clear story upon which actions can be based. From illustrating how the Covid-19 pandemic made countries poorer, to showing how the processing-power of cryptocurrencies may have driven up the price of high-street graphics cards; data visualization is crucial to society obtaining meaning from data.
However, no current CDT focuses upon training its students in data visualization. This is despite government’s Department of Digital, Media, Culture and Sport listing data visualization as one of the top five skills needed by businesses – with 23% of businesses saying that their sector has insufficient capacity. Likewise, Wiley’s Digital Skills Gap Index, 2021, listed data visualization as the third most needed business and organisational skill for employees to succeed in the workplace in the next five years.
Key innovations of DIVERSE CDT will include students:
- undertaking and relating a series of applied studies with world-leading industrial and academic partners through a structured internship programme and an exchange programme with 18 leading international labs
- using an interactive digital notebook for recording, reflection and reporting which becomes a “thesis” for examination, in lieu of the traditional doctoral thesis, and in line with current best practice in data visualization methodology
- being provided with tools that mitigate against the dreaded isolation that PhD students fear, including opportunities for cohort reflection and supportive inclusion via enriching and inclusive processes for admissions, support, and a research environment that addresses barriers for students from under-represented backgrounds; specifically students who identify as female, students from ethnic minority backgrounds and students from lower socio-economic groups.
DIVERSE CDT will be led by Professor Stephanie Wilson, Co-Director of the Centre for HCI Design (HCID) and Professor Jason Dykes, Professor of Visualization and Co-Director of the giCentre, both of the School of Science & Technology at City, University of London.
Members of DIVERSE CDT’s interdisciplinary team include:
- Professor Cagatay Turkay and Dr Gregory McInerny from the Centre for Interdisciplinary Methodologies, University of Warwick
- Dr Sara Jones, Reader in Creative Interactive System Design, Bayes Business School at City
- Professor Rachel Cohen, Professor in Sociology, Work and Employment, School of Policy & Global Affairs at City
- Professor Jo Wood, Professor of Visual Analytics, and Dr Marjahan Begum, Lecturer in Computer Science, School of Science & Technology at City
- Ian Gibbs, Head of Academic Enterprise at City.
Reflecting on DIVERSE CDT, Co-Principal Investigator, Professor Stephanie Wilson said:
“This funding represents a significant investment from the EPSRC and partner organisations in our vision of an innovative approach to doctoral training. We are delighted to have the opportunity to train a new and diverse generation of PhD students to become future leaders in data visualization.”
Professor Cagatay Turkay said:
“I am thrilled to see this investment for this exciting initiative that brings City and Warwick together to train the next generation of data visualization leaders. Together with our stellar partner organisations, DIVERSE CDT will deliver a transformative training programme that will underpin pioneering interdisciplinary data visualization research that not only innovates in methods and techniques but also delivers meaningful change in the world.”
Dr Sara Jones said:
“I’m really excited to be part of this great new initiative, sharing some of the innovative approaches we’ve developed through the interdisciplinary Centre for Creativity in Professional Practice and Masters in Innovation, Creativity and Leadership, and applying them in this important field.”
Professor Rachel Cohen said:
“DIVERSE CDT puts City at the heart of interdisciplinary data visualization. Data are increasingly part of the social science and policy agenda and it is imperative that those charged with visualizing data understand both the technical and social implications of visualization”
“The CDT is committed to developing and widening the group of people who have the cutting-edge skills needed to visualize, interpret and represent key aspects of our everyday lives. As such it marks a huge step forward both in terms of skill development and representation.”
Professor Leanne Aitken, Vice-President (Research), City, University of London, said:
“Growing the number of doctoral students we prepare in the interdisciplinary field of data visualization is core to our research strategy at City. Doctoral students represent the future of research and expand the capacity and impact of our research. The strength of the DIVERSE CDT is that it draws together our commitment to providing a supportive environment for students from all backgrounds to undertake applied research that challenges current practices in partnership with a range of commercial, public and third sector organisations. This represents an exciting expansion in our doctoral training provision.”
Professor Charlotte Deane, Executive Chair of the EPSRC, part of UKRI, said:
“The Centres for Doctoral Training announced today will help to prepare the next generation of researchers, specialists and industry experts across a wide range of sectors and industries.
“Spanning locations across the UK and a wide range of disciplines, the new centres are a vivid illustration of the UK’s depth of expertise and potential, which will help us to tackle large-scale, complex challenges and benefit society and the economy.
“The high calibre of both the new centres and applicants is a testament to the abundance of research excellence across the UK, and EPSRC’s role as part of UKRI is to invest in this excellence to advance knowledge and deliver a sustainable, resilient and prosperous nation.”
Science and Technology Secretary, Michelle Donelan, said:
“As innovators across the world break new ground faster than ever, it is vital that government, business and academia invests in ambitious UK talent, giving them the tools to pioneer new discoveries that benefit all our lives while creating new jobs and growing the economy.
“By targeting critical technologies including artificial intelligence and future telecoms, we are supporting world class universities across the UK to build the skills base we need to unleash the potential of future tech and maintain our country’s reputation as a hub of cutting-edge research and development.”
ENDS
Notes to editors
Contact details:
To speak to City, University of London collaborators, contact Dr Shamim Quadir, Senior Communications Officer, School of Science & Technology, City, University of London. Tel: +44(0) 207 040 8782 Email: shamim.quadir@city.ac.uk.
To speak to University of Warwick collaborators contact Annie Slinn, Communications Officer, University of Warwick. Tel: +44 (0)7392 125 605 Email: annie.slinn@warwick.ac.uk
Further information
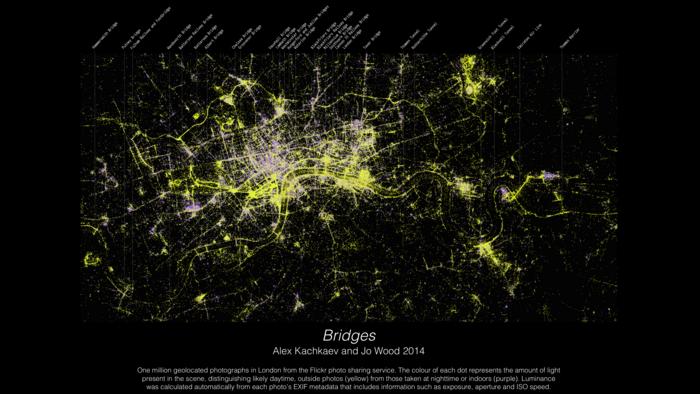
Example data visualization (image)
Bridges – Alex Kachaev and Jo Wood.
Link to image: bit.ly/3Iy3BRz Credit: Alex Kachkaev and Jo Wood, City, University of London
Data visualization for the Museum of London by Alex Kachkaev (a PhD student) with supervisor Joseph Wood, illustrating where people in London congregate in both inside and outside spaces, showing how a creative use of data can be used to build a picture of human behaviour.
Collaborating labs
Collaborators on the international exchange programme comprise the world’s leading visualization research labs, including the Visualization Group at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), USA, the Embodied Visualisation Group, Monash University, Australia; Georgia Tech, USA; AVIZ, France; the DataXExperience Lab, University of Calgary, Canada, and the ixLab, Simon Fraser University, Canada.
About the funder
The Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) is the main funding body for engineering and physical sciences research in the UK. Our portfolio covers a vast range of fields from digital technologies to clean energy, manufacturing to mathematics, advanced materials to chemistry.
EPSRC invests in world-leading research and skills, advancing knowledge and delivering a sustainable, resilient and prosperous UK. We support new ideas and transformative technologies which are the foundations of innovation, improving our economy, environment and society. Working in partnership and co-investing with industry, we deliver against national and global priorities.
About City, University of London
City, University of London is the University of business, practice and the professions.
City attracts around 20,000 students (over 40 per cent at postgraduate level) from more than 150 countries and staff from over 75 countries. In recent years City has made significant investments in its academic staff, its infrastructure, and its estate.
City’s academic range is broadly-based with world-leading strengths in business; law; health sciences; mathematics; computer science; engineering; social sciences; and the arts including journalism, dance and music.
Our research is impactful, engaged and at the frontier of practice. In the last REF (2021) 86 per cent of City research was rated as world leading 4* (40%) and internationally excellent 3* (46%).
We are committed to our students and to supporting them to get good jobs. City was one of the biggest improvers in the top half of the table in the Complete University Guide (CUG) 2023 and is 15th in UK for ‘graduate prospects on track’.
Over 150,000 former students in 170 countries are members of the City Alumni Network.
Under the leadership of our new President, Professor Sir Anthony Finkelstein, we have developed an ambitious new strategy that will direct the next phase of our development.